The Influence of O2 on Decomposition Characteristics of c-C4F8/N2 Environmental Friendly Insulating Gas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Electrode Precipitate Component Analysis
3.2. Experimental Analysis of the Decomposition Products of c-C4F8 under Micro-Oxygen Condition
4. Discussion
4.1. The Basic Properties of c-C4F8
4.2. The Decomposition Path of c-C4F8 and the Main Product Generation Mechanism
4.3. The Basic Properties of the Main Products
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the breakdown process of the c-C4F8/N2 mixed with O2 included, a large amount of black powdery substance precipitates on the surface of the ball electrode, which are mainly composed of C, O, F, and O element content accounted for 17.32%.
- (2)
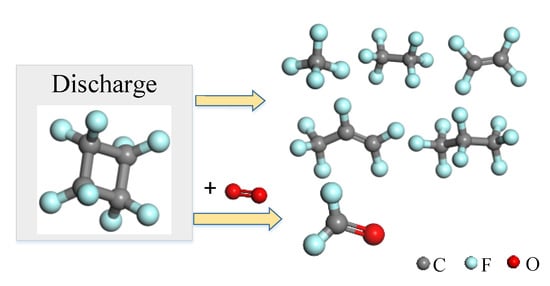
- The main products produced by c-C4F8 discharge decomposition are CF4, C2F4, C2F6, C3F6 and C3F8 and small molecules such as CF4, C2F4 and C2F6 are generated more easily. The addition of N2 weakened the decomposition of c-C4F8 gas. The decomposition products mainly come from c-C4F8 and N2 in the mixed gas does not participate in the chemical reaction. The product has good insulation properties. The presence of O2 causes the promotion of c-C4F8 decomposition and produces COF2. The increase of temperature can promote the reaction.
- (3)
- The main products produced by c-C4F8 discharge have good insulation properties, and the products basically maintain the insulation properties of the original mixed gas. However, when O2 was involved, COF2 gas was detected, which is toxic and corrosive and would be hazardous to insulation equipment and operators.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsai, W.-T. The decomposition products of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6): Reviews of environmental and health risk analysis. J. Fluor. Chem. 2007, 128, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.; Prinn, R.; Harnisch, J.; Fitzmaurice, J.; Jacoby, H.; Kicklighter, D.; Melillo, J.; Stone, P.; Sokolov, A.; Wang, C. Multi-gas assessment of the Kyoto Protocol. Nature 1999, 401, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Xiao, S.; Chen, D.; Tang, J.; Zhou, R. Decomposition mechanism of the C5-PFK/CO2 gas mixture as an alternative gas for SF6. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, A.A.; McCulloch, A. Regulating to reduce emissions of fluorinated greenhouse gases. J. Fluor. Chem. 2005, 126, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Solomon, S.; Turnipseed, A.A.; Warren, R.F. Atmospheric lifetimes of long-lived halogenated species. Science 1993, 259, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffel, Y.; Irwin, T.; Ponchon, P.; Owens, J. Green gas to replace SF6 in electrical grids. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2016, 14, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota-Babiloni, A.; Navarro-Esbrí, J.; Barragán-Cervera, Á.; Molés, F.; Peris, B. Analysis based on EU Regulation No 517/2014 of new HFC/HFO mixtures as alternatives of high GWP refrigerants in refrigeration and HVAC systems. Int. J. Refrig. 2015, 52, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, H.; Tang, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances in decomposition of the most potent greenhouse gas SF6. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1763–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijk, A.K. The nature of metal-electrodes/SF6 reactions in SF6 decomposition due to direct-current interruption under simulated circuit-breaker conditions. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1976, EI-11, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wock, S. On the toxicity of SF6 insulating gas. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1984, EI-19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.D. Genetic Toxicity Evaluation of Iodotrifluoromethane (CF3I). Volume I: Results of Salmonella Typhimurium Histidine Reversion Assay (Ames Assay); Genesys Research Inc.: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Han, Y.; Dai, Q. Analysis of the feasibility of CF3I/CO2 used in C-GIS by partial discharge inception voltages in positive half cycle and breakdown voltages. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyrenbach, M.; Hintzen, T.; Müller, P.; Owens, J. Alternative gas insulation in medium-voltage switchgear. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Electricity Distribution, Lyon, France, 15–18 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, M.P.S.; Kyte, M.; Andersen, S.T.; Nielsen, C.J.; Nielsen, O.J. Atmospheric chemistry of (CF3)2CF–CN: A replacement compound for the most potent industrial greenhouse gas, SF6. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, S.; Chen, Q.; Tang, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, D. Decomposition properties of C4F7N/N2 gas mixture: An environmentally friendly gas to replace SF6. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 5173–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.; Lin, H. Insulation characteristics of c-C4F8-N2 and CF3I-N2 mixtures as possible substitutes for SF6. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2017, 32, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Wenhao, N.; Guoqiang, Z.; Haijiang, X. Investigation of voltage and potential gradient of arc column in fluorocarbon gas and its gas mixtures. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Busan, Korea, 26–29 October 2013; pp. 2255–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, D. Analysis of the insulation characteristics of c-C4F8/CO2 gas mixtures by the Monte Carlo method. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 41, 015206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christophorou, L.G.; Olthoff, J.K.; Green, D.S. Gases for Electrical Insulation and Arc Interruption: Possible Present and Future Alternatives to Pure SF6; Technical Note (NIST TN)-1425; NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 1997.
- Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Jia, S.; Murphy, A.B. Prediction of the dielectric strength for c-C4F8 mixtures with CF4, CO2, N2, O2 and air by Boltzmann equation analysis. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 425204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Wenhao, N.; Tao, L.; Guoqiang, Z.; Haijiang, X. Study of the decomposition of c-C4F8 and its mixture with N2 under 50 Hz ac corona discharge. In Proceedings of the Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Shenzhen, China, 20–23 October 2013; pp. 1229–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Sekine, M.; Hori, M.; Kono, A.; Suu, K. Dissociation channels of c-C4F8 to CF2 radical in reactive plasma. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 036203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, L. Improving the accuracy of SF6 leakage detection for high voltage switchgear. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2011, 18, 1835–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, O.; Takuma, T.; Hamada, S.; Yamakawa, Y.; Yashima, M. Applying a gas mixtures containing c-C4F8 as an insulation medium. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2001, 8, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrini, W.; Venturini, F.; Tortelli, V.; Basak, S.; Pimparkar, K.P.; Adamo, A.; Jensen, K.F. Direct fluorination of carbon monoxide in microreactors. J. Fluor. Chem. 2012, 142, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.Y. SF6 decomposition in gas-insulated equipment. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1986, EI-21, 693–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, J. Partial discharge recognition through an analysis of SF6 decomposition products part 1: Decomposition characteristics of SF6 under four different partial discharges. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2012, 19, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, D.; Zeng, F.; Tang, B.; Li, K.; Yao, Q.; Miao, Y. Correlation characteristics between gas pressure and SF6 decomposition under negative DC partial discharge. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2017, 12, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Palanisamy, S.; Chen, S.; Wu, P.; Yao, L.; Lou, B.S. Mechanism of formation of SF6 decomposition gas products and its identification by GC-MS and electrochemical methods: A mini Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 4223–4231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, S.; Xiao, S.; Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; Tang, J. Insulation strength and decomposition characteristics of a C6F12O and N2 gas mixture. Energies 2017, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, J.; Tian, S.; Deng, Z. Formation mechanism of CF3I discharge components and effect of oxygen on decomposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 155601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Wang, Y. Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1992, 45, 13244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, J.; Ueta, G.; Okabe, S.; Hikita, M. Dielectric properties of gas mixtures with per-fluorocarbon gas and gas with low liquefaction temperature. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2016, 23, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devins, J.C. Replacement gases for SF6. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1980, EI-15, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xiao, D. Analysis of the insulation characteristics of CF3I gas mixtures with Ar, Xe, He, N2, and CO2 using Boltzmann equation method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 096201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Itoh, A.; Nakamura, T.; Tachibana, K. Radical kinetics for polymer film deposition in fluorocarbon (C4F8, C3F6, and C5F8) plasmas. Thin Solid Films 2000, 374, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivy, D.J.; Rigby, M.; Baasandorj, M.; Burkholder, J.B.; Prinn, R.G. Global emission estimates and radiative impact of C4F10, C5F12, C6F14, C7F16 and C8F18. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 7635–7645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Surhone, L.M.; Timpledon, M.T.; Marseken, S.F. Novec 1230. Landolt Börnstein Group IV Phys. Chem. 2010, 26, 263–291. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, S.; Limão-Vieira, P.; Kendall, P.A.; Mason, N.J.; Delwiche, J.; Hubin-Franskin, M.J.; Tanaka, T.; Kitajima, M.; Tanaka, H.; Cho, H.; et al. Electronic excitation of tetrafluoroethylene, C2F4. Chem. Phys. 2004, 297, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Element | Concentration (%) (Precision: 0.01%) |
|---|---|
| C1s | 58.44 |
| O1s | 17.32 |
| N1s | 0.75 |
| F1s | 23.49 |
| Products | 0% O2 | 3% O2 | The Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CF4 | 1,052,859 | 2,898,954 | 275.34 |
| C2F6 | 1,944,746 | 3,808,650 | 195.84 |
| C3F8 | 196,263 | 275,746 | 140.50 |
| C2F4 | 8,377,435 | 11,928,574 | 142.39 |
| C3F6 | 1,479,519 | 1,627,829 | 110.02 |
| Pathway | Chemical Equation | Reaction Energy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| (1) | c-C4F8 | 173.8539 |
| (2) | c-C4F8 | 342.3815 |
| (3) | c-C4F8 → C4F7⋅ + F⋅ | 434.8436 |
| No | Chemical Equation | Energy Changes (kJ·mol−1) | Activation Energy (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | −307.37 | — | |
| B2 | −83.7318 | — | |
| B3 | −190.262 | — | |
| B4 | −332.313 | — | |
| B5 | −373.811 | — | |
| B6 | −81.21444 | 80.97188 |
| No | Chemical Equation | Energy Changes (kJ·mol−1) | Activation Energy (kJ·mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | + O2→COF2 + O· | −138.52 | 180.18 |
| C2 | + O·→COF2 + | −112.64 | 184.61 |
| Gas | Dielectric Strength Relative to SF6 [33,34,35,36] | Boiling Point (°C) [29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] | GWP (100-Year) [5,36] | Lifetime (Year) [36,37,38,39] | Acute Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF6 | 1 | −63 | 23,900 | 3200 | >500,000 ppm/4 h, LC50 |
| c-C4F8 | 1.12 | −6 | 8700 | 2600 | 78 pph/2 h, LCLo |
| CF4 | 0.39 | −186.8 | 6300 | 50,000 | 895,000 ppm/15 min, LCLo |
| C2F6 | 0.78–0.79 | −78 | 9200 | 10,000 | >20 pph/2 h, LC |
| C3F8 | 0.96–0.97 | −37 | 7000 | 2600 | 750 ppm/4 h, LC50 |
| C3F6 | — | −28 | — | <10 | 750 ppm/4 h, LC50 |
| C2F4 | — | −76.3 | 0 | 1.9 days | 40,000 ppm/4 h, LC50 |
| COF2 | — | −84 | 0 | --- | 270 mg/m3, 4 h, LC50 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, S.; Tian, S.; Zhang, X.; Cressault, Y.; Tang, J.; Deng, Z.; Li, Y. The Influence of O2 on Decomposition Characteristics of c-C4F8/N2 Environmental Friendly Insulating Gas. Processes 2018, 6, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6100174
Xiao S, Tian S, Zhang X, Cressault Y, Tang J, Deng Z, Li Y. The Influence of O2 on Decomposition Characteristics of c-C4F8/N2 Environmental Friendly Insulating Gas. Processes. 2018; 6(10):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6100174
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Song, Shuangshuang Tian, Xiaoxing Zhang, Yann Cressault, Ju Tang, Zaitao Deng, and Yi Li. 2018. "The Influence of O2 on Decomposition Characteristics of c-C4F8/N2 Environmental Friendly Insulating Gas" Processes 6, no. 10: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6100174
APA StyleXiao, S., Tian, S., Zhang, X., Cressault, Y., Tang, J., Deng, Z., & Li, Y. (2018). The Influence of O2 on Decomposition Characteristics of c-C4F8/N2 Environmental Friendly Insulating Gas. Processes, 6(10), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr6100174