Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Biochar and Modified Biochar
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Influence of Solid-to-Liquid Ratio on Methylene Blue (MB) Adsorption
2.4.2. Influence of Initial pH of Solution on MB Adsorption
2.4.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.4. Adsorption Isotherm
2.4.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Biochars
3.2. Effect of Solid-to-Liquid Ratio and Initial pHon MB Removal
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics of MB on Biochars
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
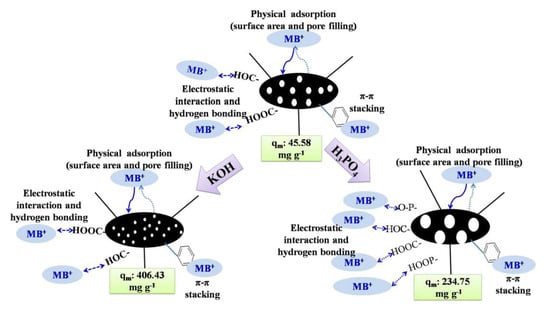
3.5. Discussion of Activation Mechanism and Adsorption Mechanism
3.5.1. Activation Mechanism
3.5.2. Removal Mechanism of Methylene Blue by Biochar
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Statement of Novelty
References
- Rajoriya, S.; Bargole, S.; George, S.; Saharan, V.K. Treatment of textile dyeing industry effluent using hydrodynamic cavitation in combination with advanced oxidation reagents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, M.; Shengyan, P.; Yaqi, H.; Rongxin, Z.; Anatoly, Z.; Wei, C. A highly efficient magnetic chitosan “fluid” adsorbent with a high capacity and fast adsorption kinetics for dyeing wastewater purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, L.; Schnoor, J.L. Insight into Multiple and Multilevel Structures of Biochars and Their Potential Environmental Applications: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5027–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal AU—Inyang, Mandu I. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Ok, Y.S.; Pittman, C.U. Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, B.-S.; Le, T.K.P.; Werner, D.; Phuong, H.N.; Luu, L.T. Rice Husk Biochars Modified with Magnetized Iron Oxides and Nano Zero Valent Iron for Decolorization of Dyeing Wastewater. Processes 2019, 7, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lou, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Cai, J. Synthesis of Porous Fe/C Bio-Char Adsorbent for Rhodamine B from Waste Wood: Characterization, Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Processes 2019, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.-Q. Development of Biochar-Based Functional Materials: Toward a Sustainable Platform Carbon Material. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12251–12285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, A.U.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhang, M.; Vithanage, M.; Mandal, S.; Gao, B.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S. Engineered/designer biochar for contaminant removal/immobilization from soil and water: Potential and implication of biochar modification. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.-F.; Liu, S.-B.; Liu, Y.-G.; Gu, Y.-L.; Zeng, G.-M.; Hu, X.-J.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.-H.; Jiang, L.-H. Biochar as potential sustainable precursors for activated carbon production: Multiple applications in environmental protection and energy storage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 227, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Hung, I.; Gan, Z.; Rojas, O.J.; Lim, K.H.; Park, S. Activated carbon from biochar: Influence of its physicochemical properties on the sorption characteristics of phenanthrene. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 149, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehkhoda, A.M.; Ellis, N.; Gyenge, E. Effect of activated biochar porous structure on the capacitive deionization of NaCl and ZnCl2 solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 224, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Hao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Su, R.; Feng, W.; Li, S.; Jia, B. Effect of Physical and Mechanical Activation on the Physicochemical Structure of Coal-Based Activated Carbons for SO2 Adsorption. Processes 2019, 7, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, X.; Ge, C.; Müller, K.; Yu, H.; Huang, P.; Li, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J. Sorption of norfloxacin, sulfamerazine and oxytetracycline by KOH-modified biochar under single and ternary systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, S.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H. Comparing the adsorption mechanism of Cd by rice straw pristine and KOH-modified biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11875–11883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tang, J.; Gao, K.; He, R.; Zhao, H.; Werner, D. Characterization of KOH modified biochars from different pyrolysis temperatures and enhanced adsorption of antibiotics. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14640–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Luo, L.; Deng, S.; Shi, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, O.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L. Sorption of tetracycline on H3PO4 modified biochar derived from rice straw and swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Gao, P.; Chu, G.; Pan, B.; Peng, J.; Xing, B. Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Zhao, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, J. Adsorption and coadsorption mechanisms of Cr(VI) and organic contaminants on H3PO4 treated biochar. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Ren, L.; Hong, J.; Xu, C. Environmental impact assessment of corn straw utilization in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H. Development, modification, and application of low-cost and available biochar derived from corn straw for the removal of vanadium(v) from aqueous solution and real contaminated groundwater. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21480–21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. About the Theory of So-Called Adsorption of Solution Substances. K. Sven. Vetensk. Handl. 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, G.; Maunaye, M.; Martin, G. Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Res. 1984, 18, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rong, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, H.L.; Zheng, C. Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel 2007, 86, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, K.; Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y. Sorption of simazine to corn straw biochars prepared at different pyrolytic temperatures. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2594–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, N.; Tong, L.; Lv, Y. Structural and adsorption characteristics of potassium carbonate activated biochar. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 21012–21019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sun, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. One-pot synthesis of porous carbon foam derived from corn straw: Atrazine adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Jiang, K.; Jiao, P.; Ji, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhuang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Bio-butanol sorption performance on novel porous-carbon adsorbents from corncob prepared via hydrothermal carbonization and post-pyrolysis method. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Ye, X.; Geng, Z.; Zhou, H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, G. The influence of biochar type on long-term stabilization for Cd and Cu in contaminated paddy soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Chen, Z.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Magnetic Porous Carbonaceous Material Produced from Tea Waste for Efficient Removal of As(V), Cr(VI), Humic Acid, and Dyes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4371–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.; Sarmah, A.K. Characterisation of agricultural waste-derived biochars and their sorption potential for sulfamethoxazole in pasture soil: A spectroscopic investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, F.; Cui, G.; Liu, Z.; Duo, L.; Zhang, G.; Xing, B. One-step synthesis of a novel N-doped microporous biochar derived from crop straws with high dye adsorption capacity. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosas, J.M.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. Kinetic study of the oxidation resistance of phosphorus-containing activated carbons. Carbon 2012, 50, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas, J.M.; Bedia, J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T. HEMP-derived activated carbon fibers by chemical activation with phosphoric acid. Fuel 2009, 88, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puziy, A.M.; Poddubnaya, O.I.; Ziatdinov, A.M. On the chemical structure of phosphorus compounds in phosphoric acid-activated carbon. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 8036–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Huang, Q.; Meng, X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Polyethylene into Aromatics by H3PO4-Activated Carbon. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 9772–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puziy, A.M.; Poddubnaya, O.I.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Suárez-García, F.; Tascón, J.M.D. Surface chemistry of phosphorus-containing carbons of lignocellulosic origin. Carbon 2005, 43, 2857–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.Y.; Gan, S.; Tan, M.S.Y.; Lim, S.S.; Lee, X.J.; Lam, Y.F. Effective removal of Acid Blue 113 dye using overripe Cucumis sativus peel as an eco-friendly biosorbent from agricultural residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, B.; Ghorbani, M.; Salehi, M.A. Application of polyrhodanine modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes for high efficiency removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelan, V.; Kumar, K.V. Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process. Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Shimizu, K. Predicting equilibrium time by adsorption kinetic equations and modifying Langmuir isotherm by fractal-like approach. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, G.; Wei, D.; Yan, T.; Xue, X.; Shi, S.; Wei, Q. Preparation and utilization of anaerobic granular sludge-based biochar for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 198, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Piñero, E.; Azaïs, P.; Cacciaguerra, T.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A.; Béguin, F. KOH and NaOH activation mechanisms of multiwalled carbon nanotubes with different structural organisation. Carbon 2005, 43, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Castelló, D.; Calo, J.M.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A. Carbon activation with KOH as explored by temperature programmed techniques, and the effects of hydrogen. Carbon 2007, 45, 2529–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Z.; Xing, W.; Shen, H.; Bi, X.; Zhu, T.; Qiu, Z.; Zhuo, S. A New Approach to Tuning Carbon Ultramicropore Size at Sub-Angstrom Level for Maximizing Specific Capacitance and CO2 Uptake. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7955–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kaskel, S. KOH activation of carbon-based materials for energy storage. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23710–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkhoda, A.M.; Gyenge, E.; Ellis, N. A novel method to tailor the porous structure of KOH-activated biochar and its application in capacitive deionization and energy storage. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 87, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagtoyen, M.; Derbyshire, F. Activated carbons from yellow poplar and white oak by H3PO4 activation. Carbon 1998, 36, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Singh, N.; Purakayastha, T.J. Characterization of pesticide sorption behaviour of slow pyrolysis biochars as low cost adsorbent for atrazine and imidacloprid removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrellas, S.Á.; Lovera, R.G.; Escalona, N.; Sepúlveda, C.; Sotelo, J.L.; García, J. Chemical-activated carbons from peach stones for the adsorption of emerging contaminants in aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, R.; Xu, Q. Adsorption of methylene blue by a high-efficiency adsorbent (polydopamine microspheres): Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamics and mechanism analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Tang, T. Converting real-world mixed waste plastics into porous carbon nanosheets with excellent performance in the adsorption of an organic dye from wastewater. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Zhang, C.; Liao, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Meng, L.; Jiang, J. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: Kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 198, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, X. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by sewage sludge-derived biochar: Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics and mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, X. Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 220, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Yuan, X.; Huang, H.; Shao, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zeng, G. Bio-char derived from sewage sludge by liquefaction: Characterization and application for dye adsorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.-D.; Wang, C.-C.; Liu, J.-G.; Zhao, X.-D.; Zhong, J.; Li, Y.-X.; Li, J.; Wang, P. Extensive and selective adsorption of ZIF-67 towards organic dyes: Performance and mechanism. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 506, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wen, X.; Mijowska, E.; Tang, T.; Chen, X. A facile approach to prepare porous cup-stacked carbon nanotube with high performance in adsorption of methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 445, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; Hu, K. Facile synthesis of tea waste/Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite for hexavalent chromium removal from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 7576–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]












| Samples | Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Pore Size (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|
| corn stalk biochar (CSBC) | 24 | 0.021 | 34.0 |
| KOH-CSBC | 474 | 0.24 | 20.4 |
| H3PO4-CSBC | 3 | 0.0025 | 35.1 |
| CSBC | KOH-CSBC | H3PO4-CSBC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment | Wavenumber (cm−1) | Assignment |
| 3443 | –OH | 3450 | –OH | 3425 | –OH |
| 2925 | aliphatic C | 2372 | C–O vibrations | ||
| 1633 | C=O and C=C | 1637 | C=O and C=C | 1637 | C=O and C=C |
| 1560 | C=O stretching | 1271 | aromatic C–O stretching | 1401 | –COOH or O–H bending |
| 1075 | Si–O stretching vibrations | 1151 | phenolic O–H band | 1145 | amino phosphonic acid functional group |
| 539 | aromatic C–H stretching | 1103 | C–H bending of alkenes | 998 | P–OH bond |
| 1025 | C–O–C stretch | 495 | Si–O–Si | ||
| 867 | Aromatic C–H | ||||
| 676 | CH–of alkenes and alkanes | ||||
| Functional Groups | CSBC | KOH-CSBC | H3PO4-CSBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C–C/C–H | 284.77 a | 284.78 | 284.78 |
| 72.55% b | 66.57% | 68.70% | ||
| C–O | 285.58 | 285.74 | 286.07 | |
| 24.23% | 33.43% | 31.30% | ||
| O=C–O | 288.34 | |||
| 3.22% | ||||
| O | C–O | 531.73 | 532.19 | 531.23 (C=O/O=P) |
| 58.23% | 61.00% | 15.77% | ||
| C=O–OH | 533.12 | 533.88 | 533.10 | |
| 41.77% | 39.00% | 30.19% | ||
| O–C/COH/C–O–C/P-O | 532.91 | |||
| 54.04% | ||||
| N | Pyrimidine nitrogen | 398.72 | 398.41 | 398.99 |
| 33.39% | 6.27% | 25.83% | ||
| Pyrrole nitrogen/pyridine nitrogen | 400.57 | 400.19 | 401.16 | |
| 66.61% | 93.73% | 74.17% | ||
| P | C–PO3/C2–PO2 | 133.38 | ||
| 41.90% | ||||
| C–O–PO3 | 134.22 | 134.23 | 134.33 | |
| 58.10% | 65.48% | 88.94% | ||
| P2O5 | 135.33 | 136.60 | ||
| 34.52% | 11.06% | |||
| Samples | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | k2 (g mg−1·min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | |
| CSBC-50 | 0.21345 | 20.32061 | 0.83583 | 0.01439 | 21.47248 | 0.90152 |
| CSBC-100 | 0.29512 | 28.16607 | 0.96912 | 0.02148 | 29.00599 | 0.98949 |
| KOH-CSBC-100 | 0.22694 | 195.77074 | 0.99472 | 0.00238 | 201.40582 | 0.99655 |
| KOH-CSBC-200 | 0.14885 | 343.79494 | 0.91663 | 6.55037 × 10−4 | 361.7548 | 0.97949 |
| H3PO4-CSBC-100 | 0.06862 | 81.7322 | 0.89829 | 0.00112 | 87.36304 | 0.95485 |
| H3PO4-CSBC-200 | 0.14954 | 87.97926 | 0.76541 | 0.00273 | 92.28821 | 0.84763 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm(mg·g−1) | KL (L·mg−1) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| CSBC | 45.58 | 0.04415 | 0.9535 | 4.232 | 0.5245 | 0.9145 |
| KOH-CSBC | 406.43 | 7.553 | 0.9084 | 283.21 | 0.1321 | 0.8665 |
| H3PO4-CSBC | 234.75 | 0.1267 | 0.9746 | 86.67 | 0.2058 | 0.9955 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution. Processes 2019, 7, 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120891
Liu L, Li Y, Fan S. Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution. Processes. 2019; 7(12):891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120891
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Li, Yang Li, and Shisuo Fan. 2019. "Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution" Processes 7, no. 12: 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120891
APA StyleLiu, L., Li, Y., & Fan, S. (2019). Preparation of KOH and H3PO4 Modified Biochar and Its Application in Methylene Blue Removal from Aqueous Solution. Processes, 7(12), 891. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120891