Increasing Salt Rejection of Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Membranes via the Addition of Immobilized and Aligned Aquaporins
Abstract
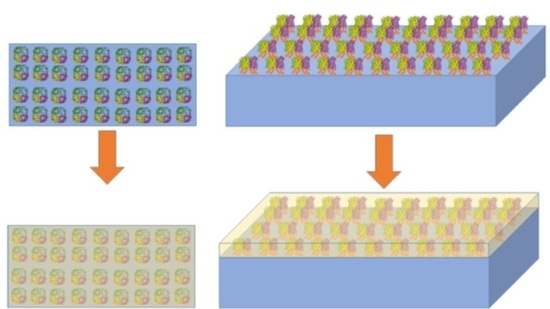
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Polybenzimidazole (PBI)
2.1.2. PVA-Alkyl
2.1.3. AquaporinZ Modification with Single Cysteine at the N-Terminus
2.1.4. AquaporinZ Expression and Purification
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. PBI Membranes Casting
2.2.2. Surface Activation of Membranes
2.2.3. Preparation of PVA–Alkyl
2.2.4. Chemical Attachment of –Cys Modified Aqp to PBI Backbone
2.2.5. Surface Modification of PBI Membrane Using PVA-Alkyl
2.2.6. Membrane Characterization
Dynamic Light Scattering
Molecular Weight Cut Off (MWCO)
Contact Angle Measurements
Zeta Potential and Surface Charge Analysis
Elemental Analysis
Membrane Morphology
Flux Analysis
2.2.7. Estimation of Aquaporin Packing in Membrane Assembly:
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
3.2. MWCO Analysis
3.3. Aquaporin Attachment Verification through Elemental Analysis
3.4. Hydrophobicity
3.5. Zeta Potential and Surface Charge Analysis:
3.6. Membrane Morphology
3.7. Flux Analysis
3.8. Estimations of Aquaporin Packing in Membrane Assembly
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gena, P.; Pellegrini-Calace, M.; Biasco, A.; Svelto, M.; Calamita, G. Aquaporin Membrane Channels: Biophysics, Classification, Functions, and Possible Biotechnological Applications. Food Biophys. 2011, 6, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chung, T.S.; Tong, Y.W.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A.; Chen, Z.; Hong, M.; Meier, W. Highly permeable and selective pore-spanning biomimetic membrane embedded with aquaporin Z. Small 2012, 8, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taubert, A. Controlling water transport through artificial polymer/protein hybrid membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20643–20644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agre, P. Aquaporin Water Channels. Biosci. Rep. 2005, 24, 127–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Shao, H.B.; Chu, L.Y. Aquaporin structure-function relationships: Water flow through plant living cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 62, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, P.S.; Chung, T.-S.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A. Aquaporin-embedded biomimetic membranes for nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407-408, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, R.; Tang, C.; Vararattanavech, A.; Zhao, Y.; Torres, J.; Fane, T. Preparation of supported lipid membranes for aquaporin Z incorporation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 94, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.S.; Wang, R.; Wicaksana, F.; Tang, C.Y.; Torres, J.; Fane, A.G. Preparation of high performance nanofiltration (NF) membranes incorporated with aquaporin Z. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, W.; Vararattanavech, A.; Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Torres, J.; Fane, A.G.; Hélix-Nielsen, C. Aquaporin Based Thin Film Composite Membranes. Patents WO/2013/043118, 28 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.N.; Petrinic, I.; Fane, A.G.; Helix-Nielsen, C. Biomimetic aquaporin membranes coming of age. Desalination 2015, 368, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, C.; Li, X.; Vararattanavech, A.; Shen, W.; Torres, J.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Wang, R.; Hu, X.; Fane, A.G.; et al. Synthesis of robust and high-performance aquaporin-based biomimetic membranes by interfacial polymerization-membrane preparation and RO performance characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Vararattanavech, A.; Li, X.; Helixnielsen, C.; Vissing, T.; Torres, J.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y. Effects of proteoliposome composition and draw solution types on separation performance of aquaporin-based proteoliposomes: Implications for seawater desalination using aquaporin-based biomimetic membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A.; Chung, T.S. A novel method of AquaporinZ incorporation via binary-lipid Langmuir monolayers. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 89, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.F.; Chung, T.S.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A. Stabilization and immobilization of aquaporin reconstituted lipid vesicles for water purification. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.F.; Chung, T.S.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A. A layer-by-layer self-assembly approach to developing an aquaporin-embedded mixed matrix membrane. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chung, T.-S.; Tong, Y.W.; Meier, W.; Chen, Z.; Hong, M.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A. Preparation and characterization of pore-suspending biomimetic membranes embedded with Aquaporin Z on carboxylated polyethylene glycol polymer cushion. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7274–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Chung, T.S.; Tong, Y.W.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A.; Duong, H.H.P.; Fu, F.J.; Seah, H.; Yang, J.; Hong, M.H. Mechanically robust and highly permeable AquaporinZ biomimetic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.Y.; He, F.; Wang, B.F.; Chung, T.S.; Jeyaseelan, K.; Armugam, A.; Tong, Y.W. An aquaporin-based vesicle-embedded polymeric membrane for low energy water filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7592–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzelakowski, M.; Cherenet, M.F.; Shen, Y.X.; Kumar, M. A framework for accurate evaluation of the promise of aquaporin based biomimetic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 479, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Grzelakowski, M.; Zilles, J.; Clark, M.; Meier, W. Highly permeable polymeric membranes based on the incorporation of the functional water channel protein Aquaporin Z. Proce. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20719–20724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.-X.; Saboe, P.O.; Sines, I.T.; Erbakan, M.; Kumar, M. Biomimetic membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 359–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, J.; Hansen, M.; Kynde, S.; Larsen, N.; Midtgaard, S.R.; Jensen, G.V.; Bomholt, J.; Ogbonna, A.; Almdal, K.; Schulz, A.; et al. Aquaporin-Based Biomimetic Polymeric Membranes: Approaches and Challenges. Membranes 2015, 5, 307–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, C.H. Biomimetic membranes for sensor and separation applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 697–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Fane, A.G. Desalination by biomimetic aquaporin membranes: Review of status and prospects. Desalination 2013, 308, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Hansen, J.S.; Vissing, T.; Perry, M.E.; Nielsen, C.H. Biometric Membranes and Uses Thereof. Patents WO2010146365A1, 23 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, P.H. Biomimetic Water Membrane Comprising Aquaporins Used in the Production of Salinity Power. Patents US20090007555A1, 8 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.; Grinberg, S.; Linder, C.; Heldman, E.; Gilron, J.; Freger, V. Fusion of Bolaamphiphile Micelles: A Method to Prepare Stable Supported Biomimetic Membranes. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tanner, P.; Graff, A.; Palivan, C.G.; Meier, W. Mimicking the cell membrane with block copolymer membranes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 2293–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanner, P.; Baumann, P.; Enea, R.; Onaca, O.; Palivan, C.; Meier, W. Polymeric Vesicles: From Drug Carriers to Nanoreactors and Artificial Organelles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J.; Montemagno, C.D. Artificial Organelle: ATP Synthesis from Cellular Mimetic Polymersomes. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2538–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriezema, D.M.; Garcia, P.M.L.; Sancho Oltra, N.; Hatzakis, N.S.; Kuiper, S.M.; Nolte, R.J.M.; Rowan, A.E.; van Hest, J.C.M. Positional Assembly of Enzymes in Polymersome Nanoreactors for Cascade Reactions. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7522–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoenescu, R.; Graff, A.; Meier, W. Asymmetric ABC-Triblock Copolymer Membranes Induce a Directed Insertion of Membrane Proteins. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, A.; Fraysse-Ailhas, C.; Palivan, C.G.; Grzelakowski, M.; Friedrich, T.; Vebert, C.; Gescheidt, G.; Meier, W. Amphiphilic Copolymer Membranes Promote NADH:Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Activity: Towards an Electron-Transfer Nanodevice. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Habel, J.E.O.; Shen, Y.-X.; Meier, W.P.; Walz, T. High-Density Reconstitution of Functional Water Channels into Vesicular and Planar Block Copolymer Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18631–18637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Chung, T.-S.; Tong, Y.W. Study on water transport through a mechanically robust Aquaporin Z biomimetic membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 445, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalter, M.; Hilty, C.; Bezrukov, S.M.; Nardin, C.; Meier, W.; Fournier, D. Controlling membrane permeability with bacterial porins: application to encapsulated enzymes. Talanta 2001, 55, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M. Biomimetic Membranes as New Materials for Applications in Environmental Engineering and Biology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.; Berman, A.; Freger, V. Supported Lipid Bilayer Membranes for Water Purification by Reverse Osmosis. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7388–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Q.; Wang, Z.N.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, S.Z.; Ding, W.D.; Gao, C.J. Layer-by-Layer Assembly of Aquaporin Z-Incorporated Biomimetic Membranes for Water Purification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3761–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagh, P.; Parungao, G.; Viola, R.E.; Escobar, I.C. A new technique to fabricate high-performance biologically inspired membranes for water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Digman, B.; Escobar, I.C.; Hausman, R.; Coleman, M.; Chung, T.S. Surface functionalization of polybenzimidizole membranes to increase hydrophilicity and charge. ACS Symp. Ser. 2011, 1078, 303–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hausman, R.; Digman, B.; Escobar, I.C.; Coleman, M.; Chung, T.-S. Functionalization of polybenzimidizole membranes to impart negative charge and hydrophilicity. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 363, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, M.F.; Escobar, I.C. Novel charged and hydrophilized polybenzimidazole (PBI) membranes for forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.C.; Jones, R.S. Observations on the structure of first generation polybenzimidazole reverse osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1984, 20, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.-P.; Sun, S.-P.; Gao, J.; Fu, F.-J.; Chung, T.-S. Dual-layer polybenzimidazole/polyethersulfone (PBI/PES) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metals removal from wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 456, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, O.; Teramura, Y.; Iwata, H. Retention dynamics of amphiphilic polymers PEG-lipids and PVA-Alkyl on the cell surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramura, Y.; Kaneda, Y.; Totani, T.; Iwata, H. Behavior of synthetic polymers immobilized on a cell membrane. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ye, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Cysteine residue is not essential for CPM protein thermal-stability assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3683–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitz, E.; Wu, B.; Holm, L.M.; Schultz, J.E.; Zeuthen, T. Point mutations in the aromatic/arginine region in aquaporin 1 allow passage of urea, glycerol, ammonia, and protons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, L.; Helix-Nielsen, C.; Su, H.B.; Torres, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G.; Mu, Y.G. Population Shift between the Open and Closed States Changes the Water Permeability of an Aquaporin Z Mutant. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosono, M.; Sugii, S.; Kitamaru, R.; Hong, Y.M.; Tsuji, W. Polyelectrolyte complex prepared from carboxymethylated and aminoacetalized derivatives of Poly(vinyl) alcohol. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1977, 21, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totani, T.; Teramura, Y.; Iwata, H. Immobilization of urokinase on the islet surface by amphiphilic poly(vinyl alcohol) that carries alkyl side chains. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2878–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gung, B.W.; Dickson, H.D.; Seggerson, S.; Bluhm, K. A short synthesis of an acetylenic alcohol from the sponge Cribrochalina vasculum. Synth. Commun. 2002, 32, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q. A colorimetric method for the molecular weight determination of polyethylene glycol using gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dohmen, M.P.J.; Pereira, A.M.; Timmer, J.M.K.; Benes, N.E.; Keurentjes, J.T.F. Hydrodynamic Radii of Polyethylene Glycols in Different Solvents Determined from Viscosity Measurements. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, L.; Junter, G.A. Diffusion of sucrose and dextran through agar gel membranes. Enzym. Microbial Technol. 1993, 15, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Porter, C.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Bhattacharyya, D. Layer-by-layer assembled membranes with immobilized porins. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56123–56136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, S.G.; Solomon, A.K. Determination of the Effective Hydrodynamic Radii of Small Molecules by Viscometry. J. Gen. Physiol. 1961, 44, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Goh, P.S.; Hilal, N.; Ooi, B.S. Characterization Methods of Thin Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2015, 44, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bit Bucket. Available online: https://bitbucket.org/pkhlab/pkh-lab-analyses (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Shang, Y.; Peng, Y. UF membrane of PVA modified with TDI. Desalination 2008, 221, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, T.; Walz, T. The structure of aquaporins. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2006, 39, 361–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelachvili, J.N. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 710. [Google Scholar]
- Braghetta, A.; DiGiano, F.A.; Ball, W.P. Nanofiltration of Natural Organic Matter: pH and Ionic Strength Effects. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lebrun, R.E. Investigation of the solute separation by charged nanofiltration membrane: effect of pH, ionic strength and solute type. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 158, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekenes-Huskey, P.M.; Gillette, A.K.; McCammon, J.A. Predicting the influence of long-range molecular interactions on macroscopic-scale diffusion by homogenization of the Smoluchowski equation. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 174106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burykin, A.; Warshel, A. What Really Prevents Proton Transport through Aquaporin? Charge Self-Energy versus Proton Wire Proposals. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 3696–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, G.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, J. Insights into the mechanisms of the selectivity filter of Escherichia coli aquaporin Z. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 3731–3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fields, J.B.; Németh-Cahalan, K.L.; Freites, F.A.; Vorontsova, I.; Hall, J.E.; Tobias, D.J. Calmodulin Gates Aquaporin 0 Permeability through a Positively Charged Cytoplasmic Loop. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kekenes-Huskey, P.M.; Scott, C.E.; Atalay, S. Quantifying the Influence of the Crowded Cytoplasm on Small Molecule Diffusion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 8696–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| Solute | Mol. Wt. (gm/mol) | Stokes-Einstein Radii (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| PEG 200 | 200 | 0.41 |
| Sucrose | 342.3 | 0.47 |
| PEG 400 | 400 | 0.57 |
| PEG 600 | 600 | 0.68 |
| PEG 1000 | 1000 | 0.94 |
| Membrane | Rejection > 90% |
|---|---|
| Unmodified PBI | 0.94 nm (94.2% ± 2.5 %) |
| PBI-CMBA | 0.94 nm (93.0% ± 2.4 %) |
| PVA-alkyl modified PBI | 0.68 nm (91.3% ± 1 %) |
| Carbon | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Sulfur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | 85.22 | 10.7 | 4 | 0.07 |
| Level 1 | 86.28 | 10.28 | 3.39 | 0.05 |
| Level 2 | 86.2 | 10.39 | 3.33 | 0.09 |
| Level 3 | 87.3 | 10.56 | 2.11 | 0.03 |
| Carbon | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Sulfur | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | 92.13 | 4.07 | 3.3 | 0.5 |
| Level 1 | 87.18 | 8.93 | 3.41 | 0.48 |
| Level 2 | 87.58 | 8.73 | 2.99 | 0.7 |
| Level 3 | 86.82 | 8.02 | 3.05 | 0.62 |
| Membrane | Contact Angle |
|---|---|
| Unmodified PBI | 75° ± 0.55 |
| –COOH modified PBI | 70.56° ± 1.04 |
| PVA-alkyl modified PBI | 60.5° ± 1.44 |
| Aqp-SH modified PBI | 57.5° ± 0.93 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wagh, P.; Zhang, X.; Blood, R.; Kekenes-Huskey, P.M.; Rajapaksha, P.; Wei, Y.; Escobar, I.C. Increasing Salt Rejection of Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Membranes via the Addition of Immobilized and Aligned Aquaporins. Processes 2019, 7, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7020076
Wagh P, Zhang X, Blood R, Kekenes-Huskey PM, Rajapaksha P, Wei Y, Escobar IC. Increasing Salt Rejection of Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Membranes via the Addition of Immobilized and Aligned Aquaporins. Processes. 2019; 7(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleWagh, Priyesh, Xinyi Zhang, Ryan Blood, Peter M. Kekenes-Huskey, Prasangi Rajapaksha, Yinan Wei, and Isabel C. Escobar. 2019. "Increasing Salt Rejection of Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Membranes via the Addition of Immobilized and Aligned Aquaporins" Processes 7, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7020076
APA StyleWagh, P., Zhang, X., Blood, R., Kekenes-Huskey, P. M., Rajapaksha, P., Wei, Y., & Escobar, I. C. (2019). Increasing Salt Rejection of Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Membranes via the Addition of Immobilized and Aligned Aquaporins. Processes, 7(2), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7020076