Evaluation of the Influences of Scrap Melting and Dissolution during Dynamic Linz–Donawitz (LD) Converter Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
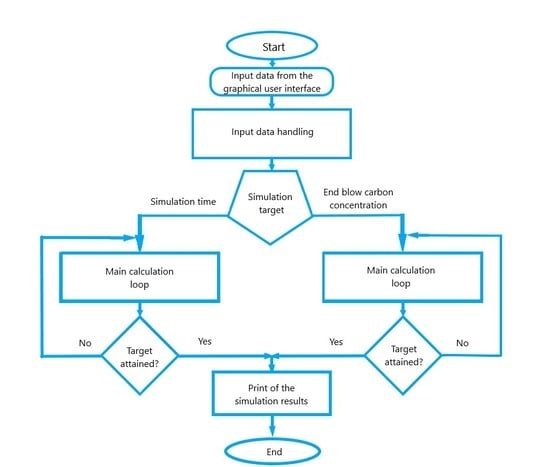
2. Description of the Dynamic LD Converter Model
- At the interfacial surface all reactions are expeditious and equilibrated at each time step.
- The mass transfer kinetics in the metal and slag phases are the limitation for reaction rates.
3. Mechanisms of Scrap Melting in the LD Model
4. Simulation Parameters
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Influence on the Melting and Dissolution Behavior of Scrap
5.2. Influence on the Final Crude Steel Temperature
5.3. Influence on the Final Carbon Content
5.4. Influence on the Final Phosphorus Content
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turkdogan, E.T. Fundamentals of Steelmaking; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1996; pp. 209–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Chatterjee, A. Ironmaking and Steelmaking Theory and Practice; PHI Learning Private Limited: Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Chigwedu, C. Beitrag zur Modellierung des LD-Sauerstoffaufblasverfahrens zur Stahlerzeugung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Clausthal, Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Penz, F.M.; Bundschuh, P.; Schenk, J.; Panhofer, H.; Pastucha, K.; Paul, A. Effect of Scrap Composition on the Thermodynamics of Kinetic Modelling of BOF Converter. In Proceedings of the 2nd VDEh-ISIJ-JK Symposium, Stockholm, Sweden, 12–13 June 2017; pp. 124–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hiebler, H.; Krieger, W. Die Metallurgie des LD-Prozesses. BHM 1992, 137, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskopf, A.; Holappa, L. Scrap melting model for steel converter founded on interfacial solid/liquid phenomena. Metall. Res. Technol. 2018, 115, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskopf, A.; Louhenkilpi, S. 1-Dimensional scrap melting model for steel converter (BOF). In Proceedings of the METEC & 2nd ESTAD, Düsseldorf, Germany, 15–19 June 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskopf, A. A Model for Scrap Melting in Steel Converter. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Swickard, D.; Alavanja, M.; Bradley, J. Numerical Simulation of Heavy Scrap Melting in BOF steelmaking. Iron Steel Technol. 2013, 10, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sethi, G.; Shukla, A.K.; Das, P.C.; Chandra, P.; Deo, B. Theoretical Aspects of Scrap Dissolution in Oxygen Steelmaking Converters. In Proceedings of the AISTech, Nashville, TN, USA, 15–17 September 2004; Volume II, pp. 915–926. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.K.; Deo, B. Coupled heat and mass transfer approach to simulate the scrap dissolution in steelmaking process. In Proceedings of the International Symposium for Research Scholars on Metallurgy, Materials Science & Engineering, Chennai, India, 18–20 December 2006; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.K.; Deo, B.; Robertson, D. Scrap Dissolution in Molten Iron Containing Carbon for the Case of Coupled Heat and Mass Transfer Control. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 1407–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvynyuk, Y.; Schenk, J.; Hiebler, M.; Sormann, A. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Model of the Converter Steelmaking Process. Part 1: The Description of the BOF Model. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvynyuk, Y. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Modelling of Metallurgical Processes. Ph.D. Dissertation, Montanuniversität Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, M.; Tsujino, R.; Mukai, T.; Harada, T.; Masanao, O. Mechanism of Post Combustion in the Converter. Trans. ISIJ 1987, 27, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, P.; Schenk, J.; Hiebler, M.; Panhofer, H.; Sormann, A. Influence of CaO Dissolution on the Kinetics of Metallurgical Reactions in BOF-process. In Proceedings of the 7th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference, Trinec, Czech Republic, 9–11 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boychenko, B.; Okhotskiy, V.; Kharlashin, P. The Converter Steelmaking; Dnipro-VAL: Dnipropetrovsk, Ukraine, 2006; pp. 22–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ohguchi, S.; Robertson, D.; Deo, B.; Grieveson, P.; Jeffes, J. Simultaneous dephosphorization and desulphurization of molten pig iron. Iron Steelmak. 1984, 11, 202–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, S.; Kitamura, T.; Shibata, K.; Mizukami, Y.; Mukawa, S.; Nakagawa, J. Effect of stirring energy, temperature and flux composition on hot metal dephosphorization kinetics. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Kitamura, T.; Aida, T.; Sakomura, E.; Koneko, R.; Nuibe, T. Development of analyses and control method for hot metal dephosphorization process by computer simulation. ISIJ Int. 1991, 31, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S.; Shibata, H.; Maruoka, N. Kinetic Model of Hot Metal Dephosphorization by Liquid and Solid coexisting slags. Steel Res. Int. 2008, 79, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevani, F.; Kitamura, S.; Shibata, H.; Maruoka, N. Kinetic Model Dephosphorization in Converter. In Proceedings of the SteelSim, Leoben, Austria, 8–10 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mukawa, S.; Mizukami, Y. Effect of stirring energy and rate of oxygen supply on the rate of hot metal dephosphorization. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M. Analysis of hot metal desiliconization behaviour in converter experiments by coupled reaction model. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Tago, Y.; Takatani, K.; Fukagawa, S. Effect of stirring and slag condition on reoxidation on molten steel. ISIJ 1998, 84, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lytvynyuk, Y.; Schenk, J.; Hiebler, M.; Mizelli, H. Thermodynamic and kinetic modelling of the devanadization process in the steelmaking converter. In Proceedings of the 6th European Oxygen Steelmaking Conference, Stockholm, Sweden, 7–9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Penz, F.M.; Bundschuh, P.; Schenk, J.; Panhofer, H.; Pastucha, K.; Maunz, B. Scrap melting in BOF: Influence of particle surface and size during dynamic converter modelling. In Proceedings of the 3rd ABM week, São Paulo, Brazil, 2–6 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoryan, A.H.; Stomakhin, A.J.; Ponomarenko, A.G. Physico-Chemical Calculations of the Electric Steel Process; Metallurgy: Moscow, Russia, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnikova, K.; Gogunskii, V.; Olekh, T. Calculation of equilibrium in the system metal-slag during steelmaking in electric arc furnace. Metall. Min. Ind. 2016, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sigworth, G.K.; Elliot, J.F. The thermodynamics of liquid dilute iron alloys. Met. Sci. 1974, 8, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvynyuk, Y.; Schenk, J.; Hiebler, M.; Sormann, A. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Model of the Converter Steelmaking Process. Part 2: The Model Validation. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadell, H. Volume, shape, and roundness of quartz particles. J. Geol. 1935, 43, 250–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penz, F.M. Charakterisierung des Hochofeneinsatzstoffes Sinter, Mittels Optischer 3D-Partikelanalyse. Bachelor’s Thesis, Montanuniversitaet Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Medhibozhskiy, M.Y. Basis of Thermodynamic and Kinetic of Steelmaking; Vischa shkola: Kyiv, Ukraine, 1979; p. 229. [Google Scholar]
- Isobe, K.; Maede, H.; Ozawa, K.; Umezawa, K.; Saito, C. Analysis of the Scrap Melting Rate in High Carbon Molten Iron. ISIJ 1990, 76, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zarl, M. Development and Evaluation of a BOF Pre-Processor Model. Master’s Thesis, Montanuniversität Leoben, Leoben, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]












| Definition | Unit | Hot Metal | Standard Scrap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon content | wt.% | 4.536 | 0.737 |
| Silicon content | wt.% | 0.410 | 0.349 |
| Manganese content | wt.% | 1.171 | 1.060 |
| Phosphorus content | wt.% | 0.100 | 0.013 |
| Iron content | wt.% | 93.783 | 97.841 |
| Mass | t | 53.60 | 15.72 |
| Temperature | °C | 1318 | 20 |
| Name | Unit | Initial Slag | Dust Pellets | Sand | Lime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 content | wt.% | 11.32 | - | 92.79 | 0.980 |
| MnO content | wt.% | 11.93 | 2.960 | - | - |
| P2O5 content | wt.% | 1.330 | - | - | - |
| FeO content | wt.% | 29.66 | - | - | - |
| CaO content | wt.% | 40.08 | 7.320 | - | 92.37 |
| MgO content | wt.% | 4.380 | 4.580 | - | 3.080 |
| CO2 content | wt.% | - | - | - | 2.400 |
| H2O content | wt.% | - | - | - | 0.170 |
| Fe2O3 content | wt.% | - | 67.88 | - | - |
| Fe content | wt.% | - | 11.09 | - | - |
| Amount of charged material | t | 0.001 | 1.000 | 0.172 | 2.800 |
| Name and Unit | Standard Scrap | Lower Value | Higher Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon content (wt.%) | 0.7370 | 0.40 | −45.7% | 1.00 | 35.68% |
| Silicon content (wt.%) | 0.3488 | 0.10 | −71.3% | 0.70 | 100.7% |
| Phosphorus content (wt.%) | 0.0130 | - | - | 0.05 | 273.1% |
| Size (m) | 0.1 | 0.08 | −20.0% | 0.12 | 20.00% |
| Mass (t) | 15.72 | 13.0 | −17.3% | 17.0 | % |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penz, F.M.; Schenk, J.; Ammer, R.; Klösch, G.; Pastucha, K. Evaluation of the Influences of Scrap Melting and Dissolution during Dynamic Linz–Donawitz (LD) Converter Modelling. Processes 2019, 7, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040186
Penz FM, Schenk J, Ammer R, Klösch G, Pastucha K. Evaluation of the Influences of Scrap Melting and Dissolution during Dynamic Linz–Donawitz (LD) Converter Modelling. Processes. 2019; 7(4):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040186
Chicago/Turabian StylePenz, Florian Markus, Johannes Schenk, Rainer Ammer, Gerald Klösch, and Krzysztof Pastucha. 2019. "Evaluation of the Influences of Scrap Melting and Dissolution during Dynamic Linz–Donawitz (LD) Converter Modelling" Processes 7, no. 4: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040186
APA StylePenz, F. M., Schenk, J., Ammer, R., Klösch, G., & Pastucha, K. (2019). Evaluation of the Influences of Scrap Melting and Dissolution during Dynamic Linz–Donawitz (LD) Converter Modelling. Processes, 7(4), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040186