Explicit Residence Time Distribution of a Generalised Cascade of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors for a Description of Short Recirculation Time (Bypassing)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of RTD Modelling
3. RTD Models and Their Limits
3.1. Ideal Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)
3.2. Ideal Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
3.3. Tanks-in-Series (TIS)
3.4. Diffusion Model
3.5. Convection Model
4. Generalised Cascade of n Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors: The n-CSTR Model
4.1. The Γ(n) Function
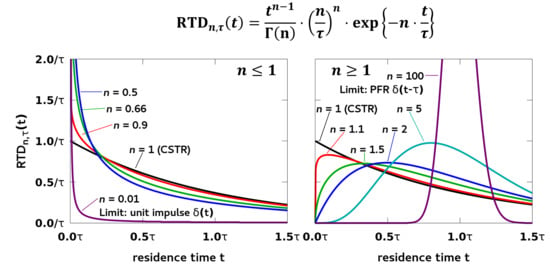
4.2. Influence of Shape Parameter n
4.3. Quantification of Bypassing Material Fraction
4.4. Filtering of Mass Flow Fluctuations in a Continuous Manufacturing Line
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plumb, K. Continuous Processing in the Pharmaceutical Industry. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2005, 83, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, S.D.; Gerogiorgis, D.I.; Ramachandran, R.; Evans, J.M.B.; Barton, P.I.; Trout, B.L. Economic Analysis of Integrated Continuous and Batch Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Case Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10083–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, G.; Cain, Y.T.; Cooney, C.; Garcia, T.; Bizjak, T.G.; Holte, O.; Jagota, N.; Komas, B.; Korakianiti, E.; Kourti, D.; et al. Regulatory and Quality Considerations for Continuous Manufacturing May 20–21, 2014 Continuous Manufacturing Symposium. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, I.; Hsiao, W.-K.; Dujmovic, D.; Stegemann, S.; Khinast, J. Methodology for Economic and Technical Comparison of Continuous and Batch Processes to Enhance Early Stage Decision-making. In Continuous Manufacturing of Pharmaceuticals; Kleinebudde, P., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 485–505. ISBN 978-1-119-00134-8. [Google Scholar]
- Adam, S.; Suzzi, D.; Radeke, C.; Khinast, J.G. An integrated Quality by Design (QbD) approach towards design space definition of a blending unit operation by Discrete Element Method (DEM) simulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.X. Pharmaceutical Quality by Design: Product and Process Development, Understanding, and Control. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaya, A.; De Belder, L.; Meyer, R.; Nagapudi, K.; Lin, H.-R.H.; Leavesley, I.; Jayanth, J.; Bajwa, G.; DiNunzio, J.; Tantuccio, A.; et al. Control Strategies for Drug Product Continuous Direct Compression—State of Control, Product Collection Strategies, and Startup/Shutdown Operations for the Production of Clinical Trial Materials and Commercial Products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engisch, W.; Muzzio, F. Using Residence Time Distributions (RTDs) to Address the Traceability of Raw Materials in Continuous Pharmaceutical Manufacturing. J. Pharm. Innov. 2016, 11, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehrl, J.; Kruisz, J.; Sacher, S.; Khinast, J.; Horn, M. Optimized continuous pharmaceutical manufacturing via model-predictive control. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruisz, J.; Rehrl, J.; Sacher, S.; Aigner, I.; Horn, M.; Khinast, J.G. RTD modeling of a continuous dry granulation process for process control and materials diversion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinetz, M.C.; Karttunen, A.-P.; Sacher, S.; Wahl, P.; Ketolainen, J.; Khinast, J.G.; Korhonen, O. RTD-based material tracking in a fully-continuous dry granulation tableting line. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, F.; Chatellier, P.; Esposito, G.; Fabbricino, M.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Lens, P.N.L. Hydrodynamic Mathematical Modelling of Aerobic Plug Flow and Nonideal Flow Reactors: A Critical and Historical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 2642–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzalski, A.S.; Harrington, G.W.; Coronell, O. Modeling Water Treatment Reactor Hydraulics Using Reactor Networks. J.-Am. Water Works Assoc. 2018, 110, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheoran, M.; Chandra, A.; Bhunia, H.; Bajpai, P.K.; Pant, H.J. Residence time distribution studies using radiotracers in chemical industry—A review. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMullin, R.; Weber, M. The theory of short-circuiting in continuous-flow mixing vessels in series and the kinetics of chemical reactions in such systems. Trans. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1935, 31, 409–458. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 978-0-471-25424-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fogler, H.S. Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall PTR International Series in the Physical and Chemical Engineering Sciences; Prentice Hall PTR: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-13-047394-3. [Google Scholar]
- Levenspiel, O.; Smith, W.K. Notes on the diffusion-type model for the longitudinal mixing of fluids in flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1957, 6, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.B.; Levenspiel, O. Fluid dispersion-generalization and comparison of mathematical models—I generalization of models. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1962, 17, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, E.T. Notes on the diffusion-type model for the longitudinal mixing in flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1958, 7, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthakrishnan, V.; Gill, W.N.; Barduhn, A.J. Laminar dispersion in capillaries: Part I. Mathematical analysis. AIChE J. 1965, 11, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruthven, D.M. The residence time distribution for ideal laminar flow in helical tube. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1971, 26, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levien, K.L.; Levenspiel, O. Optimal product distribution from laminar flow reactors: Newtonian and other power-law fluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1999, 54, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.G.C.C.; Dias, E.F.T.S.; Gut, J.A.W. Residence time distribution in holding tubes using generalized convection model and numerical convolution for non-ideal tracer detection. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.D. Interpretation of residence time distribution data. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.M.; Roberts, E.P.L.; Hill, A.; Campen, A.K.; Brown, N.W. Continuous water treatment by adsorption and electrochemical regeneration. Water Res. 2011, 45, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittrich, E.; Klincsik, M. Analysis of conservative tracer measurement results using the Frechet distribution at planted horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands filled with coarse gravel and showing the effect of clogging processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17104–17122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, B.M.; Tavares, R.P. Description of a New Tundish Model for Treating RTD Data and Discussion of the Communication “New Insight into Combined Model and Revised Model for RTD Curves in a Multi-strand Tundish” by Lei. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 2128–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toson, P.; Siegmann, E.; Trogrlic, M.; Kureck, H.; Khinast, J.; Jajcevic, D.; Doshi, P.; Blackwood, D.; Bonnassieux, A.; Daugherity, P.D.; et al. Detailed modeling and process design of an advanced continuous powder mixer. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 552, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heibel, A.K.; Lebens, P.J.M.; Middelhoff, J.W.; Kapteijn, F.; Moulijn, J. Liquid residence time distribution in the film flow monolith reactor. AIChE J. 2005, 51, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Serna, J.; García-Verdugo, E.; Hyde, J.R.; Fraga-Dubreuil, J.; Yan, C.; Poliakoff, M.; Cocero, M.J. Modelling residence time distribution in chemical reactors: A novel generalised n-laminar model. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2007, 41, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leray, S.; Engdahl, N.B.; Massoudieh, A.; Bresciani, E.; McCallum, J. Residence time distributions for hydrologic systems: Mechanistic foundations and steady-state analytical solutions. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, P.J. Leonhard Euler’s Integral: A Historical Profile of the Gamma Function: In Memoriam: Milton Abramowitz. Am. Math. Mon. 1959, 66, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free Software Foundation The GNU C Library: Special Functions. Available online: http://www.gnu.org/software/libc/manual/html_node/Special-Functions.html (accessed on 23 January 2018).
- The Scipy Community Scipy.Special.Gamma—SciPy v0.14.0 Reference Guide. Available online: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy-0.14.0/reference/generated/scipy.special.gamma.html (accessed on 23 January 2018).
- Mathworks Inc. Gamma Function-MATLAB Gamma-MathWorks. Available online: https://mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/gamma.html?requestedDomain=true (accessed on 23 January 2018).
- Microsoft Corporation GAMMA Function. Available online: https://support.office.com/en-us/article/gamma-function-ce1702b1-cf55-471d-8307-f83be0fc5297 (accessed on 23 January 2018).
- Mo, Y.; Jensen, K.F. A miniature CSTR cascade for continuous flow of reactions containing solids. React. Chem. Eng. 2016, 1, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elgeti, K. A new equation for correlating a pipe flow reactor with a cascade of mixed reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1996, 51, 5077–5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Muzzio, F.; Ierapetritou, M. Characterization of feeder effects on continuous solid mixing using fourier series analysis. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toson, P.; Doshi, P.; Jajcevic, D. Explicit Residence Time Distribution of a Generalised Cascade of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors for a Description of Short Recirculation Time (Bypassing). Processes 2019, 7, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7090615
Toson P, Doshi P, Jajcevic D. Explicit Residence Time Distribution of a Generalised Cascade of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors for a Description of Short Recirculation Time (Bypassing). Processes. 2019; 7(9):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7090615
Chicago/Turabian StyleToson, Peter, Pankaj Doshi, and Dalibor Jajcevic. 2019. "Explicit Residence Time Distribution of a Generalised Cascade of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors for a Description of Short Recirculation Time (Bypassing)" Processes 7, no. 9: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7090615
APA StyleToson, P., Doshi, P., & Jajcevic, D. (2019). Explicit Residence Time Distribution of a Generalised Cascade of Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors for a Description of Short Recirculation Time (Bypassing). Processes, 7(9), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7090615