Competing Endogenous RNAs in Cervical Carcinogenesis: A New Layer of Complexity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Cross-Regulatory Mechanisms Involving lncRNAs and miRNAs
3. The ceRNA Hypothesis: A miRNA-Mediated Interplay through Complex Networks of Interactions between Coding and Noncoding RNAs
4. LncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Axes in Cervical Tissue: Unveiling Important Networks in CC
4.1. In Silico Predictions and In Vitro Strategies Reveal Molecular Interactions between Different Components of the Proposed ceRNA Networks
4.2. In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments Demonstrate the Final Biological Impacts of the Respective Molecules/ceRNA Axes over Important Cellular Processes and Tumor Growth
4.3. Evaluating Patients: Corroborating the Involvement of lncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Networks in Cervical Carcinogenesis
5. Important Cancer-Related RNAs Working through Different lncRNA-Mediated Axes in CC
5.1. HOTAIR, MALAT1, NEAT1, OIP5-AS1, and XIST
5.2. MiR-140-5p, miR-143-3p, miR-148a-3p, and miR-206
5.3. MAPK1, PTEN, and ROCK1
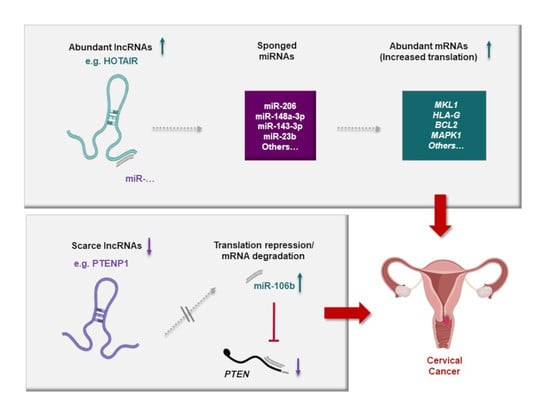
6. Protumorigenic and Tumor-Suppressive lncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Axes Involved in Cervical Carcinogenesis
7. Remarks and Perspectives
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tota, J.E.; Isidean, S.D.; Franco, E.L. Defining benchmarks for tolerable risk thresholds in cancer screening: Impact of HPV vaccination on the future of cervical cancer screening. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 3305–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, E.E.L.; Zielonke, N.; Gini, A.; Anttila, A.; Segnan, N.; Vokó, Z.; Ivanuš, U.; McKee, M.; de Koning, H.J.; de Kok, I.M.C.M.; et al. Effect of organised cervical cancer screening on cervical cancer mortality in Europe: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 127, 207–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mandal, R.; Basu, P. Cancer screening and early diagnosis in low and middle income countries: Current situation and future perspectives. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforsch. Gesundh. 2018, 61, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Urrutia, E.; Bustamante Montes, L.P.; Ladrón de Guevara Cervantes, D.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Campos-Parra, A.D. Crosstalk Between Long Non-coding RNAs, Micro-RNAs and mRNAs: Deciphering Molecular Mechanisms of Master Regulators in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Xing, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Cui, M.; Jiang, B. MicroRNAs and ceRNAs: RNA networks in pathogenesis of cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 25, 235–239. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, M.; Du, S.; Feng, W.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Jia, G.; Wu, L.; Hu, X.; et al. Competitive endogenous RNA is an intrinsic component of EMT regulatory circuits and modulates EMT. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Chen, Y. Competing endogenous RNA networks in cervical cancer: Function, mechanism and perspective. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 709–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Cullen, B.R. The imprinted H19 noncoding RNA is a primary microRNA precursor. RNA 2007, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leucci, E.; Patella, F.; Waage, J.; Holmstrøm, K.; Lindow, M.; Porse, B.; Kauppinen, S.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA-9 targets the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for degradation in the nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Modarresi, F.; Van der Brug, M.P.; Nalls, M.A.; Cookson, M.R.; St-Laurent, G.; Wahlestedt, C. Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Lieberman, J.; Lal, A. Desperately seeking microRNA targets. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, L.W.; Fletcher, S.; Wilton, S.D. Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by the untranslated gene regions and other non-coding elements. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3613–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhäusser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H. Redefining MicroRNA Targets. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, I.V.; Hennelly, S.P.; Sanbonmatsu, K.Y. Sizing up long non-coding RNAs: Do lncRNAs have secondary and tertiary structure? Bioarchitecture 2012, 2, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchese, F.P.; Raimondi, I.; Huarte, M. The multidimensional mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, W.; Chen, Q.; Chen, M. Non-Coding RNAs and their Integrated Networks. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Shen, B. Decoding competing endogenous RNA networks for cancer biomarker discovery. Brief. Bioinform. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ala, U. Competing Endogenous RNAs, Non-Coding RNAs and Diseases: An Intertwined Story. Cells 2020, 9, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jiang, H.; Shu, C.; Hu, M.Q.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.F.; Wei, Y.Z. Integrated analysis of circular RNA-associated ceRNA network in cervical cancer: Observational Study. Medicine 2019, 98, e16922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Guo, X. Overexpression of circular RNA hsa_circ_0001038 promotes cervical cancer cell progression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-337-3p to regulate cyclin-M3 and metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1 expression. Gene 2020, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, L. LncRNA BBOX1-AS1 upregulates HOXC6 expression through miR-361-3p and HuR to drive cervical cancer progression. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Ye, W.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, J. Long non-coding RNA C5orf66-AS1 promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer by targeting miR-637/RING1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Liu, W.; Bai, X.; Pan, W.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, W. LncRNA-CTS promotes metastasis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulating miR-505/ZEB2 axis in cervical cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 465, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Zhang, C.; Guan, H.; Liu, J.; Cui, Y. LncRNA DANCR promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating ROCK1 via sponging miR-335-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7266–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Jin, H.; Zheng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Li, X.; Dong, L. DANCR-mediated microRNA-665 regulates proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer through the ERK/SMAD pathway. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rui, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ji, L.; Jiang, X. LncRNA DLG1-AS1 Promotes Cell Proliferation by Competitively Binding with miR-107 and Up-Regulating ZHX1 Expression in Cervical Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hong, L.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L. LncRNA GAS5 suppresses the tumorigenesis of cervical cancer by downregulating miR-196a and miR-205. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, H.M.; Fang, D.M.; Meng, Q.J.; Xin, Y.H. LncRNA HCP5 promotes the development of cervical cancer by regulating MACC1 via suppression of microRNA-15a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4812–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Chao, X.; Shi, S.; Liang, M.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhu, Z. HOTAIR contributes to cell proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer via targetting miR-23b/MAPK1 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, P.; Yin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, T.C. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes cell migration and invasion by regulating MKL1 via inhibition miR206 expression in HeLa cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Chu, H.; Ji, J.; Huo, G.; Song, Q.; Zhang, X. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates HLA-G expression by absorbing miR-148a in human cervical cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, R. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.J.; Du, X.J.; Wang, H.P.; Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.F. Long non-coding RNA 00152 promotes cell proliferation in cervical cancer via regulating miR-216b-5p/HOXA1 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 3654–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.C.; Xin, L.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, Y. Long Intervening Noncoding 00467 RNA Contributes to Tumorigenesis by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA against miR-107 in Cervical Cancer Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2293–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, X.; Song, G.; Zhan, L.; Cao, Y. Long non-coding RNA Linc00483 accelerated tumorigenesis of cervical cancer by regulating miR-508-3p/RGS17 axis. Life Sci. 2019, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Fang, X. LINC01128 expedites cervical cancer progression by regulating miR-383-5p/SFN axis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Long non-coding RNA LINC01535 promotes cervical cancer progression via targeting the miR-214/EZH2 feedback loop. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6098–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W. Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1/microRNA-202-3p/periostin axis modulates invasion and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human cervical cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14170–14180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Song, L.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, L. MALAT1-miR-124-RBG2 axis is involved in growth and invasion of HR-HPV-positive cervical cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Lin, S.; Zheng, M.; Cai, Q.; Tu, Y. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 promotes the growth of cervical cancer cells via sponging miR-9-5p. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, H. Long non-coding nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1 acts as prognosis biomarker and increases cell growth and invasion in cervical cancer by sequestering microRNA-101. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.Y.; Zhou, M.; Lv, H.; Qin, X.; Zhou, J.; Mao, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, H. Involvement of NEAT1/miR-133a axis in promoting cervical cancer progression via targeting SOX4. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18985–18993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, J.; Nan, G.; Lyu, Y.; Ni, G. LncRNA NOC2L-4.1 functions as a tumor oncogene in cervical cancer progression by regulating the miR-630/YAP1 pathway. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 16913–16920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Qu, C.; Wang, N. Long non-coding RNA NORAD upregulate SIP1 expression to promote cell proliferation and invasion in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, D.; Yang, H.; Ye, L.; Mei, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Shang, X.; Wang, K.; Huang, L. Long noncoding RNA OPA-interacting protein 5 antisense transcript 1 upregulated SMAD3 expression to contribute to metastasis of cervical cancer by sponging miR-143-3p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5264–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, L.; Pan, X.; Yang, C. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 targets ROCK1 to promote cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis through a mechanism involving miR-143-3p in cervical cancer. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Sun, L.; Feng, G. SP1-mediated long noncoding RNA POU3F3 accelerates the cervical cancer through miR-127-5p/FOXD1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Sheng, W.; Meng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, R. LncRNA PTENP1 inhibits cervical cancer progression by suppressing miR-106b. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Lv, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Ren, Y.; et al. Long non-coding RNA RP11-552M11.4 favors tumorigenesis and development of cervical cancer via modulating miR-3941/ATF1 signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, X.; Que, S.; Yang, X.; Fan, H.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. LncRNA RSU1P2 contributes to tumorigenesis by acting as a ceRNA against let-7a in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43768–43781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Feng, J.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Xi, J.; Yang, J. LncRNA SBF2-AS1 promotes the progression of cervical cancer by regulating miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Hong, J.; Wijayakulathilaka, W.S.M.A. Long non-coding RNA SNHG4 promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating c-Met via targeting miR-148a-3p. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.J.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Hu, W.S.; Ou, R.Y.; Li, S.; Xue, J.S.; Chen, L.L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, H. Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 promotes the progression of cervical cancer via modulating miR-125b/STAT3 axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 6624–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Wang, Y.; Bao, G.; Yan, J.; Ji, S. LncRNA SNHG14 promotes the progression of cervical cancer by regulating miR-206/YWHAZ. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, S.; Li, S.; Yan, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, H. LncRNA SNHG20 promotes cell proliferation and invasion via miR-140-5p-ADAM10 axis in cervical cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z. Long noncoding RNA SOX21-AS1 promotes cervical cancer progression by competitively sponging miR-7/VDAC1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17494–17504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA STXBP5-AS1 suppressed cervical cancer progression via targeting miR-96-5p/PTEN axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Ying, F.; Zou, R.; Lin, F.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, X.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; et al. LncRNA-TCONS_00026907 is involved in the progression and prognosis of cervical cancer through inhibiting miR-143-5p. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 1409–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Mo, K.; Su, S.; Wang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhou, R. The lncRNA TDRG1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-326 to regulate MAPK1 expression in cervical cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, M.M.; Rao, Q.X.; Huang, M.L.; Wang, L.J.; Lin, S.D.; Chen, Q.; Liu, C.H. Long noncoding RNA TP73-AS1 targets microRNA-329-3p to regulate expression of the SMAD2 gene in human cervical cancer tissue and cell lines. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 8131–8141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, R.; Yue, Q.; Hao, M. Long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis in cervical cancer via miR-573/E2F3. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. LncRNA TUSC8 inhibits the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cells via miR-641/PTEN axis. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.G.; Guo, L.L.; Xia, X.; Pan, Y. Long non-coding RNA WT1-AS inhibits cell aggressiveness via miR-203a-5p/FOXN2 axis and is associated with prognosis in cervical cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, T.; Yu, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L. LncRNA XIST accelerates cervical cancer progression via upregulating Fus through competitively binding with miR-200a. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, D.; Ye, L.; Wang, K.; Huang, L.; Mei, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Lai, X.; Zheng, L.; et al. Up-regulated lncRNA XIST contributes to progression of cervical cancer via regulating miR-140-5p and ORC1. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y. Long noncoding RNA ZNF667-AS1 reduces tumor invasion and metastasis in cervical cancer by counteracting microRNA-93-3p-dependent PEG3 downregulation. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 2375–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.H.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of Mammalian MicroRNA Targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, L.; Yuan, X.; Jiang, B.; Tang, Z.; Li, G.-C. LncRNAs: Key players and novel insights into cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clancy, J.L.; Nousch, M.; Humphreys, D.T.; Westman, B.J.; Beilharz, T.H.; Preiss, T. Methods to Analyze Mi-croRNA-Mediated Control of mRNA Translation. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 431, 83–111. [Google Scholar]
- Tornesello, M.L.; Faraonio, R.; Buonaguro, L.; Annunziata, C.; Starita, N.; Cerasuolo, A.; Pezzuto, F.; Tornesello, A.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. The Role of microRNAs, Long Non-coding RNAs, and Circular RNAs in Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajagopal, T.; Talluri, S.; Akshaya, R.L.; Dunna, N.R. HOTAIR LncRNA: A novel oncogenic propellant in human cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 503, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjari, M.; Salavaty, A. HOTAIR: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Alsager, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Shan, B. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, Q. LncRNA PVT1 regulates prostate cancer cell growth by inducing the methylation of miR-146a. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalijahan, H.; Ghorbian, S. Long non-coding RNAs and cervical cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 106, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q. Regulatory networks of lncrna malat-1 in cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 10181–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K. NEAT1: A novel cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klec, C.; Prinz, F.; Pichler, M. Involvement of the long noncoding RNA NEAT1 in carcinogenesis. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Han, X.; Feng, H.; Han, J. Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 in cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 499, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, F.; Lin-lin, L.; Liu, C.; Songyang, Y.-y.; Sun, C.-c.; Li, D. Long non coding RNA XIST as a prognostic cancer marker—A meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 482, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weakley, S.M.; Wang, H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Expression and function of a large non-coding RNA gene XIST in human cancer. World J. Surg. 2011, 35, 1751–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, J. MiR-140-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in colorectal carcinoma by targeting SOX4. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, T.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Mao, J. MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits invasion and angiogenesis through targeting VEGF-A in breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, X.; Yin, D.; Xue, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; et al. Effect of miR-140-5p on the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis in NSCLC and its underlying mechanism. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.F.; Qin, B.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.H.; Li, W.C.; Chen, K.S. Downregulation of circDYNC1H1 exhibits inhibitor effect on cell proliferation and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma through miR-140-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17775–17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Yu, Z. The effects of miR-140-5p on the biological characteristics of ovarian cancer cells through the Wnt signaling pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, B.; Hai, J.; Duan, S.; Dong, X.; Chen, C. Long noncoding RNA opa-interacting protein 5 antisense transcript 1 promotes proliferation and invasion through elevating integrin α6 expression by sponging miR-143-3p in cervical cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Jiang, N. MiR-143-3p suppresses the progression of ovarian cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 866–874. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Peng, W.; Wen, T. MiR-143-3p suppresses tumorigenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting KRAS. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Yang, Y.; Kong, F.; Kong, Q.; Shan, C. MiR-143-3p inhibits the proliferation, cell migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells by modulating the expression of MAPK7. Biochimie 2018, 147, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhan, M.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; Long, M.; Shen, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q.; Mohan, M.; Wang, J. MiR-143-5p Deficiency Triggers EMT and Metastasis by Targeting HIF-1α in Gallbladder Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2078–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, H.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Misono, S.; Uchida, A.; Yamada, Y.; Moriya, S.; Kikkawa, N.; Machida, K.; Kumamoto, T.; et al. Involvement of dual strands of miR-143 (miR-143-5p and miR-143-3p) and their target oncogenes in the molecular pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Shen, S.; Zheng, X.; Ye, K.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ge, H. Long noncoding RNA HAGLR acts as a microRNA-143-5p sponge to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastatic potential in esophageal cancer by regulating LAMP3. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10490–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qin, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Shen, H.; Cong, T.; Schiferle, E.; Xiao, S. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA-206 sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y. MiR-206 inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting BAG3 in human cervical cancer. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Tian, Y.; Hao, F. Downregulation of lncRNA UCA1 inhibits proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells through miR-206 expression. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Buse, M.; Busuioc, C.; Drula, R.; Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Rusu, A.; Irimie, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Slaby, O.; et al. A comprehensive review on MAPK: A promising therapeutic target in cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Qiu, M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, T.; Guo, W. PTEN, Insulin Resistance and Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderali, E.; Khaki, A.A.; Rad, J.S.; Ali-Hemmati, A.; Rahmati, M.; Charoudeh, H.N. Regulation and modulation of PTEN activity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 2869–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Chen, J.; He, L.; Stiles, B.L. PTEN: Tumor suppressor and metabolic regulator. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Surma, M.; Shi, S.; Lambert-Cheatham, N.; Shi, J. Novel Insights into the Roles of Rho Kinase in Cancer. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz) 2016, 64, 259–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Jiao, H.; Liao, J.; Xu, X. Cytokinesis and cancer: Polo loves ROCK’n’ Rho(A). J. Genet. Genom. 2010, 37, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahbazi, R.; Baradaran, B.; Khordadmehr, M.; Safaei, S.; Baghbanzadeh, A.; Jigari, F.; Ezzati, H. Targeting ROCK signaling in health, malignant and non-malignant diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 219, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Hann, S.S. HOTAIR: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in cervical cancer: Molecular marker, mechanistic insight, and therapeutic target. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2020, 97, 117–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhu, Q.N.; Zhang, H.B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.S. MALAT1: A potential biomarker in cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6757–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Rao, L. MicroRNA-140-5p targets insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) to suppress cervical cancer growth and metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68397–68411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, H. MicroRNA-206 suppresses proliferation and predict poor prognosis of HR-HPV-positive cervical cancer cells by targeting G6PD. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5946–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Deng, X.; Zeng, X.; Peng, X. The role of Mir-148a in cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milella, M.; Falcone, I.; Conciatori, F.; Incani, U.C.; Del Curatolo, A.; Inzerilli, N.; Nuzzo, C.M.A.; Vaccaro, V.; Vari, S.; Cognetti, F.; et al. PTEN: Multiple functions in human malignant tumors. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabili, M.N.; Dunagin, M.C.; McClanahan, P.D.; Biaesch, A.; Padovan-Merhar, O.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Raj, A. Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolla, G.A. A non-canonical landscape of the microRNA system. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, A.K.L. The Whereabouts of microRNA Actions: Cytoplasm and Beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhi, H.; Li, X.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. LnCeCell: A comprehensive database of predicted lncRNA-associated ceRNA networks at single-cell resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D125–D133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowling, S.; Morris, K.V. Non-coding RNA and antisense RNA. Nature’s trash or treasure? Biochimie 2011, 93, 1922–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sen, R.; Ghosal, S.; Das, S.; Balti, S.; Chakrabarti, J. Competing endogenous RNA: The key to posttranscriptional regulation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Kameyama, H.; Takabe, K.; Okuda, S.; Wakai, T. Next generation sequencing-based gene panel tests for the management of solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. RNA-based therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsui, M.; Corey, D.R. Non-coding RNAs as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Investigated Molecular Targets | Study Design (Strategies) | LncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Networks (Axes) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lncRNA | miRNA | mRNA | Protein | In Silico | In Vitro | In Vivo | Patients | ||
| A [29] | BBOX1-AS1 | miR-361-3p | HOXC6 | HOXC6 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | BBOX1-AS1/miR-361-3p/HOXC6 axis * |
| A [30] | C5orf66-AS1 | miR-637 | RING1 | RING1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | C5orf66-AS1/miR-637/RING1 axis |
| A [31] | CTS | miR-505 | ZEB2 | ZEB2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | CTS/miR-505/ZEB2 axis ** |
| A [32] | DANCR | miR-335-5p | ROCK1 | ROCK1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | DANCR/miR-335-5p/ROCK1 |
| A [33] | DANCR | miR-665 | TGFBR1 | TGFBR1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | DANCR/miR-665/TGFBR1 axis |
| B [34] | DLG1-AS1 | miR-107 | ZHX1 | - | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | DLG1-AS1/miR-107/ZHX1 axis |
| A [35] | GAS5 | miR-196a | - | FOXO | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | GAS5/miR-196a/FOXO1 axis |
| A [35] | GAS5 | miR-205 | - | PTEN | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | GAS5/miR-205/PTEN axis |
| B [36] | HCP5 | miR-15a | MACC1 | MACC1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | HCP5/miR-15a/MACC1 axis |
| A [37] | HOTAIR | miR-23b | MAPK1 | MAPK1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | HOTAIR/miR-23b/MAPK1 axis |
| B [38] | HOTAIR | miR-206 | MKL1 | MKL1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | HOTAIR/miR-206/MKL1 axis *** |
| A [39] | HOTAIR | miR-148a | HLA-G | HLA-G | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | HOTAIR/miR-148a/HLA-G axis |
| A [40] | HOTAIR | miR-143-3p | BCL2 | Bcl-2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | HOTAIR/miR-143-3p/BCL2 axis |
| A [41] | LINC00152 | miR-216b-5p | HOXA1 | HOXA1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | LINC00152/miR-216b-5p/HOXA1 axis |
| A [42] | LINC00467 | miR-107 | KIF23 | KIF23 | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | LINC00467/miR-107/KIF23 axis |
| A [43] | LINC00483 | miR-508-3p | RGS17 | RGS17 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | LINC00483/miR-508-3p/RGS17 axis |
| A [44] | LINC01128 | miR-383-5p | SFN | Stratifin | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | LINC01128/miR-383-5p/SFN axis |
| A [45] | LINC01535 | miR-214 | - | EZH2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | LINC01535/miR-214/EZH2 axis *** |
| B [46] | MALAT1 | miR-202-3p | POSTN | Periostin | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | MALAT1/miR-202-3p/POSTN axis |
| B [47] | MALAT1 | miR-124 | GRB2 | Grb2 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | MALAT1/miR-124/GRB2 axis |
| A [48] | NEAT1 | miR-9-5p | PTEN | PTEN | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | NEAT1/miR-9-5p/PTEN axis |
| A [48] | NEAT1 | miR-9-5p | POU2F1 | POU2F1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | NEAT1/miR-9-5p/POU2F1 axis |
| A [49] | NEAT1 | miR-101 | FOS | - | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | NEAT1/miR-101/FOS axis |
| B [50] | NEAT1 | miR-133a | SOX4 | SOX4 | X | ✓ | ✓ | X | NEAT1/miR-133a/SOX4 axis |
| B [51] | NOC2L-4.1 | miR-630 | YAP1 | YAP1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | X | NOC2L-4.1/miR-630/YAP1 axis |
| A [52] | NORAD | miR-590-3p | SIP1 | SIP1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | NORAD/miR-590-3p/SIP1 axis |
| B [53] | OIP5-AS1 | miR-143-3p | SMAD3 | SMAD3 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/SMAD3 axis |
| A [54] | OIP5-AS1 | miR-143-3p | ROCK1 | ROCK1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/ROCK1 axis |
| A [55] | POU3F3 | miR-127-5p | FOXD1 | FOXD1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | POU3F3/miR-127-5p/FOXD1 axis 1 |
| A [56] | PTENP1 | miR-106b | PTEN | PTEN | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | PTENP1/miR-106b/PTEN axis |
| A [57] | RP11-552-M11.4 | miR-3941 | ATF1 | ATF1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | RP11-552M11.4/miR-3941/ATF1 axis |
| A [58] | RSU1P2 | let-7a | IGF1R | IGF1R | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | RSU1P2/let-7a/IGF1R axis |
| A [58] | RSU1P2 | let-7a | NMYC | N-Myc | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | RSU1P2/let-7a/NMYC axis |
| A [58] | RSU1P2 | let-7a | EPHA4 | EPHA4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | RSU1P2/let-7a/EPHA4 axis |
| A [59] | SBF2-AS1 | miR-361-5p | FOXM1 | FOXM1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | SBF2-AS1/miR-361-5p/FOXM1 axis |
| A [60] | SNHG4 | miR-148a-3p | MET | c-Met | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | SNHG4/miR-148a-3p/MET axis |
| B [61] | SNHG12 | miR-125b | STAT3 | STAT3 | ✓ | ✓ | X | X | SNHG12/miR-125b/STAT3 axis |
| A [62] | SNHG14 | miR-206 | YWHAZ | YWHAZ | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | SNHG14/miR-206/YWHAZ axis |
| A [63] | SNHG20 | miR-140-5p | ADAM10 | ADAM10 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | SNHG20/miR-140-5p/ADAM10 axis |
| A [64] | SOX21-AS1 | miR-7 | VDAC1 | VDAC1 | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | SOX21-AS1/miR-7/VDAC1 axis |
| A [65] | STXBP5-AS1 | miR-96-5p | PTEN | PTEN | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | STXBP5-AS1/miR-96-5p/PTEN axis |
| A [66] | TCONS_00026907 | miR-143-5p | ELK1 | ELK1 | X | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | TCONS_00026907/miR-143-5p/ELK1 axis |
| A [67] | TDRG1 | miR-326 | MAPK1 | MAPK1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | TDRG1/miR-326/MAPK1 axis |
| A [68] | TP73-AS1 | miR-329-3p | SMAD2 | SMAD2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | TP73-AS1/miR-329-3p/SMAD2 axis |
| A [69] | TTN-AS1 | miR-573 | E2F3 | E2F3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | TTN-AS1/miR-573/E2F3 axis |
| A [70] | TUSC8 | miR-641 | PTEN | PTEN | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | TUSC8/miR-641/PTEN axis |
| A [71] | WT1-AS | miR-203a-5p | FOXN2 | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | WT1-AS/miR-203a-5p/FOXN2 axis |
| A [72] | XIST | miR-200a | FUS | FUS | ✓ | ✓ | X | ✓ | XIST/miR-200a/FUS axis |
| A [73] | XIST | miR-140-5p | ORC1 | ORC1 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | XIST/miR-140-5p/ORC1 axis |
| A [74] | ZNF667-AS1 | miR-93-3p | PEG3 | PEG3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ZNF667-AS1/miR-93-3p/PEG3 axis |
| LncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Networks (Axes) [Ref] | Cell Proliferation | Colony Formation | Cell Cycle Progression | Migration | Invasion | Apoptosis | Metastasis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBOX1-AS1/miR-361-3p/HOXC6 [29] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - * |
| C5orf66-AS1/miR-637/RING1 [30] | ↑ (C-4 I/SiHa) | ↑ (C-4 I/SiHa) | ↑ (C-4 I/SiHa) | - | - | ↓ (C-4 I/SiHa) | - |
| CTS/miR-505/ZEB2 axis [31] | - | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - ** |
| DANCR/miR-665/TGFBR1 [33] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - |
| DANCR/miR-335-5p/ROCK1 [32] | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | - | - | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | - | - * |
| DLG1-AS1/miR-107/ZHX1 [34] | ↑ (C4-1/HeLa) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| GAS5/miR-196a/FOXO1 [35] *** | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | - | - | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | ↑ (ME180/SiHa) | - |
| GAS5/miR-205/PTEN [35] *** | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | - | - | ↓ (ME180/SiHa) | ↑ (ME180/SiHa) | - |
| HCP5/miR-15a/MACC1 [36] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HOTAIR/miR-23b/MAPK1 [37] | ↑ (HeLa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa) | ↑ (HeLa) | ↓ (HeLa) | - * |
| HOTAIR/miR-206/MKL1 [38] | - | - | - | ↑ (HeLa) | ↑ (HeLa) | - | - |
| HOTAIR/miR-148a/HLA-G [39] 1 | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | - | - | - * | - * | ↓ (CaSki/HeLa) | - |
| HOTAIR/miR-143-3p/BCL2 [40] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | - | - | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| LINC00152/miR-216b-5p/HOXA1 [41] | ↑ (CaSki/C33A) | - | ↑ (CaSki/C33A) | - | - | ↓ (CaSki/C33A) | - |
| LINC00467/miR-107/KIF23 [42] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - ** |
| LINC00483/miR-508-3p/RGS17 [43] 2 | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | - | - | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↓ (CasKi/HeLa) | - ** |
| LINC01128/miR-383-5p/SFN [44] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| LINC01535/miR-214/EZH2 [45] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (CasKi/HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (CasKi/HeLa/SiHa) | - | - |
| MALAT1/miR-202-3p/POSTN [46] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - |
| MALAT1/miR-124/GRB2 [47] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| NEAT1/miR-9-5p/POU2F1 [48] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | - | - |
| NEAT1/miR-9-5p/PTEN [48] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | - | - |
| NEAT1/miR-101/FOS [49] | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↓ (CaSki/HeLa) | - |
| NEAT1/miR-133a/SOX4 [50] | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | - | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | ↓ (C33A/SiHa) | - |
| NOC2L-4.1/miR-630/YAP1 [51] | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | - | - | - |
| NORAD/miR-590-3p/SIP1 [52] | ↑ (CaSki/SiHa) | ↑ (CaSki/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (CaSki/SiHa) | - | - |
| OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/SMAD3 [53] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - * |
| OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/ROCK1 [54] | ↑ (C33A) | - | - | - | - | ↓ (C33A) | - |
| POU3F3/miR-127-5p/FOXD1 [55] | ↑ (CaSki/HT-3) | ↑ (CaSki/HT-3) | - | - | ↑ (CaSki/HT-3) | - | - |
| PTENP1/miR-106b/PTEN [56] *** | ↓ (CaSki/HeLa) | - | - | - | - | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | - ** |
| RP11-552M11.4/miR-3941/ATF1 [57] | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↑ (CaSki/HeLa) | ↓ (CaSki/HeLa) | - |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/IGF1R [58] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/NMYC [58] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/EPHA4 [58] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - |
| SBF2-AS1/miR-361-5p/FOXM1 [59] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| SNHG4/miR-148a-3p/MET [60] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | - | - | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| SNHG12/miR-125b/STAT3 [61] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - |
| SNHG14/miR-206/YWHAZ [62] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - * |
| SNHG20/miR-140-5p/ADAM10 [63] | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SW756) | - | - |
| SOX21-AS1/miR-7/VDAC1 [64] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - * |
| STXBP5-AS1/miR-96-5p/PTEN [65] *** | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | - | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - ** |
| TCONS_00026907/miR-143-5p/ELK1 [66] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| TDRG1/miR-326/MAPK1 [67] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - * |
| TP73-AS1/miR-329-3p/SMAD2 [68] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - |
| TTN-AS1/miR-573/E2F3 [69] | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (C33A/SiHa) | - | - * |
| TUSC8/miR-641/PTEN [70] *** | - | - | - | ↓ (HeLa) | ↓ (HeLa) | - | - |
| WT1-AS/miR-203a-5p/FOXN2 [71] *** | ↓ (CaSki/SiHa) | - | - | ↓ (CaSki/SiHa) | ↓ (CaSki/SiHa) | - | - ** |
| XIST/miR-140-5p/ORC1 [73] | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | ↑ (C33A/HeLa) | - | - | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - |
| XIST/miR-200a/FUS [72] | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | - | - | ↑ (HeLa/SiHa) | ↓ (HeLa/SiHa) | - |
| ZNF667-AS1/miR-93-3p/PEG3 [74] *** | - | - | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - | ↓ (C33A/HeLa) | - | - ** |
| LncRNA-Mediated ceRNA Networks [Ref] | Sample Description | Observed Results | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | CC (n) | SCC (n) | AD (n) | NTT (n) | Normal (n) | SIL/CIN (n) | Expression Levels of Target Molecules (RNAs by RT-qPCR/Proteins by WB) | |
| BBOX1-AS1/miR-361-3p/HOXC6 [29] | C | 100 | - | - | 100 | - | - | BBOX1-AS1 (Up), miR-361-3p (Down), HOXC6 (Up) |
| C5orf66-AS1/miR-637/RING1 * [30] | C | 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | C5orf66-AS1 (Up), miR-637 (Down) |
| CTS/miR-505/ZEB2 [31] ** | C | - | 50 | - | - | 50 | - | CTS (Up), miR-505 (Down) |
| DANCR/miR-335-5p/ROCK1 [32] | C | 65 | - | - | 65 | - | - | DANCR (Up), miR-335-5p (Down), ROCK1 (Up) |
| DANCR/miR-665/TGFBR1 [33] | C | 33 | - | - | 33 | - | - | DANCR (Up), miR-665 (Down), TGFBR1 mRNA (Up) |
| DLG1-AS1/miR-107/ZHX1 [34] | C | 112 | - | - | 112 | - | - | DLG1-AS1 (Up), miR-107 (Down), ZHX1 mRNA (Up) |
| GAS5/miR-196a/FOXO1 [35] *** | C | 41 | - | - | 41 | - | - | GAS5 (Down) |
| GAS5/miR-205/PTEN [35] *** | C | 41 | - | - | 41 | - | - | GAS5 (Down) |
| HCP5/miR-15a/MACC1 [36] | C | 48 | - | - | 48 | - | - | HCP5 (Up), miR-15a (Down), MACC1 mRNA (Up) |
| HOTAIR/miR-23b/MAPK1 * [37] | C | 33 | - | - | 33 | - | - | HOTAIR (Up), miR-23b (Down) |
| HOTAIR/miR-206 */MKL1 [38] | C | 31 | - | - | 31 | - | - | HOTAIR (Up), MKL1 mRNA (Up) |
| HOTAIR/miR-148a/HLA-G [39] | C | 59 | 50 | 09 | 59 | - | - | HOTAIR (Up), miR-148a (Down), HLA-G mRNA (Up), HLA-G protein (Up) |
| HOTAIR/miR-143-3p/BCL2 [40] | C | 22 | - | - | 22 | - | - | HOTAIR (Up), miR-143-3p (Down) |
| LINC00152/miR-216b-5p/HOXA1 [41] | C | 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | LINC00152 (Up), miR-216b-5p (Down), HOXA1 (Up) |
| LINC00467/miR-107/KIF23 [42] | C | 54 | - | - | 54 | - | - | LINC00467 (Up), miR-107 (Down), KIF23 mRNA (Up), KIF23 protein (Up) |
| LINC00483/miR-508-3p/RGS17 [43] | C | 40 | 38 | 02 | 40 | - | - | LINC00483 (Up), miR-508-3p (Down), RGS17 (Up) |
| LINC01128/miR-383-5p/SFN [44] | C | 33 | 10 | 23 | 33 | - | - | LINC01128 (Up), miR-383-5p (Down), SFN (Up) |
| LINC01535/miR-214/EZH2 [45] | C | 80 | 55 | 25 | 80 | - | - | LINC01535 (Up), miR-214 (Down) |
| MALAT1/miR-202-3p/POSTN [46] | C | 23 | - | - | 23 | - | - | MALAT1 (Up), miR-202-3p (Down), POSTN mRNA (Up), Periostin (Up) |
| MALAT1/miR-124/GRB2 [47] | C | 22 | - | - | - | 22 | - | MALAT1 (Up), miR-124 (Down) |
| NEAT1/miR-9-5p/POU2F1 [48] | C | 50 | - | - | 50 | - | - | NEAT1 (Up), miR-9-5p (Down) |
| NEAT1/miR-9-5p/PTEN [48] | C | 50 | - | - | 50 | - | - | NEAT1 (Up), miR-9-5p (Down) |
| NEAT1/miR-101/FOS [49] | C | 68 | 50 | 18 | 68 | - | - | NEAT (Up), miR-101 (Down) |
| NORAD/miR-590-3p/SIP1 [52] | C | 47 | 34 | 13 | 47 | - | - | NORAD (Up), miR-590-3p (Down) |
| OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/SMAD3 [53] | C | 16 | - | - | 15 | OIP5-AS1 (Up), miR-143-3p (Down), SMAD3 (Up) | ||
| OIP5-AS1/miR-143-3p/ROCK1 [54] | C | 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | OIP5-AS1 (Up), GAPDH (Up) |
| POU3F3/miR-127-5p/FOXD1 [55] | C | 36 | - | - | 36 | - | POU3F3 (Up) | |
| PTENP1/miR-106b/PTEN [56] *** | C | 54 | - | - | 54 | - | - | PTENP1 (Down), miR-106b (Up), PTEN mRNA (Down), PTEN protein (Down) |
| RP11-552M11.4/miR-3941/ATF1 [57] | C | 92 | 44 | 48 | 92 | - | - | RP11-552M11.4 (Up), mir-3941 (Down), ATF1 mRNA (Up) |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/IGF1R [58] | C | 14 | - | - | 14 | - | - | RSU1P2 (Up), let-7a (Down), IGF1R (Up) |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/NMYC [58] | C | 14 | - | - | 14 | - | - | RSU1P2 (Up), let-7a (Down), NMYC (Up) |
| RSU1P2/let-7a/EPHA4 [58] | C | 14 | - | - | 14 | - | - | RSU1P2 (Up), let-7a (Down), EPHA4 (Up) |
| SBF2-AS1/miR-361-5p/FOXM1 [59] | C | 66 | - | - | 66 | - | - | SBF2-AS1 (Up), miR-361-5p (Down), FOXM1 mRNA (Up) |
| SNHG4/miR-148a-3p/MET l [60] | R | - | 27 | - | 27 | - | - | SNHG4 (Up), miR-148a-3p (Down) |
| SNHG14/miR-206/YWHAZ [62] | C | 80 | 46 | 34 | 80 | - | - | SNHG14 (Up), miR-206 (Down), YWHAZ mRNA (Up) |
| SNHG20/miR-140-5p/ADAM10 [63] | C | 93 | - | - | 93 | - | - | SNHG20 (Up), miR-140-5p (Down), ADAM10 mRNA (Up) |
| SOX21-AS1/miR-7/VDAC1 [64] | C | 160 | - | - | 160 | - | - | SOX21-AS1 (Up) |
| STXBP5-AS1/miR-96-5p/PTEN [65] *** | C | 37 | - | - | 37 | - | - | STXBP5-AS1 (Down), miR-96-5p (Up), PTEN (Down) |
| TCONS_00026907/miR-143-5p/ELK1 [66] | C | 83 | 56 | 27 | 83 | - | - | TCONS_00026907 (Up) |
| TDRG1/miR-326/MAPK1 [67] | C | 30 | - | - | - | 30 | - | TDRG1 (Up), miR-326 (Down), MAPK1 mRNA (Up), MAPK1 protein (Up) |
| TP73-AS1/miR-329-3p/SMAD2 [68] | C | 30 | - | - | - | 30 | - | TP73-AS1 (Up), miR-329-3p (Down) |
| TTN-AS1/miR-573/E2F3 [69] | C | 45 | 34 | 11 | 45 | - | - | TTN-AS1 (Up), miR-573 (Down), E2F3 mRNA (Up) |
| TUSC8/miR-641/PTEN [70] *** | C | 40 | - | - | 40 | - | - | TUSC8 (Down), miR-641 (Up), PTEN mRNA (Down), PTEN protein (Down) |
| WT1-AS/miR-203a-5p/FOXN2 [71] *** | C | 47 | - | - | 47 | - | - | WT1-AS mRNA (Down), WT1-AS protein (Down) 1 |
| XIST/miR-200a/FUS [72] | C | 52 | - | - | 52 | - | - | XIST (Up), miR-200a (Down), FUS mRNA (Up) |
| XIST/miR-140-5p/ORC1 [73] | C | 30 | 14 | 16 | 30 | - | - | XIST (Up), miR-140-5p (Down), ORC1 mRNA (Up) |
| ZNF667-AS1/miR-93-3p/PEG3 [74] *** | C | 64 | 43 | 21 | 64 | - | - | ZNF667-AS1 (Down), miR-93-3p (Up), PEG3 (Down) |
| Molecule | Biological Role | Oncogene or TS Role | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer | CC | |||
| LncRNA | ||||
| HOTAIR | HOTAIR binds LSD1 and PRC2 and serves as a scaffold to assemble these regulators at the HOXD gene cluster, thereby promoting epigenetic repression of HOXD | Oncogene | Oncogene | [77,78,79,80,81,82] |
| MALAT1 | MALAT1 is retained in the nucleus, where it is thought to form molecular scaffolds for ribonucleoprotein complexes. It may act as a transcriptional regulator for numerous genes, including some genes involved in cancer metastasis and cell migration, and it is involved in cell cycle regulation. | Oncogene | Oncogene | [77,83,84,85] |
| NEAT1 | NEAT1 is retained in the nucleus, where it forms the core structural component of the paraspeckle suborganelles. It may act as a transcriptional regulator for numerous genes, including some genes involved in cancer progression. | Oncogene | Oncogene | [84,86,87] |
| OIP5-AS1 | OIP5-AS1 maintains cell proliferation in embryonic stem cells and can bind to and negatively regulate the activity of multiple cellular RNAs and microRNAs, including cyclin G associated kinase and HuR | Oncogene | Oncogene | [84,88] |
| XIST | Besides regulating X chromosome inactivation, XIST is a classic example of how lncRNAs can exert multilayered and fine-tuned regulatory functions by acting as a molecular scaffold for the recruitment of distinct protein factors as well as acting as a transcriptional regulator for numerous genes | Oncogene | Oncogene | [84,89,90] |
| miRNA | ||||
| miR-140-5p | Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as induction of apoptosis | TS | TS | [63,73,91,92,93,94,95] |
| miR-143-3p | Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as induction of apoptosis | TS | TS | [40,54,96,97,98,99,100,101,102] |
| miR-148a-3p * | Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as induction of apoptosis/promotion of cell proliferation | Oncogene/TS | TS | [39,60] |
| miR-206 | Inhibition of cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, as well as induction of apoptosis | TS | TS | [62,103,104,105] |
| mRNA/Protein | ||||
| MAPK1/MAPK1 | MAPK1 is part of the MAPK pathway—an important bridge in the switch from extracellular signals to intracellular responses—that is ultimately involved in stimulating cell proliferation and differentiation as well as modulating transcription regulation and development | Oncogene | Oncogene | [106,107] |
| PTEN/PTEN | PTEN is a very well-described tumor-suppressive protein, regulating proliferation and cell survival | TS | TS/ Oncogene ** | [108,109,110] |
| ROCK1/ROCK1 | ROCK1 is part of the ROCK family, which plays a central role in the organization of the actin cytoskeleton and is involved in a wide range of fundamental cellular functions. Stimulates tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. | Oncogene | Oncogene | [111,112,113] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berti, F.C.B.; Lobo-Alves, S.C.; Oliveira-Toré, C.d.F.; Salviano-Silva, A.; de Oliveira, K.B.; de Araújo-Souza, P.S.; Park, J.K.; Cipolla, G.A.; Malheiros, D. Competing Endogenous RNAs in Cervical Carcinogenesis: A New Layer of Complexity. Processes 2021, 9, 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9060991
Berti FCB, Lobo-Alves SC, Oliveira-Toré CdF, Salviano-Silva A, de Oliveira KB, de Araújo-Souza PS, Park JK, Cipolla GA, Malheiros D. Competing Endogenous RNAs in Cervical Carcinogenesis: A New Layer of Complexity. Processes. 2021; 9(6):991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9060991
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerti, Fernanda Costa Brandão, Sara Cristina Lobo-Alves, Camila de Freitas Oliveira-Toré, Amanda Salviano-Silva, Karen Brajão de Oliveira, Patrícia Savio de Araújo-Souza, Jong Kook Park, Gabriel Adelman Cipolla, and Danielle Malheiros. 2021. "Competing Endogenous RNAs in Cervical Carcinogenesis: A New Layer of Complexity" Processes 9, no. 6: 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9060991
APA StyleBerti, F. C. B., Lobo-Alves, S. C., Oliveira-Toré, C. d. F., Salviano-Silva, A., de Oliveira, K. B., de Araújo-Souza, P. S., Park, J. K., Cipolla, G. A., & Malheiros, D. (2021). Competing Endogenous RNAs in Cervical Carcinogenesis: A New Layer of Complexity. Processes, 9(6), 991. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9060991