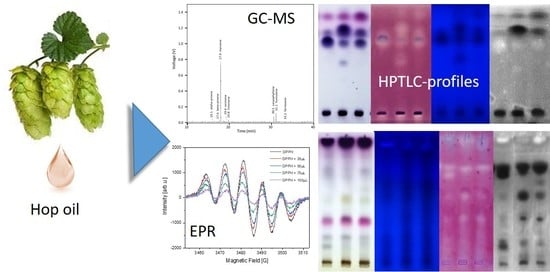
A Comparison of Quantitative Composition and Bioactivity of Oils Derived from Seven North American Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Hydrodistillation of Hop Pellets
2.3. Gas Chromatography Working Conditions
2.4. EPR Spectroscopic Assessment of Antioxidant Capacities of Hop Oils
2.5. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography—Effect-Directed Analysis (HPTLC–EDA) of Hop Oils and Selected Essential Oil Standards
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. GC–MS and GC-FID Analyses of Commercial Hop Oils and Hop Oils Hydrodistilled from Commercial Hop Pellets
3.2. EPR Spectroscopic Assessment of Antioxidant Capacity of Hop Oils
3.3. Screening for Hop Oil Bioactive Components by HPTLC Hyphenations
3.4. Identification of Bioactive Compounds by SPME-GC-MS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Košir, I.J.; Ocvirk, M. Evolution of Beer Aroma. In Food Aroma Evolution, 1st. ed.; Series: Food Analysis & Properties; Bordiga, M., Nollet, L.M.L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 353–363. ISBN 9780429441837. [Google Scholar]
- King, A.J.; Dickinson, J.R. Biotransformation of Hop Aroma Terpenoids by Ale and Lager Yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res. 2003, 3, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, C.; Cook, D.; Huismann, M.; Wilson, C.; Ford, R. The Multisensory Perception of Hop Essential Oil: A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2020, 126, 320–342. [Google Scholar]
- Eyres, G.; Dufour, J.-P. Hop Essential Oil: Analysis, Chemical Composition and Odor Characteristics. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar]
- Rutnik, K.; Hrnčič, M.K.; Košir, I.J. Hop Essential Oil: Chemical Composition, Extraction, Analysis, and Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 38, 529–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, T. Medicinal Properties of Terpenes Found in Cannabis Sativa and Humulus Lupulus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 198–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabín, M.; Hudcová, T.; Jelínek, L.; Dostálek, P. Biologically Active Compounds from Hops and Prospects for Their Use. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 542–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mimica-Dukić, N.; Orčić, D.; Lesjak, M.; Šibul, F. Essential Oils as Powerful Antioxidants: Misconception or Scientific Fact? In Medicinal and Aromatic Crops: Production, Phytochemistry, and Utilization; American Chemical Society: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 187–208. [Google Scholar]
- Krofta, K.; Mikyška, A.; Hašková, D. Antioxidant Characteristics of Hops and Hop Products. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Cervantes, G.I.; Ortega, D.R.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Pérez de la Cruz, V.; Esquivel, D.F.G.; Salazar, A.; Pineda, B. Redox and Anti-Inflammatory Properties from Hop Components in Beer-Related to Neuroprotection. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirovetz, L.; Bail, S.; Buchbauer, G.; Denkova, Z.; Slavchev, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Schmidt, E.; Geissler, M. Antimicrobial Testings, Gas Chromatographic Analysis and Olfactory Evaluation of an Essential Oil of Hop Cones (Humulus Lupulus, L.) from Bavaria and Some of Its Main Compounds. Sci. Pharm. 2006, 74, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bocquet, L.; Sahpaz, S.; Rivière, C. An Overview of the Antimicrobial Properties of Hop. In Natural Antimicrobial Agents; Sustainable Development and Biodiversity; Mérillon, J.-M., Riviere, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 19, pp. 31–54. ISBN 978-3-319-67043-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kovačevič, M.; Kač, M. Determination and Verification of Hop Varieties by Analysis of Essential Oils. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, P.L.-P.; Goldstein, H. Preparation and Purification of Hop Acids and Their Derivatives. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1996, 54, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, S.; Miks, M.H.; de Carvalho, B.T.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. The Molecular Biology of Fruity and Floral Aromas in Beer and Other Alcoholic Beverages. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 193–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rettberg, N.; Biendl, M.; Garbe, L.-A. Hop Aroma and Hoppy Beer Flavor: Chemical Backgrounds and Analytical Tools—A Review. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2018, 76, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, N.B.; Lederer, C.L.; Nickerson, G.B.; Libbey, L.M.; McDaniel, M.R. Sensory and Analytical Evaluation of Hop Oil Oxygenated Fractions. Dev. Food Sci. 1992, 29, 371–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, M. Hop Aromatic Compounds. In Proceedings of the European Brewery Convention Monograph 22—Symposium on Hops, Zoeterwoude, The Netherlands, 1994; Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 165–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, D. Hop Flavour and Aroma Products. In Proceedings of the European Brewery Convention Monograph 22—Symposium on Hops, Zoeterwoude, The Netherlands, 1994; Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 1994; pp. 114–124. [Google Scholar]
- Dresel, M.; Van Opstaele, F.; Praet, T.; Jaskula-Goiris, B.; Van Holle, A.; Naudts, D.; De Keukeleire, D.; De Cooman, L.; Aerts, G. Investigation of the Impact of the Hop Variety and the Hopping Technology on the Analytical Volatile Profile of Single-Hopped Worts and Beers. Brew. Sci. 2013, 66, 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Takoi, K.; Itoga, Y.; Takayanagi, J.; Kosugi, T.; Shioi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Watari, J. Screening of Geraniol-Rich Flavor Hop and Interesting Behavior of β-Citronellol during Fermentation under Various Hop-Addition Timings. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2014, 72, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, S.; Stettner, G. Influence of Late Hopping on Fermentation Performance of Yeast. In Proceedings of the 37th European Brewery Convention Congress, Antwerp, Belgium, 2–6 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oladokun, O.; James, S.; Cowley, T.; Smart, K.; Hort, J.; Cook, D. Dry-Hopping: The Effects of Temperature and Hop Variety on the Bittering Profiles and Properties of Resultant Beers. Brew. Sci. 2017, 70, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Takoi, K.; Itoga, Y.; Koie, K.; Takayanagi, J.; Kaneko, T.; Watanabe, T.; Matsumoto, I.; Nomura, M. Behaviour of Hop-Derived Branched-Chain Esters during Fermentation and Unique Characteristics of Huell Melon and Ekuanot (HBC366) Hops. Brew. Sci. 2018, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chenot, C.; Collin, S. Ability of the Mandarina Bavaria Hop Variety to Release Free Odorant Polyfunctional Thiols in Late-hopped Beers. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanekata, A.; Tanigawa, A.; Takoi, K.; Nakayama, Y.; Tsuchiya, Y. Identification and Characterization of Geranic Acid as a Unique Flavor Compound of Hops (Humulus Lupulus, L.) Variety Sorachi Ace. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12285–12295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spevacek, A.R.; Benson, K.H.; Bamforth, C.W.; Slupsky, C.M. Beer Metabolomics: Molecular Details of the Brewing Process and the Differential Effects of Late and Dry Hopping on Yeast Purine Metabolism. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, B.; Schönberger, C.; Drexler, G.; Gahr, A.; Newman, R.; Pöschl, M.; Geiger, E. The Influence of Hop Harvest Date on Hop Aroma in Dry-Hopped Beers. MBAA Tech. Q. 2009, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiotis, S.T.; Langezaal, C.R.; Scheffer, J.J.C.; Verpoorte, R. Comparative Study of the Essential Oils from Hops of Various Humulus Lupulus, L. Cultivars. Flavour Fragr. J. 1989, 4, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, M.R.; Setzer, W.N. Volatile Components of Aroma Hops (Humulus Lupulus, L.) Commonly Used in Beer Brewing. J. Brew. Distill. 2011, 2, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Morlock, G.; Schwack, W. Hyphenations in Planar Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6600–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Móricz, Á.M.; Häbe, T.T.; Böszörményi, A.; Ott, P.G.; Morlock, G.E. Tracking and Identification of Antibacterial Components in the Essential Oil of Tanacetum Vulgare, L. by the Combination of High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography with Direct Bioautography and Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1422, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kac, J.; Mlinarič, A.; Umek, A. HPTLC Determination of Xanthohumol in Hops (Humulus Lupulus, L.) and Hop Products. J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2006, 19, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jóźwiak, G.; Majer-Dziedzic, B.; Kwiecińska, J.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M. Comparison of the Microbiological Activities of Different Varieties of Hop (Humulus Lupulus) Extracts by Thin-Layer Chromatography—Direct Bioautography. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2017, 30, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristivojević, P.M.; Morlock, G.E. Effect-Directed Classification of Biological, Biochemical and Chemical Profiles of 50 German Beers. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ristivojević, P.M.; Morlock, G.E. Phenolic Fingerprints and Quality Assessment of Three Types of Beer. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2019, 32, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Móricz, Á.M.; Jamshidi-Aidji, M.; Krüzselyi, D.; Darcsi, A.; Böszörményi, A.; Csontos, P.; Béni, S.; Ott, P.G.; Morlock, G.E. Distinction and Valorization of 30 Root Extracts of Five Goldenrod (Solidago) Species. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1611, 460602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.E.; Heil, J.; Inarejos-Garcia, A.M.; Maeder, J. Effect-Directed Profiling of Powdered Tea Extracts for Catechins, Theaflavins, Flavonols and Caffeine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.M.S. TLC Bioautographic Method for Detecting Lipase Inhibitors. Phytochem. Anal. 2012, 23, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirir, A.M.; Daou, M.; Yousef, A.F.; Yousef, L.F. A Review of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Plants as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Type-2 Diabetes. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 1049–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-T.; Liu, X.-T.; Chen, Q.-X.; Shi, Y. Lipase Inhibitors for Obesity: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polish Pharmocopoeia, 6th ed.; Polish Pharmaceutical Society: Warsaw, Poland, 2003; p. 151. (In Polish)
- Nagy, J.K.; Móricz, Á.M.; Böszörményi, A.; Ambrus, Á.; Schwarczinger, I. Antibacterial Effect of Essential Oils and Their Components against Xanthomonas Arboricola Pv. Pruni Revealed by Microdilution and Direct Bioautographic Assays. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1204027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orłowska, M.; Kowalska, T.; Sajewicz, M.; Pytlakowska, K.; Bartoszek, M.; Polak, J.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M. Antioxidant Activity of Selected Thyme (Thymus, L.) Species and Study of the Equivalence of Different Measuring Methodologies. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Móricz, Á.M.; Häbe, T.T.; Ott, P.G.; Morlock, G.E. Comparison of High-Performance Thin-Layer with Overpressured Layer Chromatography Combined with Direct Bioautography and Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry for Tansy Root. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrnčič, M.K.; Španinger, E.; Košir, I.; Knez, Ž.; Bren, U. Hop Compounds: Extraction Techniques, Chemical Analyses, Antioxidative, Antimicrobial, and Anticarcinogenic Effects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Staško, A.; Brezová, V.; Mazúr, M.; Čertík, M.; Kaliňák, M.; Gescheidt, G. A Comparative Study on the Antioxidant Properties of Slovakian and Austrian Wines. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopka, P.; Křížová, J.; Vrchotová, N.; Bábíková, P.; Tříska, J.; Balík, J.; Kyseláková, M. Antioxidant Activity of Wines and Related Matters Studied by EPR Spectroscopy. Czech J. Food Sci. 2009, 26, S49–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polak, J.; Bartoszek, M.; Stanimirova, I. A Study of the Antioxidant Properties of Beers Using Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3042–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrisor, D.; Damian, G.; Simon, S.; Hosu, A.; Miclaus, V. Antioxidant Activity of Some Types of White Wines and Juices Investigated by EPR Spectroscopy. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2008, 22, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumiyoshi, M.; Kimura, Y. Hop (Humulus Lupulus, L.) Extract Inhibits Obesity in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet over the Long Term. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Yin, H.; Liu, G.; Dong, J.; Qian, Z.; Miao, J. Xanthohumol, a Prenylated Chalcone from Beer Hops, Acts as an α-Glucosidase Inhibitor in Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5548–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Johnpaul, I.A.; Hong, K.; Song, Y.; Yang, X.; Lv, C.; Ma, C. Exploring Two Types of Prenylated Bitter Compounds from Hop Plant (Humulus Lupulus, L.) against α-Glucosidase in Vitro and in Silico. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostálek, P.; Karabín, M.; Jelínek, L. Hop Phytochemicals and Their Potential Role in Metabolic Syndrome Prevention and Therapy. Molecules 2017, 22, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayabe, T.; Ohya, R.; Kondo, K.; Ano, Y. Iso-α-Acids, Bitter Components of Beer, Prevent Obesity-Induced Cognitive Decline. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, R.E.; Whyand, T.; Caplin, M.E. Benefits of Xanthohumol in Hyperlipidaemia, Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review. J. Obes. Chronic Dis. 2019, 3, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Mohan, S.; Verma, S.C. Antidiabetic Potential of Naturally Occurring Sesquiterpenes: A Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Kury, L.T.; Abdoh, A.; Ikbariah, K.; Sadek, B.; Mahgoub, M. In Vitro and In Vivo Antidiabetic Potential of Monoterpenoids: An Update. Molecules 2021, 27, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | Retention Time, tR [min] | Calibration Curve y = ax +b | Correlation Coefficient, r | LOD [ng mL−1] | LOQ [ng mL−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Pinene | 16.1 | y = 257.4 x − 227.6 | 0.989 | 0.51 | 1.59 |
| β-Pinene | 17.6 | y = 256.0 x − 252.7 | 0.986 | 1.80 | 5.47 |
| β-Myrcene | 17.9 | y = 233.1 x − 204.6 | 0.978 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Methyl heptanoate | 18.7 | y = 179.4 x − 156.0 | 0.955 | 2.26 | 6.86 |
| β-Ocimene | 19.4 | y = 227.4 x − 140.4 | 0.963 | 0.58 | 1.76 |
| Limonene | 19.8 | y = 176.6 x − 164.4 | 0.977 | 1.87 | 5.66 |
| β-Caryophyllene | 30.5 | y = 267.2 x − 113.1 | 0.971 | 2.72 | 8.23 |
| α-Humulene | 31.1 | y = 248.2 x − 115.7 | 0.975 | 20.47 | 62.13 |
| Hop Oil Variety | Source | Content in Hop Oil [μg mL−1] (RSD [%]) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Pinene | β-Pinene | β-Myrcene | Methyl Heptanoate | β-Ocimene | Limonene | β-Caryophyllene | α-Humulene | ||
| Amarillo | c | 0.89 b (6.13) | 1.07 c (4.24) | 5.63 b (3.44) | 0.92 cd (5.12) | 0.65 b (2.89) | 0.94 b (4.78) | 0.63 c (3.17) | 1.01 c (5.34) |
| Amarillo | h | 0.91 (4.75) | 1.03 (4.13) | 1.17 (6.27) | 0.88 (5.74) | 0.63 (7.18) | 0.95 (3.49) | 0.58 (6.22) | 3.43 * (2.88) |
| Azacca | c | 0.89 b (4.44) | 1.04 c (3.69) | 4.21 c (4.21) | 0.98 bd (5.02) | 0.64 b (2.79) | 1.09 a (3.97) | 0.69 c (6.18) | 0.94 c (4.34) |
| Azacca | h | 0.90 (3.75) | 1.01 (3.99) | 2.52 * (4.17) | 1.01 (6.02) | 0.69 (4.86) | 0.99 (6.68) | 2.55 * (3.87) | 5.65 * (4.91) |
| Cascade | c | 1.08 a (4.28) | 2.65 a (3.16) | 6.39 a (5.27) | 2.54 a (4.17) | 1.09 a (3.99) | 1.04 ab (4.12) | 1.65 a (4.68) | 2.71 a (5.38) |
| Cascade | h | 0.90 (5.74) | 1.08 * (3.34) | 6.40 (4.92) | 0.99 * (7.67) | 0.70 * (4.83) | 0.98 (6.01) | 2.42 * (5.01) | 5.65 * (2.98) |
| Chinook | c | 0.89 b (3.19) | 1.06 c (2.96) | 4.15 c (3.99) | 1.13 b (4.54) | 0.64 b (4.99) | 0.94 b (4.21) | 0.73 c (5.27) | 1.08 bc (4.96) |
| Chinook | h | 0.92 (3.71) | 1.07 (5.24) | 0.90 * (4.89) | 1.52 * (4.26) | 0.66 (2.87) | 1.00 (6.48) | 0.68 (4.90) | 1.36 * (3.73) |
| Centennial | c | 0.91 b (4.12) | 1.19 b (3.84) | 6.40 a (4.92) | 1.05 bc (3.91) | 0.69 b (4.03) | 0.94 b (3.76) | 0.85 b (5.28) | 1.22 b (5.69) |
| Centennial | h | 1.02 (3.28) | 1.03 (4.04) | 1.47 * (4.89) | 1.20 (5.74) | 0.77 (6.03) | 0.94 (4.27) | 1.96 * (5.63) | 4.88 * (3.99) |
| Saaz | c | 0.89 b (3.77) | 1.02 c (2.99) | 2.74 d (4.02) | 0.87 d (3.89) | 0.67 b (4.11) | 0.94 b (4.99) | 0.49 d (5.01) | 0.67 d (4.66) |
| Saaz | h | 0.89 (4.88) | 1.01 (5.17) | 2.92 (6.11) | 0.88 (4.73) | 0.64 (5.12) | 0.94 (4.81) | 1.18 * (4.99) | 3.52 * (5.08) |
| Ahhhroma | c | 0.89 b (4.19) | 1.01 c (3.67) | 2.68 d (3.92) | 0.93 cd (4.71) | 0.63 b (4.44) | 0.99 ab (3.79) | 0.52 d (4.09) | 0.61 d (5.11) |
| Hop Oil Variety | TREAC * [µmol TR/100 mL Sample] (±SD) | GAEAC * [µmol GA/100 mL Sample] (±SD) | AAEAC * [µmol AA/100 mL Sample] (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amarillo | 27.51 (±0.50) c | 12.02 (±0.20) c | 28.55 (±0.47) c |
| Azacca | 39.90 (±0.91) b | 17.11 (±0.38) b | 40.33 (±0.87) b |
| Cascade | 0.00 e | 0.00 e | 0.00 e |
| Chinook | 38.81 (±2.37) b | 16.66 (±0.97) b | 39.30 (±2.26) b |
| Centennial | 3.31(±0.63) d | 2.08 (±0.24) d | 5.33 (±0.29) d |
| Saaz | 0.00 e | 0.00 e | 0.00 e |
| Ahhhroma | 44.74 (±1.95) a | 19.10 (±0.80) a | 44.99 (±1.97) a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Móricz, Á.M.; Bartoszek, M.; Polak, J.; Marczewska, P.; Knaś, M.; Böszörményi, A.; Fodor, J.; Kowalska, T.; Sajewicz, M. A Comparison of Quantitative Composition and Bioactivity of Oils Derived from Seven North American Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Separations 2023, 10, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070402
Móricz ÁM, Bartoszek M, Polak J, Marczewska P, Knaś M, Böszörményi A, Fodor J, Kowalska T, Sajewicz M. A Comparison of Quantitative Composition and Bioactivity of Oils Derived from Seven North American Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Separations. 2023; 10(7):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070402
Chicago/Turabian StyleMóricz, Ágnes M., Mariola Bartoszek, Justyna Polak, Patrycja Marczewska, Magdalena Knaś, Andrea Böszörményi, József Fodor, Teresa Kowalska, and Mieczysław Sajewicz. 2023. "A Comparison of Quantitative Composition and Bioactivity of Oils Derived from Seven North American Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.)" Separations 10, no. 7: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070402
APA StyleMóricz, Á. M., Bartoszek, M., Polak, J., Marczewska, P., Knaś, M., Böszörményi, A., Fodor, J., Kowalska, T., & Sajewicz, M. (2023). A Comparison of Quantitative Composition and Bioactivity of Oils Derived from Seven North American Varieties of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.). Separations, 10(7), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070402