Phytochemical Constituents Identified from the Aerial Parts of Lespedeza cuneata and Their Effects on Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Extraction and Isolation
2.3. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.4. Oil Red O Staining
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
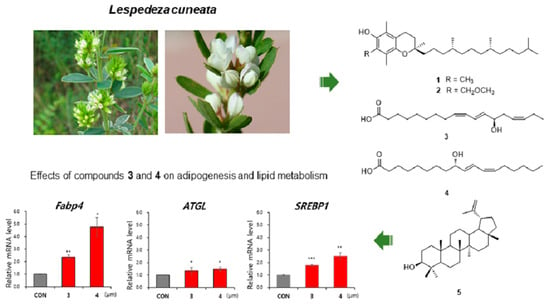
3.1. Isolation and Identification of the Compounds
3.2. Evaluation of Effects of the Compounds on Lipid Metabolism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spiegelman, B.M.; Flier, J.S. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell 2001, 104, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, U.; Kahn, B.B. Adipose tissue regulates insulin sensitivity: Role of adipogenesis, de novo lipogenesis and novel lipids. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 280, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Sharma, B.R.; Rhyu, D.Y. Beneficial effect of Lespedeza cuneata (G. Don) water extract on streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes and cytokine-induced beta-cell damage. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2016, 22, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, D. Two new phenylpropanoid glycosides from the aerial parts of Lespedeza cuneata. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Min, J.Y.; Shim, S.H. Chemical constituents from Lespedeza cuneata G. Don (leguminosae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 66, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, K.; Jho, E.H.; Jung, Y.J.; Nho, C.W.; Um, B.H.; Pan, C.H. Hepatoprotective effect of flavonoid glycosides from Lespedeza cuneata against oxidative stress induced by tert-butyl hyperoxide. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.Z.; Li, C.J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.M. Three new lignanosides from the aerial parts of Lespedeza cuneata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, C.W.; Kwon, J.E.; Negi, M.; Koo, Y.T.; Lee, S.H.; Baek, D.H.; Noh, Y.H.; Kang, S.C. Effects of Lespedeza cuneata aqueous extract on testosterone-induced prostatic hyperplasia. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.; Kwon, J.E.; Cho, S.M.; Kim, C.W.; Koo, Y.T.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.M.; Kang, S.C. Protective effect of Lespedeza cuneata ethanol extract on bisphenol a-induced testicular dysfunction in vivo and in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacother 2018, 102, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, S.; Iinuma, M.; Ito, E.; Takami, H.; Kagei, K. Studies on the constituents of the useful plants. Viii. The constituents of Lespedeza cuneata G. Don (author’s transl). Yakugaku Zasshi 1978, 98, 1542–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, G.; Park, S.J.; Lee, T.H.; Yang, H.; Baek, Y.S.; Kim, N.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.H. Flavonoids isolated from Lespedeza cuneata G. Don and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglia cells. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Li, C.J.; Yang, J.Z.; Ma, J.; Wu, L.Q.; Wang, W.J.; Zhang, D.M. Phenylpropanoid and lignan glycosides from the aerial parts of Lespedeza cuneata. Phytochemistry 2016, 121, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.R.; Kang, H.S.; Yoo, M.J.; Yi, S.A.; Beemelmanns, C.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, K.H. Anti-adipogenic Pregnane Steroid from a Hydractinia-associated Fungus, Cladosporium sphaerospermum SW67. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Ryoo, R.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Trichothecene and tremulane sesquiterpenes from a hallucinogenic mushroom Gymnopilus junonius and their cytotoxicity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.A.; Park, E.J.; Lee, D.; Song, J.H.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S.; Yoo, J.E. Estrogenic activity of sanguiin H-6 through activation of estrogen receptor α coactivator-binding site. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2019, 25, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Jang, W.; Kim, K.H. Mushrooms: An Important Source of Natural Bioactive Compounds. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2020, 26, 118–131. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.; Lee, D.; Lee, T.K.; Song, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, S.W.; Kang, K.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, S.; et al. (−)-9′-O-(α-L-rhamnopyranosyl) lyoniresinol from Lespedeza cuneata suppresses ovarian cancer cell proliferation through induction of apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Lee, T.K.; Song, J.H.; Choi, E.; Ko, H.J.; Lee, S.; Choi, S.U.; Lee, S.; Yoo, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Lignan glycosides and flavonoid glycosides from the aerial portion of Lespedeza cuneata and their biological evaluations. Molecules 2018, 23, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, B.S.; Alishir, A.; Ko, Y.J.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, K.H. Aviculin isolated from Lespedeza cuneata induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells through mitochondria-mediated caspase activation pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.R.; Chao, L.H.; Liao, Y.W.; Chang, C.I.; Pan, M.H. Tocopherols and triterpenoids from Sida acuta. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waridel, P.; Wolfender, J.L.; Lachavanne, J.B.; Hostettmann, K. Ent-labdane glycosides from the aquatic plant Potamogeton lucens and analytical evaluation of the lipophilic extract constituents of various potamogeton species. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, S.V.; Gupta, P.; Kumar, P. Enantioselective syntheses of (−)-pinellic acid, α-and β-dimorphecolic acid. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 7624–7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotie, J.; Bohle, D.S.; Leimanis, M.L.; Georges, E.; Rukunga, G.; Nkengfack, A.E. Lupeol long-chain fatty acid esters with antimalarial activity from Holarrhena floribunda. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcelin, G.; Chua, S., Jr. Contributions of adipocyte lipid metabolism to body fat content and implications for the treatment of obesity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.R.; Yi, S.A.; Nam, K.H.; Ryoo, R.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.H. Pantheric acids A–C from a poisonous mushroom, Amanita pantherina, promote lipid accumulation in adipocytes. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3489–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.A.; Lee, J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, J.W.; Lee, M.G.; Nam, K.H.; Park, J.H.; Oh, H.; Kim, S.; et al. Fermented ginseng extract, BST204, disturbs adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through inhibition of S6 kinase 1 signaling. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olzmann, J.A.; Carvalho, P. Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokta, T.; Strat, A.; Papasani, M.; Szasz, J.; Dodson, M.; Hill, R. Regulation of lipid accumulation in 3t3-l1 cells: Insulin-independent and combined effects of fatty acids and insulin. Animal 2008, 2, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Walther, T.C.; Rao, M.; Stuurman, N.; Goshima, G.; Terayama, K.; Wong, J.S.; Vale, R.D.; Walter, P.; Farese, R.V. Functional genomic screen reveals genes involved in lipid-droplet formation and utilization. Nature 2008, 453, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Gene | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | 5′-ACGGCCAGGTCATCACTATTG-3′ | 5′-TGGATGCCACAGGATTCCA-3′ |
| Fabp4 | 5′-AAGGTGAAGAGCATCATAACCCT-3′ | 5′-TCACGCCTTTCATAACACATTCC-3′ |
| ATGL | 5′-TTCACCATCCGCTTGTTGGAG-3′ | 5′-AGATGGTCACCCAATTTCCTC-3′ |
| SREBP1 | 5′-AACGTCACTTCCAGCTAGAC-3′ | 5′-CCACTAAGGTGCCTACAGAGC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Yoo, M.J.; Yi, S.A.; Kim, T.W.; Ha, J.W.; Na, M.W.; Park, K.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Han, J.-W.; Jang, T.S.; et al. Phytochemical Constituents Identified from the Aerial Parts of Lespedeza cuneata and Their Effects on Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation. Separations 2021, 8, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110203
Kang H, Yoo MJ, Yi SA, Kim TW, Ha JW, Na MW, Park KH, Kim S-H, Han J-W, Jang TS, et al. Phytochemical Constituents Identified from the Aerial Parts of Lespedeza cuneata and Their Effects on Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation. Separations. 2021; 8(11):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110203
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Heesun, Min Jeong Yoo, Sang Ah Yi, Tae Wan Kim, Ji Won Ha, Myung Woo Na, Kun Hee Park, Seon-Hee Kim, Jeung-Whan Han, Tae Su Jang, and et al. 2021. "Phytochemical Constituents Identified from the Aerial Parts of Lespedeza cuneata and Their Effects on Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation" Separations 8, no. 11: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110203
APA StyleKang, H., Yoo, M. J., Yi, S. A., Kim, T. W., Ha, J. W., Na, M. W., Park, K. H., Kim, S. -H., Han, J. -W., Jang, T. S., & Kim, K. H. (2021). Phytochemical Constituents Identified from the Aerial Parts of Lespedeza cuneata and Their Effects on Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation. Separations, 8(11), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8110203