Integrated Electro-Ozonation and Fixed-Bed Column for the Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthetic Wastewater
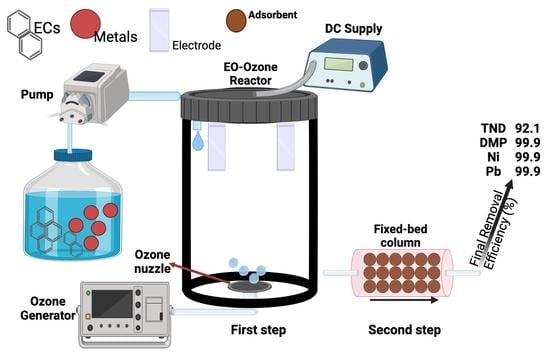
2.2. Electro-Ozonation Reactor
2.3. Composite Adsorbent
2.4. Optimization Process and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Ozone Consumption (OC) and Specific Energy Consumption (SEC)
2.6. Study of the Adsorption Isotherm
2.7. Analytical Methods and Experimental Processes
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Removal of ECs and Heavy Metals with the Electro-Ozonation
3.2. Ozone Consumption (OC) and Specific Energy Consumption (SEC)
3.3. Removal of ECs and Heavy Metals with a Fixed-Bed Column and an Adsorption Isotherm
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Priya, A.K.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Hoang, T.K.A.; Sekar, K.; Chong, K.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Ng, H.S.; Show, P.L. A critical and recent developments on adsorption technique for removal of heavy metals from wastewater–A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Govarthanan, M.; Iqbal, J.; Alfadul, S.M. Emerging contaminants of high concern for the environment: Current trends and future research. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Morales, J.; Gómez, M.J.; Herrera, S.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Calvo, E.; Rosal, R. Oxidative and photochemical processes for the removal of galaxolide and tonalide from wastewater. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4435–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosal, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Perdigón-Melón, J.A.; Petre, A.; García-Calvo, E.; Gómez, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Occurrence of emerging pollutants in urban wastewater and their removal through biological treatment followed by ozonation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Košnář, Z.; Mercl, F.; Chane, A.D.; Pierdonà, L.; Míchal, P.; Tlustoš, P. Occurrence of synthetic polycyclic and nitro musk compounds in sewage sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xiong, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiong, X. A novel simultaneous coupling of memory photocatalysts and microbial communities for alternate removal of dimethyl phthalate and nitrate in water under light/dark cycles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wan, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Pu, M. Targeted degradation of dimethyl phthalate by activating persulfate using molecularly imprinted Fe-MOF-74. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, B.; Xu, G.; Guan, Y. Characterizing fluvial heavy metal pollutions under different rainfall conditions: Implication for aquatic environment protection. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Rafatullah, M.; Yuan, J.; Zwain, H.M.; Mojiri, A.; Gholami, Z.; Gholami, F.; Wang, W.; Giwa, A.S.; Yu, Y.; et al. Nickel ion removal from aqueous solutions through the adsorption process: A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 755–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, S.; Mojiri, A.; Park, J.; Nawrot, N.; Wojciechowska, E.; Marraiki, N.; Zaghloul, N.S.S. Removal of lead ions from wastewater using lanthanum sulfide nanoparticle decorated over magnetic graphene oxide. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 111959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojiri, A.; Aziz, H.A.; Zaman, N.Q.; Aziz, S.Q.; Zahed, M.A. Metals removal from municipal landfill leachate and wastewater using adsorbents combined with biological method. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2819–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Mojiri, A.; Kindaichi, T.; Cagnetta, G.; Yuan, J.; Wang, B.; Giwa, A.S. Cross-linked chitosan/zeolite as a fixed-bed column for organic micropollutants removal from aqueous solution, optimization with RSM and artificial neural network. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Nieto-Delgado, C. Carbamazepine degradation by visible-light-driven photocatalyst Ag3PO4/GO: Mechanism and pathway. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2022, 9, 100143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, C.G.; Farm, Y.Y.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Pang, C.K.; Nga, J.L.H.; Li Puma, G. Ozonation treatment processes for the remediation of detergent wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiese, A.; Naddeo, V.; Uyguner-Demirel, C.S.; Prado, M.; Cesaro, A.; Zarra, T.; Liu, H.; Belgiorno, V.; Ballesteros, F., Jr. Removal of Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater by Sonolysis, Photocatalysis and Ozonation. Glob. NEST J. 2018, 21, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Costa, R.; Quinta-Ferreira, R.M.; Martins, R.C. Application of ozonation for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Falyouna, O.; Malloum, A.; Othmani, A.; Bornman, C.; Bedair, H.; Onyeaka, H.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Jacob, A.O.; Miri, T.; et al. A general review on the use of advance oxidation and adsorption processes for the removal of furfural from industrial effluents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 331, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwarciak-Kozłowska, A. Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by ozonation, advance oxidation processes, and membrane separation. In Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Waste Management and Treatment Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 151–171. [Google Scholar]
- Alfonso-Muniozguren, P.; Cotillas, S.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Moreira, F.C.; Lee, J.; Vilar, V.J.P. Single and combined electrochemical oxidation driven processes for the treatment of slaughterhouse wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 121858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jin, X.; Hu, S.; Guo, Y.; Qian, Z.; Jin, P. Enhanced removal of organics and ammonia by a composite anode in the electrochemically assisted ozonation (EAO) processes with reduced sludge and alleviated passivation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacıosmanoğlu, G.G.; Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Antibiotic adsorption by natural and modified clay minerals as designer adsorbents for wastewater treatment: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thotagamuge, R.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Mahadi, A.H.; Lim, C.M.; Abu, M.; Jan, A.; Hanipah, A.H.A.; Khiong, Y.Y.; Shofry, A. Copper modified activated bamboo charcoal to enhance adsorption of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimi, N.; Kooh, M.R.R.; Lim, C.M.; Chou Chao, C.-T.; Chou Chau, Y.-F.; Mahadi, A.H.; Chiang, H.-P.; Haji Hassan, N.H.; Thotagamuge, R. The Use of Gigantochloa Bamboo-Derived Biochar for the Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Aziz, H.A.; Zaman, N.Q.; Aziz, S.Q.; Zahed, M.A. Powdered ZELIAC augmented sequencing batch reactors (SBR) process for co-treatment of landfill leachate and domestic wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 139, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokokwe, G.; Letshwenyo, M.W. Utilisation of cement brick waste as low cost adsorbent for the adsorptive removal of copper, nickel and iron from aqueous solution: Batch and column studies. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 126, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngana, B.N.; Seumo, P.M.T.; Sambang, L.M.; Dedzo, G.K.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Ngameni, E. Grafting of reactive dyes onto lignocellulosic material: Application for Pb(II) adsorption and electrochemical detection in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Chen, H.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, B. Fixed bed column performance of Al-modified biochar for the removal of sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Vakili, M.; Farraji, H.; Aziz, S.Q. Combined ozone oxidation process and adsorption methods for the removal of acetaminophen and amoxicillin from aqueous solution; kinetic and optimisation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 15, 100404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Ziyang, L.; Hui, W.; Ahmad, Z.; Tajuddin, R.M.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Kindaichi, T.; Aziz, H.A.; Farraji, H. Concentrated landfill leachate treatment with a combined system including electro-ozonation and composite adsorbent augmented sequencing batch reactor process. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Mo, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Y.; Nie, J.; Wang, Z.; Liang, H. Boron-doped diamond (BDD) electro-oxidation coupled with nanofiltration for secondary wastewater treatment: Antibiotics degradation and biofouling. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachter, N.; Aquino, J.M.; Denadai, M.; Barreiro, J.C.; Silva, A.J.; Cass, Q.B.; Bocchi, N.; Rocha-Filho, R.C. Electrochemical degradation of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin in a flow reactor using distinct BDD anodes: Reaction kinetics, identification and toxicity of the degradation products. Chemosphere 2019, 234, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Espinoza, J.D.; Mijaylova-Nacheva, P.; Avilés-Flores, M. Electrochemical carbamazepine degradation: Effect of the generated active chlorine, transformation pathways and toxicity. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.Q.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Bashir, M.J.K. Landfill leachate treatment using powdered activated carbon augmented sequencing batch reactor (SBR) process: Optimization by response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, I.M.D.; Moratalla, A.; Eguiluz, K.I.B.; Salazar-Banda, G.R.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Saez, C. Influence of the doping level of boron-doped diamond anodes on the removal of penicillin G from urine matrixes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Mojiri, A.; Zwain, H.M.; Yuan, J.; Giwa, A.S.; Wang, W.; Gholami, F.; Guo, X.; Cagnetta, G.; Yu, G. Effect of beading parameters on cross-linked chitosan adsorptive properties. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 144, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Nazari, V.M.; Rezania, S.; Farraji, H.; Vakili, M. Biochar enhanced the performance of microalgae/bacteria consortium for insecticides removal from synthetic wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 157, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Leal, L.; Temmink, H.; Zeeman, G.; Buisman, C.J.N. Removal of micropollutants from aerobically treated grey water via ozone and activated carbon. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2887–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.; Tripathi, R.D.; Kumar, R.; Seth, C.S.; Gupta, D.K. Lead detoxification by coontail (Ceratophyllum demersum L.) involves induction of phytochelatins and antioxidant system in response to its accumulation. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1027–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Stüber, J.; Herrmann, N.; McDowell, D.; Ried, A.; Kampmann, M.; Teiser, B. Ozonation: A tool for removal of pharmaceuticals, contrast media and musk fragrances from wastewater? Water Res. 2003, 37, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, F.; Lu, P.; Li, X. Catalytic ozonation of dimethyl phthalate over cerium supported on activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; He, X. Catalytic ozonation of dimethyl phthalate and chlorination disinfection by-product precursors over Ru/AC. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanakaraju, D.; Glass, B.D.; Oelgemöller, M. Advanced oxidation process-mediated removal of pharmaceuticals from water: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 219, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Coetsier, C.; Causserand, C.; Groenen Serrano, K. An experimental and modelling study of the electrochemical oxidation of pharmaceuticals using a boron-doped diamond anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Cruz, A.; Fernandes, A.; Ciríaco, L.; Pacheco, M.J.; Carvalho, F.; Afonso, A.; Madeira, L.; Luz, S.; Lopes, A. Electrochemical Oxidation of Effluents from Food Processing Industries: A Short Review and a Case-Study. Water 2020, 12, 3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Lai, B. Decontamination of heavy metal complexes by advanced oxidation processes: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rame, R.; Pranoto, H.; Winahyu, R.; Sofie, M.; Raharjo, B.; Utomo, A. Catalytic Ozonation Based Advanced Oxidation Process for Effective Treating Wastewater from Hospital and Community Health Centre Facility by FLASH WWT Catalyst System in Indonesia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1095, 12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.M.S.; Spiliotopoulou, A.; Chhetri, R.K.; Escolà Casas, M.; Bester, K.; Andersen, H.R. Ozonation for source treatment of pharmaceuticals in hospital wastewater—Ozone lifetime and required ozone dose. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M’Arimi, M.M.; Mecha, C.A.; Kiprop, A.K.; Ramkat, R. Recent trends in applications of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in bioenergy production: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 121, 109669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portjanskaja, E. Ozone Science and Technology-Ozone reactions with Inorganic and Organic Compounds in Water; Encyclopedia of Life Support System (EOLSS): Paris, France, 2010; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Rifi, S.K.; Souabi, S.; El Fels, L.; Driouich, A.; Nassri, I.; Haddaji, C.; Hafidi, M. Optimization of coagulation process for treatment of olive oil mill wastewater using Moringa oleifera as a natural coagulant, CCD combined with RSM for treatment optimization. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, M.; Katoch, S.S.; Kadier, A.; Ma, P.-C. Treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater containing cefazolin by electrocoagulation (EC): Optimization of various parameters using response surface methodology (RSM), kinetics and isotherms study. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 176, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulgader, M.; Yu, Q.J.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Williams, P.; Rahimi, Z. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for process analysis and optimization of milk processing wastewater treatment using multistage flexible fiber biofilm reactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizaoui, C.; Bouselmi, L.; Mansouri, L.; Ghrabi, A. Landfill leachate treatment with ozone and ozone/hydrogen peroxide systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 140, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Amr, S.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Adlan, M.N.; Bashir, M.J.K. Pretreatment of stabilized leachate using ozone/persulfate oxidation process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 221, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, M.S.; Al-Sarawy, A.A.; El-Dein, W.A.S. Electrochemical degradation of some organic dyes by electrochemical oxidation on a Pb/PbO2 electrode. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 26, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Usha, U.N.; Rekha, H.B.; Bhavya, J.G.B. Performance of Electrochemical Oxidation in Treating Textile Dye Wastewater by Stainless Steel Anode. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2011, 2, 484. [Google Scholar]
- Mojiri, A.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Pollutants removal from synthetic wastewater by the combined electrochemical, adsorption and sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasselli, S.; Valenti, E.; Guzzella, L. Polycyclic musk fragrance (PMF) removal, adsorption and biodegradation in a conventional activated sludge wastewater treatment plant in Northern Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 38054–38064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Du, X.; Lu, X. UiO series of metal-organic frameworks composites as advanced sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: Synthesis, applications and adsorption mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, T.; Ganeshalingam, S.; Nadarajah, K. Mechanisms of emerging contaminants removal by novel neem chip biochar. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Jin, N.; Deng, S.; Zhao, B.; Liu, M.; Ran, B.; Zhang, L. Ni(II), Cr(VI), Cu(II) and nitrate removal by the co-system of Pseudomonas hibiscicola strain L1 immobilized on peanut shell biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Kim, Y.-T.; Stewart, A.C.; O’Keefe, S.F.; Neilson, A.P.; He, Z.; Huang, H. Grape pomace and its secondary waste management: Biochar production for a broad range of lead (Pb) removal from water. Environ. Res. 2020, 186, 109442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyatnyk, I.; Oesterle, P.; Wurzer, C.; Mašek, O.; Jansson, S. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern from multicomponent systems using carbon dioxide activated biochar from lignocellulosic feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shaheen, S.M.; Azeem, M.; Zhang, L.; Feng, C.; Peng, J.; Qi, W.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.; et al. Removal of lead (Pb+2) from contaminated water using a novel MoO3-biochar composite: Performance and mechanism. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Ali, A.; Ouda, M.; Naddeo, V.; Puig, S.; Hasan, S.W. Integrated electrochemical-adsorption process for the removal of trace heavy metals from wastewater. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 4, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Compounds/Elements | Composition (%) | Compounds/Elements | Composition (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 15.6 | K2O | 1.2 |
| CaO | 38.9 | MgO | 1.0 |
| SiO2 | 34.7 | Na2O | 1.0 |
| Al2O3 | 5.1 | SO3 | 0.5 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.6 | Others | 0.4 |
| Run | A * (min) | B (mg L−1) | C (mg L−1) | D (mg L−1) | TND Removal (%) | TND Removed (mg L−1) | DMP Removal (%) | DMP Removed (mg L−1) | Ni Removal (%) | Ni Removed (mg L−1) | Pb Removal (%) | Pb Removed (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 5 | 0.2 | 10 | 46.7 | 0.10 | 53.1 | 0.106 | 32.3 | 3.2 | 30.4 | 3.0 |
| 2 | 20 | 10 | 0.2 | 10 | 49.2 | 0.10 | 57.9 | 0.116 | 33.8 | 3.4 | 31.5 | 3.2 |
| 3 | 30 | 15 | 0.2 | 10 | 54.3 | 0.11 | 61.7 | 0.123 | 35.1 | 3.5 | 34.6 | 3.5 |
| 4 | 40 | 20 | 0.2 | 10 | 58.8 | 0.12 | 66.5 | 0.133 | 41.5 | 4.2 | 40.2 | 4.0 |
| 5 | 50 | 25 | 0.2 | 10 | 65.3 | 0.13 | 73.8 | 0.148 | 50.3 | 5.0 | 49.1 | 4.9 |
| 6 | 60 | 30 | 0.2 | 10 | 64.5 | 0.13 | 73.3 | 0.147 | 51.4 | 5.1 | 51.0 | 5.1 |
| 7 | 10 | 5 | 0.4 | 20 | 43.6 | 0.17 | 52.1 | 0.208 | 31.3 | 6.3 | 29.8 | 6.0 |
| 8 | 20 | 10 | 0.4 | 20 | 51.7 | 0.21 | 56.4 | 0.226 | 34.5 | 6.9 | 32.5 | 6.5 |
| 9 | 30 | 15 | 0.4 | 20 | 54.1 | 0.22 | 61.1 | 0.244 | 39.7 | 7.9 | 35.6 | 7.1 |
| 10 | 40 | 20 | 0.4 | 20 | 56.4 | 0.23 | 64.7 | 0.259 | 41.1 | 8.2 | 40.8 | 8.2 |
| 11 | 50 | 25 | 0.4 | 20 | 57.3 | 0.23 | 70.6 | 0.282 | 52.9 | 10.6 | 51.8 | 10.4 |
| 12 | 60 | 30 | 0.4 | 20 | 60.3 | 0.24 | 68.2 | 0.273 | 53.5 | 10.7 | 52.1 | 10.4 |
| 13 | 10 | 5 | 0.6 | 30 | 38.4 | 0.23 | 46.0 | 0.276 | 29.1 | 8.7 | 29.4 | 8.8 |
| 14 | 20 | 10 | 0.6 | 30 | 42.5 | 0.26 | 50.1 | 0.301 | 31.8 | 9.5 | 30.6 | 9.2 |
| 15 | 30 | 15 | 0.6 | 30 | 52.9 | 0.32 | 59.8 | 0.359 | 34.7 | 10.4 | 33.2 | 10.0 |
| 16 | 40 | 20 | 0.6 | 30 | 60.4 | 0.36 | 66.9 | 0.401 | 40.6 | 12.2 | 40.3 | 12.1 |
| 17 | 50 | 25 | 0.6 | 30 | 63.6 | 0.38 | 73.2 | 0.439 | 54.3 | 16.3 | 53.9 | 16.2 |
| 18 | 60 | 30 | 0.6 | 30 | 61.5 | 0.37 | 68.6 | 0.412 | 56.2 | 16.9 | 56.6 | 17.0 |
| 19 | 10 | 5 | 0.8 | 40 | 33.3 | 0.27 | 41.4 | 0.331 | 28.9 | 11.6 | 27.6 | 11.0 |
| 20 | 20 | 10 | 0.8 | 40 | 42.1 | 0.34 | 48.4 | 0.387 | 33.9 | 13.6 | 31.4 | 12.6 |
| 21 | 30 | 15 | 0.8 | 40 | 48.8 | 0.39 | 57.8 | 0.462 | 47.2 | 18.9 | 45.7 | 18.3 |
| 22 | 40 | 20 | 0.8 | 40 | 61.4 | 0.49 | 66.0 | 0.528 | 50.6 | 20.2 | 50.6 | 20.2 |
| 23 | 50 | 25 | 0.8 | 40 | 66.2 | 0.53 | 74.6 | 0.597 | 56.3 | 22.5 | 55.0 | 22.0 |
| 24 | 60 | 30 | 0.8 | 40 | 63.5 | 0.51 | 73.4 | 0.587 | 58.2 | 23.3 | 56.4 | 22.6 |
| 25 | 10 | 5 | 1.0 | 50 | 29.4 | 0.29 | 40.8 | 0.408 | 27.3 | 13.7 | 26.8 | 13.4 |
| 26 | 20 | 10 | 1.0 | 50 | 39.6 | 0.40 | 47.6 | 0.476 | 30.4 | 15.2 | 29.5 | 14.8 |
| 27 | 30 | 15 | 1.0 | 50 | 53.1 | 0.53 | 61.7 | 0.617 | 40.1 | 20.1 | 40.6 | 20.3 |
| 28 | 40 | 20 | 1.0 | 50 | 65.3 | 0.65 | 74.9 | 0.749 | 45.2 | 22.6 | 46.8 | 23.4 |
| 29 | 50 | 25 | 1.0 | 50 | 71.3 | 0.71 | 80.1 | 0.801 | 51.7 | 25.9 | 49.3 | 24.7 |
| 30 | 60 | 30 | 1.0 | 50 | 68.9 | 0.69 | 77.6 | 0.776 | 56.1 | 28.1 | 56.0 | 28.0 |
| 31 | 10 | 5 | 1.2 | 60 | 25.7 | 0.31 | 35.6 | 0.427 | 25.9 | 15.5 | 25.4 | 15.2 |
| 32 | 20 | 10 | 1.2 | 60 | 40.5 | 0.49 | 50.2 | 0.602 | 28.6 | 17.2 | 27.1 | 16.3 |
| 33 | 30 | 15 | 1.2 | 60 | 50.3 | 0.60 | 61.1 | 0.733 | 45.8 | 27.5 | 43.1 | 25.9 |
| 34 | 40 | 20 | 1.2 | 60 | 61.1 | 0.73 | 72.4 | 0.869 | 50.3 | 30.2 | 48.6 | 29.2 |
| 35 | 50 | 25 | 1.2 | 60 | 67.4 | 0.81 | 75.4 | 0.905 | 55.3 | 33.2 | 54.0 | 32.4 |
| 36 | 60 | 30 | 1.2 | 60 | 67.1 | 0.81 | 74.8 | 0.898 | 56.4 | 33.8 | 55.2 | 33.1 |
| Reponses | R2 * | Adj. R2 | Adec. P | SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TND removal | 0.943 | 0.934 | 36.50 | 3.01 | 5.60 |
| DMP removal | 0.937 | 0.903 | 33.27 | 3.18 | 5.11 |
| Ni removal | 0.915 | 0.901 | 25.52 | 3.29 | 7.73 |
| Pb removal | 0.919 | 0.906 | 25.60 | 3.24 | 7.82 |
| Reaction Time (min) | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| OC (kg O3/kg ECs) | 1.11 | 1.39 | 2.1 | 3.05 | 3.95 | 3.81 |
| Pollutants | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg g−1) | KL | R2 | KF (mg g−1 (L/mg)1/n) | 1/n | R2 | |
| TND | 13.1 | 0.03 | 0.897 | 2.2 | 0.54 | 0.920 |
| DMP | 17.2 | 0.04 | 0.872 | 2.9 | 0.60 | 0.951 |
| Ni | 21.4 | 0.07 | 0.812 | 9.7 | 0.26 | 0.975 |
| Pb | 20.7 | 0.09 | 0.840 | 10.3 | 1.11 | 0.995 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mojiri, A.; Ozaki, N.; Zhou, J.L.; Kazeroon, R.A.; Zahed, M.A.; Rezania, S.; Vakili, M.; Gavanji, S.; Farraji, H. Integrated Electro-Ozonation and Fixed-Bed Column for the Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Separations 2022, 9, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100276
Mojiri A, Ozaki N, Zhou JL, Kazeroon RA, Zahed MA, Rezania S, Vakili M, Gavanji S, Farraji H. Integrated Electro-Ozonation and Fixed-Bed Column for the Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Separations. 2022; 9(10):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100276
Chicago/Turabian StyleMojiri, Amin, Noriatsu Ozaki, John L. Zhou, Reza Andasht Kazeroon, Mohammad Ali Zahed, Shahabaldin Rezania, Mohammadtaghi Vakili, Shahin Gavanji, and Hossein Farraji. 2022. "Integrated Electro-Ozonation and Fixed-Bed Column for the Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions" Separations 9, no. 10: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100276
APA StyleMojiri, A., Ozaki, N., Zhou, J. L., Kazeroon, R. A., Zahed, M. A., Rezania, S., Vakili, M., Gavanji, S., & Farraji, H. (2022). Integrated Electro-Ozonation and Fixed-Bed Column for the Simultaneous Removal of Emerging Contaminants and Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Separations, 9(10), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9100276