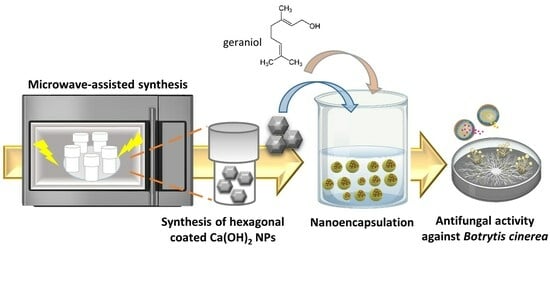
Microwave-Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles Destined for Geraniol Encapsulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Ca(OH)2@OAm NPs
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Calcium-Based Nanocapsules
2.3. pH-Dependent Release Profiles and Kinetic Analysis of CaGer2 Nanocapsules
2.4. In vitro Evaluation of Antifungal Activity of Ca-Based NPs and NCs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Ca(OH)2@OAm NPs
3.3. Preparation of CaGer Nanocapsules
3.4. Characterization Techniques
3.5. Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity
3.6. pH-Dependent Release Profiles of Geraniol
3.7. Fungal Strain and Growth Conditions
3.8. Antifungal Activity Assay
3.9. Statistical Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernardes, M.F.F.; Pazin, M.; Pereira, L.C.; Dorta, D.J. Impact of Pesticides on Environmental and Human Health. In Toxicology Studies-Cells, Drugs, and Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 195–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-O.; Shin, J.-H.; Gumilang, A.; Chung, K.; Kim, K.S. Effectiveness of different classes of fungicides on Botrytis cinerea causing gray mold on fruit and vegetables. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, A.F.; Gil, F.; Lacasaña, M.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Requena, M.; Alarcón, R. Pesticide exposure and genetic variation in xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes interact to induce biochemical liver damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 61, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Yadav, A.N. Natural products as fungicide and their role in crop protection. In Natural Bioactive Products in Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Chapter 9; pp. 131–219. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.-L.; Luo, Y.-X.; Yuan, S.-H.; Li, L.-W.; Liu, N.-N. Antifungal nanomaterials: Current progress and future directions. Innov. Digit. Health Diagn. Biomark. 2021, 1, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Li, X.; Maier, M.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Heath, D.E.; O’Connor, A.J. Using inorganic nanoparticles to fight fungal infections in the antimicrobial resistant era. Acta Biomater. 2023, 158, 56–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Viljoen, A.M. Geraniol-A review of a commercially important fragrance material. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, M.H.P.; de Andrade Júnior, F.P.; Moraes, G.F.Q.; Macena, G.S.; Pereira, F.O.; Lima, I.O. Antimicrobial activity of geraniol: An integrative review. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2020, 32, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, P.; Kamou, N.N.; Pavlou, A.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Nanocapsules of ZnO nanorods and geraniol as a novel mean for the effective control of Botrytis cinerea in tomato and cucumber plants. Plants 2023, 12, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database_en (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Chaudhari, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Das, S.; Dubey, N.K. Nanoencapsulation of essential oils and their bioactive constituents: A novel strategy to control mycotoxin contamination in the food system. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, L.; Perinelli, D.R.; Bonacucina, G.; Cespi, M.; Palmieri, G.P. An overview of micro- and nanoemulsions as vehicles for essential oils: Formulation, preparation and stability. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, S.; Davari, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Ebadollahi, A.; Feizpoor, S. Enhancement of the antifungal properties of Zataria multiflora essential oil through nanoencapsulation with ZnO nanomaterial. Res. Sq. 2021, 42, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtari, A.; Davari, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Ebadollahi, A.; Feizpour, S. Antifungal activities of pure and ZnO-encapsulated essential oil of Zataria multiflora on Alternaria solani as the pathogenic agent of tomato early blight disease. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 932475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamou, N.N.; Kalogiouri, N.P.; Tryfon, P.; Papadopoulou, A.; Karamanoli, K.; Dendrinou-Samara, C.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U. Impact of geraniol and geraniol nanoemulsions on Botrytis cinerea and effect of geraniol on cucumber plants’ metabolic profile analyzed by LC-QTOF-MS. Plants 2022, 11, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, P.J.; Broadley, M.R. Calcium in plants. Ann. Bot. 2003, 92, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S.; Wimmer, R. Calcium physiology and terrestrial ecosystem processes. New Phytol. 1999, 142, 373–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Terraza, S.; Villarreal-Romero, M.; Sánchez-Peña, P.; Corrales-Madrid, J.L.; Hernández-Verdugo, S. Effect of calcium and osmotic potential of the nutrient solution on the blossom end rot, mineral composition and yield of tomato. Interscience 2008, 33, 449–456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Poovaiah, W.B. Calcium signaling and biotic defense responses in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2014, 9, e973818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Outcome of the Consultation with Member States and EFSA on the Basic Substance Application for Approval of Calcium Hydroxide for the Extension of Use in Plant Protection as a Fungicide in Grapevine and Peach, and as Insecticide in Grapevine, Plum, Peach, Apricot, Apple, Pear, Almond and Strawberry; EFSA Publications: Parma, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Ding, J.; Dong, Y.; Cao, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Camaiti, M. Nano Ca(OH)2: A review on synthesis, properties and applications. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 50, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanthi, R.; Ravindran, V. Role of calcium hydroxide in dentistry: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2020, 12, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar]
- Harish; Kumari, S.; Parihar, J.; Akash; Kumari, J.; Kumar, L.; Debnath, M.; Kumar, V.; Mishra, R.K.; Gwag, J.S.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of calcium hydroxide nanoparticles against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, P.; Antonoglou, O.; Vourlias, G.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Tailoring Ca-based nanoparticles by polyol process for use as nematicidals and pH adjusters in Agriculture. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3870–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, M.B.; Shelke, S.N.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Microwave-Assisted Chemistry: Synthetic Applications for Rapid Assembly of Nanomaterials and Organics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musamali, R.W.; Isa, Y.M. Production of clean hydrogen from methane decomposition over molten NiO-LiOH catalyst systems supported on CaO: Synergistic effect of molten LiOH on catalyst activity. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 16, e2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Wang, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Green synthesis of spherical calcium hydroxide nanoparticles in the presence of tannic acid. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9501897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuzhi, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. The effects of crystallinity on the mechanical properties and the limiting PV (pressure × velocity) value of PTFE. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumari, J.; Kumar, L.; Salim, A.; Singhal, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Joshi, R.P. Influence of chemical synthesis process on the properties of calcium hydroxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 60, 153–159. [Google Scholar]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Oleylamine in nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Cortie, M.B.; Liu, X.; Xie, Q.; Wang, X.; Peng, D.L. Shape-selective formation of monodisperse copper nanospheres and nanocubes via disproportionation reaction route and their optical properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 9801–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Malhotra, B.; Phalswal, P.; Khanna, P.K.; Salim, A.; Singhal, R.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Effect of reaction rate on the properties of chemically synthesized calcium hydroxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 2305–2310. [Google Scholar]
- Khachani, M.; El Hamidi, A.; Halim, M.; Arsalane, S. Non-isothermal kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the dehydroxylation process of synthetic calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 615–624. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, A.; Podder, S.; Ghosh, C.K.; Bhattacharya, M.; Ghosh, J.; Mallik, A.K.; Dey, A.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. ROS mediated high anti-bacterial efficacy of strain tolerant layered phase pure nano-calcium hydroxide. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 72, 110–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Bai, J.; Wang, H. The preparation of oleylamine modified micro-size sphere silver particles and its application in crystalline silicon solar cells. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenin, R.; Joy, P.A. Role of primary and secondary surfactant layers on the thermal conductivity of lauric acid coated magnetite nanofluids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 11640–11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvakidis, K.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Makridis, A.; Paulidou, E.; Angelakeris, M.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Magnetic hyperthermia efficiency and MRI contrast sensitivity of colloidal soft/hard ferrite nanoclusters. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 511, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonoglou, A.; Giannousi, K.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Magnetic nanoemulsions as candidates for alzheimer’s disease dual imaging theranostics. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 465702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.; Mosleh, M.H.; Mandal, P.; Lea-Langton, A.; Sedighi, M. Emissions of volatile organic compounds from crude oil processing—Global emission inventory and environmental release. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K. Pesticides and environment. Pestic. Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 1, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zarepour, A.; Zarrabi, A.; Larsen, K.L. Fabricating β-cyclodextrin based pH-responsive nanotheranostics as a programmable polymeric nanocapsule for simultaneous diagnosis and therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7017–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, L.; Atif, R.; Salah Eldeen, T.; Yahya, I.; Omara, A.; Eltayeb, M. Study the using of nanoparticles as drug delivery system based on mathematical models for controlled release. IJLTEMAS 2019, 8, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Zhou, W.; Liang, X.; Zhou, G.; Han, C.C.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Mechanism of a long-term controlled drug release system based on simple blended electrospun fibers. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yegin, Y.; Perez-Lewis, K.; Zhang, M.; Akbulut, M.; Taylor, T.M. Development and characterization of geraniol-loaded polymeric nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity against foodborne bacterial pathogens. J. Food Eng. 2016, 170, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondo, F.; Baldassarre, F.; Vergaro, V.; Ciccarella, G. Controlled Biocide Release from Smart Delivery Systems: Materials Engineering to Tune Release Rate, Biointeractions, and Responsiveness. In Nanotechnology-Based Sustainable Alternatives for the Management of Plant Diseases; Balestra, G.M., Fortunati, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D. Elements of X-ray Diffraction, 2nd ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Co., Ltd.: Reading, MA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Toufiq, A.M.; Tariq, F.; Khan, Y.; Hussain, R.; Akhtar, N.; Rahman, S. Influence of Fe doping on the structural, optical, and thermal properties of α-MnO2 Nanowires. Mat. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.A.; Mott, N.F. Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos. Mag. A 1970, 22, 903–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, V. Release kinetic studies of aspirin microcapsules from ethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate phthalate and their mixtures by emulsion solvent evaporation method. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokhandwala, H.; Deshpande, A.; Deshpande, S. Kinetic modeling and dissolution profiles comparison: An overview. Int. J. Pharm. Bio. Sci. 2013, 4, 728–773. [Google Scholar]
- Ramteke, K.H.; Dighe, P.A.; Kharat, A.R.; Patil, S.V. Mathematical models of drug dissolution: A review. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2014, 3, 388396. [Google Scholar]
- Banik, S.; Pérez-de-Luque, A. In vitro effects of copper nanoparticles on plant pathogens, beneficial microbes, and crop plants. Span. J. Agricult. Res. 2017, 15, e1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryfon, P.; Kamou, N.N.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Karamanoli, K.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. CuZn and ZnO Nanoflowers as nano-fungicides against Botrytis cinerea and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum: Phytoprotection, translocation, and impact after foliar application. Materials 2021, 14, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Nano-Formulations | Mass Ratio NPs/Geraniol | Encapsulation Efficacy (%) | Loading Capacity (%) | DLS (d.nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaGer1 NCs | 1:1 | 43 | 5 | 351 ± 1.1 | 0.064 | −35.2 ± 0.57 |
| CaGer2 NCs | 1:2 | 95 | 20 | 306 ± 2.3 | 0.161 | −35.4 ± 0.74 |
| CaGer3 NCs | 1:3 | 80 | 24 | 382 ± 1.1 | 0.423 | −41.3 ± 0.52 |
| Treatments | EC50 Values (μg/mL) ± SDV |
|---|---|
| Ca(OH)2@OAm NPs | 654 ± 0.54 |
| Ca NCs | 395 ± 0.73 |
| CaGer2 NCs | 507 ± 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tryfon, P.; Kamou, N.N.; Mourdikoudis, S.; Vourlias, G.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Dendrinou-Samara, C. Microwave-Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles Destined for Geraniol Encapsulation. Inorganics 2023, 11, 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120470
Tryfon P, Kamou NN, Mourdikoudis S, Vourlias G, Menkissoglu-Spiroudi U, Dendrinou-Samara C. Microwave-Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles Destined for Geraniol Encapsulation. Inorganics. 2023; 11(12):470. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120470
Chicago/Turabian StyleTryfon, Panagiota, Nathalie N. Kamou, Stefanos Mourdikoudis, George Vourlias, Urania Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, and Catherine Dendrinou-Samara. 2023. "Microwave-Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles Destined for Geraniol Encapsulation" Inorganics 11, no. 12: 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120470
APA StyleTryfon, P., Kamou, N. N., Mourdikoudis, S., Vourlias, G., Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U., & Dendrinou-Samara, C. (2023). Microwave-Mediated Synthesis and Characterization of Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles Destined for Geraniol Encapsulation. Inorganics, 11(12), 470. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11120470