Reactivity of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: Oxidative Addition of Chalcogen Elements to a Chiral NH-Sn System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
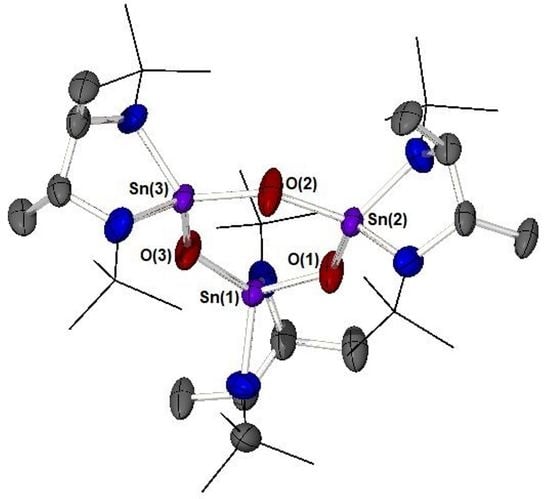
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mizuhata, Y.; Sasamori, T.; Tokitoh, N. Stable Heavier Carbene Analogues. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3479–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, L.; Cabeza, J.A.; García-Álvarez, P.; Polo, D. The transition-metal chemistry of amidinatosilylenes, -germylenes and -stannylenes. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 300, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Nikonov, G.I. Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination at Main-Group Element Centers. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3608–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, P.P. Main-group elements as transition metals. Nature 2010, 463, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, B.; Gallego, D.; Driess, M. N-heterocyclic silylene complexes in catalysis: New frontiers in an emerging field. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.V. Electronic Properties of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes and Their Experimental Determination. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 9457–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahfuss, M.J.; Radius, U. N-Heterocyclic Silylenes as Metal–Metal Bridges and Metal–Halide Activators in Transition Metal Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 10976–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krahfuss, M.J.; Radius, U. N-Heterocyclic silylenes as ambiphilic activators and ligands. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 6752–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoufmoghaddam, S.; Zhou, Y.-P.; Wang, Y.; Driess, M. N-heterocyclic silylenes as powerful steering ligands in catalysis. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 829, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, C.A.; Kennedy, A.R.; Spicer, M.D. N-Heterocyclic Germylenes: Structural Characterisation of Some Heavy Analogues of the Ubiquitous N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Heteroat. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, R.; Das, S.; Hiwase, S.; Pati, S.K.; Khan, S. N-Heterocyclic Germylene and Stannylene Catalyzed Cyanosilylation and Hydroboration of Aldehydes. Organometallics 2019, 38, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsdóttir, L.; Oldroyd, N.L.; Grabiner, R.; Knights, A.W.; Heilmann, A.; Protchenko, A.V.; Niu, H.; Kolychev, E.L.; Campos, J.; Hicks, J.; et al. Synthetic, structural and reaction chemistry of N-heterocyclic germylene and stannylene compounds featuringN-boryl substituents. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 11951–11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-W. A Non-innocent Ligand Supported Germylene and Its Diverse Reactions. Organometallics 2020, 39, 4645–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmant, J.P.H.; Haddow, M.F.; Hahn, F.E.; Heitmann, D.; Fröhlich, R.; Mansell, S.M.; Russell, C.A.; Wass, D.F. Syntheses and molecular structures of some saturated N-heterocyclic plumbylenes. Dalton Trans. 2008, 6055–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansell, S.M.; Herber, R.H.; Nowik, I.; Ross, D.H.; Russell, C.A.; Wass, D.F. Coordination Chemistry of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: A Combined Synthetic and Mössbauer Spectroscopy Study. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansell, S.M.; Russell, C.A.; Wass, D.F. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of Tin Analogues of N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11367–11375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansell, S.M.; Russell, C.A.; Wass, D.F. Synthesis of chelating diamido Sn(iv) compounds from oxidation of Sn(ii) and directly from Sn(iv) precursors. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 9756–9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bačić, G.; Zanders, D.; Mallick, B.; Devi, A.; Barry, S.T. Designing Stability into Thermally Reactive Plumbylenes. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 8218–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, F.E.; Heitmann, D.; Pape, T. Synthesis and Characterization of Stable N-Heterocyclic Plumbylenes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 2008, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickschat, J.V.; Urban, S.; Pape, T.; Glorius, F.; Hahn, F.E. Sterically demanding and chiral N,N′-disubstituted N-heterocyclic germylenes and stannylenes. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 11519–11521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Kireenko, M.M.; Zaitsev, K.V.; Oprunenko, Y.F.; Churakov, A.V.; Howard, J.A.K.; Lermontova, E.K.; Sorokin, D.; Linder, T.; Sundermeyer, J.; et al. Stabilized Germylenes Based on Diethylenetriamines and Related Diamines: Synthesis, Structures, and Chemical Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 2012, 3712–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupski, S.; Pöttgen, R.; Schellenberg, I.; Hahn, F.E. Benzannulated N-heterocyclic germylenes and stannylenes with sterically demanding N,N′-substituents. Dalton Trans. 2013, 43, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-H.; Lee, G.-H.; Peng, S.-M.; Chiu, C.-W.; Chen, H.-Y. Benzannulated N-heterocyclic plumbylene: An efficient catalyst in ring opening polymerization of -lactide. Polymer 2019, 180, 121748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduengo, A.J.; Kline, M.; Calabrese, J.C.; Davidson, F. Synthesis of a reverse ylide from a nucleophilic carbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 113, 9704–9705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrhus, B.; Lappert, M.F.; Heinicke, J.; Boese, R.; Bläser, D. Synthesis, structures and reactions of new thermally stable silylenes. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aysin, R.R.; Leites, L.A.; Bukalov, S.S.; Zabula, A.V.; West, R. Molecular Structures of N,N′-Dimethylbenzimidazoline-2-germylene and -stannylene in Solution and in Solid State by Means of Optical (Raman and UV–vis) Spectroscopy and Quantum Chemistry Methods. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 4698–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, F.E.; Zabula, A.V.; Pape, T.; Hepp, A. Preparation and Molecular Structures of Stable Bis(germylenes) with Pincer Topology. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 2007, 2405–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Hock, A.S.; Gordon, R.G. Low Temperature Atomic Layer Deposition of Tin Oxide. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4964–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Kim, S.B.; Gordon, R.G. Atomic layer deposition of tin oxide with nitric oxide as an oxidant gas. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 4599–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, J.; Liu, Y.; Sinsermsuksakul, P.; Li, Z.; Sun, L.; Noh, W.; Gordon, R.G. (Sn,Al)Ox Films Grown by Atomic Layer Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 10277–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.B.; Sinsermsuksakul, P.; Hock, A.S.; Pike, R.D.; Gordon, R.G. Synthesis of N-Heterocyclic Stannylene (Sn(II)) and Germylene (Ge(II)) and a Sn(II) Amidinate and Their Application as Precursors for Atomic Layer Deposition. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, M.S.; Hu, B.; Kraft, S.J.; Gordon, R.G.; Segre, C.U.; Hock, A.S. Synthetic and Spectroscopic Study of the Mechanism of Atomic Layer Deposition of Tin Dioxide. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; O’Brien, P. Precursor Chemistry—Main Group Metal Chalcogenides. In Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II, 2nd ed.; Reedijk, J., Poeppelmeier, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1001–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, A.; Roychowdhury, S.; Biswas, K. The journey of tin chalcogenides towards high-performance thermoelectrics and topological materials. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6573–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Li, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Wu, M.; Shek, C.-H.; Wu, C.M.L.; Lai, J.K.L. Recent Advances in Tin Dioxide Materials: Some Developments in Thin Films, Nanowires, and Nanorods. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7442–7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.J.; Kevin, P.; Bakr, O.; Muryn, C.A.; Malik, M.A.; O’Brien, P. Routes to tin chalcogenide materials as thin films or nanoparticles: A potentially important class of semiconductor for sustainable solar energy conversion. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, M.A.; Afzaal, M.; O’brien, P. Precursor Chemistry for Main Group Elements in Semiconducting Materials. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4417–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, M.O. Tin Oxide Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmet, I.Y.; Hill, M.S.; Raithby, P.R.; Johnson, A.L. Tin guanidinato complexes: Oxidative control of Sn, SnS, SnSe and SnTe thin film deposition. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5031–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmet, I.Y.; Thompson, J.R.; Johnson, A.L. Oxidative Addition to Sn II Guanidinate Complexes: Precursors to Tin(II) Chalcogenide Nanocrystals. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 2018, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Ahmet, I.Y.; Johnson, A.L.; Kociok-Köhn, G. Tin(IV) Chalcogenide Complexes: Single Source Precursors for SnS, SnSe and SnTe Nanoparticle Synthesis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2016, 4711–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pore, V.; Hatanpää, T.; Ritala, M.; Leskelä, M. Atomic Layer Deposition of Metal Tellurides and Selenides Using Alkylsilyl Compounds of Tellurium and Selenium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3478–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, J.R.; Incarvito, C.; Rheingold, A.L.; Fettinger, J.C.; Sita, L.R. Double Heterocumulene Metathesis of Cyclic Bis(trimethylsilylamido)stannylenes and Tethered Bimetallic Bisamidinates from the Resulting α,ω-Biscarbodiimides. Organometallics 1999, 18, 5729–5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwamm, R.J.; von Randow, C.A.; Mouchfiq, A.; Evans, M.J.; Coles, M.P.; Fulton, J.R. Synthesis of Heavy N- Heterocyclic Tetrylenes: Influence of Ligand Sterics on Structure. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 3466–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(i) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: Structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, τ4. Dalton Trans. 2007, 9, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, M. Cyclic Nitrogen Derivatives of Tetra- and Divalent Tin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1975, 14, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veith, M.; Becker, S.; Huch, V. A Base-Stabilized Ge–S Double Bond. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1989, 28, 1237–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hitchcock, P.B.; Jang, E.; Lappert, M.F. Synthesis and structures of bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)amido]-tin(IV) cyclic chalcogenides [{Sn[N(SiMe3)2]2(µ-E)}2] and a heterobimetallic analogue [{(Me3Si)2N}2Ge(µ-Te)2Sn-{N(SiMe3)2}2](E = S, Se or Te). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1995, 3179–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, M.K.; Nembenna, S. Mixed guanidinato-amido Ge(iv) and Sn(iv) complexes with Ge=E (E = S, Se) double bond and SnS4, Sn2Se2 rings. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.R.; Yap, G.P.A.; Richeson, D.S. Formation of Novel Tetrasulfido Tin Complexes and Their Ability To Catalyze the Cyclotrimerization of Aryl Isocyanates. Organometallics 1999, 18, 4700–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhashi, Y.; Tokitoh, N.; Okazaki, R.; Goto, M.; Nagase, S. Synthesis and structure of 1,2,3,4,5-tetrachalcogenastannolanes. Organometallics 2002, 12, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, N.; Hosoda, N.; Takahashi, S.; Ishii, A. Chlorogermylenes and -stannylenes stabilized by diimidosulfinate ligands: Synthesis, structures, and reactivity. Dalton Trans. 2017, 47, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Tokitoh, N.; Okazaki, R. The First Kinetically Stabilized Stannaneselone and Diselenastannirane: Synthesis by Deselenation of a Tetraselenastannolane and Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 11124–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardin, C.J.; Cardin, D.J.; Devereux, M.M.; Convery, M.A. µ-Peroxo-µ-oxo-bis[bis(trimethylsilylmethyl)tin]: The first structurally characterised main-group metal η2-peroxide, a formal tin analogue of an ozonide. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1990, 1461–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, M.A.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Lappert, M.F. Unusual kinetically stable dialkyltin(IV) oxides; X-ray structures of [{SnR2(µ-O)}2] and [{SnR2(OH)}2(µ-O)][R = CH(SiMe3)2]. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1990, 1116–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, C.; Hitchcock, P.B.; Lappert, M.F. Dilithium diamides [{Li(OC4H8)}2{C20H12(NR)2}](R = SiMe3or CH2But) derived from R-, S- or R,S-2,2′-diamino-1,1′-binaphthyl derivatives. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 3595–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamune, S.; Sita, L.R.; Williams, D.J. Cyclotristannoxane (R2SnO)3 and cyclotristannane (R2Sn)3 systems. Synthesis and crystal structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 105, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puff, H.; Schuh, W.; Sievers, R.; Wald, W.; Zimmer, R. Niedermolekulare diorganozinn-sauerstoff-verbindungen: Di-t-butyl- und di-t-amylzinnoxid. J. Organomet. Chem. 1984, 260, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Fanwick, P.E.; Rothwell, I.P. Synthesis, structure, and spectroscopic properties of germanium and tin compounds containing aryloxide ligation: Comparison of aryloxide bonding to group 4 and group 14 metal centers. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 29, 3221–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoono, R.; Sakamoto, K.; Suzuki, T. Dual dynamic chirality generated in the assembly of three achiral rods through the three-fold twisting of a macrocycle. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 5503–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, M.; Kang, D.; Lee, H.-M.; Choi, W.-H.; Park, J.W.; Yi, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.-S. Selective SnOx Atomic Layer Deposition Driven by Oxygen Reactants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33335–33342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmstead, M.M.; Power, P.P. Structural studies of tin(II) and lead(II) dimethylamides: X-ray crystal structure of [Sn(NMe2)2]2 and isolation of its lead analog. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 413–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldberg, T.; Lappert, M.F.; Power, P.P.; Thorne, A.J.; Hope, H. Molecular structures of the main group 4 metal(II) bis(trimethylsilyl)-amides M[N(SiMe3)2]2 in the crystal (X-ray) and vapour (gas-phase electron diffraction). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1983, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, A.C.; Hill, N.J.; West, R. Synthesis and characterization of three new thermally stable N-heterocyclic germylenes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2009, 694, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Cascarano, G.; Giacovazzo, C.; Guagliardi, A.; Burla, M.C.; Polidori, G.; Camalli, M. SIR92—A program for automatic solution of crystal structures by direct methods. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Compound [a] | δ(1H) [b] | δ(13C) [c] | δ(119Sn) [d] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.20 (d, 6H, 3JH-H = 6.2 Hz, {CMeH}) 1.25 (s, 18H, {N-CMe3}) 3.32 (q, 2H, 3JH-H = 6.1 Hz, {CMeH}) | 29.0 ({CMeH}) 34.5 ({N-CMe3}) 56.3 ({CMeH}) 64.8 ({N-CMe3}) | 455 |
| 4 | 1.11 (d, 6H, 3JH-H = 5 Hz, {CMeH}) 1.47 (s, 18H, {N-CMe3}) 2.74–3.02 (m, 2H, {CMeH}) | 26.5 ({CMeH}) 26.6 ({CMeH}) 33.3 ({N-CMe3}) 33.4 ({N-CMe3}) 55.4 ({N-CMe3}) 55.5 ({N-CMe3}) 58.3 ({CMeH}) 54.4 ({CMeH}) | −79 (J119Sn-117Sn = 589 Hz) −84 (J119Sn-117Sn = 582 Hz) |
| 5 | 1.11 (d, 6H, 3JH-H = 5 Hz, {CMeH}) 1.47 (s, 18H, {N-CMe3}) 2.82–2.86 (m, 2H, {CMeH}) | 26.2 ({CMeH}) 26.7 ({CMeH}) 33.3 ({N-CMe3}) 33.4 ({N-CMe3}) 55.8 ({N-CMe3}) 55.9 ({N-CMe3}) 58.6 ({CMeH}) 58.7 ({CMeH}) | −357 −362 |
| 6 | 1.08 (d, 12H, 3JH-H = 5 Hz, {CMeH}) 1.55 (s, 32H, {N-CMe3}) 2.77 (q, 4H, 3JH-H = 5 Hz, {CMeH}) | 26.7 ({CMeH}) 26.8 ({CMeH}) 33.5 ({N-CMe3}) 33.7 ({N-CMe3}) 56.5 ({N-CMe3}) 59.0 ({CMeH}) 59.1 ({CMeH}) | −957 −961 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flanagan, K.R.; Parish, J.D.; Kociok-Köhn, G.; Johnson, A.L. Reactivity of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: Oxidative Addition of Chalcogen Elements to a Chiral NH-Sn System. Inorganics 2023, 11, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080318
Flanagan KR, Parish JD, Kociok-Köhn G, Johnson AL. Reactivity of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: Oxidative Addition of Chalcogen Elements to a Chiral NH-Sn System. Inorganics. 2023; 11(8):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080318
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlanagan, Kerry R., James D. Parish, Gabriele Kociok-Köhn, and Andrew L. Johnson. 2023. "Reactivity of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: Oxidative Addition of Chalcogen Elements to a Chiral NH-Sn System" Inorganics 11, no. 8: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080318
APA StyleFlanagan, K. R., Parish, J. D., Kociok-Köhn, G., & Johnson, A. L. (2023). Reactivity of N-Heterocyclic Stannylenes: Oxidative Addition of Chalcogen Elements to a Chiral NH-Sn System. Inorganics, 11(8), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080318