Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates: Phosphine Oxide Formation vs. Thiolate Disulfide Exchange
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phosphine Oxide Formation in DMSO

| R3PAuSRʹ | R*SSR* | R3P=O (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ph3PAuSC6H4NO2 | DTNB 1 | 100 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4CH3 | DTNB | 68 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4NO2 | (SC6H4NO2)2 | 67 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4Cl | DTNB | 40 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4Cl | (SC6H4NO2)2 | 31 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4CH3 | (SC6H4NO2)2 | 23 |
| Et3PAu(TATG) 2 | DTNB | 20 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4NO2 | (SC6H4Cl)2 | 15 |
| Et3PAu(TATG) | (SC6H4NO2)2 | 11 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4CH3 | (SC6H4Cl)2 | 4 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4Cl | (SC6H4Cl)2 | 3 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4NO2 | (SC6H4CH3)2 | 3 |
| Et3PAu(TATG) | (SC6H4Cl)2 | <1 |
| Et3PAu(TATG) | (SC6H4CH3)2 | <1 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4CH3 | (SC6H4CH3)2 | 0 |
| Ph3PAuSC6H4Cl | (SC6H4CH3)2 | 0 |
2.2. Possible Mechanistic Pathways for Phosphine Oxide Formation in DMSO


2.3. No Evidence for Dissociation of Phosphine from Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolate in DMSO
2.4. Water Is the Source of Oxygen for the Formation of Ph3P=O
2.5. What Is the Fate of Gold(I)?
2.6. Mechanistic Reaction Sequence of Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates
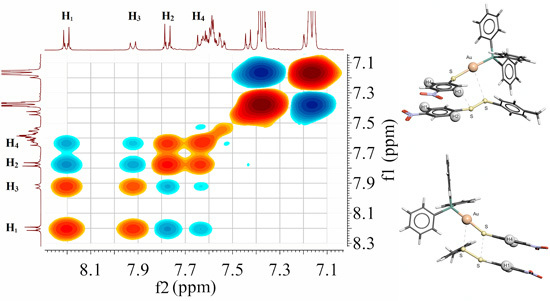
2.7. Scheme 1B Is Supported by 2D (1H-1H) NMR Experiments
2.8. 2D (1H-1H) NMR ROESY Experiments


2.9. Visualizing the Association of Disulfide and the Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolate Complex


3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemicals and Instrumentation
3.2. Calibration of 31P NMR Integrals for a Mixture of Ph3PAuSC6H4CH3 and Ph3PO
3.3. Procedure for Measuring % of Phosphine Oxide
3.4. Test for Free Phosphine; Reaction of PPh3 and N3Bz in DMSO-d6
3.5. Test for Influence of Water
3.6. GC-MS Experiment for Source of Water
3.7. Reaction of Au(tht)Cl and Na[SC6H4NO2]
3.8. 2D (1H-1H) ROESY Experiment
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whitesides, G.M.; Lilburn, J.E.; Szajewski, R.P. Rates of thiol-disulfide interchange reactions between mono- and dithiols and Ellman’s reagent. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. Theoretical insights into the mechanism for thiol/disulfide exchange. Chemistry 2004, 10, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiLorenzo, M.; Ganesh, S.; Tadayon, L.; Chen, J.; Bruce, M.R.M.; Bruce, A.E. Reactions of organic disulfides and gold(I) complexes. Met.-Based Drugs 1999, 6, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Abdou, H.E.; Chen, J.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. Perspectives in Inorganic and Bioinorganic Gold Sulfur Chemistry. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2002, 23, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garusinghe, G.S.P. Kinetic Analysis of Metal Assisted-Thiolate Disulfide Exchange (M = Au, Zn). Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bachman, R.E.; Bodolosky-Bettis, S.A.; Pyle, C.J.; Gray, M.A. Reversible Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination of Fluorinated Disulfides at Gold(I) Thiolate Complexes: A New Ligand Exchange Mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14303–14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garusinghe, G.S.P.; Bessey, S.M.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. Interactions between Metal Thiolate, R3PAuSC6H4NO2 (R = Ph and Et) and Bis(4-nitrophenyl) Disulfide. In Proceedings of the 36th Northeast Regional Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Hartford, CT, USA, 7–10 October 2009.
- Chandrasoma, A.; Bruce, A.; Bruce, M. Insight into Metal-Mediated Thiol–Disulfide Exchange. In Proceedings of the 37th Northeast Regional Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Burlington, VT, USA, 29 June–2 July 2008.
- Aghamoosa, M.; Briggs, B.; Harriman, E.; Cashman, A.; Bruce, A.; Bruce, M. Gold(I)-Mediated Disulfide Exchange Kinetics as a Function of Solvent Dielectric Constant. In Proceedings of the 37th Northeast Regional Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Burlington, VT, USA, 29 June–2 July 2008.
- DiLorenzo, M.A.; Ganesh, S.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. Gold(I) mediated thiolate/disulfide exchange reactions. In Proceedings of the 213th ACS National Meeting, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 April 1997.
- Garusinghe, G.S.P.; Bessey, S.M.; Boyd, C.; Aghamoosa, M.; Frederick, B.; Bruce, M.R.M.; Bruce, A.E.; (University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA). Determination of dimethyl sulfide in dimethyl sulfoxide. Unpublished work. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Overman, L.E.; Matzinge, D.; Oconnor, E.M.; Overman, J.D. Nucleophilic Cleavage of Sulfur–Sulfur Bond by Phosphorus Nucleophiles—Kinetic Study of Reduction of Aryl Disulfides with Triphenylphosphine and Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 6081–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, O.; Thorpe, C.; Bach, R.D. Mechanism of SN2 Disulfide Bond Cleavage by Phosphorus Nucleophiles. Implications for Biochemical Disulfide Reducing Agents. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 8298–8307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, C.F.; Isab, A.A.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Starich, M.; Locke, J.; Schulteis, P.; Xiao, J. Oxidation of the phosphine from the auranofin analog, triisopropylphosphine(2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-1-thio-β-D-glucopyranosato-S)gold(I), via a protein-bound phosphonium intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.T.; Isab, A.A.; Griswold, D.E.; DiMartino, M.J.; Matz, E.D.; Figueroa, A.L.; Wawro, J.E.; DeBrosse, C.; Reiff, W.M.; Elder, R.C.; et al. Seleno-Auranofin (Et3PAuSe-tagl): Synthesis, Spectroscopic (EXAFS, 197Au Mossbauer, 31P, 1H, 13C, and 77Se NMR, ESI-MS) Characterization, Biological Activity, and Rapid Serum Albumin-Induced Triethylphosphine Oxide Generation. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 7663–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.L.; Hoyt, H.M.; van Halbeek, H.; Bergman, R.G.; Bertozzi, C.R. Mechanistic investigation of the Staudinger ligation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 2686–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woehrle, G.H.; Hutchison, J.E. Thiol-functionalized undecagold clusters by ligand exchange: Synthesis, mechanism, and properties. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6149–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerzel, H.; Koeckert, M.; Bu, W.; Spingler, B.; Lippard, S.J. Zinc-Bound Thiolate-Disulfide Exchange: A Strategy for Inhibiting Metallo-β-Lactamases. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acharige, A. Reactions of Sulfur Compounds with Zn(II), Au(I), and Hg(II) and Metal Linker Polyaniline Electrodes for Energy Storage. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maine, Orono, ME, USA, May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Binotti, B.; Macchioni, A.; Zuccaccia, C.; Zuccaccia, D. Application of NOE and PGSE NMR methodologies to investigate non-covalent intimate inorganic adducts in solution. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2002, 23, 417–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, J.S.; Bernal, I. Crystal structure of α-bis(p-nitrophenyl) disulfide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 4078–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, F. The Cambridge Structural Database: A quarter of a million crystal structures and rising. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 2002, 58, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Young, M.A.; Parkhurst, E.; Ouellette, M.; Kerr, M.E.; Ho, D.M.; Elder, R.C.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. Synthesis, structure, and electronic spectroscopy of neutral, dinuclear gold(I) complexes. Gold(I)–gold(I) interactions in solution and in the solid state. Inorg. Chem. 1993, 32, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isab, A.A.; Sadler, P.J. A 13C Nuclear Magnetic-Resonance Study of Thiol-Exchange Reactions of Gold(I) Thiomalate (Myocrisin) Including Applications to Cysteine Derivatives. Dalton Trans. 1982, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uson, R.; Laguna, A.; Laguna, M.; Briggs, D.A.; Murray, H.H.; Fackler, J.P. (Tetrahydrothiophene) Gold(I) or Gold(III) Complexes. In Inorganic Syntheses; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bordwell, F.G.; Hughes, D.L. Thiol Acidities and Thiolate Ion Reactivities toward Butyl Chloride in Dimethylsulfoxide Solution—The Question of Curvature in Bronsted Plots. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 3224–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garusinghe, G.S.P.; Bessey, S.M.; Aghamoosa, M.; McKinnon, M.; Bruce, A.E.; Bruce, M.R.M. Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates: Phosphine Oxide Formation vs. Thiolate Disulfide Exchange. Inorganics 2015, 3, 40-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010040
Garusinghe GSP, Bessey SM, Aghamoosa M, McKinnon M, Bruce AE, Bruce MRM. Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates: Phosphine Oxide Formation vs. Thiolate Disulfide Exchange. Inorganics. 2015; 3(1):40-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010040
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarusinghe, Gamage S. P., S. Max Bessey, Mostapha Aghamoosa, Meaghan McKinnon, Alice E. Bruce, and Mitchell R. M. Bruce. 2015. "Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates: Phosphine Oxide Formation vs. Thiolate Disulfide Exchange" Inorganics 3, no. 1: 40-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010040
APA StyleGarusinghe, G. S. P., Bessey, S. M., Aghamoosa, M., McKinnon, M., Bruce, A. E., & Bruce, M. R. M. (2015). Disulfide Competition for Phosphine Gold(I) Thiolates: Phosphine Oxide Formation vs. Thiolate Disulfide Exchange. Inorganics, 3(1), 40-54. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics3010040