The Versatile SALSAC Approach to Heteroleptic Copper(I) Dye Assembly in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Ligand Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of [Cu(4)2][PF6]
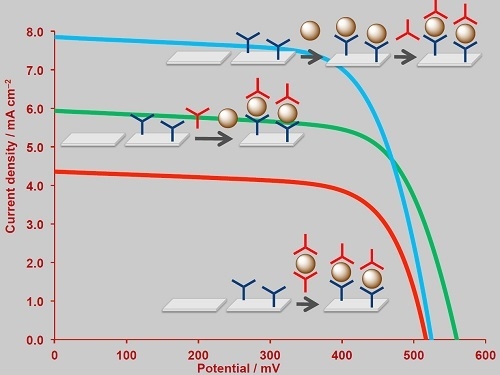
2.3. The SALSAC Approach to On-Surface Dye Assembly
2.4. The SALSAC Approach to On-Surface Dye Assembly
2.5. DSSC Performances
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Compound 4
3.3. Compound [Cu(4)2][PF6]
3.4. DSSC Fabrication
3.5. Electrodes for Solid-State Absorption Spectroscopy
3.6. DSSC and External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Reagan, B.; Grätzel, M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Baranoff, E.; Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. A brief overview. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Recent Advances in Sensitized Mesoscopic Solar Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grätzel, M. Solar energy conversion by dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.; Yeh, C.Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)-based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashino, T.; Imahori, H. Porphyrins as excellent dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: Recent developments and insights. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Kyomen, T.; Hanaya, M. Fabrication of a high-performance dye-sensitized solar cell with 12.8% conversion efficiency using organic silyl-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6315–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Yella, A.; Gao, P.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Curchod, B.F.; Ashari-Astani, N.; Tavernelli, I.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W.-H. Porphyrin Cosensitization for a Photovoltaic Efficiency of 11.5%: A Record for Non-Ruthenium Solar Cells Based on Iodine Electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14055–14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Fujisawa, J.-I.; Hanaya, M. Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15894–15897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, C.E. The Emergence of copper(I)-based dye sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8386–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magni, M.; Biagini, P.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Valore, A. Versatile copper complexes as a convenient springboard for both dyes and redox mediators in dyes sensiatized solar cells. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 322, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazorski, M.S.; Castellano, F.N. Advances in the light conversion properties of Cu(I)-based photosensitizers. Polyhedron 2014, 82, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Pellegron, Y.; Odobel, F. Heteroleptic bis-diimine copper(I) complexes for applications in solar energy conversion. Compt. Rendus Chim. 2016, 19, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubikova, E.; Bowman, D.N. Fe(II)-Polypyridines as Chromophores in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Computational Perspective. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Persson, P.; Sundström, V.; Wärnmark, K. Fe N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes as Promising Photosensitizers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malzner, F.J.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M. Halos show the path to perfection: Peripheral iodo-substituents improve the efficiencies of bis(diimine)copper(I) dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48712–48723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Favereau, L.; Planchat, A.; Akdas-Kilig, H.; Szuwarski, N.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E.; Le Bozec, H.; Boujtita, M.; Odobel, F. Heteroleptic copper(I)–polypyridine complexes as efficient sensitizers for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9944–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzner, F.J.; Willgert, M.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. The way to panchromatic copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells: Co-sensitization with the organic dye SQ2. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13717–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürer, S.O.; Bozic-Weber, B.; Schefer, T.; Wobill, C.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Willgert, M. Understanding why replacing I3–/I– by cobalt(II)/(III) electrolytes in bis(diimine)copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells improves performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12995–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashbrook, L.N.; Elliott, C.M. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Studies of a Donor-Appended Bis(2,9-dimethyl- 1,10-phenanthroline) Cu(I) Dye Paired with a Cobalt-Based Mediator. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3853–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürer, S.O.; Luu, L.Y.N.; Bozic-Weber, B.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Improving performance of copper(I)-based dye sensitized solar cells through I3–/I– electrolyte manipulation. Dyes Pigment. 2016, 132, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, C.; Magni, M.; Colombo, A.; Melchiorre, F.; Biagini, P.; Roberto, D. Coupling of a Copper Dyes with a Copper Electrolyte: A Fascinating Springboard for Sustainable Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Ener. Mater. 2018, 1, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpacheva, M.; Malzner, F.J.; Wobill, C.; Büttner, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Cuprophilia: Dye-sensitized solar cells with copper(I) dyes and copper(I)/(II) redox shuttles. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 156, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Fürer, S.O.; Housecroft, C.E.; Wright, I.A. Hole-transport functionalized copper(I) dye sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snaith, H.J. How should you measure your excitonic solar cells? Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6513–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez Redondo, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Towards sustainable dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chimia 2009, 63, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Kayanuma, M.; Planchat, A.; Szuwarski, N.; Blart, E.; Pellegrin, Y.; Daniel, C.; Boujtita, M.; Odobel, F. First application of the HETPHEN concept to new heteroleptic bis(diimine) copper(I) complexes as sensitizers in dye sensitized solar cells. Dalton. Trans. 2013, 42, 10818–10827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsani, V.; Bodenstedt, H.; Fenske, D.; Schmittel, M. Supramolecular copper phenanthroline racks: Structures, mechanistic insight and dynamic Nature. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 10, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich-Buchecker, C.O.; Sauvage, J.P.; Kintzinger, J.P. Une nouvelle famille de molecules: Les metallo-catenanes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983, 24, 5095–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, U.; Rehahn, M. First synthesis of soluble, well defined coordination polymers from kinetically unstable copper(I) complexes. Chem. Commun. 1996, 23, 2639–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.S.; Carroll, P.J.; Swager, T.M. Conducting polymetallorotazanes: A supramolecular approach to transition metal ion sensors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8713–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Kopecky, P.; Neuburger, M.; Zampese, J.A. The intramolecular aryl embrace: From light emission to light absorption. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 12584–12594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büttner, A.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Vogt, R.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Combining phosphonic acid-functionalized anchoring ligands with asymmetric ancillary ligands in bis(diimine)copper(I) dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5205–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brauchli, S.Y.; Malzner, F.J.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells with sterically demanding anchoring ligands: Bigger is not always better. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48516–48525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleston, M.K.; McMillin, D.R.; Koenig, K.S.; Pallenberg, A.J. Steric Effects in the Ground and Excited States of Cu(NN)2+ Systems. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.T.; Gantzel, P.K.; Karpishin, T.B. Structures of the copper(I) and copper(II) complexes of 2,9-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline: Implications for excited-state structural distortion. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 2285–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushurst, A.K.I.; McMillin, D.R.; Dietrich-Buchecker, C.O.; Sauvage, J.P. Comparative studies of the photophysical properties of copper phenanthrolines: From Cu(dmp)2+ to the copper(I) catenates. Inorg. Chem. 1989, 28, 4070–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, A.J.; Malzner, F.J.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. The influence of phosphonic acid protonation state on the efficiency of bis(diimine)copper(I) dye-sensitized solar cells. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Fürer, S.O.; Housecroft, C.E.; Malzner, F.J.; Wright, I.A.; Zampese, J.A. Improving the photoresponse of copper(I) dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells by tuning ancillary and anchoring ligand modules. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12293–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, Y.M.; Willgert, M.; Prescimone, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Positional isomerism makes a difference: Phosphonic acid anchoring ligands with thienyl spacers in copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 4659–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumgartner, Y.; Klein, Y.M.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Willgert, M. Cyanoacrylic- and (1-cyanovinyl)phosphonic acid anchoring ligands for application in copper-based dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86220–86231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunner, F.; Klein, M.; Keller, S.; Morris, C.D.; Prescimone, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. The beneficial effects of trifluoromethyl-substituents on the photoconversion efficiency of copper(I) dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58694–58703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröhnke, F. The specific synthesis of pyridines and oligopyridines. Synthesis. 1976, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubas, G.J. Tetrakis(Acetonitrile)Copper(I) Hexafluorophosphate. Inorg. Synth. 1979, 19, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Complex | /V (Epc − Epa/mV) | /V | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Cu(4)2][PF6] | +0.36 (49) | −1.96 irr | this work |
| [Cu(2)2][PF6] | +0.36 (86) | a | 40 |
| Dye | Dipping Procedure a | Cell Number | On the Day of DSSC Fabrication | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSC/mA cm−2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |||
| [Cu(3)(1)]+ | Ligand exchange | 1 | 6.68 | 582 | 74.0 | 2.88 | 38.8 |
| [Cu(3)(1)]+ | Ligand exchange | 2 | 6.92 | 576 | 72.6 | 2.89 | 38.9 |
| N719 b | - | - | 16.08 | 641 | 72.0 | 7.43 | 100 |
| [Cu(3)(1)]+ | 1:1 | 1 | 6.82 | 551 | 69.1 | 2.59 | 34.4 |
| [Cu(3)(1)]+ | 1:1 | 2 | 7.01 | 559 | 70.2 | 2.75 | 36.5 |
| N719 c | - | - | 16.88 | 641 | 69.6 | 7.54 | 100 |
| Dye | Dipping Procedure a | Cell Number | On the Day of DSSC Fabrication | ||||
| JSC/mA cm−2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |||
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 1 | 4.36 | 517 | 69.0 | 1.55 | 22.7 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 2 | 4.88 | 528 | 70.1 | 1.80 | 26.4 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 1 | 5.95 | 560 | 68.2 | 2.27 | 33.2 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 2 | 6.17 | 550 | 67.3 | 2.29 | 33.4 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 1 | 7.85 | 524 | 68.3 | 2.81 | 41.1 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 2 | 7.73 | 517 | 67.8 | 2.71 | 39.6 |
| N719 | - | - | 15.33 | 615 | 72.6 | 6.84 | 100 |
| Dye | Dipping Procedure a | Cell Number | 3 Days after DSSC Fabrication | ||||
| JSC/mA cm−2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |||
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 1 | 2.63 | 499 | 67.8 | 0.89 | 12.2 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 2 | 3.45 | 514 | 69.4 | 1.23 | 16.8 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 1 | 5.69 | 560 | 69.4 | 2.21 | 30.2 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 2 | 6.38 | 560 | 68.9 | 2.46 | 33.7 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 1 | 6.58 | 515 | 71.4 | 2.42 | 33.1 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 2 | 7.77 | 545 | 63.7 | 2.69 | 36.8 |
| N719 | 15.73 | 638 | 72.9 | 7.31 | 100 | ||
| Dye | Dipping Procedure a | Cell Number | 7 Days after DSSC Fabrication | ||||
| JSC/mA cm−2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |||
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 1 | 2.61 | 501 | 68.1 | 0.89 | 12.1 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Ligand exchange | 2 | 3.33 | 505 | 69.0 | 1.16 | 15.7 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 1 | 5.60 | 561 | 70.6 | 2.22 | 30.1 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | 1:1 | 2 | 6.18 | 560 | 70.2 | 2.43 | 32.9 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 1 | 7.13 | 535 | 69.4 | 2.65 | 35.9 |
| [Cu(3)(4)]+ | Sequential | 2 | 8.10 | 561 | 57.6 | 2.61 | 35.5 |
| N719 | 15.16 | 672 | 72.4 | 7.37 | 100.0 | ||
| Cell Number | Dipping Procedure a | λmax/nm | EQEmax/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ligand exchange | 480 | 29.8 |
| 2 | Ligand exchange | 480 | 31.9 |
| 1 | 1:1 | 470 | 47.0 |
| 2 | 1:1 | 470 | 49.1 |
| 1 | Sequential | 460 | 52.5 |
| 2 | Sequential | 480 | 51.7 |
| N719 | 540 | 68.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malzner, F.J.; Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. The Versatile SALSAC Approach to Heteroleptic Copper(I) Dye Assembly in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics 2018, 6, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020057
Malzner FJ, Housecroft CE, Constable EC. The Versatile SALSAC Approach to Heteroleptic Copper(I) Dye Assembly in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics. 2018; 6(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020057
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalzner, Frederik J., Catherine E. Housecroft, and Edwin C. Constable. 2018. "The Versatile SALSAC Approach to Heteroleptic Copper(I) Dye Assembly in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Inorganics 6, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020057
APA StyleMalzner, F. J., Housecroft, C. E., & Constable, E. C. (2018). The Versatile SALSAC Approach to Heteroleptic Copper(I) Dye Assembly in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics, 6(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020057