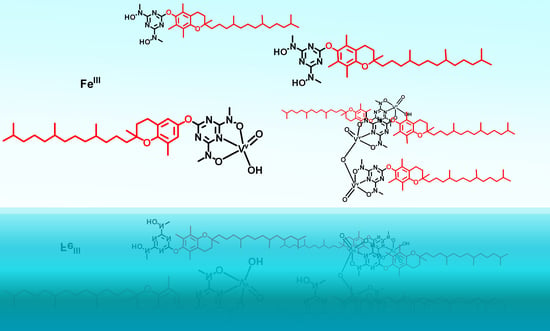
Vanadium(V) Complexes with Siderophore Vitamin E-Hydroxylamino-Triazine Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Spectroscopic Studies
2.4. Reactivity with DPPH•
2.5. Measurement of Oxidative Inducing Effect of Vanadium Compounds by EPR Spectroscopy
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Measurement of Cell Viability
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterisation
3.2. Complexes Characterisation by IR
3.3. Complex Characterisation by 51V NMR, 2D {1H} grNOESY
3.4. Complexes Characterisation by UV-Vis
3.5. Characterisation of the Complexes in 10% DMSO:90% D2O Solutions by 51V NMR
3.6. Characterisation of the Complexes in 10% DMSO:90% D2O Solutions by UV-Vis Spectroscopy
3.7. Reactivity with DPPH•
3.8. Oxidative Inducing Effect of Vanadium Compounds by EPR Spectroscopy
3.9. Cytotoxic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michibata, H.; Sakurai, H. Vanadium in Biological Systems; Chasteen, N.D., Ed.; Kluer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 153–171. [Google Scholar]
- Crans, D.C.; Keramidas, A.D.; Hoover-Litty, H.; Anderson, O.P.; Miller, M.M.; Lemoine, L.M.; Pleasic-Williams, S.; Vandenberg, M.; Rossomando, A.J.; Sweet, L.J. Synthesis, structure, and biological activity of a new insulinomimetic peroxovanadium compound: Bisperoxovanadium imidazole monoanion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 5447–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, D. The coordination chemistry of vanadium as related to its biological functions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 182, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kioseoglou, E.; Petanidis, S.; Gabriel, C.; Salifoglou, A. The chemistry and biology of vanadium compounds in cancer therapeutics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301–302, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, A.; Lay, P.A. Stabilities and Biological Activities of Vanadium Drugs: What is the Nature of the Active Species? Chem. Asian J. 2017, 12, 1692–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, C.S. Iron-Only and Vanadium Nitrogenases: Fail-Safe Enzymes or Something More? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amante, C.; De Sousa-Coelho, A.L.; Aureliano, M. Vanadium and melanoma: A systematic review. Metals 2021, 11, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, G.; Maréchal, J.D.; Garribba, E. Integrated experimental/computational approaches to characterize the systems formed by vanadium with proteins and enzymes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 1951–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Pessoa, J.; Garribba, E.; Santos, M.F.A.; Santos, S. Vanadium and proteins: Uptake, transport, structure, activity and function. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301–302, 49–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, J.C.; Etcheverry, S.; Gambino, D. Vanadium compounds in medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301–302, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehder, D. The future of/for vanadium. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 11749–11761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Trujillo, A.M.; Pharazyn, P.S.; Cohen, M.D. How environment affects drug activity: Localization, compartmentalization and reactions of a vanadium insulin-enhancing compound, dipicolinatooxovanadium(V). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2178–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlan, C.C.; Peters, B.J.; Willsky, G.R.; Crans, D.C. Vanadium-phosphatase complexes: Phosphatase inhibitors favor the trigonal bipyramidal transition state geometries. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 301–302, 163–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsky, G.R.; Chi, L.H.; Godzala, M.; Kostyniak, P.J.; Smee, J.J.; Trujillo, A.M.; Alfano, J.A.; Ding, W.; Hu, Z.; Crans, D.C. Anti-diabetic effects of a series of vanadium dipicolinate complexes in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2258–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crans, D.C.; Tarlton, M.L.; McLauchlan, C.C. Trigonal bipyramidal or square pyramidal coordination geometry? Investigating the most potent geometry for vanadium phosphatase inhibitors. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 4450–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Schoeberl, S.; Gaidamauskas, E.; Baruah, B.; Roess, D.A. Antidiabetic vanadium compound and membrane interfaces: Interface-facilitated metal complex hydrolysis. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Lombardo, I.; Alvarez, S.; McLauchlan, C.C.; Crans, D.C. Evaluating transition state structures of vanadium-phosphatase protein complexes using shape analysis. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 147, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C. Antidiabetic, Chemical, and Physical Properties of Organic Vanadates as Presumed Transition-State Inhibitors for Phosphatases. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 11899–11915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crans, D.C.; Henry, L.; Cardiff, G.; Posner, B.I. Developing Vanadium as an Antidiabetic or Anticancer Drug: A Clinical and Historical Perspective. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2019, 19, 203–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I. Titanium and vanadium complexes as anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Waghray, A.; Patel, M.A.; Chatterjee, M. Vanadium in the detection, prevention and treatment of cancer: The in vivo evidence. Cancer Lett. 2010, 294, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelou, A.M. Vanadium in cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 42, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, I.E.; Cadavid-Vargas, J.F.; Di Virgilio, A.L.; Etcheverry, S. Vanadium, ruthenium and copper compounds: A new class of non-platinum Metallodrugs with anticancer activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 112–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Yang, L.; Haase, A.; Yang, X. Health Benefits of Vanadium and Its Potential as an Anticancer Agent. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2018, 18, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucette, K.A.; Hassell, K.N.; Crans, D.C. Selective speciation improves efficacy and lowers toxicity of platinum anticancer and vanadium antidiabetic drugs. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 165, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, B.; Stantic, M.; Zobalova, R.; Bezawork-Geleta, A.; Stapelberg, M.; Stursa, J.; Prokopova, K.; Dong, L.; Neuzil, J. Mitochondrially targeted vitamin E succinate efficiently kills breast tumour-initiating cells in a complex II-dependent manner. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.F.; Grant, G.; Massa, H.; Zobalova, R.; Akporiaye, E.; Neuzil, J. α-Tocopheryloxyacetic acid is superior to α-tocopheryl succinate in suppressing HER2-high breast carcinomas due to its higher stability. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, L.-F.; Neuzil, J. Vitamin E Analogues as Prototypic Mitochondria-Targeting Anti-cancer Agents. In Mitochondria: The Anti-Cancer Target for the Third Millennium; Neuzil, J., Pervaiz, S., Fulda, S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 151–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kovarova, J.; Bajzikova, M.; Vondrusova, M.; Stursa, J.; Goodwin, J.; Nguyen, M.; Zobalova, R.; Pesdar, E.A.; Truksa, J.; Tomasetti, M.; et al. Mitochondrial targeting of α-tocopheryl succinate enhances its anti-mesothelioma efficacy. Redox Rep. 2014, 19, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, W.N.; Chang, P.N.; Han, H.Y.; Lee, D.T.W.; Ling, M.T.; Wong, Y.C.; Yap, Y.L. γ-Tocotrienol suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion through multiple-signalling pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, J.M. Molecular and cellular activities of vitamin E analogues. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.K.; Richmond, E.S.; Minasian, L.M.; Ryan, A.M.; Ford, L.G. A nutrient approach to prostate cancer prevention: The selenium and vitamin e cancer prevention trial (SELECT). Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 896–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vraka, P.S.; Drouza, C.; Rikkou, M.P.; Odysseos, A.D.; Keramidas, A.D. Synthesis and study of the cancer cell growth inhibitory properties of α-, γ-tocopheryl and γ-tocotrienyl 2-phenylselenyl succinates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vraka, P.S.; Rikkou, M.N.; Drouza, C.; Keramidas, A.D.; Odysseos, A.D. Modulation of apoptotic signals with esterification of selenium and vitamin E in binary compounds. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Karten, B.; Wintersperger, A.; Reicher, H.; McLean, M.; Malle, E.; Sattler, W. The human breast carcinoma cell line HBL-100 acquires exogenous cholesterol from high-density lipoprotein via CLA-1 (CD-36 and LIMPII analogous 1)-mediated selective cholesteryl ester uptake. Biochem. J. 2000, 349, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiadamou, I.; Vlasiou, M.; Spanou, S.; Simos, Y.; Papanastasiou, G.; Kontargiris, E.; Dhima, I.; Ragos, V.; Karkabounas, S.; Drouza, C.; et al. Synthesis of vitamin E and aliphatic lipid vanadium(IV) and (V) complexes, and their cytotoxic properties. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2020, 208, 111074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouza, C.; Dieronitou, A.; Hadjiadamou, I.; Stylianou, M. Investigation of Phenols Activity in Early Stage Oxidation of Edible Oils by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance and19F NMR Spectroscopies Using Novel Lipid Vanadium Complexes As Radical Initiators. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2017, 65, 4942–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Koehn, J.T.; Petry, S.M.; Glover, C.M.; Wijetunga, A.; Kaur, R.; Levina, A.; Lay, P.A. Hydrophobicity may enhance membrane affinity and anti-cancer effects of Schiff base vanadium(v) catecholate complexes. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6383–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, B.G.; Richens, D.T.; Anderson, A.; Sedgwick, M.; Crans, D.C.; Johnson, M.D. Stabilization of a vanadium(v)-catechol complex by compartmentalization and reduced solvation inside reverse micelles. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crans, D.C.; Keramidas, A.D.; Mahroof-Tahir, M.; Anderson, O.P.; Miller, M.M. Factors Affecting Solution Properties of Vanadium(V) Compounds: X-ray Structure of β-cis-NH4[VO2(EDDA)]. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeltchik, I.; Gun, J.; Lev, O.; Shelkov, R.; Melman, A. Bis(hydroxyamino)triazines: Versatile and high-affinity tridentate hydroxylamine ligands for selective iron(III) chelation. Dalton Trans. 2006, 6, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakis, V.A.; Tsalavoutis, J.T.; Stylianou, M.; Evgeniou, E.; Jakusch, T.; Melman, A.; Sigalas, M.P.; Kiss, T.; Keramidas, A.D.; Kabanos, T.A. Vanadium(V) compounds with the bis-(hydroxylamino)-1,3,5-triazine ligand, H2bihyat: Synthetic, structural, and physical studies of [V 2 VO3(bihyat)2] and of the enhanced hydrolytic stability species cis-[VVO2(bihyat)]. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11698–11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianou, M.; Nikolakis, V.A.; Chilas, G.I.; Jakusch, T.; Vaimakis, T.; Kiss, T.; Sigalas, M.P.; Keramidas, A.D.; Kabanos, T.A. Molybdenum(VI) coordination chemistry of the N,N-disubstituted bis(hydroxylamido)-1,3,5-triazine ligand, H2bihyat. Water-assisted activation of the MoVI=O bond and reversible dimerization of cis-[MoVIO2(bihyat)] to [MoVI2O4(bihyat)2(H2O)2]. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 13138–13147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjithoma, S.; Papanikolaou, M.G.; Leontidis, E.; Kabanos, T.A.; Keramidas, A.D. Bis(hydroxylamino)triazines: High Selectivity and Hydrolytic Stability of Hydroxylamine-Based Ligands for Uranyl Compared to Vanadium(V) and Iron(III). Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 7631–7643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.B.; Abtab, S.M.T.; Bhattacharya, K.; Endo, A.; Shotton, E.J.; Teat, S.J.; Chaudhury, M. Hetero-bimetallic complexes involving vanadium(V) and rhenium(VII) centers, connected by unsupported μ-oxido bridge: Synthesis, characterization, and redox study. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 8830–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; Soler-Rivas, C.; Wichers, H.J.; García-Viguera, C. Anthocyanin-based natural colorants: A new source of antiradical activity for foodstuff. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2000, 48, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdikos, A.; Karkabounas, S.; Metsios, A.; Kostoula, O.; Havelas, K.; Binolis, J.; Verginadis, I.; Hatziaivazis, G.; Simos, I.; Evangelou, A. Anticancer effects on leiomyosarcoma-bearing Wistar rats after electromagnetic radiation of resonant radiofrequencies. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 10, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Drouza, C.; Keramidas, A.D. Solid state and aqueous solution characterization of rectangular tetranuclear V(IV/V)-p-semiquinonate/hydroquinonate complexes exhibiting a proton induced electron transfer. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 7211–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouza, C.; Stylianou, M.; Papaphilippou, P.; Keramidas, A.D. Structural and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) characterization of novel vanadium(V/IV) complexes with hydroquinonate-iminodiacetate ligands exhibiting “noninnocent” activity. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etcheverry, S.B.; Williams, P.A.M. Medicinal chemistry of copper and vanadium bioactive compounds. In New Developments in Medicinal Chemistry; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 105–129. [Google Scholar]


















| Compounds | k2 (M−1s−1) Toluene |
|---|---|
| α-tocTMHA | 7.0 ± 0.16 |
| δ-tocTMHA | 12.5 ± 0.08 |
| 1m | −0.88 ± 0.02 |
| 2m | −0.88 ± 0.02 |
| 3 | 5.0 ± 0.09 |
| 4 | −0.75 ± 0.02 |
| [VIVO(acac)2] | 6.8 ± 0.3 |
| α-tocopherol [33] | 560 ± 80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loizou, M.; Hadjiadamou, I.; Drouza, C.; Keramidas, A.D.; Simos, Y.V.; Peschos, D. Vanadium(V) Complexes with Siderophore Vitamin E-Hydroxylamino-Triazine Ligands. Inorganics 2021, 9, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9100073
Loizou M, Hadjiadamou I, Drouza C, Keramidas AD, Simos YV, Peschos D. Vanadium(V) Complexes with Siderophore Vitamin E-Hydroxylamino-Triazine Ligands. Inorganics. 2021; 9(10):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9100073
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoizou, Maria, Ioanna Hadjiadamou, Chryssoula Drouza, Anastasios D. Keramidas, Yannis V. Simos, and Dimitrios Peschos. 2021. "Vanadium(V) Complexes with Siderophore Vitamin E-Hydroxylamino-Triazine Ligands" Inorganics 9, no. 10: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9100073
APA StyleLoizou, M., Hadjiadamou, I., Drouza, C., Keramidas, A. D., Simos, Y. V., & Peschos, D. (2021). Vanadium(V) Complexes with Siderophore Vitamin E-Hydroxylamino-Triazine Ligands. Inorganics, 9(10), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9100073