Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles: Preparation and Characterization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
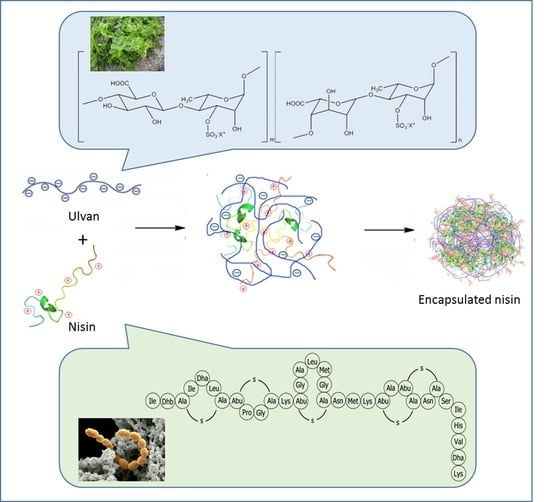
2.2. Preparation of Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles
2.3. Determination of Nisin Encapsulation Efficiency
2.4. FT-IR Spectroscopic Analysis
2.5. Physicochemical Characterization of Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles
2.6. Bacteria Cultures and Growth Conditions
2.7. Analysis of Antimicrobial Activity by Agar Diffusion Assay
2.8. Analysis of the Efficiency of Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles in Carrot Juice
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Physicochemical Characterization of Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Y.; Sarkar, P.; Bhunia, A.K.; Yao, Y. Delivery systems of antimicrobial compounds to food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 57, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Georgescu, C.; Turcus, V.; Olah, N.K.; Mathe, E. An overview of natural antimicrobials role in food. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P.M.; Kuniyoshi, T.M.; Oliveira, R.P.S.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Antimicrobials for food and feed; a bacteriocin perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilchenko, A.S.; Valyshev, A.V. Pore-forming bacteriocins: Structural-functional relationships. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gharsallaoui, A.; Oulahal, N.; Joly, C.; Degraeve, P. Nisin as a food preservative: Part 1: Physicochemical properties, antimicrobial activity, and main uses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bennik, M.H.J.; Verheul, A.; Abee, T.; Naaktgeboren-Stoffels, G.; Gorris, L.G.M.; Smid, E.J. Interaction of nisin and pediocin PA-1 with closely related lactic acid bacteria that manifest over 100-fold differences in bacteriocin sensitivity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3628–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, N.E.; Smid, E.J.; Kok, J.; de Kruijff, B.; Kuipers, O.P.; Breukink, E. Resistance of Gram-positive bacteria to nisin is not determined by Lipid II levels. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 239, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balciunas, E.M.; Martinez, F.A.C.; Todorov, S.D.; De Melo Franco, B.D.G.; Converti, A.; De Souza Oliveira, R.P. Novel biotechnological applications of bacteriocins: A review. Food Control 2013, 32, 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Breukink, E.; van Heusden, H.E.; Vollmerhaus, P.J.; Swiezewska, E.; Brunner, L.; Walker, S.; Heck, A.J.R.; de Kruijff, B. Lipid II is an intrinsic component of the pore induced by nisin in bacterial membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19898–19903. [Google Scholar]
- Hasper, H.E.; de Kruijff, B.; Breukink, E. Assembly and stability of nisin-lipid II pores. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11567–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasper, H.E.; Kramer, N.E.; Smith, J.L.; Hillman, J.D.; Zachariah, C.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Kruijff, B.; Breukink, E. An alternative bactericidal mechanism of action for lantibiotic peptides that target lipid II. Science 2006, 313, 1636–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helander, I.M.; Mattila-Sandholm, T. Permeability barrier of the Gram-negative bacterial outer membrane with special reference to nisin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 60, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diels, A.M.; De Taeye, J.; Michiels, C.V. Sensitisation of Escherichia coli to antibacterial peptides and enzymes by high-pressure homogenization. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 105, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novickij, V.; Zinkeviciene, A.; Staneviciene, R.; Gruskiene, R.; Serviene, E.; Vepstaite-Monstavice, I.; Krivorotova, T.; Lastauskiene, E.; Sereikaite, J.; Girkontaite, I.; et al. Inactivation of Escherichia coli using nanosecond electric fields and nisin nanoparticles: A kinetics study. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, S.; Hammami, R.; Cotter, P.D.; Rebuffat, S.; Said, L.B.; Gaudreau, H.; Bedard, F.; Biron, E.; Drider, D.; Fliss, I. Bacteriocins as a new generation of antimicrobials: Toxicity aspects and regulations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, A.; Delshadi, R.; Jafari, S.M.; Williams, L. Nanoencapsulated nisin: An engineered natural antimicrobial system for the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ahmad, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Spotti, M.J.; Bakry, A.M.; Khan, I.M.; Zhao, L.; Riaz, T.; Tong, Q. Pectin polymers as wall materials for the nano-encapsulation of bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Donsi, F.; McClements, D.J. Protein-based delivery systems for the nanoencapsulation of food ingredients. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 920–936. [Google Scholar]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. Ulvan, a bioactive marine sulphated polysaccharide as a key constituent of hybrid biomaterials: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 355–370. [Google Scholar]
- Kidgell, J.T.; Magnusson, M.; de Nys, R.; Glasson, C.R.K. Ulvan: A systematic review of extraction, composition and function. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101422. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as multifunctional materials in drug delivery applications. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulphated polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.V.; Truong, H.B.; Tran, N.H.V.; Quach, T.M.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Bui, M.L.; Yuguchi, Y.; Thanh, T.T.T. Structure, conformation in aqueous solution and antimicrobial activity of ulvan extracted from green seaweed Ulva reticulata. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.C.; Choi, H.; Kikionis, S.; Seo, J.; Youn, W.; Ioannou, E.; Han, S.Y.; Cho, H.; Roussis, V.; Choi, I.S. Fabrication and characterization of neurocompatible ulvan-based layer-by-layer films. Langmuir 2020, 36, 11610–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Pippa, N.; Georgantea, P.; Ioannou, E.; Demetzos, C.; Roussis, V. Marine sulfated polysaccharides as versatile polyelectrolytes for the development of drug delivery nanoplatforms: Complexation of ulvan with lysozyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.-C.; Joshi, P.; McGuire, J.; Neff, J.A. Nisin adsorption to hydrophobic surfaces coated with the PEO-PPO-PEO triblock surfactant Pluronic ®F108. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M.; Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C. Protein-polysaccharide interaction: Phase-ordering kinetics, thermodynamic and structural aspects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Perez, S. Thermodynamics and chemical characterization of protein-carbohydrate interactions: The multivalency issue. Comptes Rendus Chimie 2011, 14, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotova, T.; Cirkovas, A.; Maciulyte, S.; Staneviciene, R.; Budriene, S.; Serviene, E.; Sereikaite, J. Nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles for food preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, E.A.; Milne, C.F.; Bevis, H.E.; Potter, R.W.; Harris, J.M.; Williams, G.C.; Thomas, L.V.; Delves-Broughton, J. Effective use of nisin to control lactic acid bacterial spoilage in vacuum-packed bologna-type sausage. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Jastimi, R.; Lafleur, M. Structural characterization of free and membrane-bound nisin by infrared spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1324, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maquelin, K.; Kirschner, C.; Choo-Smith, L.-P.; van den Braak, N.; Endtz, H.P.; Naumann, D.; Puppels, G.J. Identification of medically relevant microorganisms by vibrational spectroscopy. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 51, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.; Lahaye, M. Cell-wall polysaccharides from the marine green alga Ulva “rigida” (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Chemical structure of ulvan. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 274, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlstrom, N.; Nylander, F.; Malmhall-Bah, E.; Sjovold, K.; Edlund, U.; Westman, G.; Albers, E. Composition and structure of cell wall ulvans recovered from Ulva spp. along the Swedish coast. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 233, 115852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.C.S.; Juarez, A.C.; Montich, G.G.; Alvarez, R.M.S. Interaction of the antibiotic peptide nisin with anionic membranes in different phase-states: A vibrational study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 212, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vass, E.; Hollosi, M.; Besson, F.; Buchet, R. Vibrational spectroscopic detection of beta- and gamma-turns in synthetic and natural peptides and proteins. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 1917–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacurakova, M.; Capek, P.; Sasinkova, V.; Wellner, N.; Ebringerova, A. FT-IR study of plant cell wall model compounds: Pectic polysaccharides and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 43, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasupo, N.A.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Narbad, A.; Gasson, M.J. Inhibition of Bacillus subtilis and Listeria innocua by nisin in combination with some naturally occurring organic compounds. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Vu, K.D.; Riedl, B.; Lacroix, M. Optimization of the antimicrobial activity of nisin, Na–EDTA and pH against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2015, 61, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotova, T.; Staneviciene, R.; Luksa, J.; Serviene, E.; Sereikaite, J. Impact of pectin esterification on the antimicrobial activity of nisin-loaded pectin particles. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokhrel, P.T.; Toniazzo, T.; Boulet, C.; Oner, M.E.; Sablani, S.S.; Tang, J.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V. Inactivation of Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli in carrot juice by combining high pressure processing, nisin, and mild thermal treatments. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo’o, F.R.C.; Wilar, G.; Devkota, H.P.; Wathoni, N. Ulvan, a polysaccharide from macroalga Ulva sp.: A review of chemistry, biological activities and potential for food and biomedical applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimet, P.; Mombru, A.W.; Faccio, R.; Brugnini, G.; Miraballes, I.; Rufo, C.; Pardo, H. Optimization and characterization of nisin-loaded aliginate-chitosan nanoparticles with antimicrobial activity in lean beef. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 ; 0.1 mg/mL—
; 0.1 mg/mL—  ; 0.2 mg/mL—
; 0.2 mg/mL—  . Final concentration of ulvan in the solution was equal to 0.4 mg/mL. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the mean of the size of particles within the group of each pH value.
. Final concentration of ulvan in the solution was equal to 0.4 mg/mL. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the mean of the size of particles within the group of each pH value.
 ; 0.1 mg/mL—
; 0.1 mg/mL—  ; 0.2 mg/mL—
; 0.2 mg/mL—  . Final concentration of ulvan in the solution was equal to 0.4 mg/mL. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the mean of the size of particles within the group of each pH value.
. Final concentration of ulvan in the solution was equal to 0.4 mg/mL. Different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) in the mean of the size of particles within the group of each pH value.





| The Concentration of Nisin, mg/mL | Encapsulation Efficiency, % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | ||||
| 4.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 7.0 | |
| 0.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 0.2 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 0.3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 0.4 | 98.5 ± 0.1 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 0.5 | 96.2 ± 3.5 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 0.6 | 92.6 ± 0.2 | 86.0 ± 1.3 | 98.2 ± 0.5 | 99.9 ± 0.1 |
| 1.0 | 71.5 ± 3.8 | 75.8 ± 2.4 | 80.7 ± 4.7 | 91.8 ± 8.3 |
| Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Nisin, µg/mL | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-Positive Bacteria | Gram-Negative Bacteria | |||
| B. subtilis | L. innocua | E. coli | K. pneumoniae | |
| Free nisin | 0.012 | 0.781 | 37.5 | 100 |
| Encapsulated nisin | 0.024 | 1.563 | 50 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruskiene, R.; Kavleiskaja, T.; Staneviciene, R.; Kikionis, S.; Ioannou, E.; Serviene, E.; Roussis, V.; Sereikaite, J. Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles: Preparation and Characterization. Foods 2021, 10, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051007
Gruskiene R, Kavleiskaja T, Staneviciene R, Kikionis S, Ioannou E, Serviene E, Roussis V, Sereikaite J. Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles: Preparation and Characterization. Foods. 2021; 10(5):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051007
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruskiene, Ruta, Tatjana Kavleiskaja, Ramune Staneviciene, Stefanos Kikionis, Efstathia Ioannou, Elena Serviene, Vassilios Roussis, and Jolanta Sereikaite. 2021. "Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles: Preparation and Characterization" Foods 10, no. 5: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051007
APA StyleGruskiene, R., Kavleiskaja, T., Staneviciene, R., Kikionis, S., Ioannou, E., Serviene, E., Roussis, V., & Sereikaite, J. (2021). Nisin-Loaded Ulvan Particles: Preparation and Characterization. Foods, 10(5), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051007