Antioxidant and Cryoprotective Effects of Bone Hydrolysates from Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in Freeze-Thawed Fish Fillets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Fish Bone Pretreatment
2.3. Preparation of Fish Bone Hydrolysates
2.4. Determination of Molecular Weight Distribution
2.5. Determination of Antioxidant Activities of Hydrolysates
2.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.3. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5.4. Ferrous Iron’s Chelating Activity
2.6. Fillets Preparation
2.7. Preparation of Myofibrillar Protein
2.8. Determination of Sulfhydryl Groups
2.9. Determination of Protein Carbonyls
2.10. Determination of Ca2+-ATPase Activity
2.11. Determination of Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Substances
2.12. Determination of Drip Loss
2.13. Determination of Textural Properties
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Weight Distribution of Bone Hydrolysates
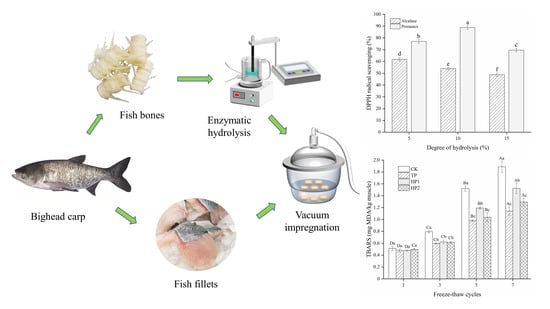
3.2. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Bone Hydrolysates
3.3. Effect of Bone Hydrolysates on Protein Oxidation of Frozen Fish Fillets
3.3.1. Sulfhydryl Content
3.3.2. Carbonyl Content
3.3.3. Ca2+-ATPase Activity
3.4. Effect of Bone Hydrolysates on Lipid Oxidation of Frozen Fish Fillets
3.5. Physical Quality Changes of Frozen Fish Fillets
3.5.1. Drip Loss
3.5.2. Textural Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Shan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Hong, X.; Ye, W. Prevention of protein and lipid oxidation in freeze-thawed bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) fillets using silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fin hydrolysates. LWT 2020, 123, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, B.; Kong, B.; Shi, S.; Xia, X. Decreased gelling properties of protein in mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio) are due to protein aggregation and structure deterioration when subjected to cycles. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasemi, M. Prevention of denaturation of freshwater crayfish muscle subjected to different freeze-thaw cycles by gelatin hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falowo, A.B.; Fayemi, P.O.; Muchenje, V. Natural antioxidants against lipid–protein oxidative deterioration in meat and meat products: A review. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S. Natural Preservatives for Extending the Shelf-Life of Seafood: A Revisit. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Saf. 2018, 17, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zamorano-Apodaca, J.C.; García-Sifuentes, C.O.; Carvajal-Millán, E.; Vallejo-Galland, B.; Scheuren-Acevedo, S.M.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E. Biological and functional properties of peptide fractions obtained from collagen hydrolysate derived from mixed by-products of different fish species. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, A.C.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Alashi, M.A.; Aluko, R.E.; FitzGerald, R.J. Peptide identification in a salmon gelatin hydrolysate with antihypertensive, dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidant activities. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.C.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) with angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory, and antioxidant activities. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Regenstein, J.M.; Noori, F.; Piri Gheshlaghi, S. Autolysis of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) by-products: Enzymatic activities, lipid and protein oxidation, and antioxidant activity of protein hydrolysates. LWT 2021, 140, 110702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez, M.I.; Suárez, M.D.; Alarcón, F.J.; Martínez, T.F. Assessing the Potential of Algae Extracts for Extending the Shelf Life of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Fillets. Foods 2021, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, S.; Hong, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Effects of pomegranate peel extract on quality and microbiota composition of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets during chilled storage. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; He, Y.; Yang, H. Vacuum impregnation of fish gelatin combined with grape seed extract inhibits protein oxidation and degradation of chilled tilapia fillets. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, L.; Cao, A.; Cai, L.; Ji, H.; Liu, S. Effect of vacuum impregnation of red sea bream (Pagrosomus major) with herring AFP combined with CS@Fe3O4 nanoparticles during freeze-thaw cycles. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Wongmaneepratip, W.; He, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, H. Effect of vacuum impregnated fish gelatin and grape seed extract on moisture state, microbiota composition, and quality of chilled seabass fillets. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishery and Fisheries Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas of the People’s Republic of China; National Fisheries Technology Extension Center; China Society of Fisheries. China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abdollahi, M.; Wu, H.; Undeland, I. Impact of Processing Technology on Macro- and Micronutrient Profile of Protein-Enriched Products from Fish Backbones. Foods 2021, 10, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanti, I.; Singh, A.; Benjakul, S.; Sookchoo, P. Textural, Sensory, and Chemical Characteristic of Threadfin Bream (Nemipterus sp.) Surimi Gel Fortified with Bio-Calcium from Bone of Asian Sea Bass (Lates calcarifer). Foods 2021, 10, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsholm, S.; Oterhals, Å.; Underhaug, J.; Aspevik, T. Emulsion and Surface-Active Properties of Fish Solubles Based on Direct Extraction and after Hydrolysis of Atlantic Cod and Atlantic Salmon Backbones. Foods 2021, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisavoey, T.; Sangtanoo, P.; Reamtong, O.; Karnchanatat, A. Free radical scavenging and anti-inflammatory potential of a protein hydrolysate derived from salmon bones on RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5112–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-R.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Chi, C.-F.; Wang, B. Preparation and Characterization of Gelatin and Antioxidant Peptides from Gelatin Hydrolysate of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) Bone Stimulated by in vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tu, D.; Shen, Q.; Dai, Z. Fish Scale Valorization by Hydrothermal Pretreatment Followed by Enzymatic Hydrolysis for Gelatin Hydrolysate Production. Molecules 2019, 24, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Su, G. Practical problems when using ABTS assay to assess the radical-scavenging activity of peptides: Importance of controlling reaction pH and time. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, K.O.; da Costa de Quadros, C.; Rocha, M.d.; Jocelino Gomes de Lacerda, J.T.; Juliano, M.A.; Dias, M.; Mendes, M.A.; Prentice, C. Bioactivity and bioaccessibility of protein hydrolyzates from industrial byproducts of Stripped weakfish (Cynoscion guatucupa). LWT 2019, 111, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Noisa, P.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Chemical and Cellular Antioxidant Activities of In Vitro Digesta of Tilapia Protein and Its Hydrolysates. Foods 2020, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Prevention of protein oxidation and enhancement of gel properties of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi by addition of protein hydrolysates derived from surimi processing by-products. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Changes in chemical interactions and gel properties of heat-induced surimi gels from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) fillets during setting and heating: Effects of different washing solutions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunyaboon, S.; Thumanu, K.; Park, J.W.; Khongla, C.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Evaluation of Lipid Oxidation, Volatile Compounds and Vibrational Spectroscopy of Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) during Ice Storage as Related to the Quality of Its Washed Mince. Foods 2021, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Y. Antioxidant and cryoprotective effects of hydrolysate from gill protein of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) in preventing denaturation of frozen surimi. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S.; Xu, X. Antioxidant and cryoprotective effects of Amur sturgeon skin gelatin hydrolysate in unwashed fish mince. Food Chem. 2015, 181, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, L.Y.; Toh, G.T.; Ismail, A. Application of Proteases for the Production of Bioactive Peptides. In Enzymes in Food Biotechnology; Kuddus, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Wu, X.; Lv, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mi, G.; Li, J. The neuroprotective and antioxidant activities of protein hydrolysates from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3750–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Cryoprotective effect of gelatin hydrolysate from blacktip shark skin on surimi subjected to different freeze-thaw cycles. LWT 2012, 47, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Xia, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, P. Inhibition of frozen storage-induced oxidation and structural changes in myofibril of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) surimi by cryoprotectant and hydrolysed whey protein addition. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S.; Ahmadi Gavlighi, H.; Xu, X.; Regenstein, J.M. Hydrolysates from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) processing by-products: Properties when added to fish mince with different freeze-thaw cycles. Food Biosci. 2019, 30, 100418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.N.; Heinonen, M.; Baron, C.P.; Estévez, M. Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S. Dual cryoprotective strategies for ice-binding and stabilizing of frozen seafood: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Benjakul, S. Potential application of seafood-derived peptides as bifunctional ingredients, antioxidant–cryoprotectant: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ren, L.; Jin, R.; Xue, J.; Yao, H.; Dai, Z. Effect of cryogenic immersion freezing on quality changes of vacuum-packed bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) during frozen storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkelunas, P.J.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Production and assessment of Pacific hake (Merluccius productus) hydrolysates as cryoprotectants for frozen fish mince. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkaczewska, J. Peptides and protein hydrolysates as food preservatives and bioactive components of edible films and coatings—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Texture Parameters | Times | CK | TP | HP1 | HP2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (N) | 1 | 2.92 ± 0.47 Ab | 3.63 ± 0.07 Aa | 3.33 ± 0.18 Aa | 3.27 ± 0.06 Aa |
| 3 | 2.31 ± 0.09 ABc | 3.17 ± 0.13 Ba | 3.12 ± 0.15 ABa | 2.70 ± 0.13 Bb | |
| 5 | 2.08 ± 0.14 Bb | 2.48 ± 0.12 Cab | 2.72 ± 0.21 Ba | 2.66 ± 0.18 Ba | |
| 7 | 1.97 ± 0.06 Ba | 2.28 ± 0.05 Ca | 2.28 ± 0.09 Ba | 2.27 ± 0.11 Cb | |
| Springiness (mm) | 1 | 4.22 ± 0.15 Ac | 4.43 ± 0.16 Ab | 4.84 ± 0.11 Aa | 4.40 ± 0.10 Ab |
| 3 | 2.93 ± 0.08 Bc | 4.63 ± 0.21 Aa | 4.24 ± 0.16 Bab | 4.11 ± 0.14 Ab | |
| 5 | 2.42 ± 0.04 Cc | 3.71 ± 0.15 Bab | 3.80 ± 0.08 Ba | 3.48 ± 0.07 Ab | |
| 7 | 0.63 ± 0.06 Db | 1.21 ± 0.22 Ca | 0.85 ± 0.05 Ca | 0.99 ± 0.08 Ca |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Dai, Z. Antioxidant and Cryoprotective Effects of Bone Hydrolysates from Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in Freeze-Thawed Fish Fillets. Foods 2021, 10, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061409
Zhang Y, Dong Y, Dai Z. Antioxidant and Cryoprotective Effects of Bone Hydrolysates from Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in Freeze-Thawed Fish Fillets. Foods. 2021; 10(6):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061409
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yiqi, Ye Dong, and Zhiyuan Dai. 2021. "Antioxidant and Cryoprotective Effects of Bone Hydrolysates from Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in Freeze-Thawed Fish Fillets" Foods 10, no. 6: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061409
APA StyleZhang, Y., Dong, Y., & Dai, Z. (2021). Antioxidant and Cryoprotective Effects of Bone Hydrolysates from Bighead Carp (Aristichthys nobilis) in Freeze-Thawed Fish Fillets. Foods, 10(6), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061409