The Effects of Hydrocolloids-Protein Mixture as a Fat Replacer on Physicochemical Characteristics of Sugar-Free Muffin Cake: Modeling and Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
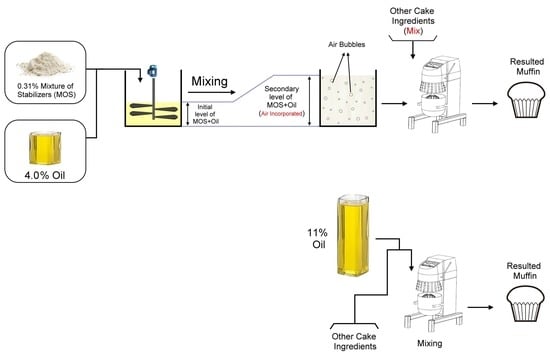
2.2. Emulsion Preparation
2.3. Batter and Cake Preparation
2.4. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Batter Characteristics
2.5.1. Microstructure Analysis of Cakes by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.5.2. Moisture Content
2.5.3. Water Activity
2.5.4. Crumb Texture
2.5.5. Specific Volume
2.5.6. Color
2.5.7. Sensory Analysis
2.5.8. Optimization and Verification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Design and Model Fitting
3.2. Moisture Content
3.3. Water Activity
3.4. Specific Volume
3.5. Hardness
3.6. Springiness
3.7. Cohesiveness
3.8. Color
3.9. Optimization
3.10. Microstructural Characteristics of Cake Crumb
3.11. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vieira, S.A.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Challenges of utilizing healthy fats in foods. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 309S–317S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, W.P. The Science of Bakery Products; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Yao, Y. Carbohydrates as fat replacers. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 331–351. [Google Scholar]
- Godoi, F.C.; Ningtyas, D.W.; Geoffroy, Z.; Prakash, S. Protein-based hydrocolloids: Effect on the particle size distribution, tribo-rheological behaviour and mouthfeel characteristics of low-fat chocolate flavoured milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, S.A.; Masoodi, F.A.; Akhter, R.; Rather, J.A.; Gani, A.; Wani, S.M.; Malik, A.H. Application of guar–xanthan gum mixture as a partial fat replacer in meat emulsions. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2876–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohajdová, Z.; Karovičová, J.; Schmidt, Š. Significance of emulsifiers and hydrocolloids in bakery industry. Acta Chim. Slov. 2009, 2, 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, T.J.; Jaishankar, A.; McKinley, G.H. Describing the firmness, springiness and rubberiness of food gels using fractional calculus. Part I: Theoretical framework. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sandoval, L.; Cofrades, S.; Pérez, C.R.C.; Solas, M.T.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F. Healthier oils stabilized in konjac matrix as fat replacers in n−3 PUFA enriched frankfurters. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S.; Herrero, A.M.; Fernández-Martín, F.; Rodríguez-Salas, L.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Konjac gel fat analogue for use in meat products: Comparison with pork fats. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 26, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M.; Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C. Protein–polysaccharide interactions: Phase-ordering kinetics, thermodynamic and structural aspects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykan, V.; Sezgin, E.; Guzel-Seydim, Z.B. Use of fat replacers in the production of reduced-calorie vanilla ice cream. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Sabapathy, S.N.; Bawa, A.S. Functional and edible uses of soy protein products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Y.H.; Corke, H.; De Leyn, I.; Nip, W.K.; Cross, N.A. (Eds.) Bakery Products: Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Felisberto, M.H.F.; Wahanik, A.L.; Gomes-Ruffi, C.R.; Clerici, M.T.P.S.; Chang, Y.K.; Steel, C.J. Use of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) mucilage gel to reduce fat in pound cakes. LWT 2015, 63, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, S.S.; de las Mercedes Salas-Mellado, M. Addition of chia seed mucilage for reduction of fat content in bread and cakes. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Cervera, S.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Cellulose ether emulsions as fat replacers in muffins: Rheological, thermal and textural properties. LWT 2015, 63, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, S.; Pepke, F.; Rohm, H. Effect of inulin as a fat replacer on texture and sensory properties of muffins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2531–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Sánchez, E.; Llorca, E.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I. Using different fibers to replace fat in sponge cakes: In vitro starch digestion and physico-structural studies. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, R.V.; Garzón, R.; Lannes, S.C.; Rosell, C.M. Use of succinyl chitosan as fat replacer on cake formulations. LWT 2018, 96, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quiles, A.; Llorca, E.; Schmidt, C.; Reißner, A.M.; Struck, S.; Rohm, H.; Hernando, I. Use of berry pomace to replace flour, fat or sugar in cakes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sandoval, E.; Prasca-Sierra, I.; Hernandez, V. Effect of modified cassava starch as a fat replacer on the texture and quality characteristics of muffins. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román, L.; Santos, I.; Martínez, M.M.; Gómez, M. Effect of extruded wheat flour as a fat replacer on batter characteristics and cake quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 8188–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akesowan, A. Influence of konjac flour on foaming properties of milk protein concentrate and quality characteristics of gluten-free cookie. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol 2010, 51, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneuville, S.I.; Paquin, P.; Turgeon, S.L. Formula optimization of a low-fat food system containing whey protein isolate-xanthan gum complexes as fat replacer. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, s513–s519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, M.; Shafafizenoozian, M.; Moghimi, M. Effect of soy protein isolate, guar gum and Ocimum basilicum seed powder as replacers of fat on porosity, color and texture of muffin cake. Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2015, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.N.; Park, S.; Shin, W.S. Textural and sensory characteristics of rice chiffon cake formulated with sugar alcohols instead of sucrose. J. Food Qual. 2014, 37, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmohammadi, E.; Peighambardoust, S.H. New concept in reduced-calorie sponge cake production by xylitol and oligofructose. J. Food Qual. 2016, 39, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronda, F.; Gómez, M.; Blanco, C.A.; Caballero, P.A. Effects of polyols and nondigestible oligosaccharides on the quality of sugar-free sponge cakes. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez Erazo, E.M. Edible Oil Structuring Using Vegetable Protein: Polysaccharide Electrostatic Complexes. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, Brazil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. International Method 10-05, Guidelines for Measurement of Volume by Rapeseed Displacement; St. Atwater, W.O., Benedict, F., Bryant, A., Smith, A., Eds.; Approved method of the American Association of Cereal Chemists; AACC: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, I.; Alamprese, C.; Mariotti, M.; Lucisano, M.; Rossi, M. Optimisation of cake fat quantity and composition using response surface methodology. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, F.; Azmoon, E.; Nouri, M. Effect of thermal processing and mixing time on textural and sensory properties of stick chewing gum. Food Struct. 2019, 22, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of American Association of Cereal Chemists; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Giacomozzi, A.S.; Carrín, M.E.; Palla, C.A. Muffins elaborated with optimized monoglycerides oleogels: From solid fat replacer obtention to product quality evaluation. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobelna, A.; Kalisz, S.; Kieliszek, M. The effect of the addition of blue honeysuckle berry juice to apple juice on the selected quality characteristics, anthocyanin stability, and antioxidant properties. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noorlaila, A.; Hasanah, H.N.; Yusoff, A.; Sarijo, S.H.; Asmeda, R. Effects of xanthan gum and HPMC on physicochemical and microstructure properties of sponge cakes during storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3532–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.E.; Karim, R.; Muhammad, S.K.S.; Bakar, J.A.; Hashim, D.M.; Rahman, R.A. Optimization of the basic formulation of a traditional baked cassava cake using response surface methodology. LWT 2007, 40, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, F.; Despinoy, P.; Ormenese, R.C.S.C.; Faria, E.V. The use of guar and xanthan gums in the production of ‘light’low fat cakes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goranova, Z.; Marudova, M.; Baeva, M. Influence of functional ingredients on starch gelatinization in sponge cake batter. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, R.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Effect of native and gelatinized starches from various sources on sponge cake making characteristics of wheat flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharaie, Z.; Azizi, M.H.; Barzegar, M.; Gavlighi, H.A. Gum tragacanth oil/gels as an alternative to shortening in cookies: Rheological, chemical and textural properties. LWT 2019, 105, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasabi, M.; Naderi, B.; Akbari, M.; Aktar, T.; Kieliszek, M.; Amini, M. Physical, Structural and Sensory Properties of Wafer Batter and Wafer Sheets Influenced by Various Sources of Grains. LWT 2021, 149, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Carrillo, E.; González-Fernández, A.G.; Morales-Garza, S.M.; Treviño-Garza, E.E.; Guajardo-Flores, S.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O.; Sánchez-Hernández, D. Effect of sodium stearoyl-2-lactylate, carboxymethyl cellulose and guar–xanthan gums on muffins enriched with soybean milk powder and amaranth flour. CyTA J. Food 2017, 15, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Dai, S.; Wang, L.; Ni, X.; Yan, W.; Fang, Y.; Corke, H.; Jiang, F. Carboxymethyl modification of konjac glucomannan affects water binding properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Juliano, P. Physical and chemical properties of food powders. In Encapsulated and Powdered Foods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 51–86. [Google Scholar]
- Noorlaila, A.; Hasanah, H.N.; Asmeda, R.; Yusoff, A. The effects of xanthan gum and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose on physical properties of sponge cakes. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2020, 19, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjatoleslami, M.; Azizi, M.H. Impact of tragacanth and xanthan gums on the physical and textural characteristics of gluten-free cake. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pratiwi, A.R.; Ananingsih, V.K. Physicochemical Characteristics of Mocaf Steamed Cake with Beet Root Extract Addition as Natural Colorant. Available online: http://repository.unika.ac.id/22708/ (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Shao, Y.Y.; Lin, K.H.; Chen, Y.H. Batter and product quality of eggless cakes made of different types of flours and gums. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 2959–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| % | Ingredients |
|---|---|
| 29.47 | Flour |
| 17.5 | Water |
| 17 | Xylitol |
| 15 | Whole pasteurized egg |
| 11 | Sunflower oil |
| 5 | Liquid sorbitol |
| 2 | Glycerin |
| 1.3 | Cake gel |
| 1.2 | Baking powder |
| 0.03 | Potassium sorbate |
| 0 | Powder emulsion mixture |
| 0 | Emulsion water |
| 0.3 | Salt |
| 0.2 | Flavorings |
| Independent Variable | Coded Symbols | Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1.41 | −1 | 0 | +1 | +1.41 | ||
| Oil | χ1 | 2.20 | 2.52 | 3.30 | 4.08 | 4.40 |
| MOS | χ2 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.35 |
| Moisture (%) | Water Activity | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Hardness (N) | Springiness | Cohesiveness | L* | a* | b* | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | |
| Sequential model sum of squares (p-values) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Linear | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0664 | 0.059 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| 2FI | 0.9024 | 0.8196 | 0.9041 | 0.566 | 0.425 | 0.5233 | 1 | 0.0391 | 1 | 0.8021 | 1 | 0.9651 | 0.8946 | 0.7143 | 0.5216 | 0.173 | 0.51 | 0.5257 |
| Quadratic | 0.0034 | <0.0001 | 0.9634 | 0.8418 | 0.6591 | 0.5477 | 0.6019 | 0.2283 | 0.0262 | 0.2423 | 0.0003 | 0.0026 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 0.0246 | 0.4296 | 0.0253 | 0.0281 |
| Lack-of-fit Tests (p-values) of significant model | ||||||||||||||||||
| Linear | 0.0414 | 0.0014 | 0.1748 | 0.3748 | 0.1659 | 0.3258 | 0.7707 | 0.0324 | 0.1759 | 0.8544 | 0.0094 | 0.0151 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.0268 | 0.2325 | 0.0201 | 0.0194 |
| 2FI | 0.0312 | 0.001 | 0.1368 | 0.3253 | 0.1503 | 0.2845 | 0.7006 | 0.0624 | 0.1374 | 0.7923 | 0.0069 | 0.0112 | 0.0074 | 0.1197 | 0.0219 | 0.2598 | 0.0165 | 0.0158 |
| Quadratic | 0.3159 | 0.4086 | 0.0688 | 0.1944 | 0.0941 | 0.2095 | 0.5946 | 0.0663 | 0.4589 | 0.9751 | 0.2566 | 0.1366 | 0.0715 | 0.6079 | 0.078 | 0.2146 | 0.058 | 0.0523 |
| X1 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0181 | 0.0027 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.0006 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0047 | 0.0026 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0057 | 0.0057 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| X1X2 | 0.8438 | 0.2677 | 0.9156 | 0.606 | 0.4598 | 0.5434 | 1 | 0.034 | 1 | 0.784 | 1 | 0.9286 | 0.8001 | 0.5456 | 0.3513 | 0.1985 | 0.3404 | 0.3644 |
| X12 | 0.0043 | <0.0001 | 0.9833 | 0.6166 | 0.5241 | 0.378 | 0.5088 | 0.3675 | 0.6548 | 0.7908 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.0036 | 0.0127 | 0.0244 | 0.2277 | 0.0248 | 0.0266 |
| X22 | 0.006 | 0.0116 | 0.7965 | 0.7193 | 0.5883 | 0.61 | 0.4163 | 0.1202 | 0.009 | 0.1038 | 0.109 | 0.0777 | 0.0116 | 0.0167 | 0.0357 | 0.5845 | 0.0371 | 0.0414 |
| Predictive parameter of significant model | ||||||||||||||||||
| R2 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.882 | 0.844 | 0.984 | 0.983 | 0.996 | 0.983 | 0.995 | 0.987 | 0.941 | 0.92 | 0.998 | 0.995 | 0.99 | 0.945 | 0.989 | 0.989 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.998 | 0.994 | 0.757 | 0.812 | 0.979 | 0.977 | 0.995 | 0.977 | 0.991 | 0.985 | 0.899 | 0.863 | 0.996 | 0.991 | 0.982 | 0.934 | 0.981 | 0.981 |
| Predicted R2 | 0.995 | 0.985 | 0.596 | 0.71 | 0.966 | 0.967 | 0.994 | 0.941 | 0.98 | 0.982 | 0.713 | 0.559 | 0.987 | 0.982 | 0.939 | 0.898 | 0.934 | 0.931 |
| Treatments | MOS %: Oil %: Water % | Crumb Moisture (%) | Crumb Water Activity | Specific Volume (cm3/g) | Hardness (N) | Springiness | Cohesiveness | L* crumb | a* crumb | b* crumb | ΔE* crumb | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | ||
| Blank | 0:11:00 | 25.71 | 23.33 | 0.811 | 0.78 | 2.66 | 2.47 | 13.59 | 17.28 | 0.711 | 0.487 | 0.315 | 0.165 | 83.27 | 80.65 | 5.32 | 5.51 | 40.91 | 42.01 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0.13:2.52:8.35 | 25.79 | 20.27 | 0.835 | 0.821 | 2.39 | 2.31 | 15.34 | 19.44 | 0.482 | 0.339 | 0.584 | 0.437 | 84.65 | 82.75 | 4.11 | 4.23 | 31.59 | 32.24 | 9.5 | 10.07 |
| 2 | 0.13:4.08:6.79 | 23.88 | 19.37 | 0.788 | 0.77 | 2.56 | 2.48 | 14.36 | 17.95 | 0.522 | 0.391 | 0.456 | 0.302 | 88.19 | 86.94 | 2.15 | 2.19 | 20.72 | 21.12 | 21.02 | 22.07 |
| 3 | 0.31:2.52:8.17 | 25.22 | 21.98 | 0.832 | 0.811 | 2.59 | 2.51 | 14.55 | 18.35 | 0.703 | 0.555 | 0.414 | 0.271 | 85.32 | 83.57 | 4.19 | 4.3 | 32.24 | 32.78 | 8.98 | 9.76 |
| 4 | 0.31:4.08:6.61 | 23.71 | 20.5 | 0.746 | 0.728 | 2.73 | 2.65 | 13.57 | 17.29 | 0.746 | 0.601 | 0.311 | 0.169 | 89.04 | 88.12 | 2.34 | 2.37 | 23.99 | 24.29 | 18.12 | 19.48 |
| 5 | 0.22:2.20:8.58 | 25.99 | 21.14 | 0.847 | 0.828 | 2.44 | 2.37 | 15.22 | 19.13 | 0.563 | 0.432 | 0.508 | 0.349 | 85.16 | 83.29 | 4.31 | 4.42 | 33.16 | 33.7 | 8.04 | 8.79 |
| 6 | 0.22:4.40:6.38 | 23.42 | 20.03 | 0.765 | 0.749 | 2.66 | 2.58 | 13.75 | 17.61 | 0.621 | 0.495 | 0.405 | 0.252 | 88.55 | 87.23 | 2.22 | 2.25 | 23.17 | 23.48 | 18.77 | 19.93 |
| 7 | 0.09:3.30:7.61 | 25.04 | 19.65 | 0.849 | 0.825 | 2.39 | 2.31 | 15.06 | 18.89 | 0.456 | 0.321 | 0.594 | 0.451 | 85.62 | 83.02 | 3.98 | 4.04 | 30.61 | 30.8 | 10.65 | 11.55 |
| 8 | 0.35:3.30:7.35 | 24.67 | 21.5 | 0.801 | 0.785 | 2.68 | 2.6 | 13.9 | 17.75 | 0.77 | 0.632 | 0.352 | 0.211 | 87.91 | 86.54 | 3.84 | 4.01 | 29.53 | 30.57 | 12.38 | 12.95 |
| 9 | 0.22:3.30:7.48 | 24.91 | 20.53 | 0.827 | 0.811 | 2.57 | 2.49 | 14.46 | 18.35 | 0.594 | 0.463 | 0.459 | 0.316 | 86.54 | 86.55 | 3.92 | 3.99 | 30.17 | 30.51 | 11.31 | 13.01 |
| 10 | 0.22:3.30:7.48 | 24.88 | 20.49 | 0.828 | 0.812 | 2.55 | 2.48 | 14.45 | 18.33 | 0.603 | 0.473 | 0.463 | 0.32 | 86.51 | 86.65 | 3.95 | 4.02 | 30.39 | 30.69 | 11.09 | 12.9 |
| 11 | 0.22:3.30:7.48 | 24.87 | 20.48 | 0.827 | 0.81 | 2.55 | 2.47 | 14.52 | 18.45 | 0.585 | 0.459 | 0.458 | 0.305 | 86.54 | 86.75 | 3.97 | 4.03 | 30.51 | 30.72 | 10.99 | 12.92 |
| 12 | 0.22:3.30:7.48 | 24.88 | 20.49 | 0.828 | 0.811 | 2.54 | 2.46 | 14.48 | 18.39 | 0.598 | 0.462 | 0.454 | 0.312 | 86.53 | 86.46 | 3.96 | 4.03 | 30.46 | 30.74 | 11.03 | 12.77 |
| 13 | 0.22:3.30:7.48 | 24.84 | 20.41 | 0.825 | 0.81 | 2.54 | 2.47 | 14.55 | 18.41 | 0.608 | 0.473 | 0.457 | 0.319 | 86.44 | 86.55 | 3.89 | 4.06 | 30.04 | 30.79 | 11.41 | 12.76 |
| Parameter | Aim | Day-1 | Day-15 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lowest Quantity | Highest Quantity | Predicted Quantity | Obtained Quantity | Control Sample | Lowest Quantity | Highest Quantity | Predicted Quantity | Obtained Quantity | Control Sample | ||
| Moisture (%) | In range | 23.42 | 25.99 | 25.22 | 25.92 | 25.71 | 19.37 | 21.50 | 21.38 | 22.21 | 22.33 |
| aw | Min. | 0.746 | 0.849 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.791 | 0.809 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.78 |
| Specific volume | Max. | 1.90 | 2.15 | 2.06 | 2.11 | 2.21 | 1.85 | 2.20 | 2.01 | 2.09 | 2.17 |
| L* | In range | 83.45 | 90.52 | 87.88 | 88.53 | 88.10 | 81.75 | 88.79 | 86.07 | 87.14 | 87.43 |
| a* | In range | 2.15 | 3.41 | 3.03 | 3.06 | 3.08 | 2.25 | 3.48 | 3.15 | 3.19 | 3.13 |
| b* | In range | 25.73 | 40.91 | 36.34 | 35.29 | 34.98 | 25.77 | 40.95 | 36.37 | 36.97 | 36.34 |
| Hardness | Min. | 13.57 | 15.34 | 13.57 | 13.21 | 13.59 | 17.29 | 19.44 | 17.40 | 17.95 | 17.28 |
| Springiness | In range | 0.45 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.321 | 0.632 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.478 |
| Cohesiveness | In range | 0.38 | 0.66 | 0.57 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.218 | 0.432 | 0.39 | 0.37 | 0.35 |
| Image Processing Parameters | Muffin Cakes | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Optimized | |
| Porosity | 0.524 a | 0.539 a |
| Energy | 0.00048 ± 0.00003 a | 0.00044 ± 0.00004 a |
| Contrast | 1729 ± 62 a | 1699 ± 56 a |
| Homogeneity | 0.242 ± 0.01 a | 0.132 ± 0.012 a |
| Entropy | 12.451 ± 0.7 a | 14.842 ± 0.4 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azmoon, E.; Saberi, F.; Kouhsari, F.; Akbari, M.; Kieliszek, M.; Vakilinezam, A. The Effects of Hydrocolloids-Protein Mixture as a Fat Replacer on Physicochemical Characteristics of Sugar-Free Muffin Cake: Modeling and Optimization. Foods 2021, 10, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071549
Azmoon E, Saberi F, Kouhsari F, Akbari M, Kieliszek M, Vakilinezam A. The Effects of Hydrocolloids-Protein Mixture as a Fat Replacer on Physicochemical Characteristics of Sugar-Free Muffin Cake: Modeling and Optimization. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071549
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzmoon, Elahe, Farzad Saberi, Fatemeh Kouhsari, Mehdi Akbari, Marek Kieliszek, and Amir Vakilinezam. 2021. "The Effects of Hydrocolloids-Protein Mixture as a Fat Replacer on Physicochemical Characteristics of Sugar-Free Muffin Cake: Modeling and Optimization" Foods 10, no. 7: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071549
APA StyleAzmoon, E., Saberi, F., Kouhsari, F., Akbari, M., Kieliszek, M., & Vakilinezam, A. (2021). The Effects of Hydrocolloids-Protein Mixture as a Fat Replacer on Physicochemical Characteristics of Sugar-Free Muffin Cake: Modeling and Optimization. Foods, 10(7), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071549