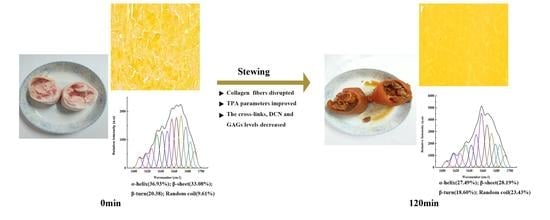
The Texture Change of Chinese Traditional Pig Trotter with Soy Sauce during Stewing Processing: Based on a Thermal Degradation Model of Collagen Fibers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedures for Pig Trotter Stewed with Soy Sauce
2.2. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) Measurements
2.3. Histochemical Morphology
2.4. Raman Spectroscopy
2.5. Determination of Cross-Links Degree and GAGs Content
2.6. Determination DCN Content
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Stewing Time on the TPA Parameters
3.2. The Influence of Stewing Time on the Ultra Structure of Subcutaneous Fat
3.3. The Influence of Stewing Time on the Ultra Structure of Collagen Fibers
3.4. The Influence of Stewing Time on the Secondary Structure of Collagen Proteins
3.5. The Influence of Stewing Time on Cross-Links, DCN and GAGs Levels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.C.; Chien, J.T.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Formation and inhibition of cholesterol oxidation products during marinating of pig feet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Hwang, S.A.; Lee, J.W. Sensory property improvement of jokbal (korean pettitoes) made from frozen pig feet by addition of herbal mixture. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2016, 36, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, H.J.; Na, Y.J.; Cho, J.I.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, K.S. Effects of temperature and packaging on the growth kinetics of clostridium perfringens in ready-to-eat jokbal (pig’s trotters). Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, W.L.; Lin, S.J.; Jee, S.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Lin, L.C.; So, P.T.C.; Dong, C.Y. Investigating mechanisms of collagen thermal denaturation by high resolution second-harmonic generation imaging. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2620–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asserin, J.; Lati, E.; Shioya, T.; Prawitt, J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: Evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, H.H.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L. Influence of stewing time on the texture, ultrastructure and in vitro digestibility of meat from the yellow-feathered chicken breed. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Li, C.B.; Zhao, F.; Lin, X.S.; Bai, Y.; Zhou, G.H. The effects of long-duration stewing combined with different cooking and heating methods on the quality of pork belly. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2016, 40, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, Q.N.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.M.; Dai, R.T. Changes in shear parameters, protein degradation and ultrastructure of pork following water bath and ohmic cooking. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Huang, M.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Influence of heat on protein degradation, ultrastructure and eating quality indicators of pork. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Wang, Q.A.; Xu, X.L.; Li, C.B.; Huang, M.; Zhou, G.H.; Dai, Y. Effect of heat-induced changes of connective tissue and collagen on meat texture properties of beef semitendinosus muscle. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcelikkale, A.; Han, B. Thermal destabilization of collagen matrix hierarchical structure by freeze/thaw. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, N.T.; Humphrey, J.D. Denaturation of collagen via heating: An irreversible rate process. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 4, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.; Gor, J.; Perkins, S.J.; Ishikawa, Y.; Bachinger, H.P.; Hohenester, E. The concave face of decorin mediates reversible dimerization and collagen binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35526–35533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pins, G.D.; Christiansen, D.L.; Patel, R.; Silver, F.H. Self-assembly of collagen fibers. Influence of fibrillar alignment and decorin on mechanical properties. Biophys. J. 1997, 73, 2164–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietrucha, K.; Marzec, E. Dielectric properties of the collagen–glycosaminoglycans scaffolds in the temperature range of thermal decomposition. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 118, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, J.M.; David, A. Effects of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycan on the in vitro assembly and thermal stability of collagen fibrils. Biopolymers 2010, 19, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.J.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Li, C.B. Influence of weak organic acids and sodium chloride marination on characteristics of connective tissue collagen and textural properties of beef semitendinosus muscle. J. Texture Stud. 2010, 41, 279–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, M.D.; Santaella, M.; Martinez, C.; Periago, M.J.; Blanco, A.; Vazquez, J.M.; Albors, O.L. Muscle tissue structure and flesh texture in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata L., fillets preserved by refrigeration and by vacuum packaging. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurniak, C.B.; Chevessier, F.; Jokwitz, M.; Jonsson, F.; Perlas, E.; Richter, H.; Matern, G.; Boyl, P.P.; Chaponnier, C.; Furst, D.; et al. Severe protein aggregate myopathy in a knockout mouse model points to an essential role of cofilin2 in sarcomeric actin exchange and muscle maintenance. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 93, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitha, B.; Donoghue, M. Clinical and histopathological evaluation of collagen fiber orientation in patients with oral submucous fibrosis. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Pathol. 2011, 15, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alix, A.J.P.; Pedanou, G.; Berjot, M. Fast determination of the quantitative secondary structure of proteins by using some parameters of the raman amide I-Band. J. Mol. Struct. 1988, 174, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.J.; Sun, Y.Y.; Pan, D.D.; Wang, Y.; Ou, C.R.; Cao, J.X. The effect of structural change on the digestibility of sarcoplasmic proteins in Nanjing dry-cured duck during processing. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 4450–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubost, A.; Micol, D.; Meunier, B.; Lethias, C.; Listrat, A. Relationships between structural characteristics of bovine intramuscular connective tissue assessed by image analysis and collagen and proteoglycan content. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Li, J.K.; Guo, X.Y.; Cui, B.W.; Peng, Z.Q. Contribution of cross-links and proteoglycans in intramuscular connective tissue to shear force in bovine muscle with different marbling levels and maturities. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G.J.; Purslow, P.P. The strength and stiffness of perimysial connective-tissue isolated from cooked beef muscle. Meat Sci. 1989, 26, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, K.; Hatakeyama, E.; Sasaki, T.; Dan, H.; Azuma, T.; Karita, K. Effects of sample hardness on human chewing force: A model study using silicone rubber. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004, 49, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhou, C.; He, J.; Cao, J. Effect of cooking temperature on texture and flavour binding of braised sauce porcine skin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandemer, G. Lipids in muscles and adipose tissues, changes during processing and sensory properties of meat products. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.B.; Thomsen, S.; Jones, M.A.; Baek, S.; Humphrey, J.D. Histological evidence for the role of mechanical stress in modulating thermal denaturation of collagen. Biomech. Modeling Mechanobiol. 2005, 4, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Calderon-Colon, X.; Trexler, M.; Elisseeff, J.; Guo, Q.Y. Thermal denaturation of type I collagen vitrified gels. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 527, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechsle, A.M.; Landenberger, M.; Gibis, M.; Irmscher, S.B.; Kohlus, R.; Weiss, J. Modulation of collagen by addition of hofmeister salts. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Farrell, H.M.; Wildermuth, R.J. Influence of neutral salts on the hydrothermal stability of acid-soluble collagen. J. Protein Chem. 2000, 19, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersen, K.A.; Afseth, N.K.; Bocker, U.; Dankel, K.R.; Rønningen, M.A.; Lislelid, A.; Ofstad, R.; Lindberg, D.; Wubshet, S.G. Post-enzymatic hydrolysis heat treatment as an essential unit operation for collagen solubilization from poultry by-products. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, T.H.; Hunt, M.C.; Dikeman, M.E. Enzymatic assay to determine collagen thermal denaturation and solubilization. Meat Sci. 2000, 54, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, N.C.; Bevilacqua, A.E.; Zaritzky, N.E. Heat-Treatment Effect on texture changes and thermal-denaturation of proteins in beef muscle. J. Food Process. Preserv. 1994, 18, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, M.D.; Abad, M.; Ruiz-Cara, T.; Estrada, J.D.; Garcia-Gallego, M. Changes in muscle collagen content during post mortem storage of farmed sea bream (Sparus aurata): Influence on textural properties. Aquac. Int. 2005, 13, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chang, S.W.; Rodriguez-Florez, N.; Buehler, M.J.; Shefelbine, S.; Dao, M.; Zeng, K. Studies of chain substitution caused sub-fibril level differences in stiffness and ultrastructure of wildtype and oim/oim collagen fibers using multifrequency-AFM and molecular modeling. Biomaterials 2016, 107, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.X.; Zhou, C.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.Y.; Pan, D.D. The effect of oxidation on the structure of G-actin and its binding ability with aroma compounds in carp grass skeletal muscle. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamov, D.R.; Pompe, T. Structure and function of ECM-inspired composite collagen type I scaffolds. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10200–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, D.; Kabla, A.; Weitz, D.; Mahadevan, L. Strain-induced alignment in collagen gels. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamov, D.; Grimmer, M.; Salchert, K.; Pompe, T.; Werner, C. Heparin intercalation into reconstituted collagen I fibrils: Impact on growth kinetics and morphology. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, V.; Paderi, J.E.; Akkus, A.; Smith, K.M.; Balachandran, D.; Beaudoin, S.; Panitch, A.; Akkus, O. Incorporation of a decorin biomimetic enhances the mechanical properties of electrochemically aligned collagen threads. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 2428–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalamajski, S.; Oldberg, A. The role of small leucine-rich proteoglycans in collagen fibrillogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Pan, D.; Wang, H.; Zhou, G.; Cao, J. The comparative research of structural and textural characteristics of six kinds of collagen-based sauce braised meat products. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Secondary Structure (%) | Stewing Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | |
| α-helix | 36.9 ± 0.6 a | 35.1 ± 0.9 a | 30.0 ± 1.2 b | 27.5 ± 0.8 b |
| β-sheet | 33.1 ± 0.6 a | 24.8 ± 0.7 c | 21.1 ± 0.7 d | 28.2 ± 1.1 b |
| β-turn | 20.4 ± 1.0 b | 26.1 ± 2.0 a | 25.5 ± 1.1 a | 18.6 ± 1.2 b |
| Random coil | 9.6 ± 0.5 c | 14.0 ± 1.6 b | 23.3 ± 0.9 a | 23.4 ± 1.0 a |
| Indicators | Stewing Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 min | 30 min | 60 min | 120 min | |
| Cross-links (μmol/g collagen) | 56.8 ± 1.5 a | 36.2 ± 3.0 b | 16.5 ± 1.7 c | 13.9 ± 0.4 c |
| Decorin (μg/g collagen) | 31.98 ± 0.70 a | 28.10 ± 0.61 b | 9.33 ± 0.12 c | 5.65 ± 0.10 d |
| GAGs (mg/g collagen) | 5.10 ± 0.08 a | 3.63 ± 0.01 b | 1.51 ± 0.01 c | 1.05 ± 0.02 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, G.; Duan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J. The Texture Change of Chinese Traditional Pig Trotter with Soy Sauce during Stewing Processing: Based on a Thermal Degradation Model of Collagen Fibers. Foods 2022, 11, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121772
Lin Y, Wang Y, Jin G, Duan J, Zhang Y, Cao J. The Texture Change of Chinese Traditional Pig Trotter with Soy Sauce during Stewing Processing: Based on a Thermal Degradation Model of Collagen Fibers. Foods. 2022; 11(12):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121772
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yuhai, Ying Wang, Guofeng Jin, Junjie Duan, Yuemei Zhang, and Jinxuan Cao. 2022. "The Texture Change of Chinese Traditional Pig Trotter with Soy Sauce during Stewing Processing: Based on a Thermal Degradation Model of Collagen Fibers" Foods 11, no. 12: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121772
APA StyleLin, Y., Wang, Y., Jin, G., Duan, J., Zhang, Y., & Cao, J. (2022). The Texture Change of Chinese Traditional Pig Trotter with Soy Sauce during Stewing Processing: Based on a Thermal Degradation Model of Collagen Fibers. Foods, 11(12), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11121772