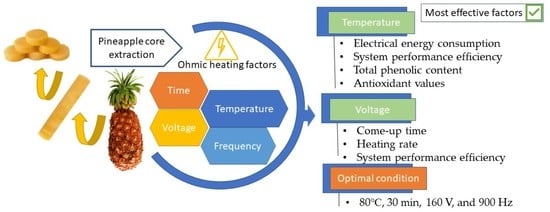
Ohmic Heating Extraction at Different Times, Temperatures, Voltages, and Frequencies: A New Energy-Saving Technique for Pineapple Core Valorization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Ohmic System and Extraction Method
2.4. Engineering Parameters
2.4.1. Come-Up Time, Heating Rate, and EF
2.4.2. Electrical Energy Consumption (EEC)
2.4.3. System Performance Efficiency (SPE)
2.5. Chemical Assessment of Extracts
2.5.1. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.5.2. DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) Assay
2.5.3. ABTS (2,20-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid)) Assay
2.6. Taguchi Method
2.6.1. Treatments in the Study Design
2.6.2. Analyzing the Effects of the Processing Parameters and Optimal Conditions
2.7. Identification by UPLC-Q-Exactive Plus Orbitrap MS/MS Analysis
2.7.1. Liquid Chromatography
2.7.2. Mass Spectrometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Come-Up Time, Heating Rate, and Electrical Parameters
3.2. Energy Consumption during Extraction
3.3. System Performance Efficiency
3.4. Extraction Yield of TPC
3.5. Radical Scavenging Assays
3.6. Comparison between the Conventional System and Ohmic Heating at Optimal Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hikal, W.M.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Said-Al Ahl, H.A.; Bratovcic, A.; Tkachenko, K.G.; Kačániová, M.; Rodriguez, R.M. Pineapple (Ananas comosus L. Merr.), Waste Streams, Characterisation and Valorisation: An Overview. Open J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 610–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Kuan, C.S.; Roan, S.F.; Lee, C.L.; Chang, J.W.; Chen, I.Z. A new pineapple cultivar, Tainung No. 23, with improved fruit quality in summer. HortScience 2019, 54, 2262–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.A.; Ribeiro, T.B.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pastrana, L.; Pintado, M.M. Integral valorization of pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) by-products through a green chemistry approach towards added value ingredients. Foods 2020, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasheed, A.; Cobham, E.; Zeighmami, M.; Ong, S. Extraction of phenolic compounds from pineapple fruit. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Processing & Drying of Foods, Fruits & Vegetables, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 18–19 June 2012; pp. 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, P.; Ragaee, S.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M. Effect of incorporation of goji berry by-product on biochemical, physical and sensory properties of selected bakery products. LWT 2019, 112, 108225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Ocampo, E.; Torrejón-Valqui, L.; Muñóz-Astecker, L.D.; Medina-Mendoza, M.; Mori-Mestanza, D.; Castro-Alayo, E.M. Antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content and phenolic compounds of pulp and bagasse of four Peruvian berries. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hilphy, A.R.; Al-Musafer, A.M.; Gavahian, M. Pilot-scale ohmic heating-assisted extraction of wheat bran bioactive compounds: Effects of the extract on corn oil stability. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavahian, M.; Chu, Y.H.; Sastry, S. Extraction from food and natural products by moderate electric field: Mechanisms, benefits, and potential industrial applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, R.N.; Coelho, M.I.; Genisheva, Z.; Fernandes, J.M.; Vicente, A.A.; Pintado, M.E.; Texixeira, J.A. Using ohmic heating effect on grape skins as a pretreatment for anthocyanins extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 124, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, N.P.; Rodrigues, R.M.; Genisheva, Z.; Oliveira, H.; Freitas, V.D.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. Effects of ohmic heating on extraction of food-grade phytochemicals from colored potato. LWT 2016, 74, 493–503. [Google Scholar]
- Torgbo, S.; Sukatta, U.; Kamonpatana, P.; Sukyai, P. Ohmic heating extraction and characterization of rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum L.) peel extract with enhanced antioxidant and antifungal activity as a bioactive and functional ingredient in white bread preparation. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.; Pereira, R.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pintado, M.E. Extraction of tomato by-products’ bioactive compounds using ohmic technology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 117, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jesus, M.S.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Pereira, R.N.; Genisheva, Z.; Carvalho, A.C.; Pereira-Wilson, C.; Teixeiraa, J.A.; Domingues, L. Ohmic heating polyphenolic extracts from vine pruning residue with enhanced biological activity. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gavahian, M.; Chu, R. Design, development, and performance evaluation of an ohmic extractor to valorize fruit by-products based on Taguchi method: Reduced energy consumption and enhanced total phenolics. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 45, e13825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llave, Y.; Udo, T.; Fukuoka, M.; Sakai, N. Ohmic heating of beef at 20 kHz and analysis of electrical conductivity at low and high frequencies. J. Food Eng. 2018, 228, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Rocha, R.S.; Guimarães, J.T.; Balthazar, C.F.; Pimentel, T.C.; Neto, R.P.C.; Tavares, M.I.B.; Esmerino, E.A.; Duarte, M.C.K.; Freitas, M.Q.; et al. Advantages of using ohmic heating in Dulce de Leche manufacturing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 65, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.J.; Park, S.H. Evaluation of energy efficacy and texture of ohmically cooked noodles. J. Food Eng. 2019, 248, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Santos, P.; Genisheva, Z.; Pereira, R.N.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rocha, C.M.R. Moderate electric fields as a potential tool for sustainable recovery of phenolic compounds from Pinus pinaster bark. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8816–8826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sridhar, K.; Charles, A.L. In vitro antioxidant activity of Kyoho grape extracts in DPPH and ABTS assays: Estimation methods for EC50 using advanced statistical programs. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.L.; Liaw, E.T.; Gavahian, M.; Chen, H.H. Development and optimization of djulis sourdough bread using taguchi grey relational analysis. Foods 2020, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.B.; Reddy, A.C. Optimization of tensile strength in TIG welding using the Taguchi method and analysis of variance (ANOVA). Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 8, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steingass, C.B.; Glock, M.P.; Schweiggert, R.M.; Carle, R. Studies into the phenolic patterns of different tissues of pineapple (Ananas comosus [L.] Merr.) infructescence by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn and GC-MS analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6463–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, N.K.; Lai, Q.D.; Le, T.K.P.; Le, N.T. Influences of AC frequency and electric field strength on changes in bioactive compounds in ohmic heating of pomelo juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 72, 102754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Jung, A.H.; Park, S.H. Efficacy of ohmic vacuum concentration for orange juice concentrates and their physicochemical properties under different voltage gradients. LWT 2022, 154, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.F.; Giordani, D.; Gurak, P.D.; Cladera-Olivera, F.; Marczak, L.D.F. Extraction of pectin from passion fruit peel using moderate electric field and conventional heating extraction methods. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkanan, Z.T.; Altemimi, A.B.; Al-Hilphy, A.R.; Watson, D.G.; Pratap-Singh, A. Ohmic heating in the food industry: Developments in concepts and applications during 2013–2020. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hilphy, A.R.; AlRikabi, A.K.; Al-Salim, A.M. Extraction of phenolic compounds from wheat bran using ohmic heating. Int. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2015, 43, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, R.P.; Cappato, L.P.; Guimarães, J.T.; Rocha, R.S.; Silva, R.; Balthazar, C.F.; Freitas, M.Q.; Silva, P.H.F.; Neto, R.P.C.; Tavares, M.I.B. Ohmic heating for infant formula processing: Evaluating the effect of different voltage gradient. J. Food Eng. 2020, 280, 109989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poojitha, P.; Athmaselvi, K. Influence of sucrose concentration on electric conductivity of banana pulp during ohmic heating. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishita, C.; Athmaselvi, K.A. Changes in pH and colour of watermelon juice during ohmic heating. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 741. [Google Scholar]
- Darvishi, H.; Khostaghaza, M.H.; Najafi, G. Ohmic heating of pomegranate juice: Electrical conductivity and pH change. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2013, 12, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darvishi, H.; Salami, P.; Fadavi, A.; Saba, M.K. Processing kinetics, quality and thermodynamic evaluation of mulberry juice concentration process using ohmic heating. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadavi, A.; Yousefi, S.; Darvishi, H.; Mirsaeedghazi, H. Comparative study of ohmic vacuum, ohmic, and conventional-vacuum heating methods on the quality of tomato concentrate. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 47, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Hosainpour, A.; Nargesi, F.; Fadavi, A. Exergy and energy analyses of liquid food in an ohmic heating process: A case study of tomato production. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.R.; Mercali, G.D.; Tessaro, I.C.; Marczak, L.D.F. Evaluation of key parameters during construction and operation of an ohmic heating apparatus. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 18, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icier, F.; Ilicali, C. Temperature dependent electrical conductivities of fruit purees during ohmic heating. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabas, B.M.; Icier, F. Ohmic heating–assisted extraction of natural color matters from red beetroot. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 2062–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Hosainpour, A.; Nargesi, F. Ohmic heating behaviour and electrical conductivity of tomato paste. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, I.K.; Ha, J.W.; Kang, D.H. Investigation of optimum ohmic heating conditions for inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes in apple juice. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, S.; Saini, C.S.; Kumar, M.; Sharma, H.K. Effect of thermal and alternate thermal processing on bottle gourd (Lagenaria siceraria) juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Mohammadi, P.; Fadavi, A.; Saba, M.K.; Behroozi-Khazaei, N. Quality preservation of orange concentrate by using hybrid ohmic–vacuum heating. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makroo, H.A.; Srivastava, B.; Jabeen, A. Influence of mild electric field (MEF) on polyphenol oxidase and quality attributes of pineapple juice during ohmic heating. LWT 2022, 156, 113021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochier, B.; Mercali, G.D.; Marczak, L.D.F. Effect of ohmic heating parameters on peroxidase inactivation, phenolic compounds degradation and color changes of sugarcane juice. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 111, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappato, L.P.; Ferreira, M.V.S.; Pires, R.P.S.; Cavalcanti, R.N.; Bisaggio, R.C.; Freitas, M.Q.; Silva, M.C.; Cruz, A.G. Whey acerola-flavoured drink submitted ohmic heating processing: Is there an optimal combination of the operational parameters? Food Chem. 2018, 245, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappato, L.P.; Ferreira, M.V.S.; Moraes, J.; Pires, R.P.S.; Rocha, R.S.; Silva, R.; Neto, R.P.C.; Tavares, M.I.B.; Freitas, M.Q.; Rodrigues, F.N. Whey acerola-flavoured drink submitted ohmic heating: Bioactive compounds, antioxidant capacity, thermal behavior, water mobility, fatty acid profile and volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, H.; Koushesh Saba, M.; Behroozi-Khazaei, N.; Nourbakhsh, H. Improving quality and quantity attributes of grape juice concentrate (molasses) using ohmic heating. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helvacıoğlu, S.; Charehsaz, M.; Güzelmeriç, E.; Acar, E.T.; Yeşilada, E.; Aydın, A. Comparatively investigation of grape molasses produced by conventional and industrial techniques. Marmara Pharm. J. 2018, 22, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ryu, S.; Kang, D.H. Effect of frequency and waveform on inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in salsa by ohmic heating. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mhatre, M.; Tilak-Jain, J.; De, S.; Devasagayam, T.P.A. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of non-transformed and transformed pineapple: A comparative study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 2696–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, G.; Vollmer, K.; Caponio, F.; Pasqualone, A.; Carle, R.; Steingass, C.B. Characterisation and classification of pineapple (Ananas comosus [L.] Merr.) juice from pulp and peel. Food Control 2019, 96, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandrić, Z.; Roberts, D.; Rathor, M.; Abrahim, A.; Islam, M.; Cannavan, A. Assessment of fruit juice authenticity using UPLC–QToF MS: A metabolomics approach. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingass, C.B.; Jutzi, M.; Müller, J.; Carle, R.; Schmarr, H.-G. Ripening-dependent metabolic changes in the volatiles of pineapple (Ananas comosus (L.) Merr.) fruit: II. Multivariate statistical profiling of pineapple aroma compounds based on comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2609–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Group * | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Voltage (V) | Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 70 | 15 | 110 | 60 |
| C2 | 70 | 30 | 160 | 340 |
| C3 | 70 | 45 | 210 | 620 |
| C4 | 70 | 60 | 260 | 900 |
| C5 | 80 | 15 | 160 | 620 |
| C6 | 80 | 30 | 110 | 900 |
| C7 | 80 | 45 | 260 | 60 |
| C8 | 80 | 60 | 210 | 340 |
| C9 | 90 | 15 | 210 | 900 |
| C10 | 90 | 30 | 260 | 620 |
| C11 | 90 | 45 | 110 | 340 |
| C12 | 90 | 60 | 160 | 60 |
| C13 | 100 | 15 | 260 | 340 |
| C14 | 100 | 30 | 210 | 60 |
| C15 | 100 | 45 | 160 | 900 |
| C16 | 100 | 60 | 110 | 620 |
| Group | EFS * (V/cm) | Current (A) | Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 12.22 ± 0.00 d | 1.63 ± 0.00 j | 0.18 ± 0.00 g |
| C2 | 17.78 ± 0.00 c | 2.68 ± 0.12 gh | 0.43 ± 0.02 f |
| C3 | 23.33 ± 0.00 b | 3.60 ± 0.29 de | 0.76 ± 0.06 d |
| C4 | 28.89 ± 0.00 a | 3.86 ± 0.99 cde | 1.01 ± 0.27 c |
| C5 | 17.78 ± 0.00 c | 2.89 ± 0.05 fg | 0.46 ± 0.01 ef |
| C6 | 12.22 ± 0.00 d | 2.00 ± 0.10 ij | 0.22 ± 0.01 g |
| C7 | 28.89 ± 0.00 a | 4.96 ± 0.16 b | 1.30 ± 0.05 b |
| C8 | 23.33 ± 0.00 b | 3.86 ± 0.22 cde | 0.81 ± 0.05 d |
| C9 | 23.33 ± 0.00 b | 4.06 ± 0.18 cd | 0.85 ± 0.04 d |
| C10 | 28.89 ± 0.00 a | 5.71 ± 0.05 a | 1.48 ± 0.01 a |
| C11 | 12.22 ± 0.00 d | 2.38 ± 0.13 hi | 0.26 ± 0.01 g |
| C12 | 17.78 ± 0.00 c | 3.56 ± 0.24 de | 0.57 ± 0.04 e |
| C13 | 28.89 ± 0.00 a | 5.75 ± 0.04 a | 1.50 ± 0.01 a |
| C14 | 23.33 ± 0.00 b | 4.19 ± 0.13 c | 0.88 ± 0.03 d |
| C15 | 17.78 ± 0.00 c | 3.37 ± 0.25 ef | 0.54 ± 0.04 ef |
| C16 | 12.22 ± 0.00 d | 2.14 ± 0.13 i | 0.24 ± 0.01 g |
| Treatment | CT * (min) | HR (°C min) | CTEC (Wh) | EEC (Wh) | SPE (%) | TPC | DPPH | ABTS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OOH | 9.54 ± 0.46 b | 7.80 ± 0.40 a | 48.58 ± 0.85 b | 61.48 ± 0.17 b | 88.70 ± 1.31 a | 26.61 ± 0.45 a | 99.73 ± 14.31 b | 189.68 ± 24.11 b |
| CH | 43.97 ± 0.64 a | 2.25 ± 0.02 b | 245.00 ± 5.00 a | 311.11 ± 11.11 a | 23.44 ± 0.34 b | 24.90 ± 0.06 b | 125.15 ± 1.83 a | 266.17 ± 0.84 a |
| No. * | Rt ** (min) | HR-ESI(−)-MS (m/z) | ESI(−)-MSn Experiment (m/z) | Area Ratio *** (OOH/CH) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.2 | 113 | 69(100), 112(8) | 129.36 |
| 2 | 16.9 | 117 | 118(5), 116(100) | 131.35 |
| 3 | 10.4 | 175 | 175(17), 147(100), 119(4) | 102.72 |
| 4 | 1.1 | 191 | 191(37), 173(5), 111(100), 87(24), 85(15) | 139.97 |
| 5 | 20.2 | 196 | 196(100), 161(56) | 122.57 |
| 6 | 20.1 | 198 | 198(100), 163(41), 161(16) | 109.88 |
| 7 | 20.6 | 200 | 200(100), 165(27), 163(31) | 107.05 |
| 8 | 20.7 | 236 | 191(17), 147(34), 124(7), 107(9), 106(7), 105(7), 104(100), 88(44) | 107.04 |
| 9 | 17.7 | 265 | 265(100), 97(7) | 134.39 |
| 10 | 17.9 | 297 | 298(7), 297(100) | 127.47 |
| 11 | 19.2 | 311 | 312(8), 311(100) | 109.7 |
| 12 | 15.8 | 325 | 326(7), 325(100) | 127.96 |
| 13 | 17.6 | 339 | 340(6), 339(100) | 95.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavahian, M.; Chu, R. Ohmic Heating Extraction at Different Times, Temperatures, Voltages, and Frequencies: A New Energy-Saving Technique for Pineapple Core Valorization. Foods 2022, 11, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142015
Gavahian M, Chu R. Ohmic Heating Extraction at Different Times, Temperatures, Voltages, and Frequencies: A New Energy-Saving Technique for Pineapple Core Valorization. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavahian, Mohsen, and Rachael Chu. 2022. "Ohmic Heating Extraction at Different Times, Temperatures, Voltages, and Frequencies: A New Energy-Saving Technique for Pineapple Core Valorization" Foods 11, no. 14: 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142015
APA StyleGavahian, M., & Chu, R. (2022). Ohmic Heating Extraction at Different Times, Temperatures, Voltages, and Frequencies: A New Energy-Saving Technique for Pineapple Core Valorization. Foods, 11(14), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142015