Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Oleogel with Esterified Rice Flour and Its Suitability as a Fat Replacer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
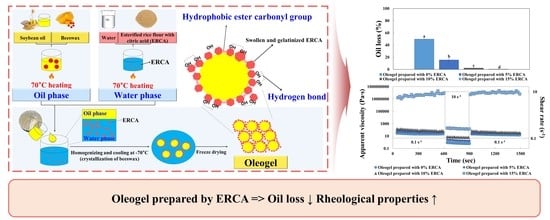
2.2. Preparation of Esterified Rice Flour with Citric Acid
2.3. Characterization of Emulsions
2.3.1. Preparation of Emulsions
2.3.2. Rheological Properties of Emulsions
Steady Shear Rheological Properties
Frequency Sweep
2.4. Preparation of Oleogels
2.5. Characterization of Oleogels
2.5.1. FT-IR Analysis
2.5.2. Oil Loss
2.6. Rheological Properties of Oleogels
2.6.1. Time-Dependent Properties
2.6.2. Frequency Sweep
2.6.3. Temperature Sweep
2.7. Oxidative Stability of Oleogels
2.7.1. Accelerated Oxidation
2.7.2. Peroxide Value
2.7.3. p-Anisidine Value
2.7.4. Total Oxidation (TOTOX) Value
2.8. Characterization of Cookies with Oleogels Prepared by ERCA
2.8.1. Preparation of Cookies
2.8.2. Dimensional Characteristics of Cookies
2.8.3. Fatty Acids Compositions of Cookies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Dicussion
3.1. Characterization of Emulsions
3.1.1. Steady Shear Rheological Properties
3.1.2. Frequency Sweep
3.2. Characterization of Oleogels
3.2.1. FT-IR Analysis
3.2.2. Oil Loss
3.3. Rheological Properties of Oleogels
3.3.1. Time-Dependent Properties
3.3.2. Frequency Sweep
3.3.3. Temperature Sweep
3.4. Oxidative Stability of Oleogels during Heat Treatment
3.5. Application of Oleogels to Cookies
Physicochemical Properties of Cookies with Oleogels Prepared with ERCA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pehlivanoğlu, H.; Demirci, M.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N.; Karasu, S.; Sagdic, O. Oleogels, a promising structured oil for decreasing saturated fatty acid concentrations: Production and food-based applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Effects of thickening agents on the formation and properties of edible oleogels based on hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Yin, S.W.; Tang, C.H.; Wu, L.Y.; Yang, X.Q. Development of antioxidant Pickering high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) stabilized by protein/polysaccharide hybrid particles as potential alternative for PHOs. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.C.; Tan, C.; Abbaspourrad, A. Combination of internal structuring and external coating in an oleogel-based delivery system for fish oil stabilization. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espert, M.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T. Cellulose ether oleogels obtained by emulsion-templated approach without additional thickeners. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Lan, Y.; Cui, L.; Monono, E.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Formation, characterization, and potential food application of rice bran wax oleogels: Expeller-pressed corn germ oil versus refined corn oil. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Q. Fabrication and characterization of resistant starch stabilized Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Bergman, C.J. The functionality of rice starch. In Starch in Food: Structure, Function and Applications; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 258–294. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca-Florido, H.A.; Vázquez-García, H.G.; Méndez-Montealvo, G.; Basilio-Cortés, U.A.; Navarro-Cortés, R.; Rodríguez-Marín, M.L.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A. Effect of acid hydrolysis and OSA esterification of waxy cassava starch on emulsifying properties in Pickering-type emulsions. LWT 2018, 91, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Effect of different pH conditions on the in vitro digestibility and physicochemical properties of citric acid-treated potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Chang, Y.H. Structural and in vitro digestibility properties of esterified maca starch with citric acid and its application as an oil-in-water (O/W) pickering emulsion stabilizer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Chang, Y.H. Structure and digestibility properties of resistant rice starch cross-linked with citric acid. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20 (Suppl. S2), 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Oleogels from sodium stearoyl lactylate-based lamellar crystals: Structural characterization and bread application. Food Chem. 2019, 292, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.Z.; Hu, X.F.; Jia, Y.J.; Pan, L.H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Mu, D.D.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jiang, S.T. Camellia oil-based oleogels structuring with tea polyphenol-palmitate particles and citrus pectin by emulsion-templated method: Preparation, characterization and potential application. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaushofer, H.; Berghofer, E.; Steyrer, W. Stärkecitrate–Produktion und anwendungs-technische Eigenschaften. Starch-Stärke 1978, 30, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Sun, Q.Q.; Vermeir, L.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R.; Van der Meeren, P. pH and protein to polysaccharide ratio control the structural properties and viscoelastic network of HIPE-templated biopolymeric oleogels. Food Struct. 2019, 21, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, M.; Dunn, C.M.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Use of caseinophosphopeptides as natural antioxidants in oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS. AOCS Official Method Cd 18-90: P-Anisidine Value, Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the AOCS; American Oil Chemists Society Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, Method 10–52; American Association of Cereal Chemists: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gibiński, M.; Kowalski, S.; Sady, M.; Krawontka, J.; Tomasik, P.; Sikora, M. Thickening of sweet and sour sauces with various polysaccharide combinations. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Q. Pickering emulsions stabilized by media-milled starch particles. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhu, X.; Zhen, W.; Li, Z.; Kang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.; Cui, S.W. Rheological properties and stabilizing effects of high-temperature extracted flaxseed gum on oil/water emulsion systems. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.Y.; Jiang, S.W.; Zheng, Z.; Cao, X.M.; Hou, Z.G.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, H.L.; Jiang, S.T.; Pan, L.J. Preparation and properties of OSA-modified taro starches and their application for stabilizing Pickering emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, P.; Tabibiazar, M.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Babazadeh, A. Development of behenic acid-ethyl cellulose oleogel stabilized Pickering emulsions as low calorie fat replacer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Halal, S.L.M.; Colussi, R.; Pinto, V.Z.; Bartz, J.; Radunz, M.; Carreño, N.L.V.; Dias, A.R.G.; da Rosa Zavareze, E. Structure, morphology and functionality of acetylated and oxidised barley starches. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Development of low-oil emulsion gel by solidifying oil droplets: Roles of internal beeswax concentration. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskeen, S.; Hong, J.S.; Choi, H.D.; Kim, J.Y. Fabrication of citric acid-modified starch nanoparticles to improve their thermal stability and hydrophobicity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xue, S.W.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.L.; Bai, Y.H. Use of high-intensity ultrasound to improve emulsifying properties of chicken myofibrillar protein and enhance the rheological properties and stability of the emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, C.; Feng, X.; Wu, D.; Meng, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X. Characterization of chitosan based polyelectrolyte films incorporated with OSA-modified gum arabic-stabilized cinnamon essential oil emulsions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naeli, M.H.; Milani, J.M.; Farmani, J.; Zargaraan, A. Development of innovative ethyl cellulose-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose biopolymer oleogels as low saturation fat replacers: Physical, rheological and microstructural characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöö, M.; Emek, S.C.; Hall, T.; Rayner, M.; Wahlgren, M. Barrier properties of heat treated starch Pickering emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R. Methylcellulose-coated microcapsules of Palm stearine as structuring templates for creating hybrid oleogels. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 195, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Sui, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z.; Xu, H. Cellulose-rich oleogels prepared with an emulsion-templated approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianingsih, R.; Gohtani, S. Dispersion characteristics of pregelatinized waxy rice starch and its performance as an emulsifier for oil-in-water emulsions: Effect of gelatinization temperature and starch concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.M.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Adhikari, B. Rheological properties of suspensions containing cross-linked starch nanoparticles prepared by spray and vacuum freeze drying methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palla, C.; Giacomozzi, A.; Genovese, D.B.; Carrín, M.E. Multi–objective optimization of high oleic sunflower oil and monoglycerides oleogels: Searching for rheological and textural properties similar to margarine. Food Struct. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Tong, J.; Su, X.; Ren, L. Hydrophobic starch nanocrystals preparations through crosslinking modification using citric acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 91, 1186–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, A.M. Understanding starch structure and functionality. In Starch in Food: Structure, Function and Applications; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 156–184. [Google Scholar]
- Öğütcü, M.; Arifoğlu, N.; Yılmaz, E. Storage stability of cod liver oil organogels formed with beeswax and carnauba wax. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Lo, Y.M.; Yan, M.; Li, P.; Cao, Y. Characterization of thermo-oxidative behavior of ethylcellulose oleogels. Food Chem. 2020, 305, 125470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, B.; Demirkesen, I. Reducing saturated fat with oleogel/shortening blends in a baked product. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | Flow Behavior Index n (−) | Consistency Index K (Pa·sn) | Apparent Viscosity ηa, 100 (Pa·s) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emulsion prepared with 5% ERCA | 0.63 ± 0.02 a1 | 0.18 ± 0.01 c | 0.03 ± 0.00 c | 0.98 |
| Emulsion prepared with 10% ERCA | 0.57 ± 0.01 b | 0.82 ± 0.06 b | 0.11 ± 0.00 b | 0.97 |
| Emulsion prepared with 15% ERCA | 0.52 ± 0.02 c | 1.71 ± 0.05 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.98 |
| Samples | Oil Loss (%) |
|---|---|
| Oleogel prepared with 0% ERCA | 49.83 ± 0.89 a1 |
| Oleogel prepared with 5% ERCA | 15.53 ± 2.88 b |
| Oleogel prepared with 10% ERCA | 2.19 ± 0.89 c |
| Oleogel prepared with 15% ERCA | 0.33 ± 0.32 d |
| Samples | Spread Factor | Loss Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Control cookie | 4.64 ± 0.17 a1 | 17.58 ± 0.29 a |
| Cookie with oleogel prepared by 0% ERCA | 4.65 ± 0.24 a | 17.09 ± 1.24 a |
| Cookie with oleogel prepared by 5% ERCA | 4.51 ± 0.25 a | 16.63 ± 0.62 a |
| Cookie with oleogel prepared by 10% ERCA | 4.55 ± 0.31 a | 16.44 ± 0.09 a |
| Cookie with oleogel prepared by 15% ERCA | 4.37 ± 0.23 a | 17.72 ± 1.52 a |
| Fatty Acids (%) | Control Cookie | Cookie with Oleogel Prepared by 15% ERCA |
|---|---|---|
| C4:0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| C6:0 | 0.04 ± 0.00 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a |
| C8:0 | 0.40 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 b |
| C10:0 | 0.31 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.00 b |
| C11:0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| C12:0 | 2.34 ± 0.02 a | 1.43 ± 0.01 b |
| C13:0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| C14:0 | 1.86 ± 0.01 a | 1.18 ± 0.01 b |
| C14:1 | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 a |
| C15:0 | 0.07 ± 0.00 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 b |
| C15:1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| C16:0 | 41.91 ± 0.22 a | 30.24 ± 0.37 b |
| C16:1 | 0.28 ± 0.01 a | 0.20 ± 0.00 b |
| C17:0 | 0.18 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 b |
| C17:1 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| C18:0 | 5.22 ± 0.01 a | 4.93 ± 0.04 b |
| C18:1 | 35.44 ± 0.13 a | 31.11 ± 0.12 b |
| C18:2 | 10.54 ± 0.05 b | 25.96 ± 0.17 a |
| C18:3 | 0.28 ± 0.01 b | 2.41 ± 0.02 a |
| C20:0 | 0.37 ± 0.00 a | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| C20:1 | 0.18 ± 0.01 b | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| C20:2 | 0.03 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 a |
| C21:0 | 0.01 ± 0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 a |
| C22:0 | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 a |
| C23:0 | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.04 ± 0.00 a |
| C24:0 | 0.10 ± 0.00 b | 0.14 ± 0.00 a |
| Saturated | 52.92 ± 0.26 a | 39.33 ± 0.45 b |
| Unsaturated | 46.77 ± 0.18 b | 60.12 ± 0.32 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, U.-h.; Chang, Y.H. Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Oleogel with Esterified Rice Flour and Its Suitability as a Fat Replacer. Foods 2022, 11, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020242
Kwon U-h, Chang YH. Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Oleogel with Esterified Rice Flour and Its Suitability as a Fat Replacer. Foods. 2022; 11(2):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020242
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, U-hui, and Yoon Hyuk Chang. 2022. "Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Oleogel with Esterified Rice Flour and Its Suitability as a Fat Replacer" Foods 11, no. 2: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020242
APA StyleKwon, U. -h., & Chang, Y. H. (2022). Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Oleogel with Esterified Rice Flour and Its Suitability as a Fat Replacer. Foods, 11(2), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020242