Comparative Analysis of Concurrent (CC), Mixed Flow (MX), and Combined Spray Drying Configurations on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Juice Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Sources
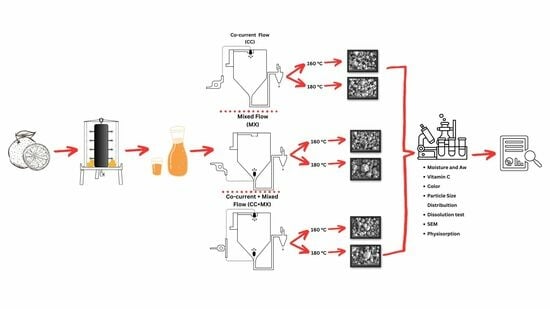
2.2. Extraction of Raw Satsuma Mandarin Juice
2.3. Characterization of SJ
2.4. Preparation of Satsuma Mandarin Mixtures
2.5. Spray Drying of SJ–MD
2.6. Physicochemical Properties of SJP
2.6.1. Moisture Content and Water Activity
2.6.2. Vitamin C
2.6.3. Color
2.6.4. Particle Size Distribution
2.6.5. Dissolution Tests
2.6.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6.7. Physisorption Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the SJ
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of SJP
3.2.1. Moisture Content and Water Activity
3.2.2. Vitamin C Content
3.2.3. Color
3.2.4. Particle Size Distribution
Correlation between SD Configuration and Inlet Air Temperature vs. Particle Size Distribution Variables
3.2.5. Dissolution Test
3.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2.7. Particle Surface Area and Total Pore Volume
3.3. Correlation Analysis between SD Configurations and Inlet Air Temperatures vs. Particle Surface Area, Pore Volume, Dissolution, Vitamin C, and Span Values of SJP
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lindler, L. Squeezing into Rural Georgia: The State’s Citrus Industry. 2020. Available online: https://www.ruralga.org/post/squeezing-into-rural-georgia-the-state-s-citrus-industry (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Price, J.; Lollar, M.; England, G. Rebirth of the Satsuma Industry? University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences. 2015. Available online: https://crec.ifas.ufl.edu/media/crecifasufledu/extension/extension-publications/2015/2015_October_satsuma.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Thompson, C. The Status of Satsuma Mandarins in Georgia. Citrus Industry Net. 2022. Available online: https://citrusindustry.net/2022/08/02/the-status-of-satsuma-mandarins-in-georgia/ (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Lipinski, B.; Craig, H.; James, L.; Lisa, K.; Searchinger, R.W. Reducing Food Losses and Waste; World Resources Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.Z.; Ayami, O.; Kitamura, Y.; Kokawa, M.; Takeshi, K.; Masayuki, K.; Norihiro, H. Micro wet milling and spray drying of whole mandarin powder and its characterization. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, A.; Ağçam, E. Citrus Juices Technology BT Food Processing: Strategies for Quality Assessment; Malik, A., Erginkaya, Z., Ahmad, S., Erten, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 37–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Prakash, D. Phytonutrients as therapeutic agents. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2014, 11, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Ikoma, Y.; Kato, M.; Nakajima, N.; Hasegawa, Y. Effect of Postharvest Temperature and Ethylene on Carotenoid Accumulation in the Flavedo and Juice Sacs of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) Fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4724–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnik, P.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Gabrić, D.; Shpigelman, A.; Cravotto, G.; Bursać Kovačević, D. An Integrated Approach to Mandarin Processing: Food Safety and Nutritional Quality, Consumer Preference, and Nutrient Bioaccessibility. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Effect of UV-C treatments on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of minimally processed Satsuma mandarin during refrigerated storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2013, 76, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.C.; Maggini, S. Vitamin C and Immune Function. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ting, J.L.; Peng, Y.; Tangjaidee, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Shan, Y.; Quek, S.Y. Comparing Three Types of Mandarin Powders Prepared via Microfluidic-Jet Spray Drying: Physical Properties, Phenolic Retention and Volatile Profiling. Foods 2021, 10, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solval, K.M.; Sundararajan, S.; Alfaro, L.; Sathivel, S. Development of cantaloupe (Cucumis melo) juice powders using spray drying technology. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Singh, S.V. Spray Drying of Fruit and Vegetable Juices—A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 701–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.; Muricio, A.C.; Sencadas, V.; Santos, J.D.; Fernandes, M.H.; Gomes, P.S. Spray Drying: An Overview. Biomater. Phys. Chem. New Ed. 2018, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Teixeira, P. Development of probiotic fruit juice powders by spray-drying: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaria, B.; Kumar, P. Effect of whey protein concentrate as drying aid and drying parameters on physicochemical and functional properties of spray dried beetroot juice concentrate. Food Biosci. 2016, 14, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, K.; Mishra, S.; Pradhan, R.C.; Nagarajan, M.; Kumar, P.K.; Singh, S.S.; Manvi, D.; Gowda, N.A.N. A comprehensive review on microencapsulation of probiotics: Technology, carriers and current trends. Appl. Food Res. 2023, 3, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eijkelboom, N.M.; Swinkels, A.C.M.; de Ruiter, J.; Boom, R.M.; Wilms, P.F.C.; Schutyser, M.A.I. High-resolution thermography and modelling allows for improved characterization of drying sessile single droplets. J. Food Eng. 2023, 341, 111340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mis Solval, K.; Bankston, J.D.; Bechtel, P.J.; Sathivel, S. Physicochemical Properties of Microencapsulated ω-3 Salmon Oil with Egg White Powder. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, E600–E609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, E.M.; Siemons, I.; Boom, R.M.; Schutyser, M.A.I. The role of viscosity in morphology development during single droplet drying. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, N.; Xiao, J.; Woo, W.; Chen, X. Frontiers in Spray Drying; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.-J.; Chen, X.D.; Pearce, D. Surface composition of industrial spray-dried milk powders. 2. Effects of spray drying conditions on the surface composition. J. Food Eng. 2019, 94, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosasih, L.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Bansal, N.; Gaiani, C. Effect of whole milk concentrate carbonation on functional, physicochemical and structural properties of the resultant spray dried powder during storage. J. Food Eng. 2016, 179, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Kumar, G.D.; Chen, J.; Mishra, A.; Solval, K.M. Comparison of concurrent and mixed-flow spray drying on viability, growth kinetics and biofilm formation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG microencapsulated with fish gelatin and maltodextrin. LWT 2020, 124, 109200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.S. (Ed.) Vitamin C Determination by Indophenol Method BT—Food Analysis Laboratory Manual; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, M.; Pike, E.R. Particle Size Distributions from Fraunhofer Diffraction. Opt. Acta Int. J. Opt. 1983, 30, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Kealey, K.; Chen, J.; Solval, K.M. Developing microencapsulated powders containing polyphenols and pectin extracted from Georgia-grown pomegranate peels. LWT 2022, 154, 112644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, Q.S.; Chok, N.K.; Swedlund, P. The physicochemical properties of spray-dried watermelon powders. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2007, 46, 386–392. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, C.; Pegg, R.B.; Kumar, G.D.; Solval, K.M. Exploring the feasibility of developing novel gelatin powders from salted, dried cannonball jellyfish (Stomolophus meleagris). Food Biosci. 2021, 44, 101397. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, M. Chapter Fourteen—Surface Area: Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET). In Progress in Filtration and Separation; Tarleton, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Barrera, D.; Sapag, K. Introducing a self-consistent test and the corresponding modification in the Barrett, Joyner and Halenda method for pore-size determination. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 200, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavender, G.; Jiang, N.; Singh, R.K.; Chen, J.; Mis Solval, K. Improving the survival of Lactobacillus plantarum NRRL B-1927 during microencapsulation with ultra-high-pressure-homogenized soymilk as a wall material. Food Res. Int. 2021, 139, 109831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochran, W.G.; Cox, G.M. Experimental Designs, 2nd ed.; Bradley, R.A., Hunter, J.S., Kendall, D.G., Watson, G.S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Jin, R.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; You, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Pan, S. Comparative study on physicochemical, nutritional and enzymatic properties of two Satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu Marc.) varieties from different regions. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 95, 103614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, J. Juice components and antioxidant capacity of citrus varieties cultivated in China. Food Chem. 2018, 106, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Kim, H.-J.; Park, K.J.; Kang, S.B.; Park, Y.; Han, S.-G.; Kim, M.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, D.-S. Metabolomic Profiling of Citrus unshiu during Different Stages of Fruit Development. Plants 2022, 11, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietel, Z.; Weiss, W.; Lewinsohn, E.; Fallik, E.; Porat, R. Improving taste and peel color of early-season Satsuma mandarins by combining high-temperature conditioning and degreening treatments. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2010, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Lopez, A.J.; Lopez-Nicolas, J.M.; Del Cerro, I.; Beltran-Gonzalez, F.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A. Effects of preservation liquid on vitamin C, instrumental color, carotenoids and sensory quality of canned satsuma mandarin. J. Food Process Eng. 2011, 34, 1464–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, L.; Yaniv, Y.; Porat, R.; Carmi, N. Mandarin fruit quality: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov Bandić, L.; Vlahoviček-Kahlina, K.; Sigurnjak Bureš, M.; Sopko Stracenski, K.; Jalšenjak, N.; Fruk, G.; Antolković, A.M.; Jurić, S. Fruit quality of satsuma mandarins from Neretva valley and their flavonoid and carotenoid content. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phisut, N. Spray drying technique of fruit juice powder: Some factors influencing the properties of product. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 1297. [Google Scholar]
- Chegini, G.R.; Ghobadian, B. Effect of Spray-Drying Conditions on Physical Properties of Orange Juice Powder. Dry. Technol. 2005, 23, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.K.; Ua-Arak, T.; Adhikari, B.P.; Howes, T.; Bhandari, B.R. Glass transition behavior of spray dried orange juice powder measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal mechanical compression test (TMCT). Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.S.; Alzamora, S.M.; Chirife, J. Effects of Water Activity (aw) on Microbial Stability as a Hurdle in Food Preservation. In Water Activity in Foods; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V., Fontana, A.J., Schmidt, S.J., Labuza, T.P., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsis, K.; Golding, J.B.; Vuong, Q.; Pristijono, P.; Stathopoulos, C.E.; Scarlett, C.J.; Bowyer, M. Encapsulation of Citrus By-Product Extracts by Spray-Drying and Freeze-Drying Using Combinations of Maltodextrin with Soybean Protein and ι-Carrageenan. Foods 2018, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhalakshmy, S.; Don Bosco, S.J.; Francis, S.; Sabeena, M. Effect of inlet temperature on physicochemical properties of spray-dried jamun fruit juice powder. Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Health. Vitamin C. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. 2021. Available online: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- Li, Y.; Schellhorn, H.E. New developments and novel therapeutic perspectives for vitamin C. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2171–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, A.; Agabbio, M.; Gambella, F.; Nicoli, M.C. Retention of Antioxidant Activity in Minimally Processed Mandarin and Satsuma Fruits. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 35, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N. Ascorbic acid metabolism and functions: A comparison of plants and mammals. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 122, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevinho, B.N.; Carlan, I.; Blaga, A.; Rocha, F. Soluble vitamins (vitamin B12 and vitamin C) microencapsulated with different biopolymers by a spray drying process. Powder Technol. 2016, 289, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Chauhan, A.K.; Singh, R.P. Optimization of the spray-drying process for developing guava powder using response surface methodology. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Moran, A.; Cubillos, A.; Gómez, A. Spray drying experiments and CFD simulation of guava juice formulation. Dry. Technol. 2021, 39, 450–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, C.C.; Germer, S.P.M.; de Aguirre, J.M. Effects of Spray-Drying Conditions on the Physicochemical Properties of Blackberry Powder. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-C.; Eun, J.-B.; Hwang, S.J. Physicochemical properties and sensory evaluation of mandarin (Citrus unshiu) beverage powder spray-dried at different inlet air temperatures with different amounts of a mixture of maltodextrin and corn syrup. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okere, E.E.; Arendse, E.; Nieuwoudt, H.; Fawole, O.A.; Perold, W.J.; Opara, U.L. Non-Invasive Methods for Predicting the Quality of Processed Horticultural Food Products, with Emphasis on Dried Powders, Juices and Oils: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, D.P.S.; Sogi, D.S. Effect of drying methods and maltodextrin concentration on pigment content of watermelon juice powder. J. Food Eng. 2015, 165, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moolchandani, V.; Augsburger, L.; Gupta, A.; Khan, M.; Langridge, J.; Hoag, S. Characterization and selection of suitable grades of lactose as functional fillers for capsule filling: Part 1. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 41, 1452–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishir, M.R.I.; Chen, W. Trends of spray drying: A critical review on drying of fruit and vegetable juices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson Correlation Coefficient; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey, K.R. Correlation methods. Automatica 1980, 16, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.; Borges, S.; Amorim, M.; Pereira, M.J.; Oliveira, A.; Pintado, M.E.; Teixeira, P. Comparison of spray drying, freeze drying and convective hot air drying for the production of a probiotic orange powder. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah, M.; Yusof, Y.A.; Chin, N.L.; Aziz, M.G. Physicochemical and flow properties of fruit powder and their effect on the dissolution of fast dissolving fruit powder tablets. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon-Parry, K.D. Scanning electron microscopy: An introduction. III-Vs Rev. 2000, 13, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilarasi, P.N.; Indrani, D.; Jena, B.S.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Freeze drying technique for microencapsulation of Garcinia fruit extract and its effect on bread quality. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Tian, G.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Lian, Y.; Wang, F.; Du, H.; et al. Effects of spray-drying temperature on the physicochemical properties and polymethoxyflavone loading efficiency of citrus oil microcapsules. LWT 2020, 133, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, D.; Langrish, T.A.G.; Braham, R. The effect of temperature on the crystallinity of lactose powders produced by spray drying. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ma, Z.; Morris, R.E.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, F.; Dai, S.; Bruce, P.G. A solid with a hierarchical tetramodal micro-meso-macro pore size distribution. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Ogi, T.; Wang, W.-N.; Gradon, L.; Okuyama, K. Template-assisted spray-drying method for the fabrication of porous particles with tunable structures. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2908–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| SD Configuration | Inlet Temperature (°C) | Moisture Content (g/100 g) 1 | Water Activity (aw) 1 | Vitamin C (mg/g) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 160 | 16.35 ± 5.52 c | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 4.01 ± 1.31 a |
| CC | 180 | 15.18 ± 4.74 c | 0.14 ± 0.02 a | 3.56 ± 2.63 a |
| MX | 160 | 25.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.02 a | 3.18 ± 2.27 c |
| MX | 180 | 19.72 ± 1.16 b | 0.17 ± 0.03 a | 2.88 ± 1.31 c |
| CC + MX | 160 | 25.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.19 ± 0.03 a | 3.33 ± 1.31 b |
| CC + MX | 180 | 25.44 ± 0.76 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 3.33 ± 1.31 b |
| Configuration | Inlet Temperature (°C) | L* 1 | a* 1 | b* 1 | Chroma 1 | Hue Angle 1 | ∆E 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 160 | 10.30 ± 1.17 a | 2.97 ± 0.35 b | 19.65 ± 1.34 b | 19.88 ± 1.30 a | 1.42 ± 0.02 a | 2.94 ± 1.20 a |
| CC | 180 | 11.95 ± 1.38 a | 2.90 ± 0.50 b | 21.58 ± 2.21 b | 21.78 ± 2.24 a | 1.44 ± 0.02 a | 3.10 ± 1.14 a |
| MX | 160 | 11.34 ± 1.34 a | 3.49 ± 0.19 b | 18.29 ± 1.61 b | 18.62 ± 1.62 b | 1.38 ± 0.02 a | 2.16 ± 0.22 a |
| MX | 180 | 10.23 ± 0.90 a | 2.94 ± 0.41 b | 17.71 ± 0.78 b | 17.95 ± 0.78 b | 1.41 ± 0.02 a | 1.75 ± 0.49 a |
| CC + MX | 160 | 12.23 ± 0.39 a | 4.12 ± 0.34 a | 20.43 ± 0.32 a | 20.84 ± 0.28 a | 1.37 ± 0.02 a | 1.14 ± 0.37 a |
| CC + MX | 180 | 10.68 ± 0.27 a | 3.78 ± 0.32 a | 22.36 ± 1.89 a | 22.68 ± 1.88 a | 1.40 ± 0.02 a | 3.93 ± 3.41 a |
| SD Configuration | Inlet Temperature (°C) | D10 [um] 1 | D50 [um] 1 | D90 [um] 1 | Span 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 160 | 0.25 ± 0.02 a | 7.51 ± 0.02 b | 8.96 ± 0.05 b | 2.32 ± 0.04 b |
| CC | 180 | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 7.20 ± 0.24 b | 9.05 ± 0.19 b | 2.61 ± 0.10 b |
| MX | 160 | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 8.83 ± 0.16 a | 26.28 ± 0.27 a | 2.95 ± 0.03 a |
| MX | 180 | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 8.69 ± 0.28 a | 26.86 ± 0.86 a | 3.06 ± 0.09 a |
| CC + MX | 160 | 0.36 ± 0.22 a | 7.34 ± 0.57 b | 9.33 ± 0.59 b | 2.57 ± 0.07 b |
| CC + MX | 180 | 0.25 ± 0.06 a | 7.21 ± 0.37 b | 16.93 ± 0.60 b | 2.32 ± 0.07 b |
| SD Configuration | Inlet Temperature (°C) | Dissolution (s) 1 | Surface Area (m2/g) 1 | Total Pore Volume (cc/g) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | 160 | 41.67 ± 7.57 a | 4.93 ± 0.17 a | 1.79 × 10−4 ± 2.91 × 10−6 a |
| CC | 180 | 36.33 ± 4.93 a | 4.00 ± 0.61 a | 1.20 × 10−4 ± 4.66 × 10−5 a |
| MX | 160 | 27.33 ± 2.52 b | 2.88 ± 1.41 a | 1.34 × 10−4 ± 4.19 × 10−5 a |
| MX | 180 | 29.33 ± 1.53 b | 4.39 ± 1.90 a | 2.22 × 10−4 ± 9.00 × 10−5 a |
| CC + MX | 160 | 22.33 ± 4.93 b | 4.58 ± 0.97 a | 2.87 × 10−4 ± 3.90 × 10−5 a |
| CC + MX | 180 | 29.33 ± 5.86 b | 4.82 ± 1.72 a | 2.11 × 10−4 ± 1.94 × 10−5 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Padilla, J.; Reyes, V.; Cavender, G.; Chotiko, A.; Gratzek, J.; Mis Solval, K. Comparative Analysis of Concurrent (CC), Mixed Flow (MX), and Combined Spray Drying Configurations on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Juice Powders. Foods 2023, 12, 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183514
Cruz-Padilla J, Reyes V, Cavender G, Chotiko A, Gratzek J, Mis Solval K. Comparative Analysis of Concurrent (CC), Mixed Flow (MX), and Combined Spray Drying Configurations on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Juice Powders. Foods. 2023; 12(18):3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183514
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Padilla, Javier, Vondel Reyes, George Cavender, Arranee Chotiko, James Gratzek, and Kevin Mis Solval. 2023. "Comparative Analysis of Concurrent (CC), Mixed Flow (MX), and Combined Spray Drying Configurations on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Juice Powders" Foods 12, no. 18: 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183514
APA StyleCruz-Padilla, J., Reyes, V., Cavender, G., Chotiko, A., Gratzek, J., & Mis Solval, K. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Concurrent (CC), Mixed Flow (MX), and Combined Spray Drying Configurations on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Satsuma Mandarin (Citrus unshiu) Juice Powders. Foods, 12(18), 3514. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183514