Effect of Digestion on Ursolic Acid Self-Stabilized Water-in-Oil Emulsion: Role of Bile Salts
Abstract
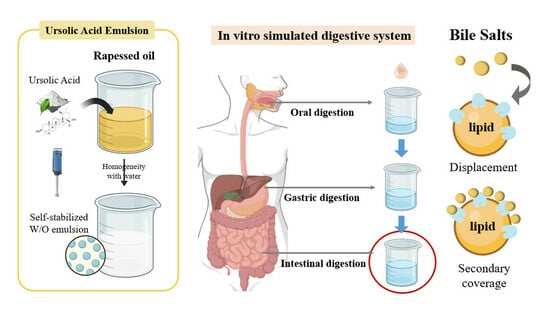
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of W/O Emulsion
2.3. In Vitro Static Simulation of Intestinal Digestion
2.4. Polarized Light Microscopy
2.5. Measurement of Droplet Size
2.6. ζ-Potential Measurements
2.7. In Vitro Dynamic Oral–Gastrointestinal Simulation of Digestion
2.7.1. Oral Phase
2.7.2. Gastric Phase
2.7.3. Intestinal Phase
2.8. Measurement of Digestive Properties
2.9. Determination of UA Content via HPLC
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of pH and Intestinal Salts on Emulsion Stability
3.1.1. Appearance and Microstructure
3.1.2. Particle Size and ζ-Potential
3.2. Effect of Different Bile Salt Concentrations on Emulsion Stability
3.2.1. Appearance and Microstructure
3.2.2. Particle Size and ζ-Potential
3.3. Effect of Different Bile Salt Concentrations on the In Vitro Simulated Digestion of Emulsion
3.3.1. Appearance
3.3.2. Particle Size and ζ-Potential
3.3.3. Free Fatty Acid Release Rate (FFA%) and Bioaccessibility

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.-Q.; Ding, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.-M. Ursolic acid protects mouse liver against CCl 4 -induced oxidative stress and inflammation by the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Kan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Zhu, L. Asiatic acid ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via mitochondria-targeted protective mechanism. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 338, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Pathan, S.K.; Wadher, S.J. In silico PASS analysis and determination of antimycobacterial, antifungal, and antioxidant efficacies of maslinic acid in an extract rich in pentacyclic triterpenoids. Int. J. Mycobacteriol. 2016, 5, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaps, A.; Gwiazdon, P.; Chodurek, E. Nanoformulations for Delivery of Pentacyclic Triterpenoids in Anticancer Therapies. Molecules 2021, 26, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdes, K.; Morales, J.; Rodriguez, L.; Gunther, G. Potential use of nanocarriers with pentacyclic triterpenes in cancer treatments. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3139–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Liang, N.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.-S. Recent progress on betulinic acid and its derivatives as antitumor agents: A mini review. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 19, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, N.A.J.C.; Pirson, L.; Edelberg, H.; Miranda, L.M.; Loira-Pastoriza, C.; Preat, V.; Larondelle, Y.; Andre, C.M. Pentacyclic Triterpene Bioavailability: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Navarro del Hierro, J.; Villanueva Bermejo, D.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Fornari, T.; Reglero, G. Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Activity of Calendula officinalis Supercritical Extract as Affected by in Vitro Codigestion with Olive Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8828–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Zou, L.; Zhang, R.; Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Kumosani, T.; Xiao, H. Enhancing Nutraceutical Performance Using Excipient Foods: Designing Food Structures and Compositions to Increase Bioavailability. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 824–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Cao, C.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L.; Huang, Q.; Song, B. Evaluation of emulsion stability by monitoring the interaction between droplets. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 132, 109804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboalnaja, K.O.; Yaghmoor, S.; Kumosani, T.A.; McClements, D.J. Utilization of nanoemulsions to enhance bioactivity of pharmaceuticals, supplements, and nutraceuticals: Nanoemulsion delivery systems and nanoemulsion excipient systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, B.; Argin, S.; Ozilgen, M.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsion delivery systems for oil-soluble vitamins: Influence of carrier oil type on lipid digestion and vitamin D-3 bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidov-Pardo, G.; McClements, D.J. Nutraceutical delivery systems: Resveratrol encapsulation in grape seed oil nanoemulsions formed by spontaneous emulsification. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danielsen, E.M.; Hansen, G.H.; Rasmussen, K.; Niels-Christiansen, L.-L. Permeabilization of enterocytes induced by absorption of dietary fat. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2013, 30, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kesarla, R.; Omri, A. Formulation strategies to improve the bioavailability of poorly absorbed drugs with special emphasis on self-emulsifying systems. ISRN Pharm. 2013, 4, 848043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, E.; Jakob, S.; Mosenthin, R. Principles of Physiology of Lipid Digestion. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 18, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Park, Y.; Weiss, J. Designing food structure to control stability, digestion, release and absorption of lipophilic food components. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Holmberg, K.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Lipases at interfaces: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.; Holmberg, K.; Miller, R. Interfacial mechanism of lipolysis as self-regulated process. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 147, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Wilde, P.; Macierzanka, A.; Mackie, A. The role of bile salts in digestion. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macierzanka, A.; Torcello-Gomez, A.; Jungnickel, C.; Maldonado-Valderrama, J. Bile salts in digestion and transport of lipids. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 274, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.G.; Xia, H.P.; Guo, S.Y.; Lu, X.Y.; Zeng, C.X. Development and characterization of a novel naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpene self-stabilized pickering emulsion. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 634, 127908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, C.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Edible pentacyclic triterpenes: A review of their sources, bioactivities, bioavailability, self-assembly behavior, and emerging applications as functional delivery vehicles. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Decker, E.A.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsion delivery systems: Influence of carrier oil on beta-carotene bioaccessibility. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Horne, D.S.; Singh, H. Interactions of milk protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with bile salts in a simulated upper intestinal model. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Chen, C.; Yuanfa, L.; Peirang, C.; Qiu, L. Digestion fates of different edible oils vary with their composition specificities and interactions with bile salts. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 281–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda-Serna, I.E.; Rocha-Guzman, N.E.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A.; Chairez-Ramirez, M.H.; Rosas-Flores, W.; Perez-Martinez, J.D.; Moreno-Jimenez, M.R.; Gonzalez-Laredo, R.F. Water-in-oil organogel based emulsions as a tool for increasing bioaccessibility and cell permeability of poorly water-soluble nutraceuticals. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-J.; Huang, X.-N.; Yin, S.-W.; Yu, Y.-G.; Yang, X.-Q. Bioavailability of quercetin in zein-based colloidal particles-stabilized Pickering emulsions investigated by the in vitro digestion coupled with Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 130152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzi, L.; Goumas, K.; Kalioras, V.; Abrahamsson, B.; Dressman, J.B.; Reppas, C. Characterization of the human upper gastrointestinal contents under conditions simulating bioavailability/bioequivalence studies. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 76–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; Kim, H.J.; McClements, D.J. Factors influencing the production of o/w emulsions stabilized by beta-lactoglobulin-pectin membranes. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmyrzaev, A.; Chanamai, R.; McClements, D.J. Influence of pH and CaCl2 on the stability of dilute whey protein stabilized emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jódar-Reyes, A.B.; Torcello-Gómez, A.; Wulff-Pérez, M.; Gálvez-Ruiz, M.J.; Martín-Rodríguez, A. Different stability regimes of oil-in-water emulsions in the presence of bile salts. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.J.; Gunning, A.P. Microscopy, microstructure and displacement of proteins from interfaces: Implications for food quality and digestion. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Valderrama, J.; Woodward, N.C.; Gunning, A.P.; Ridout, M.J.; Husband, F.A.; Mackie, A.R.; Morris, V.J.; Wilde, P.J. Interfacial characterization of beta-lactoglobulin networks: Displacement by bile salts. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6759–6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winuprasith, T.; Chantarak, S.; Suphantharika, M.; He, L.; McClements, D.J. Alterations in nanoparticle protein corona by biological surfactants: Impact of bile salts on beta-lactoglobulin-coated gold nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 426, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.; Rigby, N.M.; Ridout, M.J.; Gunning, A.P.; Wilde, P.J. The adsorption-desorption behaviour and structure function relationships of bile salts. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 6457–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of emulsifier type on in vitro digestibility of lipid droplets by pancreatic lipase. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euston, S.R.; Baird, W.G.; Campbell, L.; Kuhns, M. Competitive Adsorption of Dihydroxy and Trihydroxy Bile Salts with Whey Protein and Casein in Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunbing, T.; Zhiyun, Z.; Hualu, Z.; Hang, X.; McClements, D.J. Factors impacting lipid digestion and beta-carotene bioaccessibility assessed by standardized gastrointestinal model (INFOGEST): Oil droplet concentration. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7126–7137. [Google Scholar]
- Euston, S.R.; Bellstedt, U.; Schillbach, K.; Hughes, P.S. The adsorption and competitive adsorption of bile salts and whey protein at the oil-water interface. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8942–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, C.; Xia, H. Effect of Digestion on Ursolic Acid Self-Stabilized Water-in-Oil Emulsion: Role of Bile Salts. Foods 2023, 12, 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193657
Yan Y, Liu Y, Zeng C, Xia H. Effect of Digestion on Ursolic Acid Self-Stabilized Water-in-Oil Emulsion: Role of Bile Salts. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193657
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yumeng, Yugang Liu, Chaoxi Zeng, and Huiping Xia. 2023. "Effect of Digestion on Ursolic Acid Self-Stabilized Water-in-Oil Emulsion: Role of Bile Salts" Foods 12, no. 19: 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193657
APA StyleYan, Y., Liu, Y., Zeng, C., & Xia, H. (2023). Effect of Digestion on Ursolic Acid Self-Stabilized Water-in-Oil Emulsion: Role of Bile Salts. Foods, 12(19), 3657. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193657