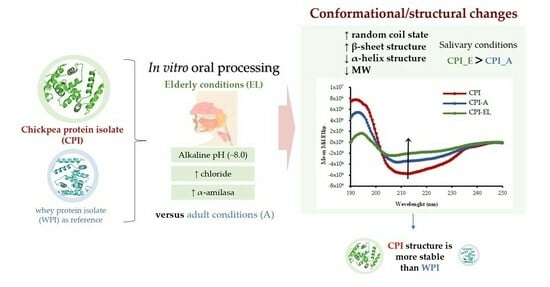
Conformational and Structural Changes in Chickpea Proteins Caused by Simulated Salivary Alterations in the Elderly
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction of Chickpea Protein Isolates (CPI)
2.3. Proximate Analysis
2.4. Amino Acidic Profile by HPLC
2.5. Surface Charge and Hydrodynamic Diameter Measurements
2.6. Water Absorption and Solubility
2.6.1. Water Absorption Index (WAI)
2.6.2. Solubility
2.7. Structural Characterization of Proteins
2.7.1. Molecular Weight Distribution by Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.7.2. Changes in Protein Structure by Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.7.3. Changes in Secondary Structure by Raman Spectroscopy
2.8. Simulated Oral Processing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility of Proteins Affected by pH of Simulated Salivary Fluid
3.2. Surface Charge of Proteins
3.3. Water Absorption Index (WAI)
3.4. Particle Size Distribution
3.5. Molecular Weight Distribution
3.6. Molecular Configuration and Secondary Structure
3.6.1. Circular Dichroism
3.6.2. Raman Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nosworthy, M.; Medina, G.; Franczyk, A.; Neufeld, J.; Appah, P.; Utioh, A.; Frohlich, P.; Tar’an, B.; House, J. Thermal processing methods differentially affect the protein quality of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Amino acid composition and digestibility of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) proteins isolated from different parts. LWT 2019, 116, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Sun, C.X.; Mata, A.; Corke, H.; Gan, R.Y.; Fang, Y. Physicochemical and pH-dependent functional properties of proteins isolated from eight traditional Chinese beans. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, A.; Kushwaha, R.; Malaviya, R.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, N. Molecular, functional and nutritional properties of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein isolates prepared by modified solubilization methods. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2352–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukid, F. Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein as a prospective plant-based ingredient: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 5435–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Prasad, K. Nutritional characteristics and value-added products of Chickpea (Cicer arietinum)—A review. J. Postharvest Technol. 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, N. Characterization of protein isolates from different Indian chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghribi, A.; Gafsi, I.; Sila, A.; Blecker, C.; Danthine, S.; Attia, H.; Bougatef, A.; Besbes, S. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on conformational and functional properties of chickpea protein isolate. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Peng, D.; Tu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, D.; Yin, Z. Advances in the formation mechanism, influencing factors and applications of egg white gels: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W.; Wang, Z. Emulsifying properties of chickpea protein isolates: Influence of pH and NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; Liu, H.; Ye, Y.; Yin, Z. The role of surface properties on protein aggregation behavior in aqueous solution of different pH values. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ming, J. Combined effect of carboxymethylcellulose and salt on structural properties of wheat gluten proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagler, R.; Hershkovich, O. Relationships between age, drugs, oral sensorial complaints and salivary profile. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lăzureanu, P.; Popescu, F.; Tudor, A.; Stef, L.; Negru, A.; Mihăilă, R. Saliva pH and flow rate in patients with periodontal disease and associated cardiovascular disease. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e931362-1–e931362-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariani, D.; Rahmayanti, F.; Sasanti, H.; Mandasari, M. The oral health of elderly residents in a state institution in Jakarta: A preliminary study. J. Int. Dent. Med. Res. 2017, 10, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, R.; Yuan, W. Composition and secondary structure of proteins isolated from six different quinoa varieties from China. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 95, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of AOAC International; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Obielodan, M.; Sismour, E.; Arnett, A.; Alzahrani, S.; Zhang, B. Physicochemical, functional, thermal and structural properties of isolated Kabuli chickpea proteins as affected by processing approaches. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enrione, J.; Char, C.; Pepczynska, M.; Padilla, C.; González-Muñoz, A.; Olguín, Y.; Quinzio, C.; Iturriaga, L.; Díaz-Calderón, P. Rheological and structural study of salmon gelatin with controlled molecular weight. Polymers 2020, 12, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, M.; Lopez-Osorio, A.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Faba bean protein flour obtained by densification: A sustainable method to develop protein concentrates with food applications. LWT 2018, 93, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contardo, I.; Villalón, M.; Bouchon, P. In Vivo study on the slow release of glucose in vacuum fried matrices. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Calderón, P.; Flores, E.; González-Muñoz, A.; Pepczynska, M.; Quero, F.; Enrione, J. Influence of extraction variables on the structure and physical properties of salmon gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 71, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Structural transformation of egg white protein particles modified by preheating combined with pH-shifting: Mechanism of enhancing heat stability. LWT 2022, 170, 114114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monago-Maraña, O.; Wold, J.P.; Rødbotten, R.; Dankel, K.R.; Afseth, N.K. Raman, near-infrared and fluorescence spectroscopy for determination of collagen content in ground meat and poultry by-products. LWT 2021, 140, 110592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas-Granillo, H.; Borges-Yañez, S.; Medina-Solís, C.; Galan-Vidal, C.; Navarrete-Hernández, J.; Escoffié-Ramirez, M.; Maupomé, G. Salivary parameters (Salivary Flow, pH and Buffering Capacity) in stimulated Saliva of Mexican Elders 60 Years old and older. West Indian Med. J. 2014, 63, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.; Zhu, J.; Bansal, N.; Boyce, M.; Le, T. Effect of pH and heat treatment on physicochemical and functional properties of spray-dried whey protein concentrate powder. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 119, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T. Complexation of rice proteins and whey protein isolates by structural interactions to prepare soluble protein composites. LWT 2019, 101, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Morr, C.; Ha, E. Structural and functional properties of caseinate and whey protein isolate as affected by temperature and pH. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 1210–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lošdorfer Božič, A.; Podgornik, R. pH dependence of charge multipole moments in proteins. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1454–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Aserin, A.; Ishai, P.; Garti, N. Interactions between whey protein isolate and gum Arabic. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalamprou, E.; Doxastakis, G.; Kiosseoglou, V. Chickpea protein isolates obtained by wet extraction as emulsifying agents. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, N.; Koocheki, A.; Varidi, M.; Kadkhodaee, R. Introducing Speckled sugar bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) protein isolates as a new source of emulsifying agent. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.H.; McClements, D.J. Modulation of pH sensitivity of surface charge and aggregation stability of protein-coated lipid droplets by chitosan addition. Food Biophys. 2007, 2, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramenko, N.; Low, N.; Nickerson, M. The effects of limited enzymatic hydrolysis on the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of a lentil protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jeganathan, B.; Dong, H.; Chen, L.; Vasanthan, T. Effect of sodium chloride on the thermodynamic, rheological, and microstructural properties of field pea protein isolate/chitosan complex coacervates. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, S.; Singh, J.; Muzaffar, K.; Dar, B. Effect of germination time on physicochemical, electrophoretic, rheological, and functional performance of chickpea protein isolates. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 1, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A.; Vioque, J.; Sánchez-Vioque, R.; Pedroche, J.; Bautista, J.; Millan, F. Factors affecting the in vitro protein digestibility of chickpea albumins. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanthi, M.; Vasiljevic, T.; Chandrapala, J. Properties of whey proteins obtained from different whey streams. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 66, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osemwota, E.; Alashi, A.; Aluko, R. Physicochemical and functional properties of albumin, globulin and glutelin fractions of green lentil seed. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 3967–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodic, I.; Stanic-Vucinic, D.; Apostolovic, D.; Mihailovic, J.; Radibratovic, M.; Radosavljevic, J.; Burazer, L.; Milcic, M.; Smiljanic, K.; van Hage, M.; et al. Influence of peanut matrix on stability of allergens in gastric-simulated digesta: 2S albumins are main contributors to the IgE reactivity of short digestion-resistant peptides. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Secondary Structure (%) | CPI | CPI-A | CPI-EL | WPI | WPI-A | WPI-EL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-helix | 44.5 ± 5 b | 42.2 ± 9 b | 28.5 ± 5 a | 40.2 ± 2 b | 31.5 ± 4 a | 28.5 ± 3 a |
| Total β-sheet | 26.0 ± 5 ab | 28.2 ± 9 abc | 35.3 ± 5 cd | 21.3 ± 3 a | 31.7 ± 6 bcd | 39.3 ± 6 d |
| β-turn | 28.6 ± 2 bc | 31.7 ± 7 bc | 33.1 ± 9 c | 26.2 ± 5 abc | 25.0 ± 7 ab | 18.3 ± 4 a |
| Random coil | 4.5 ± 2 a | 3.4 ± 2 a | 9.8 ± 1 b | 3.2 ± 2 a | 11.2 ± 3 b | 15.2 ± 4 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contardo, I.; Guzmán, F.; Enrione, J. Conformational and Structural Changes in Chickpea Proteins Caused by Simulated Salivary Alterations in the Elderly. Foods 2023, 12, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193668
Contardo I, Guzmán F, Enrione J. Conformational and Structural Changes in Chickpea Proteins Caused by Simulated Salivary Alterations in the Elderly. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193668
Chicago/Turabian StyleContardo, Ingrid, Fanny Guzmán, and Javier Enrione. 2023. "Conformational and Structural Changes in Chickpea Proteins Caused by Simulated Salivary Alterations in the Elderly" Foods 12, no. 19: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193668
APA StyleContardo, I., Guzmán, F., & Enrione, J. (2023). Conformational and Structural Changes in Chickpea Proteins Caused by Simulated Salivary Alterations in the Elderly. Foods, 12(19), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193668