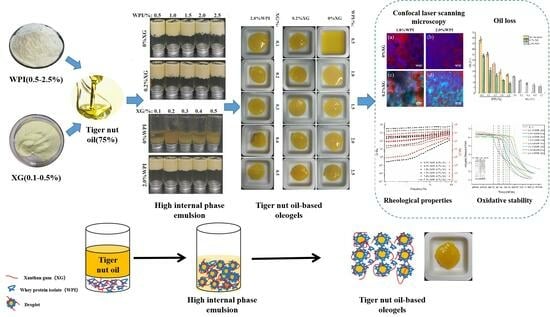
Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oil Gel: Preparation, Characterization, and Storage Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Stock Solution
2.3. Preparation of the High Internal Phase Emulsion (HIPE)
2.4. Preparation of Tiger Nuts Oleogel
2.5. Characterization of a High-Grade Internal-Phase Emulsion
2.5.1. Determination of Particle Size and Distribution
2.5.2. Optical Microstructure of High-Grade Internal-Phase Emulsion
2.5.3. Centrifugal Stability
2.5.4. Rheological Properties Measurements
2.6. Characterization of the Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel
2.6.1. Rheological Properties
2.6.2. Optical Microstructure
2.6.3. Determination of Oil Loss
2.6.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.6.5. Oxidative Stability
2.6.6. Fatty Acid Composition
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Particle Size and Size Distribution of HIPE
3.2. Macroscopic and Microstates of HIPE
3.3. Rheological Properties of the HIPE
3.4. The Centrifugal Stability Analysis of the HIPE
3.5. Rheological Properties of the Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel
3.6. Macroscopic of the Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel
3.7. Stability of the Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel
3.8. Microstructure of the Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel
3.9. Oxitest Was Used to Evaluate the Oxidation Stability of Tiger Nuts-Based Oleogels
3.10. Fatty Acid Composition of Tiger Nuts-Based Oleogels
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pehlivanoglu, H.; Demirci, M.; Toker, O.S.; Konar, N.; Karasu, S.; Sagdic, O. Oleogels, a promising structured oil for decreasing saturated fatty acid concentrations: Production and food-based applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkesen, I.; Mert, B. Recent developments of oleogel utilizations in bakery products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2460–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Masoodi, F.A.; Naqash, F.; Rashid, R. Oleogels: Promising alternatives to solid fats for food applications. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2022, 2, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolnnaleki, K.; Alizadeh, L.; Nayebzadeh, K.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shahin, R. Oleogel production based on binary and ternary mixtures of sodium caseinate, xanthan gum, and guar gum: Optimization of hydrocolloids concentration and drying method. J. Texture Stud. 2020, 51, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Cheong, L.-Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Physical Properties of Soybean Oleogels and Oil Migration Evaluation in Model Praline System. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Cao, L.; Kang, S.; Jiang, S.; Cao, L. Controlled Release of Flavor Substances from Sesame-Oil-Based Oleogels Prepared Using Biological Waxes or Monoglycerides. Foods 2021, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, G.; Li, X.; Jin, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. Roles of gelator type and gelation technology on texture and sensory properties of cookies prepared with oleogels. Food Chem. 2021, 356, 129667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Sintang, M.D.; Rimaux, T.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Oil structuring properties of monoglycerides and phytosterols mixtures. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, P.; Lo, Y.M.; Fu, H.; Cao, Y. Development of Novel Shortenings Structured by Ethylcellulose Oleogels. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Song, M.; Gao, X.; Dong, L.; Hou, T.; Lin, X.; Tan, W.; Cao, Y.; Rogers, M.; Lan, Y. Assembly pattern of multicomponent supramolecular oleogel composed of ceramide and lecithin in sunflower oil: Self-assembly or self-sorting? Food Funct. 2020, 11, 7651–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-K.; Zhang, C.; He, X.-N.; Wang, P.-Y. Effects of alkyl chain lengths on 12-hydroxystearic acid derivatives based supramolecular organogels. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 616, 126319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolmaleki, K.; Alizadeh, L.; Hosseini, S.M.; Nayebzadeh, K. Concentrated O/W emulsions formulated by binary and ternary mixtures of sodium caseinate, xanthan and guar gums: Rheological properties, microstructure, and stability. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feichtinger, A.; Scholten, E. Preparation of Protein Oleogels: Effect on Structure and Functionality. Foods 2020, 9, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.-Z.; Hu, X.-F.; Jia, Y.-J.; Pan, L.-H.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Mu, D.-D.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Jiang, S.-T. Camellia oil-based oleogels structuring with tea polyphenol-palmitate particles and citrus pectin by emulsion-templated method: Preparation, characterization and potential application. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuas, S.; Hernando, I.; Moraga, G.; Quiles, A. Structure and stability of edible oleogels prepared with different unsaturated oils and hydrocolloids. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floeter, E.; Wettlaufer, T.; Conty, V.; Scharfe, M. Oleogels-Their Applicability and Methods of Characterization. Molecules 2021, 26, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Wei, Z.; Xue, C. Recent advances on food-grade oleogels: Fabrication, application and research trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7659–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsmar, C.; Pradines, V.; Alahverdjieva, V.S.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Kraegel, J.; Leser, M.E.; Noskov, B.A.; Miller, R. Thermodynamics, adsorption kinetics and rheology of mixed protein-surfactant interfacial layers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 150, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, M.S. Emulsion-templated polymers: Contemporary contemplations. Polymer 2017, 126, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, S.; Malchione, N.; Selig, M.J.; Abbaspourrad, A. Formation of shelf stable Pickering high internal phase emulsions (HIPE) through the inclusion of whey protein microgels. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foegeding, E.A.; Davis, J.P.; Doucet, D.; McGuffey, M.K. Advances in modifying and understanding whey protein functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 13, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.C.; Ogendal, L.H.; Skibsted, L.H. Droplet surface properties and rheology of concentrated oil in water emulsions stabilized by heat-modified beta-lactoglobulin B. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Cludts, N.; Bin Sintang, M.D.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Edible oleogels based on water soluble food polymers: Preparation, characterization and potential application. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espert, M.; Hernandez, M.J.; Sanz, T.; Salvador, A. Rheological properties of emulsion templated oleogels based on xanthan gum and different structuring agents. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeh, O.; Gordon, M.H.; Niranjan, K. Tiger nut oil (Cyperus esculentus L.): A review of its composition and physico-chemical properties. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wan, C.; Huang, F.; Wei, C. Evaluation of quality properties and antioxidant activities of tiger nut (Cyperus esculentus L.) oil produced by mechanical expression or/with critical fluid extraction. LWT 2021, 141, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Morales, T.; Mateos-Díaz, C.; Pérez-Machín, R.; Wiebe, J.; Gericke, N.P.; Alarcón, C.; López-Romero, J.M. Chemical composition of industrially and laboratory processed Cyperus esculentus rhizomes. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, C.; Guan, S.; Pu, Y.; Gao, F. Tiger Nut (Cyperus esculentus L.): Nutrition, Processing, Function and Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselló-Soto, E.; Poojary, M.M.; Barba, F.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Mañes, J.; Moltó, J.C. Tiger nut and its by-products valorization: From extraction of oil and valuable compounds to development of new healthy products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Hanna, M.A.; Ali, Y.; Nan, L. Yellow nut-sedge (Cyperus esculentus L.) tuber oil as a fuel. Ind. Crops Prod. 1996, 5, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, L.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liang, L. Effect of temperature, calcium and protein concentration on aggregation of whey protein isolate: Formation of gel-like micro-particles. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 51, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Sun, Q.-Q.; Vermeir, L.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R.; Van der Meeren, P. pH and protein to polysaccharide ratio control the structural properties and viscoelastic network of HIPE-templated biopolymeric oleogels. Food Struct.-Neth. 2019, 21, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Van der Meeren, P.; Patel, A. Oleogels from Emulsion (HIPE) Templates Stabilized by Protein—Polysaccharide Complexes. In Edible Oil Structuring: Concepts, Methods and Applications; Royal Society Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Q.; Ni, X. Edible Oleogels Fabricated by Dispersing Cellulose Particles in Oil Phase: Effects from the Water Addition. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Peng, S.; Chen, J.; Zou, L.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, W. Utilization of polysaccharide-based high internal phase emulsion for nutraceutical encapsulation: Enhancement of carotenoid loading capacity and stability. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 84, 104601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, H.; Kong, B. High internal phase emulsions stabilized by pea protein isolate modified by ultrasound and pH-shifting: Effect of chitosan self-assembled particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Macro-micro structure characterization and molecular properties of emulsion-templated polysaccharide oleogels. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascuas, S.; Espert, M.; Llorca, E.; Quiles, A.; Salvador, A.; Hernando, I. Structural and sensory studies on chocolate spreads with hydrocolloid-based oleogels as a fat alternative. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 135, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polavarapu, S.; Oliver, C.M.; Ajlouni, S.; Augustin, M.A. Physicochemical characterisation and oxidative stability of fish oil and fish oil-extra virgin olive oil microencapsulated by sugar beet pectin. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, X. Thermoresponsive structured emulsions based on the fibrillar self-assembly of natural saponin glycyrrhizic acid. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, C.; Jiang, C.; Liao, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhao, Q. Complexation with whey protein fibrils and chitosan: A potential vehicle for curcumin with improved aqueous dispersion stability and enhanced antioxidant activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Geng, S.; Mo, H.; Liu, B. Fabrication of food-grade Pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by the mixture of β-cyclodextrin and sugar beet pectin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Dai, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Peng, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Preparation of high thermal stability gelatin emulsion and its application in 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.-M.; Murray, B.S.; Sarkar, A. Tribology and rheology of water-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein microgels. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, A.-Q.; Xu, X.-B.; Guo, Y.; Du, M.; Yu, C.-P.; Wu, C. Fabrication of flavour oil high internal phase emulsions by casein/pectin hybrid particles: 3D printing performance. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Gao, H.; McClements, D.J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J.; Zou, L. Stability, rheology, and β-carotene bioaccessibility of high internal phase emulsion gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, I.; Patel, A.R.; Van der Meeren, P.; Dewettinck, K. Emulsion-templated liquid oil structuring with soy protein and soy protein: Kappa-carrageenan complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Salting-out and salting-in: Competitive effects of salt on the aggregation behavior of soy protein particles and their emulsifying properties. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 5926–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Cludts, N.; Lewille, B.; De Vos, W.H.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Biopolymer-Based Structuring of Liquid Oil into Soft Solids and Oleogels Using Water-Continuous Emulsions as Templates. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.R.; Dewettinck, K. Comparative evaluation of structured oil systems: Shellac oleogel, HPMC oleogel, and HIPE gel. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 1772–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Qian, Z.; Cheng, H.; Shen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. Xanthan gum-assisted fabrication of stable emulsion-based oleogel structured with gelatin and proanthocyanidins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.I.; Marangoni, A.G. The Use of Cooling Rate to Engineer the Microstructure and Oil Binding Capacity of Wax Crystal Networks. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazza, A.; Corti, S.; Mancinelli, C.; Bignardi, C.; Corradini, C. Effect of the Addition of Chili Pepper Powder on Vegetable Oils Oxidative Stability. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabolova, M.; Johanidesova, A.; Hasalikova, E.; Fisnar, J.; Dolezal, M.; Reblova, Z. Relationship between the composition of fats and oils and their oxidative stability at different temperatures, determined using the Oxipres apparatus. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Qi, K.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Physical Properties, Microstructure, Intermolecular Forces, and Oxidation Stability of Soybean Oil Oleogels Structured by Different Cellulose Ethers. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Pieve, S.; Calligaris, S.; Panozzo, A.; Arrighetti, G.; Nicoli, M.C. Effect of monoglyceride organogel structure on cod liver oil stability. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2978–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.; Min, D.B. Mechanisms and Factors for Edible Oil Oxidation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2006, 5, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapiste, G.H.; Brevedan, M.I.V.; Carelli, A.A. Oxidation of sunflower oil during storage. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskan, M.; Karataş, Ş. Fatty acid oxidation of pistachio nuts stored under various atmospheric conditions and different temperatures. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 77, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadán, A.; Álvarez-Ortí, M.; Pardo, J.E.; Alvarruiz, A. Storage stability and composition changes of three cold-pressed nut oils under refrigeration and room temperature conditions. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.K.; Singh, M.; Roy, S.; Ansari, M.N.; Saeedan, A.S.; Kaithwas, G. Modulation of oxidative stress response by flaxseed oil: Role of lipid peroxidation and underlying mechanisms. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018, 135, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazer, B. Macro peroxide initiators based on autoxidized unsaturated plant oils: Block/graft copolymer conjugates for nanotechnology and biomedical applications. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Fatty Acid | Tiger Nut Oil | Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oleogel | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 (1 Day) | D30 (30 Day) | D1 (1 Day) | D30 (30 Day) | |
| Tetradecanoic acid (C14:0) | 0.0 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a |
| Cetylic acid (C16:0) | 12.39 ± 0.07 a | 12.15 ± 0.20 a | 12.30 ± 0.10 a | 12.27 ± 0.83 a |
| Octadecanoic acid (C18:0) | 1.96 ± 0.07 b | 1.74 ± 0.20 bc | 1.93 ± 0.11 a | 1.79 ± 0.11 c |
| Oleinic acid (C18:1) | 73.99 ± 0.60 b | 71.11 ± 0.80 b | 73.30 ± 0.19 a | 73.19 ± 0.15 c |
| Linoleic acid (C18:2) | 10.87 ± 0.24 b | 10.31 ± 0.16 b | 10.56 ± 0.13 c | 10.54 ± 0.30 a |
| Linolenic acid (C18:3) | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 c | 0.15 ± 0.04 a | 0.13 ± 0.04 bc |
| Arachidic acid (C20:0) | 0.34 ± 0.05 a | 0.20 ± 0.06 a | 0.35 ± 0.04 a | 0.30 ± 0.09 a |
| Peanut monoenic acid (C20:1) | 0.17 ± 0.02 a | 0.10 ± 0.02 a | 0.16 ± 0.05 a | 0.14 ± 0.06 a |
| Behenic acid (C22:0) | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.08 ± 0.03 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.10 ± 0.02 b |
| Saturated fatty acid (SFA) | 14.76 ± 0.06 b | 15.86 ± 0.32 b | 14.68 ± 0.04 a | 15.59 ± 0.72 ab |
| Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) | 74.17 ± 0.58 b | 70.30 ± 0.80 b | 74.50 ± 0.23 a | 72.44 ± 0.20 c |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) | 11.03 ± 0.26 b | 10.0 ± 0.16 b | 10.78 ± 0.15 c | 10.47 ± 0.34 a |
| Unsaturated fatty acid (UFA) | 85.20 ± 0.32 a | 80.11 ± 0.85 a | 84.35 ± 0.10 b | 83.06 ± 0.51 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Xin, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; Fan, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, D. Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oil Gel: Preparation, Characterization, and Storage Stability. Foods 2023, 12, 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224087
Zhang S, Xin M, Wang Z, Dong X, Yang C, Liu H, Fan H, Liu T, Wang D. Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oil Gel: Preparation, Characterization, and Storage Stability. Foods. 2023; 12(22):4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224087
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shanshan, Minghang Xin, Zhiyu Wang, Xiaolan Dong, Chenhe Yang, Hongcheng Liu, Hongxiu Fan, Tingting Liu, and Dawei Wang. 2023. "Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oil Gel: Preparation, Characterization, and Storage Stability" Foods 12, no. 22: 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224087
APA StyleZhang, S., Xin, M., Wang, Z., Dong, X., Yang, C., Liu, H., Fan, H., Liu, T., & Wang, D. (2023). Tiger Nut Oil-Based Oil Gel: Preparation, Characterization, and Storage Stability. Foods, 12(22), 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12224087