Characteristic Profile of the Hazardous, Nutritional, and Taste-Contributing Compounds during the Growth of Argopecten irradians with Different Shell Colors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Pretreatment
2.4. Methods of Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
samples/ mg of EAA in 1 g of protein of (FAO/WHO) reference pattern × 100
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Seawater Environment
3.2. Biometric Measurements
3.3. Microbial and Chemical Hazards
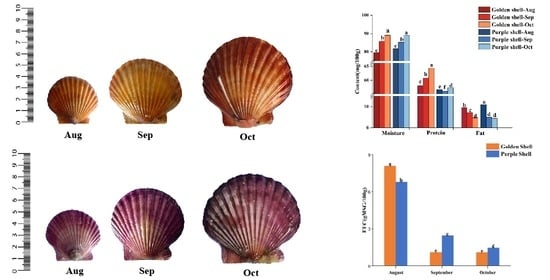
3.4. Proximate Composition
3.5. Hydrolyzed Amino Acid
3.6. Fatty Acid Content
3.7. Vitamin and Mineral Content
3.8. Taste-Contributing Compounds and Taste Activity Value
3.9. Correlation Analysis of Seawater Environment, Biometric Measurements, Nutrition Compounds, and Taste-Contributing Compounds in Bay Scallop
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NSPRC, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs Fishery Administration. National Aquatic Technology Extension Station, Chinese Society of Fisheries. In Proceedings of the 2022 Chinese Fishery Statistics Yearbook, Beijing, China, 22 February 2023; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.P.; Sun, H.L.; Fang, J.G. The present status, some problems and developing countermeasures in the cultivation of bay scallop in China. Mar. Fish. Res. 2000, 3, 77–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.Q.; Wan, Y.M.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, J. Changes in nutrient compositions and biochemical characteristics of bay scallop Argopecten irradians during keep-alive under free water at low temperature. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2014, 29, 633–637. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Milke, L.M.; Bricelj, V.M.; Parrish, C.C. Comparison of early life history stages of the bay scallop, Argopecten irradians: Effects of microalgal diets on growth and biochemical composition. Aquaculture 2006, 260, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.F.; Li, W.S. The Nutrients Analysis and Evaluation of Argopectens irradias. Acta Nutr. Sin. 2011, 33, 630–632. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.R.; Li, T.W.; Ding, M.J. Study on the nutritive content of scallop. Mar. Sci. 1997, 5, 10–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.P.; Zhang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Que, H.Y. Establishment of different shell color lines of bay scallop argopecten irradians Lamarck (1819)and their development. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2003, 6, 632–639. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Huang, H.; Yang, N.; Wu, D.P.; Yang, R.; Zhang, X. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Components in Edible Part of Chlamys nobilis. Food Ind. 2015, 36, 279–282. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.R.; Peng, J.X.; Zhao, X.N.; Wu, H.Y.; Zheng, G.C.; Zhao, Y.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Sheng, X.F.; Guo, M.M.; Tan, Z.J. Quality and safety profiles of Chlamys farreri cultured in the Shandong peninsula: Analysis of nutritional content, flavor, and hazards. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 118, 105193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Jiang, Z.J.; Wang, W.; Zou, J.; Xue, S.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.J.; Zhou, Y.M. Seasonal distribution and variation of nutrients and nutrients limitation in SanggouBay. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2010, 31, 16–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.X.; Li, S.J.; Li, X.L.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.L.; Cui, L.B. Self-pollution of Argopecten irradians culture effects on the ecological environment of aquaculture area. J. Fish. Res. 2018, 40, 324–328. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standards of China. National Food Safety Standard—Limits of Contaminants in Food GB 2762-2022. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2022. (In Chinese)
- GB 5009.265-2021; National Food Safety Standards of China. Food-Determination of Indicative Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon GB 5009.265-2021. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese)
- Wang, H. Comparative Studies on Product Quality of Scallop Cultured in Northern China Sea; The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.Y.; Zhang, B. Comparative Nutrition Components in Various Populations of Chlamys farreri. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 4073–4075. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, W.C.; Kim, H.C.; Kang, C.K. Gross biochemical and isotopic analyses of nutrition-allocation strategies for somatic growth and reproduction in the bay scallop Argopecten irradians newly introduced into Korean waters. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelin, C.; Kellner, K.; Mathieu, M. Storage metabolism in the Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) in relation to summer mortalities and reproductive cycle (West Coast of France). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 125, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.S.; He, Y.C.; Liu, X.S.; Ma, J.H.; Li, S.Y.; Qi, L.X. A report on the introduction, spat-rearing and experimental culture of bay sallop, Argopecten irradians Lamarck. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 1986, 5, 367–374. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Yu, H.H.; Xu, W.J.; He, J. Analysis of edible rate and nutritional quality of Scylla paramamosain with different degrees of ovarian plumpness. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tao, N.P.; Wu, X.G.; Wang, X.C.; Qiu, W.Q.; Ma, M.J. Comparison of flavour qualities of three sourced Eriocheir sinensis. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Zhang, M.; Shrestha, S. Compositional characteristics and nutritional quality of Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1343–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.T.; Wu, K. Nutritional evaluation of protein-Ratio coefficient of amino acid. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 1988, 2, 187–190. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kimata, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Kamada, T. Studies on relationship between sensory evaluation and chemical composition in various breed of pork. Jpn. J. Swine Sci. 2001, 38, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, M.; Türeli, C.; Çelik, M.; Yanar, Y.; Erdem, Ü.; Küçükgülmez, A. Fatty acid composition of the blue crab (Callinectes sapidus Rathbun, 1896) in the north eastern Mediterranean. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, M.; Soranna, D.; Catapano, A.L.; Corrao, G. Long-term effect of high dose omega-3 fatty acid supplementation for secondary prevention of cardiovascular outcomes: A meta-analysis of randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trials. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2013, 14, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Hu, X.P.; Zhou, D.Y.; Tan, Z.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Xie, H.K.; Rakariyatham, K.; Shahidi, F. Seasonal variation of proximate composition and lipid nutritional value of two species of scallops (Chlamys farreri and Patinopecten yessoensis). Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, V.; Turco, V.L.; Licata, P.; Panayotova, V.; Peycheva, K.; Fazio, F.; Rando, R.; Di Bella, G.; Potortì, A.G. Determination of Fatty Acid Profile in Processed Fish and Shellfish Foods. Foods 2023, 12, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krešić, G.; Koprivnjak, O.; Lešić, T.; Jurković, M.; Sokolić, D.; Gross-Bošković, A.; Branežac, K.; Pleadin, J. Consumption of canned oily fish as a source of fatty acids. Riv. Ital. Delle Sostanze Grasse 2017, 94, 239–249. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Silva, J.; Bessa, R.; Santos-Silva, F. Effect of genotype, feeding system and slaughter weight on the quality of light lambs: II. Fatty acid composition of meat. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2002, 77, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.G.; Cheng, Y.X.; Sui, L.Y.; Yang, X.Z.; Nan, T.Z.; Wang, J.Q. Biochemical composition of pond-reared and lake-stocked Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis (H. Milne-Edwards) broodstock. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.C.; Fan, Y.; Baker, G.L. Nutritional value and food safety of bivalve molluscan shellfish. J. Shellfish. Res. 2018, 37, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V.; Gopakumar, K. Shellfish: Nutritive value, health benefits, and consumer safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1219–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X. China Food Composition Tables Standard Edition, 6th ed.; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Nędzarek, A.; Czerniejewski, P. The edible tissues of the major European population of the invasive Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in the Elbe River, Germany, as a valuable and safe complement in essential elements to the human diet. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śmietana, N.; Panicz, R.; Sobczak, M.; Nędzarek, A.; Śmietana, P. Variability of elements and nutritional value of spiny-cheek crayfish (Faxonius limosus, Rafinesque, 1817): Variability of elements and nutritional value of F. limosus. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 94, 103656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Nutrient compositions and properties of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) muscle and processing by-products. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Kong, L. Biochemical Composition and Nutritional Value of Different Shell Color Strains of Pacific Oyster Crassostrea gigas. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2018, 17, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Okiyama, A.; Ueda, Y. Taste enhancements between various amino acids and IMP. Chem. Senses 2002, 27, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konosu, S.; Watanabe, K.; Koriyama, T.; Shirai, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Extractive Components of Scallop and Identification of its Taste-Active Components by Omission Test Taste-Active Components of Scall op Part I. Nippon. Shokuhin Kogyo Gakkaishi 1988, 35, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, N.M. Pathologies of the CNS and associated taurine changes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1992, 315, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Lan, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Konosu, S. Taste-active components of scallop, 2: Role of extractive components of scallop in its characteristic taste development. J. Jpn. Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 1990, 37, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuke, S.; Ueda, Y. Interactions between umami and other flavor characteristics. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuke, S.; Konosu, S. Taste-active components in some foods: A review of Japanese research. Physiol. Behav. 1991, 49, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, F.; Sun, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Xue, C. Evaluation indicators of Ruditapes philippinarum nutritional quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, W.D.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.C.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.H.; Lin, S.S.; Yu, Z.A.; Bao, X.B.; Li, S.L.; et al. Effects of Temperature and Size on Air Exposure Tolerance in Juvenile Japanese Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Fish. Sci. 2018, 37, 464–468. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Zhang, X.K.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, X.S.; Zhang, X.T. Study on Queen Scallop Growth Factor. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 4054–4056. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.M.; Jeong, W.G. Spawning impact on lysosomal stability of the Pacific Oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 2005, 244, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, B.J.; Qu, K.M.; Guo, F.; Li, Q.F.; Cui, Y. Study on adaptability of scallop Chlamys farreri to environment-Effects of salinity and pH on suvival respiration ingestion and digestion. J. Fish. Sci. China 2000, 4, 73–77. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Golden, C.D.; Koehn, J.Z.; Shepon, A.; Passarelli, S.; Free, C.M.; Viana, D.F.; Matthey, H.; Eurich, J.G.; Gephart, J.A.; Fluet-Chouinard, E.; et al. Aquatic foods to nourish nations. Nature 2021, 598, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Determination of Moisture in Food GB 5009.3-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.6-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. National Food Safety Standards-determination of Fat in Food GB 5009.6-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.5-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Determination of Protein in Food GB 5009.5-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.168-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. National Food Safety Standards-determination of Fatty Acid in Food GB 5009.168-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.124-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Determination of Amino Acids in Food GB 5009.124-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee And National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.268-2016; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2016. Determination of Multi elements in Food GB 5009.268-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.93-2007; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China, 2007. National Standards for the Determination of Se in food GB 5009.93-2007. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Lin, D.Z.; Diao, J.Y.; Lei, C.Y.; Yue, M.; Sun, Z.H.; Zang, Z. Simultaneous detection of serum levels of 19 vitamins based on LC-MS/MS. J. Guangdong Med. Univ. 2020, 38, 400–406. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Cui, F.Y.; Bie, W.; Feng, X.; Liang, N.N.; Zhang, Z.H. Simultaneous determination of 5 kinds of fat-soluble vitamins in infant formula milk powder by stable isotope dilution/liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2018, 9, 6130–6139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, J.; Han, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Regional differences in fatty acid composition of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) and scallop (Patinopecten yesoensis) in the coastal areas of China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 31, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.L.; Ayed, C.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, Y. Sensory-guided analysis of key taste active compounds in pufferfish (Takifugu obscurus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13809–13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, P.; Hellín, P.; Fenoll, J. Determination of organic acids in fruits and vegetables by liquid chromatography with tandem-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 4789.38-2012; National Food Safety Standards of China, 2012. Food Microbiology test Escherichia coli Count GB 4789.38-2012. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB 4789.7-2013; National Food Safety Standards of China, 2013. Food Microbiology Test Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Test GB 4789.7-2013. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Guo, M.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Yang, F.; Tan, Z.J.; Li, Z.X.; Zhai, Y.X. Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fishery products by improved QuEChERS-high performance liquid chromatography. Environ. Chem. 2013, 32, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- GB 5009.190-2014; National Food Safety Standards of China, 2014. Food-Determination of indicative polychlorinated biphenyls GB 5009.190-2014. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2014.
- GB 5009.213-2016; National Food Safety Standards of China, 2016. Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish GB 5009.213-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.212-2016; National Food Safety Standards of China, 2016. Determination of Diarrhoeal Shellfish Toxin in Shellfish GB 5009.212-2016. Health and Family Planning Committee and National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2016.







| Index | Golden Shell | Purple Shell | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| August | September | October | August | September | October | |
| Shell length (mm) | 35.2 ± 0.2 f | 50.5 ± 0.6 d | 67.2 ± 0.2 b | 38.3 ± 0.3 e | 54.3 ± 0.3 c | 68.3 ± 0.3 a |
| Shell height (mm) | 39.2 ± 0.2 f | 51.3 ± 0.4 c | 62.5 ± 0.5 a | 40.2 ± 0.2 e | 50.4 ± 0.5 d | 60.7 ± 0.6 b |
| Shell width (mm) | 14.1 ± 0.1 d | 20.5 ± 0.5 b | 25.2 ± 0.2 a | 18.1 ± 0.6 c | 21.1 ± 0.2 ab | 21.4 ± 0.5 a |
| Total weight (g) | 7.64 ± 0.06 d | 17.44 ± 0.49 c | 29.26 ± 0.18 a | 8.22 ± 0.18 d | 19.06 ± 0.51 b | 28.75 ± 0.28 a |
| Soft tissue weight (g) | 3.52 ± 0.08 d | 7.64 ± 0.20 c | 14.32 ± 0.29 a | 3.92 ± 0.10 d | 8.76 ± 0.30 b | 14.56 ± 0.44 a |
| Dressing percentage (%) | 46.03 ± 0.68 bc | 43.83 ± 1.49 bc | 48.95 ± 1.28 ab | 47.73 ± 0.84 ab | 45.98 ± 2.58 bc | 50.64 ± 1.92 a |
| RC | Golden Shell | Purple Shell | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| August | September | October | August | September | October | |
| Isoleucine | 1.02 | 1.06 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
| Leucine | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.93 | 0.9 |
| Lysine | 1.49 | 1.43 | 1.29 | 1.49 | 1.48 | 1.42 |
| Methionine | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.71 |
| Phenylalanine + Tyrosine | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.11 | 0.99 | 1.01 |
| Threonine | 1.25 | 1.32 | 1.18 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.22 |
| Valine | 0.66 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.65 |
| SRC (%) | 95.81 | 95.83 | 92.33 | 98.21 | 92.66 | 95.32 |
| EAAI | 46.47 | 47.05 | 44.24 | 44.86 | 48.07 | 46.88 |
| Index | RNI | INQ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Golden Shell | Purple Shell | ||||||
| August | September | October | August | September | October | ||
| Vitamin A * (µg/100 g) | 800 | 1.15 | 0.69 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 0.82 |
| Vitamin D * (µg/100 g) | 10 | 6.33 | 7.38 | 17.82 | 5.16 | 9.45 | 16.40 |
| Vitamin E * (mg/100 g) | 14 # | 0.65 | 0.56 | 1.60 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.72 |
| Vitamin B1 * (mg/100 g) | 1.4 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.1 |
| Vitamin B2 * (mg/100 g) | 1.4 | 2.54 | 2.58 | 0.53 | 3.77 | 2.26 | 0.88 |
| Vitamin B6 * (mg/100 g) | 1.4 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| Vitamin B12 * (µg/100 g) | 2.4 | 18.20 | 23.13 | 13.98 | 21.27 | 21.66 | 16.98 |
| Vitamin B5 * (mg/100 g) | 5 # | 1.09 | 0.35 | 0.67 | 0.96 | 0.2 | 0.66 |
| Vitamin B3 * (mg/100 g) | 15 | 1.39 | 0.59 | 0.3 | 1.22 | 0.67 | 0.51 |
| Ca (mg/100 g) | 800 | 4.92 | 7.88 | 7.24 | 5.95 | 6.83 | 6.94 |
| P (mg/100 g) | 720 | 8.93 | 5.58 | 7.39 | 8.18 | 14.64 | 7.51 |
| K (mg/100 g) | 2000 # | 5.3 | 5.05 | 5.3 | 5.41 | 6.26 | 4.81 |
| Mg (mg/100 g) | 330 | 2.26 | 4.17 | 2.03 | 1.92 | 2.38 | 1.83 |
| Fe (mg/100 g) | 12 | 9.37 | 23.11 | 10.72 | 6.84 | 12.87 | 5.58 |
| Zn (mg/100 g) | 12.5 | 36.56 | 53.22 | 76.4 | 43.72 | 31.41 | 49.68 |
| Se (µg/100 g) | 60 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Cu (mg/100 g) | 0.80 | 48.90 | 65.62 | 51.93 | 53.57 | 50.19 | 34.96 |
| Mn (mg/100 g) | 4.5 # | 3.90 | 5.29 | 2.35 | 2.80 | 4.28 | 2.44 |
| Compound | Taste Attribute | Golden Shell | Purple Shell | Taste Threshold (mg/100 mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| August | September | October | August | September | October | |||
| Glutamic Acid | Umami (+) | 7.89 | 2.46 | 3.39 | 8.01 | 3.52 | 3.14 | 30.00 |
| Aspartic Acid | Umami (+) | 1.31 | 0.55 | 0.45 | 0.99 | 0.24 | 0.45 | 100.00 |
| Glycine | Sweet (+) | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.64 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 130.00 |
| Alanine | Sweet (+) | 1.94 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 1.84 | 1.20 | 0.86 | 60.00 |
| Serine | Sweet (+) | 0.30 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.16 | 150.00 |
| * Threonine | Sweet (+) | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 260.00 |
| Proline | Sweet/bitter (+) | 0.45 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 300.00 |
| Arginine | Bitter/Sweet (+) | 0.53 | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 1.37 | 0.21 | 50.00 |
| Methionine * | Bitter/Sweet/sulfurous (−) | 0.58 | 0.16 | 0.23 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 30.00 |
| Histidine | Bitter (−) | 1.88 | 0.18 | 0.62 | 1.71 | 0.25 | 0.85 | 20.00 |
| * Leucine | Bitter (−) | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 190.00 |
| * Isoleucine | Bitter (−) | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 90.00 |
| * Phenylalanine | Bitter (−) | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 90.00 |
| * Valine | Sweet/bitter (−) | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 40.00 |
| * Lysine | Sweet/bitter (−) | 0.25 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.13 | 50.00 |
| IMP | Umami (+) | 0.79 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.69 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 25.00 |
| AMP | Umami/Sweet (+) | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.69 | 0.21 | 50.00 |
| GMP | Umami (+) | 0.14 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.13 | 12.5 |
| Succinic | Sour/umami | 6.95 | 3.18 | 4.60 | 4.54 | 1.41 | 4.60 | 10.6 |
| Malic | Sour/bitter | 0.43 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 49.6 |
| Citric | Sour | 0.56 | 0.44 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.45 | 45 |
| Tartaric | Sour | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.36 | 0.48 | 0.50 | 0.33 | 1.5 |
| Betaine | Sweet | 5.07 | 1.76 | 1.79 | 2.28 | 1.60 | 3.55 | 250 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Peng, J.; Zhao, X.; Lin, Y.; Song, D.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, H.; Geng, Q.; Zheng, G.; et al. Characteristic Profile of the Hazardous, Nutritional, and Taste-Contributing Compounds during the Growth of Argopecten irradians with Different Shell Colors. Foods 2023, 12, 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234354
Wang T, Peng J, Zhao X, Lin Y, Song D, Zhao Y, Jiang Y, Wu H, Geng Q, Zheng G, et al. Characteristic Profile of the Hazardous, Nutritional, and Taste-Contributing Compounds during the Growth of Argopecten irradians with Different Shell Colors. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234354
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Teng, Jixing Peng, Xinnan Zhao, Yichen Lin, Dongru Song, Yanfang Zhao, Yanhua Jiang, Haiyan Wu, Qianqian Geng, Guanchao Zheng, and et al. 2023. "Characteristic Profile of the Hazardous, Nutritional, and Taste-Contributing Compounds during the Growth of Argopecten irradians with Different Shell Colors" Foods 12, no. 23: 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234354
APA StyleWang, T., Peng, J., Zhao, X., Lin, Y., Song, D., Zhao, Y., Jiang, Y., Wu, H., Geng, Q., Zheng, G., Guo, M., & Tan, Z. (2023). Characteristic Profile of the Hazardous, Nutritional, and Taste-Contributing Compounds during the Growth of Argopecten irradians with Different Shell Colors. Foods, 12(23), 4354. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234354