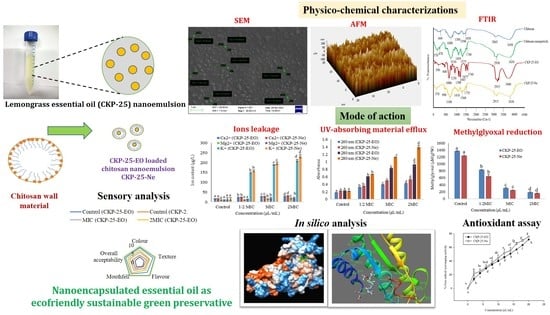
Encapsulation of Cymbopogon khasiana × Cymbopogon pendulus Essential Oil (CKP-25) in Chitosan Nanoemulsion as a Green and Novel Strategy for Mitigation of Fungal Association and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Food System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Test Fungal Strain
2.3. Extraction of Lemongrass (CKP-25) Essential Oil
2.4. Chemical Characterization of CKP-25-EO
2.5. Synthesis of CKP-25-EO Loaded Chitosan Nanoemulsion (CKP-25-Ne)
2.6. Measurement of Efficiency to Load and Encapsulate CKP-25-EO
2.7. Characterization of CKP-25-Ne
2.7.1. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.7.2. Morphological Characterization
2.7.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Analysis
2.7.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Evaluation
2.7.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Observation
2.8. Release Profile of CKP-25-Ne
2.9. Antifungal and AFB1 Inhibitory Efficacy of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne
2.10. Determination of Fungitoxic Spectrum of CKP-25- EO and CKP-25-Ne
2.11. Action Mode Related to CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne
2.11.1. Effect of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne on Ergosterol
2.11.2. Effect of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne on Cellular Constituents Leakage
2.11.3. Effect of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne on Cellular Methylglyoxal (AFB1 Inducer)
2.11.4. Molecular Docking of Citral (Major Component of CKP-25-EO) with Nor-1 and Pks-A Proteins of AFB1 Secretion
2.12. Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Content of CKP-25 and CKP-25-Ne
2.12.1. DPPH·+ Assay
2.12.2. ABTS·+ Assay
2.12.3. Total Phenolic Content Estimation
2.13. In Situ Antifungal and Anti-AFB1 Efficacy of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne in Stored S. cumini Seeds (The Model Anti-Diabetic Food System)
2.14. Effect of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne on Lipid Peroxidation of Stored S. cumini Seed
2.15. Sensory Analysis of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne Fumigated S. cumini Seeds
2.16. Safety Profile Test of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne in Mice
2.17. Analysis of Statistical Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Characterization of CKP-25-EO by GC-MS Analysis
3.2. Preparation of CKP-25-EO Loaded Chitosan Nanoemulsion (CKP-25-Ne)
3.3. Measurement of Efficiency to Load and Encapsulate CKP-25-EO
3.4. Physico-Chemical Characterization of CKP-25-Ne
3.4.1. Zeta Sizer Study
3.4.2. SEM Analysis
3.4.3. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) Analysis
3.4.4. FTIR Analysis
3.4.5. XRD Analysis
3.5. Release Characteristics of CKP-25-EO
3.6. Antifungal and AFB1 Suppressing Potentiality of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne
3.7. Fungitoxic Spectrum of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne
3.8. Action Mode Related to Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activity
3.9. In Silico Modeling of Citral with Nor-1 and Pks-A Proteins of AFB1 Biosynthesis
3.10. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic Content of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne
3.11. In Situ Antifungal and Anti-AFB1 Efficacy of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne in Stored S. cumini Seeds
3.12. Impact of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne on Lipid Peroxidation in S. cumini Seeds
3.13. Sensory Evaluation of CKP-25-EO and CKP-25-Ne Fumigated S. cumini Seeds
3.14. Acute Oral Toxicity in Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayyanar, M.; Subash-Babu, P. Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels: A review of its phytochemical constituents and traditional uses. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Hasan, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Dhumal, S.; Nishad, J.; Rais, N.; Zhang, B. Jamun (Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels) seed bioactives and its biological activities: A review. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, J.; Das, S.; Maurya, A.; Jain, S.K.; Dwivedy, A.K. Synthesis, characterization and in situ bioefficacy evaluation of Cymbopogon nardus essential oil impregnated chitosan nanoemulsion against fungal infestation and aflatoxin B1 contamination in food system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X. Multi-component immunochromatographic assay for simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A and zearalenone in agro-food. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 49, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballo, D.; Tolosa, J.; Ferrer, E.; Berrada, H. Dietary exposure assessment to mycotoxins through total diet studies. A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 128, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Eugenol loaded chitosan nanoemulsion for food protection and inhibition of Aflatoxin B1 synthesizing genes based on molecular docking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 255, 117339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Das, S.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Cistus ladanifer L. essential oil as a plant based preservative against molds infesting oil seeds, aflatoxin B1 secretion, oxidative deterioration and methylglyoxal biosynthesis. LWT 2018, 92, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Huang, B.; Luo, X.; Zeng, H.; Ban, X.; He, J.; Wang, Y. The control of Aspergillus flavus with Cinnamomum jensenianum Hand.-Mazz essential oil and its potential use as a food preservative. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Insecticidal and fungicidal efficacy of essential oils and nanoencapsulation approaches for the development of next generation ecofriendly green preservatives for management of stored food commodities: An overview. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2021, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Barkauskaite, S.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Essential oils as additives in active food packaging. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M. Introduction to the special issue: Application of essential oils in food systems. Foods 2018, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, C.; Bouquillon, S.; Fauconnier, M.L. Encapsulation of essential oils for the development of biosourced pesticides with controlled release: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R.; Ariaii, P.; Motamedzadegan, A. Characterization, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of chitosan nanoparticles loaded with nettle essential oil. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menossi, M.; Ollier, R.P.; Casalongué, C.A.; Alvarez, V.A. Essential oil-loaded bio-nanomaterials for sustainable agricultural applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, M.; Morsi, R.E.; Kerch, G.; Elsabee, M.Z.; Kaya, M.; Labidi, J.; Khawar, K.M. Current advancements in chitosan-based film production for food technology; A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande-Tovar, C.D.; Chaves-López, C.; Serio, A.; Rossi, C.; Paparella, A. Chitosan coatings enriched with essential oils: Effects on fungi involved in fruit decay and mechanisms of action. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2018, 78, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H.; Jafari, S.M. Introducing nano/microencapsulated bioactive ingredients for extending the shelf-life of food products. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwan, N.; Yadav, U.; Sangwan, R. Molecular analysis of genetic diversity in elite Indian cultivars of essential oil trade types of aromatic grasses (Cymbopogon species). Plant Cell Rep. 2001, 20, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawadogo, I.; Paré, A.; Kaboré, D.; Montet, D.; Durand, N.; Bouajila, J.; Bassolé, I.H.N. Antifungal and antiaflatoxinogenic effects of Cymbopogon citratus, Cymbopogon nardus, and Cymbopogon schoenanthus essential oils alone and in combination. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoksan, R.; Jirawutthiwongchai, J.; Arpo, K. Encapsulation of ascorbyl palmitate in chitosan nanoparticles by oil-in-water emulsion and ionic gelation processes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasheminejad, N.; Khodaiyan, F.; Safari, M. Improving the antifungal activity of clove essential oil encapsulated by chitosan nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Upadhyay, N.; Singh, P.; Dubey, N.K. Encapsulation in chitosan-based nanomatrix as an efficient green technology to boost the antimicrobial, antioxidant and in situ efficacy of Coriandrum sativum essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Kumar Singh, V.; Kumar Dwivedy, A.; Kumar Chaudhari, A.; Upadhyay, N.; Singh, A.; Dubey, N.K. Assessment of chemically characterised Myristica fragrans essential oil against fungi contaminating stored scented rice and its mode of action as novel aflatoxin inhibitor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, G.A.; Sarhan, M.M.; Abu Shahla, A.N.K.; Abou El-Khair, E.K. Effects of Cymbopogon citratus L. essential oil on the growth, morphogenesis and aflatoxin production of Aspergillus flavus ML2-strain. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedy, A.K.; Prakash, B.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Bisht, D.; Dubey, N.K. Chemically characterized Mentha cardiaca L. essential oil as plant based preservative in view of efficacy against biodeteriorating fungi of dry fruits, aflatoxin secretion, lipid peroxidation and safety profile assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahar, S.; Hamdi, B.; Flamini, G.; Mehmet, Ö.; Duru, M.E.; Bruno, M.; Maggi, F. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anticholinesterase activity of the essential oil of algerian Cachrys sicula L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 4094–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheijooni-Fumani, N.; Hassan, J.; Yousefi, S.R. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in cereals by homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Anethum graveolens essential oil encapsulation in chitosan nanomatrix: Investigations on in vitro release behavior, organoleptic attributes, and efficacy as potential delivery vehicles against biodeterioration of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Food Bioproc. Technol. 2021, 14, 831–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, A.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Das, S.; Ramsdam, M.G.; Dubey, N.K. Assessment of chitosan biopolymer encapsulated α-Terpineol against fungal, aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and free radicals mediated deterioration of stored maize and possible mode of action. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Das, S.; Prasad, J.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Improvement of in vitro and in situ antifungal, AFB1 inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Origanum majorana L. essential oil through nanoemulsion and recommending as novel food preservative. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.S.; Singh, S.; Padalia, R.C.; Tandon, S.; Venkatesh, K.T.; Chauhan, A. Essential oil composition of the sub-aerial parts of eight species of Cymbopogon (Poaceae). Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 142, 111839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, A.; Prasad, J.; Das, S.; Dwivedy, A.K. Essential oils and their application in food safety. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 653420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.L. Essential oils: What they are and how the terms are used and defined. In Essential Oils in Food Preservation, Flavor and Safety; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Wang, B.J.; Weng, Y.M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial edible zein/chitosan composite films fabricated by incorporation of phenolic compounds and dicarboxylic acids. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Y.A.; Khedr, A.I.; Alkabli, J.; Elshaarawy, R.F.; Nasr, A.M. Co-delivery of imidazolium Zn (II) salen and Origanum Syriacum essential oil by shrimp chitosan nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheow, W.S.; Hadinoto, K. Enhancing encapsulation efficiency of highly water-soluble antibiotic in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles: Modifications of standard nanoparticle preparation methods. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 370, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woranuch, S.; Yoksan, R. Eugenol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles: II. Application in bio-based plastics for active packaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Hashemi, M. Emerging chitosan nanoparticles loading-system boosted the antibacterial activity of Cinnamomum zeylanicum essential oil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 155, 112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, S.; Ojagh, S.M.; Ghorbani, M. Nanoencapsulation of lemon essential oil in Chitosan-Hicap system. Part 1: Study on its physical and structural characteristics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.F.; Zandi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Two-step method for encapsulation of oregano essential oil in chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization and in vitro release study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Singh. V. K.; Chaudhari, A.K.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Dubey, N.K. Fabrication, physico-chemical characterization, and bioactivity evaluation of chitosan-linalool composite nano-matrix as innovative controlled release delivery system for food preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 188, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. The application of thymol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to control the biodeterioration of cultural heritage sites. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 53, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Mousakhani-Ganjeh, A.; Amiri, Z.; Guo, Y.G.; Singh, A.P.; Kenari, R.E. Fabrication of cumin loaded-chitosan particles: Characterized by molecular, morphological, thermal, antioxidant and anticancer properties as well as its utilization in food system. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhai, C.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, Q. Experimental study and thermodynamic evaluation of Mg–La–Zn system. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, S.B.; Amorim, M.; Fonte, P.; Madureira, R.; Ferreira, D.; Pintado, M.; Sarmento, B. Natural extracts into chitosan nanocarriers for rosmarinic acid drug delivery. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, A.; Asgari, A. In vitro release and biological activities of Carum copticum essential oil (CEO) loaded chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, B.; Singh, P.; Kedia, A.; Dubey, N.K. Assessment of some essential oils as food preservatives based on antifungal, antiaflatoxin, antioxidant activities and in vivo efficacy in food system. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 49, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donsì, F.; Annunziata, M.; Sessa, M.; Ferrari, G. Nanoencapsulation of essential oils to enhance their antimicrobial activity in foods. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ma, P.; Li, C.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Z.; Dong, J. Combining transcriptomics and metabolomics to reveal the underlying molecular mechanism of ergosterol biosynthesis during the fruiting process of Flammulina velutipes. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Xie, Y.; Yu, H.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Synergistic antifungal mechanism of thymol and salicylic acid on Fusarium solani. LWT 2021, 140, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yuan, K.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, C.; Du, L.; Liu, F. Mechanism of antifungal activity of Perilla frutescens essential oil against Aspergillus flavus by transcriptomic analysis. Food Control 2021, 123, 107703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, K.; Anandaraj, K.; Al-Sohaibani, S. Antiaflatoxigenic food additive potential of Murraya koenigii: An in vitro and molecular interaction study. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 52, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, H.; Kou, X.; Ma, C.; Zhu, S. The antioxidant, antibacterial, antibiofilm activity of essential oil from Citrus medica L. var. sarcodactylis and its nanoemulsion. LWT 2017, 80, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuidam, N.J.; Heinrich, E. Encapsulation of aroma. In Encapsulation Technologies for Active Food Ingredients and Food Processing; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 127–160. [Google Scholar]
- Shetta, A.; Kegere, J.; Mamdouh, W. Comparative study of encapsulated peppermint and green tea essential oils in chitosan nanoparticles: Encapsulation, thermal stability, in-vitro release, antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, K.G.H.; Jin Park, H. Recent developments in microencapsulation of food ingredients. Dry. Technol. 2005, 23, 1361–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Çoban, Ö.E. Essential oils for antimicrobial and antioxidant applications in fish and other seafood products. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2017, 68, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.B.; Lei, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, W.J.; Liu, D.Y. Encapsulation of Zanthoxylum bungeanum essential oil to enhance flavor stability and inhibit lipid oxidation of Chinese-style sausage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 4035–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimifar, P.; Saei-Dehkordi, S.S.; Izadi, Z. Antibacterial, antioxidative and sensory properties of Ziziphora clinopodioides–Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil nanoencapsulated using sodium alginate in raw lamb burger patties. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, P. A Comprehensive Guide to the Hazardous Properties of Chemical Substances; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]




| S. No. | RT (min) | % Area | Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.283 | 2.45 | 5-Heptene-2-one, 6-methyl- |
| 2 | 7.392 | 1.74 | β-Myrcene |
| 3 | 8.131 | 7.80 | D-Limonene |
| 4 | 9.251 | 1.21 | Linalool |
| 5 | 10.090 | 0.95 | Citronellal |
| 6 | 10.228 | 75.67 | Citral |
| 7 | 11.581 | 1.64 | Geraniol |
| 8 | 13.354 Total | 6.21 97.66 | Geranyl acetate |
| S.N. | Chitosan: CKP-25-EO (w/v) | Encapsulation Efficiency (%) | Loading Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.000 a |
| 2 | 1:0.2 | 33.80 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.34 b |
| 3 | 1:0.4 | 44.68 ± 0.23 c | 0.59 ± 0.65 c |
| 4 | 1:0.6 | 53.07 ± 0.10 d | 1.05 ± 0.09 d |
| 5 | 1:0.8 | 83.15 ± 0.34 e | 2.21 ± 0.78 e |
| 6 | 1:1 | 65.88 ± 0.21 f | 2.19 ± 0.12 f |
| Chitosan: CKP-25 EO Ratio (w/v) | Average Particle Size (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1: 0 (chitosan nanoemulsion) | 85.41± 7.07 a | ±41.03 ± 2.01 a | 0.176 ± 0.004 a |
| 1: 0.8 (CKP-25-Ne) | 103.56 ± 3.86 b | ±33.91 ± 1.99 b | 0.162 ± 0.009 b |
| CKP-25-EO | CKP-25-Ne | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conc. (µL/mL) | Mycelial Dry Weight (g) | AFB1 Content (µg/mL) | % Ergosterol Reduction | Conc. (µL/mL) | Mycelial Dry Weight (g) | AFB1 Content (µg/mL) | % Ergosterol Reduction |
| Control | 0.35 ± 0.008 a | 32.53 ± 0.083 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | Control | 0.25 ± 0.001 a | 26.43 ± 0.602 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.001 b | 27.00 ± 0.407 b | 21.32 ± 4.23 b | 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.008 b | 22.51 ± 0.071 b | 23.80 ± 2.15 b |
| 0.1 | 021 ± 0.002 c | 23.04 ± 0.903 c | 36.31 ± 5.39 c | 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.003 c | 19.17 ± 0.016 c | 38.31 ± 4.11 c |
| 0.15 | 0.18 ± 0.001 cd | 18.94 ± 1.048 d | 53.62 ± 3.08 d | 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.012 cd | 15.98 ± 0.708 d | 54.24 ± 7.87 d |
| 0.2 | 0.14 ± 0.006 de | 15.17 ± 1.009 e | 65.54 ± 3.20 de | 0.04 | 0.12 ± 0.008 de | 13.69 ± 0.805 d | 68.32 ± 3.08 e |
| 0.25 | 0.11 ± 0.001 ef | 11.40 ± 0.407 f | 76.66 ± 5.67 ef | 0.05 | 0.09 ± 0.003 ef | 10.25 ± 1.009 e | 79.36 ± 1.30 ef |
| 0.3 | 0.07 ± 0.008 fg | 7.39 ± 0.074 g | 84.46 ± 4.85 fg | 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.005 f | 7.06 ± 0.806 f | 83.77 ± 0.95 fg |
| 0.35 | 0.04 ± 0.005 gh | 0.00 ± 0.00 h | 94.18 ± 1.78 g | 0.07 | 0.03 ± 0.005 g | 0.00 ± 0.00 g | 95.18 ± 1.60 gh |
| 0.4 | 0.00 ± 0.00 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 h | 100 ± 0.00 g | 0.08 | 0.00 ± 0.00 h | 0.00 ± 0.00 g | 100 ± 0.00 h |
| Essential Oil Component | Receptor Protein | Hydrogen Bonding Amino Acids | Bond Length (Å) | Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citral | Nor-1 | ASN 28 | 2.61 | −6.21 |
| ALA 29 | 2.54 | −6.48 | ||
| Pks-A | ARG 159 | 2.60 | −6.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prasad, J.; Das, S.; Maurya, A.; Soni, M.; Yadav, A.; Singh, B.; Dwivedy, A.K. Encapsulation of Cymbopogon khasiana × Cymbopogon pendulus Essential Oil (CKP-25) in Chitosan Nanoemulsion as a Green and Novel Strategy for Mitigation of Fungal Association and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Food System. Foods 2023, 12, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040722
Prasad J, Das S, Maurya A, Soni M, Yadav A, Singh B, Dwivedy AK. Encapsulation of Cymbopogon khasiana × Cymbopogon pendulus Essential Oil (CKP-25) in Chitosan Nanoemulsion as a Green and Novel Strategy for Mitigation of Fungal Association and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Food System. Foods. 2023; 12(4):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040722
Chicago/Turabian StylePrasad, Jitendra, Somenath Das, Akash Maurya, Monisha Soni, Arati Yadav, Bikarma Singh, and Abhishek Kumar Dwivedy. 2023. "Encapsulation of Cymbopogon khasiana × Cymbopogon pendulus Essential Oil (CKP-25) in Chitosan Nanoemulsion as a Green and Novel Strategy for Mitigation of Fungal Association and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Food System" Foods 12, no. 4: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040722
APA StylePrasad, J., Das, S., Maurya, A., Soni, M., Yadav, A., Singh, B., & Dwivedy, A. K. (2023). Encapsulation of Cymbopogon khasiana × Cymbopogon pendulus Essential Oil (CKP-25) in Chitosan Nanoemulsion as a Green and Novel Strategy for Mitigation of Fungal Association and Aflatoxin B1 Contamination in Food System. Foods, 12(4), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040722