Proximate Compositions, Texture, and Sensory Profiles of Gluten-Free Bario Rice Bread Supplemented with Potato Starch
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
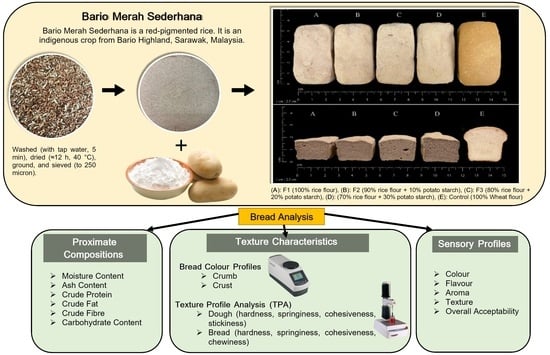
2.2.1. Dough and Bread Making
2.2.2. Bread Sample Preparation for Analysis
2.2.3. Proximate Analysis
2.2.4. Bread Colour Analysis
2.2.5. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
- Dough
- 2.
- Bread
2.2.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Analysis
3.1.1. Moisture Content
3.1.2. Crude Ash Content
3.1.3. Crude Protein Content
3.1.4. Crude Fat Content
3.1.5. Crude Fibre Content
3.1.6. Carbohydrate Content
3.2. Bread Colour Analysis
3.2.1. Crumb
3.2.2. Crust
3.3. Texture Profile Analysis for Dough and Bread
3.3.1. Hardness
3.3.2. Springiness
3.3.3. Cohesiveness
3.3.4. Stickiness
3.3.5. Chewiness
3.4. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortune Business Insight (Bakery Products Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Product Type (Bread, Cakes and Pastries, Biscuits and Cookies, and Other Bakery Products), Distribution Channel (Supermarkets/Hypermarkets, Specialty Stored, Convenience Stores and Others), and Regional Forecast, 2021–2028). Bakery Products Market Size, Analysis & Growth Report [2028]. Available online: fortunebusinessinsights.com (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Zdybel, B.; Różyło, R.; Sagan, A. Use of a waste product from the pressing of chia seed oil in wheat and gluten-free bread processing. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, J.L.; Lee, C.C.; Yang, C.W.; Chen, R.W.; Zhang, Q.F.; Lin, S.D. Physicochemical, antioxidant and sensory characteristics of bread partially substituted with aerial parts of sweet potato. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ms, V.Q.; Miss, M.S.; Miss, G.G.V.; Ms, P.J. Seaweeds in bakery and farinaceous foods: A mini-review. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 28, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coțovanu, I.; Stroe, S.G.; Ursachi, F.; Mironeasa, S. Addition of Amaranth Flour of Different Particle Sizes at Established Doses in Wheat Flour to Achieve a Nutritional Improved Wheat Bread. Foods 2023, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raczyk, M.; Kruszewski, B.; Zachariasz, E. Effect of tomato, beetroot and carrot juice addition on physicochemical, antioxidant and texture properties of wheat bread. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woomer, J.S.; Adedeji, A.A. Current applications of gluten-free grains–a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Zis, P. Neurological manifestations of gluten-related disorders. In Coeliac Disease and Gluten-Related Disorders, 1st ed.; Schieptti, A., Sanders, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 209–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sapone, A.; Bai, J.C.; Ciacci, C.; Dolinsek, J.; Green, P.H.; Hadjivassiliou, M.; Fasano, A. Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: Consensus on new nomenclature and classification. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guandalini, S.; Discepolo, V. Celiac disease. In Textbook of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Guandalini, S., Dhawan, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 525–548. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, M.M.; Sapone, A.; Catassi, C.; Fasano, A. Celiac disease and nonceliac gluten sensitivity: A review. JAMA 2017, 318, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, N.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Anderson, R.P.; Rostami, K. The gluten gene: Unlocking the understanding of gluten sensitivity and intolerance. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2021, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Rosell, C.; Matos, M.E. Market and nutrition issues of gluten-free foodstuff. In Advances in the Understanding of Gluten Related Pathology and the Evolution of Gluten-Free Foods, 1st ed.; Arranz, E., Fernandez-Banares, F., Rosell, C.M., Rodrigo, L., Pena, A.S., Eds.; OmniaScience: Madrid, Spain, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 565–604. [Google Scholar]
- Xhakollari, V.; Canavari, M.; Osman, M. Factors affecting consumers’ adherence to gluten-free diet, a systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Linter, B.R.; Linforth, R.; Foster, T.J. A comprehensive investigation of gluten free bread dough rheology, proving and baking performance and bread qualities by response surface design and principal component analysis. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5333–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigüenza-Andrés, T.; Gallego, C.; Gómez, M. Can cassava improve the quality of gluten free breads? J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizollahi, E.; Mirmoghtadaie, L.; Mohammadifar, M.A.; Jazaeri, S.; Hadaegh, H.; Nazari, B.; Lalegani, S. Sensory, digestion, and texture quality of commercial gluten-free bread: Impact of broken rice flour type. J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boeswetter, A.R.; Scherf, K.A.; Schieberle, P.; Koehler, P. Identification of the key aroma compounds in gluten-free rice bread. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masure, H.G.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Current and forward looking experimental approaches in gluten-free bread making research. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, L.; Belorio, M.; Gomez, M. Gluten-free breads: The gap between research and commercial reality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, S.; Yan, X.; Fu, Y.; Pang, M.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. The quality of gluten-free bread made of brown rice flour prepared by low temperature impact mill. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; McClements, D.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, C. Improvement in nutritional attributes of rice using superheated steam processing. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.B.; Bhattacharya, S. Characterization of the batter and gluten-free cake from extruded red rice flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 102, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Yeoh, T.K.; Wan-Nadiah, W.A.; Bhat, R. Quality evaluation of flat rice noodles (Kway Teow) prepared from Bario and Basmati rice. Sains Malays. 2014, 43, 339–347. Available online: http://journalarticle.ukm.my/6919/1/03_Rachel_Thomas.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Kevin, M.T.S.; Ahmed, O.H.; Asrina, W.Y.W.; Rajan, A.; Ahzam, M. Towards growing Bario rice on lowland soils: A preliminary nitrogen and potassium fertilization trial. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2007, 2, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronie, M.E.; Abdul Aziz, A.H.; Mohd Noor, N.Q.I.; Yahya, F.; Mamat, H. Characterisation of Bario Rice Flour Varieties: Nutritional Compositions and Physicochemical Properties. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, E.; Vogt, J.A.; Wolever, T.M. The effects of fat and protein on glycemic responses in nondiabetic humans vary with waist circumference, fasting plasma insulin, and dietary fiber intake. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2506–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yano, H.; Koda, T.; Fujita, N.; Nishioka, A. Effect of amylose content in rice flour on batter rheology and bread baking quality. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.; Laureati, M.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Erba, D.; Vezzani, M.; Lucisano, M.; Alamprese, C. Effects of red rice or buckwheat addition on nutritional, technological, and sensory quality of potato-based pasta. Foods 2021, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, H.; Ali, T.M.; Arif, S.; Akbar, Q.U.A.; Saeed, M. Effects of red rice flour addition on the rheological, textural, sensory and bioactive properties of wheat flour-based pan breads. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 1, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, I.; Aprodu, I. Investigation on Functional, Thermo-Mechanical and Bread-Making Properties of Some White and Black Rice Flours. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.J.; Sharavanan, P.S.; Sivaraj, R. RETRACTED: Health benefits of black rice—A review. Grain & Oil Science and Technology. 2019, 2, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Bioactive compounds of rice (Oryza sativa L.): Review on paradigm and its potential benefit in human health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 97, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yun, Y.; Jeong, Y. Effects of corn, potato, and tapioca starches on the quality of gluten-free rice bread. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the AACC Method 72–10, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the AACC Method 22–14, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- del Carmen Robles-Ramírez, M.; Ortega-Robles, E.; Monterrubio-López, R.; Mora-Escobedo, R.; del Carmen Beltrán-Orozco, M. Barley bread with improved sensory and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 22, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-935-58467-7. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.S. Food Analysis Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-44127-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bolea, C.A.; Grigore-Gurgu, L.; Aprodu, I.; Vizireanu, C.; Stanciuc, N. Process-structure-function in association with the main bioactive of black rice flour sieving fractions. Foods 2019, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raman, M.; Dinakaran, A.; Ravindran, A.; Sankar, T.V.; Gopal, T.K.S. Dietary supplementation of κ-carrageenan to improve the physio-chemical and functional properties of white bread. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter L, a, b Versus CIE 1976 L* a* b*. Available online: https://support.hunterlab.com/hc/en-us/article_attachments/201437795/an02_01.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2023).
- Mamat, H.; Hill, S.E. Effect of fat types on the structural and textural properties of dough and semi-sweet biscuit. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chandra, M.V.; Shamasundar, B.A. Texture profile analysis and functional properties of gelatin from the skin of three species of fresh water fish. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamul, D.K.; Lupano, C.E. Properties of gels from whey protein concentrate and honey at different pHs. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üçok, G.; Sert, D. Growth kinetics and biomass characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum L14 isolated from sourdough: Effect of fermentation time on dough machinability. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, H.; Hardan, M.O.A.; Hill, S.E. Physicochemical properties of commercial semi-sweet biscuit. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Liu, L.; Tong, L.; Zhou, S. Effect of milling methods on the properties of rice flour and gluten-free rice bread. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 108, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Sensory Evaluation of Food Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 325–327. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, N.; Reddy, C.K.; Park, E.Y.; Choi, H.D.; Lim, S.T. Antistaling effects of hydrocolloids and modified starch on bread during cold storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, U.K.; Rahman, N.A.A.; Suzihaque, M.U.H.; Hashib, S.A.; Aziz, R.A.A. Effect of baking conditions on the physical properties of bread incorporated with green coffee beans (GCB). In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 062019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, I.; Sebii, H.; Aloui, T.; Attia, H.; Hadrich, B.; Felfoul, I. Optimization of a novel, gluten-free bread’s formulation based on chickpea, carob and rice flours using response surface design. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsatsaragkou, K.; Gounaropoulos, G.; Mandala, I. Development of gluten free bread containing carob flour and resistant starch. LWT 2014, 58, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, M.; Wahab, S.; Durrani, Y. Effect of water activity (aw), moisture content and total microbial count on the overall quality of bread. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2003, 5, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Legal Research Board. Food Act 1983 (Act 281) & Regulations; International Law Book Service: Selangor, Malaysia, 2021; p. 101. ISBN 978-967-89-2768-0. [Google Scholar]
- Trisnawati, C.Y.; Srianta, I.; Nugerahani, I.; Marsono, Y. Incorporating Monascus-fermented durian seeds and rice bran into bread: Study on the bread physicochemical and sensory properties. Food Res. 2019, 3, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauline, M.; Roger, P.; Nina, N.E.S.N.; Arielle, T.; Eugene, E.E.; Robert, N. Physicochemical and nutritional characterization of cereals brans enriched breads. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.A.; Paiva, E.G.; Lisboa, H.M.; Duarte, E.; Cavalcanti-Mata, M.; Gusmão, T.; de Gusmão, R. Role of chitosan and transglutaminase on the elaboration of gluten-free bread. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Vázquez del Mercado, P.; Mojica, L.; Morales-Hernández, N. Protein Ingredients in Bread: Technological, Textural and Health Implications. Foods 2022, 11, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, A.; Hoque, S.; Kumar, U.; Das, M.; Muhammad, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahmed, M. Comparative studies on nutritional quality of commercial wheat flour in Bangladesh. Bangladesh, J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2015, 50, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gujral, H.S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P. Utilization of flour from rice brokens in wheat flour chapatti: Evaluation of dough rheology, starch digestibility, glycemic index and retrogradation behavior. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2490–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, N.T.H.; Huong, N.T.M.; Hoa, P.N.; Van Hung, P. Incorporation of germinated mung bean flour with rice flour to enhance physical, nutritional and sensory quality of gluten-free cookies. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 58, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusak, C.; Pasukamonset, P.; Chantarasinlapin, P.; Adisakwattana, S. Postprandial glycemia, insulinemia, and antioxidant status in healthy subjects after ingestion of bread made from anthocyanin-rich riceberry rice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FoodData Central Search Results: Bread, whole-wheat. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/335240/nutrients (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Aguiar, E.V.; Santos, F.G.; Krupa-Kozak, U.; Capriles, V.D. Nutritional facts regarding commercially available gluten-free bread worldwide: Recent advances and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, M.E.; Rosell, C.M. Quality indicators of rice-based gluten-free bread-like products: Relationships between dough rheology and quality characteristics. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2013, 6, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bultum, L.E.; Emire, S.A.; Wolde, Y.T. Influence of full fat rice bran from Ethiopian rice milling industries on nutritional qualities, physicochemical and sensory properties of bread and biscuits. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, D.A. Sifat Fisik Mekanik Coating Film Berbasis Pati Sagu (Metroxylon sp.) Ikat Silang Asam Sitrat. (Doctoral Dissertation); Bogor Agricultural University (IPB): Bogor, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bedier, D.F.; Salem, R.H.; Almashad, A.A.; Barakat, E.H. Quality Characteristics of Noodles Containing Various Levels of Black Rice Flour. J. Food Dairy Sci. 2020, 11, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Ud-Din, M.S.; Haque, M.A. Studies on the effect of brown rice and maize flour on the quality of bread. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2011, 9, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begum, R.; Uddin, M.J.; Rahman, M.A.; Islam, M.S. Comparative study on the development of maize flour based composite bread. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2013, 11, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, M.E.; Rosell, C.M. Chemical composition and starch digestibility of different gluten-free breads. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, S.; Nakano, K.; Yanase, E. Investigation of colour-deepening phenomenon in catechin-(4→8)-dimer as a proanthocyanidin model and structural determination of its derivatives by oxidation. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Chapter 3: Non-Saponifiable Lipids in Cereals. In Lipids in Cereal Technology, 1st ed.; Meurant, G., Ed.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc. Ltd.: London, UK, 2012; pp. 33–56. [Google Scholar]
- Paznocht, L.; Kotíková, Z.; Šulc, M.; Lachman, J.; Orsák, M.; Eliášová, M.; Martinek, P. Free and esterified carotenoids in pigmented wheat, tritordeum and barley grains. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, E.; Gormley, T.R.; Arendt, E.K. Crust and crumb characteristics of gluten free breads. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wronkowska, M.; Haros, M.; Soral-Śmietana, M. Effect of starch substitution by buckwheat flour on gluten-free bread quality. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2013, 6, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteller, M.S.; Lannes, S.C. Production and characterization of sponge-dough bread using scalded rye. J. Texture Stud. 2008, 39, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarini, L.S.; Ribotta, P.D.; León, A.E.; Pérez, G.T. Effect of hydrocolloids on gluten-free batter properties and bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. 2010, 45, 2306–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, I.; Karabela, D.; Kostaropoulos, A. Physical properties of breads containing hydrocolloids stored at low temperature. I. Effect of chilling. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shittu, T.A.; Aminu, R.A.; Abulude, E.O. Functional effects of xanthan gum on composite cassava-wheat dough and bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülcan, Ü.; Uslu, C.C.; Mutlu, C.; Arslan-Tontul, S.; Erbaş, M. Impact of inert and inhibitor baking atmosphere on HMF and acrylamide formation in bread. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culetu, A.; Fernandez-Gomez, B.; Ullate, M.; del Castillo, M.D.; Andlauer, W. Effect of theanine and polyphenols enriched fractions from decaffeinated tea dust on the formation of Maillard reaction products and sensory attributes of breads. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.S.; Bharti, D.; Pradhan, B.K.; Sahu, D.; Dhal, S.; Kim, N.M.; Pal, K. Analysis of the Physical and Structure Characteristics of Reformulated Pizza Bread. Foods 2022, 11, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, R.S.; Paz, G.; Morris, A.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Moncada, M.; King, J.M. High protein brown rice flour, tapioca starch & potato starch in the development of gluten-free cupcakes. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 152, 112326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeMiller, J.N.; Huber, K. Chapter 3: Carbohydrates. In Food Chemistry, 5th ed.; Damodaran, S., Parkin, K.L., Fennema, O.R., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 91–171. [Google Scholar]
- Cornejo, F.; Rosell, C.M. Physicochemical properties of long rice grain varieties in relation to gluten free bread quality. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renzetti, S.; Rosell, C.M. Role of enzymes in improving the functionality of proteins in non-wheat dough systems. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, M.E.; Rosell, C.M. Understanding gluten-free dough for reaching breads with physical quality and nutritional balance. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironeasa, S.; Iuga, M.; Zaharia, D.; Mironeasa, C. Rheological analysis of wheat flour dough as influenced by grape peels of different particle sizes and addition levels. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2019, 12, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Q.; Ranawana, V.; Hayes, H.E.; Hayward, N.J.; Stead, D.; Raikos, V. Addition of broad bean hull to wheat flour for the development of high-fiber bread: Effects on physical and nutritional properties. Foods 2020, 9, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encina-Zelada, C.R.; Cadavez, V.; Monteiro, F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Combined effect of xanthan gum and water content on physicochemical and textural properties of gluten-free batter and bread. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 111, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandhu, K.S.; Kaur, M.; Mukesh. Studies on noodle quality of potato and rice starches and their blends in relation to their physicochemical, pasting and gel textural properties. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Gu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Ban, X. Effects of different gelatinisation degrees of potato flour on gluten network integrity and dough stickiness. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Gou, E. Effects of potato starch on the properties of wheat dough and the quality of fresh noodles. CYTA J. Food 2020, 18, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M.C. Chapter 6: Sensory Methods of Texture and Viscosity Measurement. In Food Texture and Viscosity: Concept and Measurement, 1st ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 247–276. [Google Scholar]
- Onyango, C.; Mutungi, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Modification of gluten-free sorghum batter and bread using maize, potato, cassava or rice starch. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipini, G.; Passos, A.P.; Fernandes, S.S.; Salas-Mellado, M.D.L.M. Nutritional value, technological and sensory evaluation of gluten-free bread enriched with soybean flour and coconut oil. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 3853–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, H.L.; Magano, N.N. Sensory tools for the development of gluten-free bakery foods. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 94, 102990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Baker Ratio (%) | Formulation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control (F1) | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | |
| Wheat flour | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Rice flour | 0 | 100 | 90 | 80 | 70 |
| Potato starch | 0 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Sugar | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Dry yeast | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Salt | 1.5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Shortening | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Water | 65 | 83 | 83 | 83 | 83 |
| Bread improver | 0 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.019 |
| Xanthan gum | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Soy protein isolate | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Low-fat dairy milk | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Score | Preference |
|---|---|
| 1 | Dislike extremely |
| 2 | Dislike very much |
| 3 | Dislike moderately |
| 4 | Dislike slightly |
| 5 | Neither like nor dislike |
| 6 | Like slightly |
| 7 | Like moderately |
| 8 | Like very much |
| 9 | Like extremely |
| Parameters (%) | Wheat Bread (Control) | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 34.90 ± 0.92 b | 41.22 ± 0.70 a | 39.85 ± 0.91 a | 36.81 ± 0.69 b | 40.86 ± 0.79 a |
| Ash | 1.16 ± 0.20 c | 1.70 ± 0.05 a | 1.67 ± 0.13 ab | 1.63 ± 0.20 ab | 1.28 ± 0.15 bc |
| Crude protein | 11.43 ± 0.08 a | 10.50 ± 0.12 b | 9.78 ± 0.19 c | 9.02 ± 0.06 d | 8.10 ± 0.02 e |
| Crude fat | 3.72 ± 0.37 a | 3.50 ± 0.45 a | 3.61 ± 0.16 a | 3.88 ± 0.43 a | 3.17 ± 0.04 a |
| Crude fibre | 0.40 ± 0.06 c | 0.89 ± 0.14 a | 0.76 ± 0.08 ab | 0.70 ± 0.08 ab | 0.64 ± 0.05 b |
| Carbohydrate | 48.38 ± 1.23 a | 42.18 ± 0.69 cd | 44.33 ± 0.73 c | 47.96 ± 0.89 ab | 45.96 ± 0.76 bc |
| Samples | Crumb | Crust | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | L* | a* | b* | |
| Wheat (Control) | 80.40 ± 0.72 a | −0.06 ± 0.37 c | 22.97 ± 0.57 a | 68.37 ± 2.86 b | 7.4 ± 2.51 a | 43.66 ± 2.93 a |
| F1 | 49.0 ± 6.63 b | 9.46 ± 0.08 a | 11.69 ± 0.11 b | 79.39 ± 1.11 a | 3.6 ± 1.75 ab | 28.65 ± 2.93 b |
| F2 | 47.69 ± 0.41 b | 9.21 ± 0.11 ab | 11.44 ± 0.09 b | 81.48 ± 2.48 a | 2.74 ± 1.04 b | 17.98 ± 2.32 c |
| F3 | 50.76 ± 0.28 b | 9.07 ± 0.03 ab | 11.43 ± 0.03 b | 81.43 ± 2.71 a | 0.31 ± 0.34 b | 15.86 ± 1.84 c |
| F4 | 50.61 ± 0.19 b | 8.71 ± 0.38 b | 11.24 ± 0.45 b | 83.09 ± 0.57 a | −0.07 ± 0.93 b | 13.73 ± 1.5 c |
| Parameters | Wheat (Control) | Dough | |||
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | ||
| Hardness (g) | 137.371 ± 18.65 e | 656.339 ± 39.02 a | 546.812 ± 24.29 b | 432.027 ± 22.26 c | 354.568 ± 23.93 d |
| Springiness | 0.971 ± 0.00 a | 0.941 ± 0.17 b | 0.951 ± 0.00 ab | 0.947 ± 0.00 b | 0.943 ± 0.00 b |
| Cohesiveness | 1.013 ± 0.53 a | 0.649 ± 0.35 c | 0.732 ± 0.84 bc | 0.777 ± 0.01 bc | 0.792 ± 0.04 b |
| Stickiness | 40.122 ± 0.60 a | 12.695 ± 0.23 d | 14.946 ± 0.39 c | 16.437 ± 0.71 b | 17.454 ± 0.55 b |
| Parameters | Wheat (Control) | Bread | |||
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | ||
| Hardness (g) | 849.134 ± 115.59 c | 2846.519 ± 259.95 a | 2352.54 ± 218.41 ab | 2100.645 ± 494.57 ab | 1658.147 ± 311.19 bc |
| Springiness | 1.005 ± 0.04 a | 0.406 ± 0.06 b | 0.424 ± 0.07 b | 0.431 ± 0.05 b | 0.473 ± 0.05 b |
| Cohesiveness | 0.782 ± 0.12 a | 0.308 ± 0.02 b | 0.35 ± 0.03 b | 0.313 ± 0.03 b | 0.327 ± 0.04 b |
| Chewiness | 669.099 ± 105.58 a | 356.847 ± 68.07 b | 348.181 ± 66.22 b | 282.85 ± 75.66 b | 253.142 ± 29.78 b |
| Formulation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute | Control (Wheat Bread) | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 |
| Colour | 7.60 ± 1.19 a | 6.55 ± 1.65 c | 6.38 ± 1.63 c | 6.60 ± 1.88 bc | 7.03 ± 1.30 b |
| Flavour | 6.88 ± 1.52 a | 5.33 ± 1.56 bc | 5.38 ± 1.43 bc | 5.20 ± 1.59 c | 5.73 ± 1.38 b |
| Aroma | 6.68 ± 1.51 a | 5.76 ± 1.72 bc | 6.08 ± 1.61 b | 5.65 ± 1.51 c | 5.80 ± 1.44 bc |
| Texture | 6.80 ± 1.65 a | 4.83 ± 1.73 c | 5.25 ± 1.75 c | 5.33 ± 1.65 c | 6.03 ± 1.58 b |
| Overall acceptability | 7.15 ± 1.28 a | 5.28 ± 1.57 c | 5.58 ± 1.24 bc | 5.55 ± 1.47 c | 6.18 ± 1.30 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronie, M.E.; Mamat, H.; Abdul Aziz, A.H.; Zainol, M.K. Proximate Compositions, Texture, and Sensory Profiles of Gluten-Free Bario Rice Bread Supplemented with Potato Starch. Foods 2023, 12, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061172
Ronie ME, Mamat H, Abdul Aziz AH, Zainol MK. Proximate Compositions, Texture, and Sensory Profiles of Gluten-Free Bario Rice Bread Supplemented with Potato Starch. Foods. 2023; 12(6):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061172
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonie, Macdalyna Esther, Hasmadi Mamat, Ahmad Hazim Abdul Aziz, and Muhd Khairi Zainol. 2023. "Proximate Compositions, Texture, and Sensory Profiles of Gluten-Free Bario Rice Bread Supplemented with Potato Starch" Foods 12, no. 6: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061172
APA StyleRonie, M. E., Mamat, H., Abdul Aziz, A. H., & Zainol, M. K. (2023). Proximate Compositions, Texture, and Sensory Profiles of Gluten-Free Bario Rice Bread Supplemented with Potato Starch. Foods, 12(6), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061172