Comparison of an Ultrasound-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase System Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pomegranate Pomaces by Utilizing the Artificial Neural Network–Genetic Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
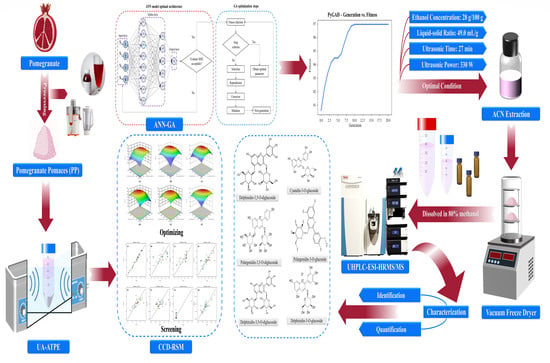
2.1. Outline
2.2. Materials and Chemicals
2.3. Preparation of Pomegranate Pomaces (PPs)
2.4. Plotting the Binodal Solubility Curve (BSC) of the Aqueous Two-Phase System (ATPS)
2.5. The UA-ATPE Procedure of ACNs
2.6. Total Monomeric ACNs
2.7. Identification and Quantification of the ACN
2.8. Central Composite Design Response Surface Model (CCD-RSM) Experimental Design
2.9. Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Model Experimental Design
2.10. Evaluation of the Accuracy of the Constructed Models
2.11. Optimization of the Genetic Algorithm (GA) Process
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ethanol–Ammonium Sulphate Extraction System Phase Diagram
3.2. CCD-RSM Modeling
3.3. Effect of Factors on ACN Yield
3.4. ANN Modeling
3.5. ANN-GA Optimization
3.6. Evaluation and Comparison of the ANN-GA and CCD-RSM Models
3.7. Characterization and Evaluation of ACN Extraction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aseri, G.; Jain, N.; Panwar, J.; Rao, A.; Meghwal, P. Biofertilizers improve plant growth, fruit yield, nutrition, metabolism and rhizosphere enzyme activities of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) in Indian Thar Desert. Sci. Hortic. 2008, 117, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertenstalcott, S.U.; Jilmastohlawetz, P.; Rios, J.; Hingorani, L.; Derendorf, H. Absorption, metabolism, and antioxidant effects of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) polyphenols after ingestion of a standardized extract in healthy human volunteers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8956–8961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Khoualdia, B.; Savoire, R.; Hobloss, S.; Buré, C.; Samia, B.A.; Subra-Paternault, P. Extraction of phenolics from pomegranate residues: Selectivity induced by the methods. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 176, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, F.; Boggia, R.; Donno, D.; Parodi, B.; Beccaro, G.; Baldassari, S.; Signorello, M.G.; Catena, S.; Alfei, S.; Zunin, P. From pomegranate marcs to a potential bioactive ingredient: A recycling proposal for pomegranate-squeezed marcs. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin biosynthesis and degradation mechanisms in solanaceous vegetables: A review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, G. Regulatory mechanisms of anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple and pear. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J. Copigmentation effects of phenolics on color enhancement and stability of blackberry wine residue anthocyanins: Chromaticity, kinetics and structural simulation. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liu, H.; Qin, Z.; Liu, M.; Zheng, M.; Cai, D.; Liu, J. Dietary antioxidant anthocyanins mitigate type II diabetes through improving the disorder of glycometabolism and insulin resistance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13350–13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Shum, H.C. Emerging aqueous two-phase systems: From fundamentals of interfaces to biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 114–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Cui, P.; Ge, S.; Cai, X.; Li, Q.; Xue, H. Ultrasound assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of polysaccharides from Cornus officinalis fruit: Modeling, optimization, purification, and characterization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Teng, G.; Zhang, J. Ethanol/salt aqueous two-phase system based ultrasonically assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Lilium davidiivar. unicolor Salisb: Physicochemical characterization and antiglycation properties. J. Mol. Liquids 2018, 256, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Kan, J. Polysaccharides from ginger stems and leaves: Effects of dual and triple frequency ultrasound assisted extraction on structural characteristics and biological activities. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Kou, X.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Li, T.; Dou, J.; Shen, D. Enhanced extraction of bioactive natural products using ultrasound-assisted aqueous two-phase system: Application to flavonoids extraction from jujube peels. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odabaş, H.İ.; Koca, I. Simultaneous separation and preliminary purification of anthocyanins from Rosa pimpinellifolia L. fruits by microwave assisted aqueous two-phase extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 125, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, J.; Sun, Z.; Ji, M.; Gu, Z.; Ahmad, W. ANN and RSM based modelling for optimization of cell dry mass of Bacillus sp. strain B67 and its antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Ma, Y. Preparation of sodium-containing coacervates via high-voltage electrostatic field treatment: Saltiness perception of prefabricated chicken patties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, K. Learning with genetic algorithms: An overview. Mach. Learn. 1988, 3, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Deng, D.; Dai, W.; Li, J.; Jin, X. Optimization of culture conditions for differentiation of melon based on artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, J.; Gao, W.; Chen, K. Comparative study on the extraction efficiency, characterization, and bioactivities of Bletilla striata polysaccharides using response surface methodology (RSM) and genetic algorithm-artificial neural network (GA-ANN). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 982–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.E.; Kim, R.H.; Lim, T.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-G.; Hwang, K.T. Optimization of accelerated solvent extraction of ellagitannins in black raspberry seeds using artificial neural network coupled with genetic algorithm. Food Chem. 2022, 396, 133712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, M.; Srivastav, P. Optimization of pulsed ultrasonic-assisted extraction of punicalagin from pomegranate (Punica granatum) peel: A comparison between response surface methodology and artificial neural network-multiobjective genetic algorithm. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, G.B.; Dash, K.K. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of phytocompounds from dragon fruit peel: Optimization, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 68, 105180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liang, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, F.; Yang, L. Aqueous two-phase extraction, identification and antioxidant activity of anthocyanins from mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.). Food Chem. 2011, 129, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. Optimisation of aqueous two-phase extraction of anthocyanins from purple sweet potatoes by response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3034–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Determination of total monomeric anthocyanin pigment content of fruit juices, beverages, natural colorants, and wines by the pH differential method: Collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammoudi, N.; Mabrouk, M.; Bouhemda, T.; Nagaz, K.; Ferchichi, A. Modeling and optimization of capsaicin extraction from Capsicum annuum L. using response surface methodology (RSM), artificial neural network (ANN), and Simulink simulation. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 171, 113869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.-L.; Wong, F.W.F.; Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.R.; Mohamed, M.S.; Ariff, A.B.; Hii, S.-L. Optimization of fermentation medium components by response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network hybrid with genetic algorithm (ANN-GA) for lipase production by Burkholderia cenocepacia ST8 using used automotive engine oil as substrate. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 50, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhylko, V.; Dai, L. Ultrasonic-assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of polysaccharides from the fruits of Ilex cornuta (Lindl. Et Paxt.): Process optimization, structural characterization and antioxidant activity study. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, H. Extraction characteristics and optimal parameters of anthocyanin from blueberry powder under microwave-assisted extraction conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 104, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirsath, S.; Sable, S.; Gaikwad, S.; Sonawane, S.; Saini, D.; Gogate, P. Intensification of extraction of curcumin from Curcuma amada using ultrasound assisted approach: Effect of different operating parameters. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, P.C.; Santos, K.A.; Hasan, S.D.M.; da Silva, E.A. Evaluation of the ethanolic ultrasound-assisted extraction from clove (Syzygium aromaticum) leaves and chemical characterization of the extracts. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gong, P.; Ma, H.; Xie, R.; Wei, J.; Xu, M. Ultrasound treatment degrades, changes the color, and improves the antioxidant activity of the anthocyanins in red radish. LWT 2022, 165, 113761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhachat, D.; Mekimene, L.; Belhachat, M.; Ferradji, A.; Aid, F. Application of response surface methodology to optimize the extraction of essential oil from ripe berries of Pistacia lentiscus using ultrasonic pretreatment. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 9, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, X.; Lin, X.; Mei, Z.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.; Bai, W. Sonodegradation of cyanidin-3-glucosylrutinoside: Degradation kinetic analysis and its impact on antioxidant capacity in vitro. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, B.; Patras, A.; Brunton, N.; Cullen, P.; O’donnell, C. Effect of ultrasound processing on anthocyanins and color of red grape juice. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patras, A.; Brunton, N.P.; O’Donnell, C.; Tiwari, B.K. Effect of thermal processing on anthocyanin stability in foods; mechanisms and kinetics of degradation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Improved extraction of oil from chickpea under ultrasound in a dynamic system. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Fakayode, O.A.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Z.; Xia, A.; Li, Q. Dual-frequency multi-angle ultrasonic processing technology and its real-time monitoring on physicochemical properties of raw soymilk and soybean protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, S.; Manickam, L.P.; Murugesan, V.; Muthukumaran, C.; Pugazhendhi, A. Pectin extraction from Helianthus annuus (sunflower) heads using RSM and ANN modelling by a genetic algorithm approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, B.; Saha, S.P.; Chakraborty, R.; Roy, S. Optimization of starch extraction from amorphophallus paeoniifolius corms using response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) for improving yield with tenable chemical attributes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 237, 124183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sit, N. Comparison of response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN) modelling for supercritical fluid extraction of phytochemicals from Terminalia chebula pulp and optimization using RSM coupled with desirability function (DF) and genetic algorithm (GA) and ANN with GA. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2021, 170, 113769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaouay, F.; Mena, P.; Garcia-Viguera, C.; Mars, M. Antioxidant activity and physico-chemical properties of Tunisian grown pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) cultivars. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2012, 40, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Cheng, F.; Yun, Y.; Yi, J.; Cai, S.; Zhou, L. Characterization of the flavor, sensory quality and in vitro bioaccessibility in cloudy pomegranate juice treated by high pressure and thermal processing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Niu, H.; Yun, Y.; Tian, J.; Lao, F.; Liao, X.; Gao, Z.; Ren, D.; Zhou, L. Analysis of coloration characteristics of Tunisian soft-seed pomegranate arils based on transcriptome and metabolome. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Cheng, F.; Yi, J.; Cai, S.; Liao, X.; Lao, F.; Zhou, L. Effect of high-pressure processing and thermal treatments on color and in vitro bioaccessibility of anthocyanin and antioxidants in cloudy pomegranate juice. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Huang, S.; Cai, S.; Cao, J.; Han, P. Digestion property and synergistic effect on biological activity of purple rice (Oryza sativa L.) anthocyanins subjected to a simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Tao, Y.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, S.; Tao, G.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. High pressure homogenization processing, thermal treatment and milk matrix affect in vitro bioaccessibility of phenolics in apple, grape and orange juice to different extents. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Szeto, Y. Total antioxidant capacity of teas by the ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchweitz, M.; Speth, M.; Kammerer, D.; Carle, R. Impact of pectin type on the storage stability of black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) anthocyanins in pectic model solutions. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Source | Sum of Squares | Dfa | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | |||||
| X1 | 108.89 | 1 | 108.89 | 136.79 | <0.0001 |
| X2 | 0.9600 | 1 | 0.9600 | 1.21 | 0.2894 |
| X3 | 105.50 | 1 | 105.50 | 132.54 | <0.0001 |
| X4 | 12.47 | 1 | 12.47 | 15.67 | 0.0013 |
| Interactions | |||||
| X1X2 | 0.1640 | 1 | 0.1640 | 0.2061 | 0.6564 |
| X1X3 | 2.74 | 1 | 2.74 | 3.44 | 0.0834 |
| X1X4 | 7.67 | 1 | 7.67 | 9.64 | 0.0072 |
| X2X3 | 0.6162 | 1 | 0.6162 | 0.7741 | 0.3928 |
| X2X4 | 3.17 | 1 | 3.17 | 3.98 | 0.0645 |
| X3X4 | 10.37 | 1 | 10.37 | 13.03 | 0.0026 |
| Quadratic | |||||
| X12 | 179.43 | 1 | 179.43 | 225.42 | <0.0001 |
| X22 | 42.53 | 1 | 42.53 | 53.43 | <0.0001 |
| X32 | 77.43 | 1 | 77.43 | 97.28 | <0.0001 |
| X42 | 77.43 | 1 | 57.69 | 72.47 | <0.0001 |
| Lack of Fit | 10.56 | 10 | 1.06 | 3.82 | 0.0760 |
| Pure Error | 1.38 | 5 | 0.2763 | ||
| Residue | 11.94 | 1 | |||
| Model | 515.32 | 14 | 36.81 | 46.24 | <0.0001 |
| Total SS | 527.26 | 29 | |||
| R2 | 0.9774 | ||||
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9562 | ||||
| Predicted R2 | 0.8809 | ||||
| Adeq Precision | 22.9694 | ||||
| Calculated Predictive Capacity | CCD-RSM | ANN-GA |
|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9773 | 0.9940 |
| MSE | 0.0083 | 0.0056 |
| RMSE | 0.6311 | 0.4322 |
| AAD (%) | 0.6211 | 0.2922 |
| Peak No. | RT (min) | Anthocyanin | Molecular Formula | MS[M]+ (m/z) | MS2 | Content (mg/g DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.37 | Delphinidin-3,5-O-diglucoside | C27H31O17 | 627.1555 | 303.0501, 304.0534, 465.1028 | 8.79 ± 1.54 |
| 2 | 7.61 | Cyanidin-3,5-O-diglucoside | C27H31O16 | 611.1606 | 271.0596 | 31.35 ± 0.58 |
| 3 | 9.05 | Pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside | C27H31O15 | 595.1657 | 287.0551, 449.1081 | 3.33 ± 0.12 |
| 4 | 9.28 | Delphinidin-3-O-glucoside | C27H31O12 | 465.1028 | 303.0497 | 18.23 ± 0.22 |
| 5 | 10.05 | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside | C21H21O11 | 449.1078 | 287.0549, 449.1090 | 57.01 ± 1.36 |
| 6 | 10.46 | Pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside | C21H31O10 | 433.1127 | 271.0603, 433.1134 | 7.30 ± 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Q.; Tian, J.; Dong, L.; Zhou, L. Comparison of an Ultrasound-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase System Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pomegranate Pomaces by Utilizing the Artificial Neural Network–Genetic Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology Models. Foods 2024, 13, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020199
Yue Q, Tian J, Dong L, Zhou L. Comparison of an Ultrasound-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase System Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pomegranate Pomaces by Utilizing the Artificial Neural Network–Genetic Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology Models. Foods. 2024; 13(2):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020199
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Qisheng, Jun Tian, Ling Dong, and Linyan Zhou. 2024. "Comparison of an Ultrasound-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase System Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pomegranate Pomaces by Utilizing the Artificial Neural Network–Genetic Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology Models" Foods 13, no. 2: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020199
APA StyleYue, Q., Tian, J., Dong, L., & Zhou, L. (2024). Comparison of an Ultrasound-Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase System Extraction of Anthocyanins from Pomegranate Pomaces by Utilizing the Artificial Neural Network–Genetic Algorithm and Response Surface Methodology Models. Foods, 13(2), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020199