Green Extraction Strategy Using Bio-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Polyphenol Valorization from Grape By-Product
Abstract
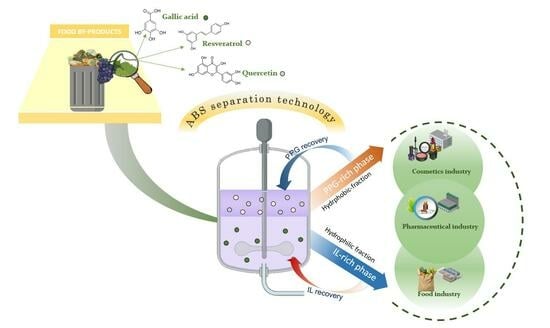
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds
2.3. Recovery of Polyphenols from Grape Stems
2.4. Solubility Determination
2.5. Quantification of Polyphenols
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Liquid–Liquid Equilibria of Cholinium-Based ABSs
3.2. Extraction of Polyphenolic Compounds
3.3. Recovery of Polyphenols from Grape Stems and Designing an Integrated Extraction and Separation Process
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tackling Food Loss and Waste: A Triple Win Opportunity, Newsroom (n.d.). Available online: https://www.fao.org/newsroom/detail/FAO-UNEP-agriculture-environment-food-loss-waste-day-2022/en (accessed on 21 February 2024).
- Torres-León, C.; Ramírez-Guzman, N.; Londoño-Hernandez, L.; Martinez-Medina, G.A.; Díaz-Herrera, R.; Navarro-Macias, V.; Alvarez-Pérez, O.B.; Picazo, B.; Villarreal-Vázquez, M.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.; et al. Food Waste and Byproducts: An Opportunity to Minimize Malnutrition and Hunger in Developing Countries. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, J.P.; Alexandre, E.M.C.; Saraiva, J.A.; Pintado, M.E. High Value-Added Compounds from Fruit and Vegetable by-Products–Characterization, Bioactivities, and Application in the Development of Novel Food Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1388–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzutti, S.; Pedrosa, R.C.; Ferreira, S.R.S. Green Processes in Foodomics. Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Bioactives. In Comprehensive Foodomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 725–743. ISBN 9780128163955. [Google Scholar]
- De la Rosa, L.A.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals; de la Rosa, L.A., Alvarez-Parrilla, E., González-Aguilar, G.A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780813803203. [Google Scholar]
- Montenegro-Landívar, M.F.; Tapia-Quirós, P.; Vecino, X.; Reig, M.; Valderrama, C.; Granados, M.; Cortina, J.L.; Saurina, J. Polyphenols and Their Potential Role to Fight Viral Diseases: An Overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allied Market Research. Polyphenol Market Size, Share & Growth—Industry Report, 2030. Available online: https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/polyphenol-market (accessed on 24 December 2023).
- Mir-Cerdà, A.; Nuñez, O.; Granados, M.; Sentellas, S.; Saurina, J. An Overview of the Extraction and Characterization of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds from Agri-Food Waste within the Framework of Circular Bioeconomy. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 161, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Han, Y.; Tian, X.; Sajid, M.; Mehmood, S.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Phenolic Composition of Grape Pomace and Its Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panouillé, M.; Ralet, M.C.; Bonnin, E.; Thibault, J.F. Recovery and Reuse of Trimmings and Pulps from Fruit and Vegetable Processing. In Handbook of Waste Management and Co-Product Recovery in Food Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 417–447. ISBN 9781845692520. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, M.; Barbhai, M.D.; Hasan, M.; Punia, S.; Dhumal, S.; Radha; Rais, N.; Chandran, D.; Pandiselvam, R.; Kothakota, A.; et al. Onion (Allium cepa L.) Peels: A Review on Bioactive Compounds and Biomedical Activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 146, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, V.; Igrejas, G.; Falco, V.; Santos, T.P.; Torres, C.; Oliveira, A.M.P.; Pereira, J.E.; Amaral, J.S.; Poeta, P. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Phenolic Compounds Extracted from Wine Industry by-Products. Food Control 2018, 92, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samota, M.K.; Sharma, M.; Kaur, K.; Sarita; Yadav, D.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Tak, Y.; Rawat, M.; Thakur, J.; Rani, H. Onion Anthocyanins: Extraction, Stability, Bioavailability, Dietary Effect, and Health Implications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 917617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.D.; Steinmaus, C.; Golub, M.S.; Castorina, R.; Thilakartne, R.; Bradman, A.; Marty, M.A. Potential Impacts of Synthetic Food Dyes on Activity and Attention in Children: A Review of the Human and Animal Evidence. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2022, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, A.; Ponnuchamy, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Kapoor, A.; Vo, D.V.N.; Prabhakar, S. Techniques and Modeling of Polyphenol Extraction from Food: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3409–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuo, S.C.; Nasir, H.M.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Mohamed, S.F.; Ahmad, A.; Wani, W.A.; Muddassir, M.; Alarifi, A. A Glimpse into the Extraction Methods of Active Compounds from Plants. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 667–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, A.; Farid, M. Effect of Temperatures on Polyphenols during Extraction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sólyom, K.; Solá, R.; Cocero, M.J.; Mato, R.B. Thermal Degradation of Grape Marc Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2014, 159, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volf, I.; Ignat, I.; Neamtu, M.; Popa, V.I. Thermal Stability, Antioxidant Activity, and Photo-Oxidation of Natural Polyphenols. Chem. Pap. 2014, 68, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, J.S.; Crerar, D.A.; Grissom, G.; Key, T.C. Aqueous thermal degradation of gallic acid. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1988, 52, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadja, B.; Angelika, K.; Rohn, S.; Kroh, L.W. Effect of Thermal Processing on the Flavonols Rutin and Quercetin. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 24, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupančič, Š.; Lavrič, Z.; Kristl, J. Stability and Solubility of Trans-Resveratrol Are Strongly Influenced by PH and Temperature. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Marsiglia, W.I.M.; Oliveira, L.D.S.C.; Almeida, R.L.J.; Santos, N.C.; da Silva Neto, J.M.; Santiago, Â.M.; de Melo, B.C.A.; da Silva, F.L.H. Thermal Stability of Total Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activities of Jaboticaba Peel: Effect of Solvents and Extraction Methods. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2023, 100, 100995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, N.M.; Selinheimo, E.; Havenaar, R.; Aura, A.M.; Mattila, I.; Lehtinen, P.; Bast, A.; Poutanen, K.; Haenen, G.R.M.M. Bioprocessing of Wheat Bran Improves in Vitro Bioaccessibility and Colonic Metabolism of Phenolic Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6148–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids—Solvents of the Future? Science 2003, 302, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinodia, M. Ionic Liquids: Environment-Friendly Greener Solvents for Organic Synthesis. Curr. Org. Synth. 2022, 19, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrijević, A.; Jocić, A. Ionic Liquids as Promising Media in (Pre)Analytical Treatments and Degradation of Organophosphate Pesticides. In Organophosphates: Detection, Exposure and Occurrence. Volume 1: Impact on Health and the Natural Environment; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 181–214. ISBN 978-1-68507-652-8. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, K.D.; Kim, H.J.; Sun, J.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Elliott, G.D. Cyto-Toxicity and Biocompatibility of a Family of Choline Phosphate Ionic Liquids Designed for Pharmaceutical Applications. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 507–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavez, P.; Figueroa, R.; Medina, M.; Millán, D.; Falcone, R.D.; Tapia, R.A. Choline [Amino Acid] Ionic Liquid/Water Mixtures: A Triple Effect for the Degradation of an Organophosphorus Pesticide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26562–26572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrijević, A.; Tavares, A.P.M.M.; Almeida, M.R.; Vraneš, M.; Sousa, A.C.A.A.; Cristóvão, A.C.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Gadžurić, S.; Freire, M.G. Valorization of Expired Energy Drinks by Designed and Integrated Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5683–5692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Donne, A.; Bodo, E. Cholinium Amino Acid-Based Ionic Liquids. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrijević, A.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Jocić, A.; Marić, S.; Trtić-Petrović, T.; Gadžurić, S.; Freire, M.G. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Comprising Copolymers and Cholinium-Based Salts or Ionic Liquids: Insights on the Mechanisms Responsible for Their Creation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; e Silva, F.A.; Quental, M.V.; Mondal, D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic-Liquid-Mediated Extraction and Separation Processes for Bioactive Compounds: Past, Present, and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6984–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.E.; Ferreira, A.M.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Almeida, M.R.; Barros, R.; Cristovão, A.C.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Reis, P.M.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; et al. Valorisation of Red Beet Waste: One-Step Extraction and Separation of Betalains and Chlorophylls Using Thermoreversible Aqueous Biphasic Systems. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 1852–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.; Sarkar, B.; Sen, K. Aqueous Biphasic Systems: A Robust Platform for Green Extraction of Biomolecules. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 363, 119882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous Biphasic Systems: A Boost Brought about by Using Ionic Liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Sharma, M.; Quental, M.V.; Tavares, A.P.M.M.; Prasad, K.; Freire, M.G. Suitability of Bio-Based Ionic Liquids for the Extraction and Purification of IgG Antibodies. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 6071–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Santos, A.; Tojo, J.; Rodríguez, A. Toxicity and Biodegradability of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, L.; Rocha, M.; Pisani, J.; Zecchi, B. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems Based on Cholinium Ionic Liquids for the Recovery of Ferulic and p-Coumaric Acids from Rice Husk Hydrolysate. Appl. Food Res. 2024, 4, 100381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, T.; Tomé, L.C.; Florindo, C.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Understanding the Role of Cholinium Carboxylate Ionic Liquids in PEG-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 2426–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, C.M.S.S.; Figueiredo, M.; Reis, P.M.; Sousa, A.C.A.; Cristóvão, A.C.; Fiadeiro, M.B.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Esperança, J.M.S.S.; Freire, M.G. Simultaneous Separation of Antioxidants and Carbohydrates from Food Wastes Using Aqueous Biphasic Systems Formed by Cholinium-Derived Ionic Liquids. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 454370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Marrucho, I.M. Ionic Liquids as Additives for Extraction of Saponins and Polyphenols from Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) and Tea (Camellia sinensis). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 12146–12153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, F. Applications of Choline Amino Acid Ionic Liquid in Extraction and Separation of Flavonoids and Pectin from Ponkan Peels. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintra, T.E.; Luís, A.; Rocha, S.N.; Ferreira, A.I.M.C.L.; Gonçalves, F.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Neves, B.M.; Freire, M.G.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Enhancing the Antioxidant Characteristics of Phenolic Acids by Their Conversion into Cholinium Salts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.; Kurnia, K.A.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Gurau, G.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Rogers, R.D.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A. Molecular Interactions in Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Polyethylene Glycol and Crystalline vs. Liquid Cholinium-Based Salts. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5723–5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; He, M. Design of Environmentally Friendly Ionic Liquid Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for the Efficient and High Activity Extraction of Proteins. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, C.C.; Neves, C.M.S.S.; Quental, M.V.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Separation of Immunoglobulin G Using Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids and Poly(Propylene Glycol). J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marić, S.; Jocić, A.; Tekić, D.; Mušović, J.; Milićević, J.; Dimitrijević, A. Customizable Cholinium-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems as Ecofriendly Extraction Platform for Removal of Pesticide from Wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 340, 126609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchuk, J.C.; Andrews, B.A.; Asenjo, J.A. Aqueous Two-Phase Systems for Protein Separation. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1998, 711, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.F.B.; Magri, A.; Quental, M.V.; Gonzalez-Miquel, M.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Alkaloids as Alternative Probes to Characterize the Relative Hydrophobicity of Aqueous Biphasic Systems. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, C.M.S.S.; Shahriari, S.; Lemus, J.; Pereira, J.F.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Aqueous Biphasic Systems Composed of Ionic Liquids and Polypropylene Glycol: Insights into Their Liquid-Liquid Demixing Mechanisms. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 20571–20582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemicalize Was Used for Predicting ILs Properties. Developed by ChemAxon. Available online: http://www.chemaxon.com (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Shaker Shiran, H.; Baghbanbashi, M.; Ghazizadeh Ahsaie, F.; Pazuki, G. Study of Curcumin Partitioning in Polymer-Salt Aqueous Two Phase Systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaković, S.; Armaković, S.J.; Vraneš, M.; Tot, A.; Gadžurić, S. DFT Study of 1-Butyl-3-Methylimidazolium Salicylate: A Third-Generation Ionic Liquid. J. Mol. Model. 2015, 21, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadžurić, S.; Tot, A.; Armaković, S.; Armaković, S.; Panić, J.; Jović, B.; Vraneš, M. Uncommon Structure Making/Breaking Behaviour of Cholinium Taurate in Water. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2017, 107, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, U.L.; Izgorodina, E.I.; MacFarlane, D.R. New Insights into the Relationship between Ion-Pair Binding Energy and Thermodynamic and Transport Properties of Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 20472–20478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demurtas, M.; Onnis, V.; Zucca, P.; Rescigno, A.; Lachowicz, J.I.; De Villiers Engelbrecht, L.; Nieddu, M.; Ennas, G.; Scano, A.; Mocci, F.; et al. Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids from Hydroxycinnamic Acids as New Promising Bioactive Agents: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tot, A.; Podlipnik, Č.; Bešter-Rogač, M.; Gadžurić, S.; Vraneš, M. Influence of Oxygen Functionalization on Physico-Chemical Properties of Imidazolium Based Ionic Liquids—Experimental and Computational Study. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 13, 1598–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazwani, M.; Alam, P.; Alqarni, M.H.; Yusufoglu, H.S.; Shakeel, F. Various Propylene Glycol + Water Mixtures. Molecules 2021, 26, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Neves, M.C.; Shimizu, K.; Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The Magic of Aqueous Solutions of Ionic Liquids: Ionic Liquids as a Powerful Class of Catanionic Hydrotropes. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3948–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, L.; Paik, S.P.; Sen, K. Poly(Propylene Glycol) vs. Sugar Alcohol-Based Aqueous Biphasic System to Extract Drugs and Subsequent Recovery of the Polymer. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 4629–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, K.E.; Broker, G.A.; Willauer, H.D.; Huddleston, J.G.; Swatloski, R.P.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Controlling the aqueous miscibility of ionic liquids: Aqueous biphasic systems of water-miscible ionic liquids and water-structuring salts for recycle, metathesis, and separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 , [Ch][DHP];
, [Ch][DHP];  , [Ch][Lac];
, [Ch][Lac];  , [Ch][DHCit];
, [Ch][DHCit];  , [Ch]Cl;
, [Ch]Cl;  , [Ch][Gal];
, [Ch][Gal];  , [Ch][Nic];
, [Ch][Nic];  , [Ch][Van]).
, [Ch][Van]).
 , [Ch][DHP];
, [Ch][DHP];  , [Ch][Lac];
, [Ch][Lac];  , [Ch][DHCit];
, [Ch][DHCit];  , [Ch]Cl;
, [Ch]Cl;  , [Ch][Gal];
, [Ch][Gal];  , [Ch][Nic];
, [Ch][Nic];  , [Ch][Van]).
, [Ch][Van]).







| Experimental Stage | IL | Polymer | Polyphenol Sample | T (°C) | System Composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL | PPG400 | ||||||||
| IL Synthesis | 1 | [Ch][Val] | / | / | 25 | / | |||
| 2 | [Ch][Gal] | ||||||||
| 3 | [Ch][Lac] | ||||||||
| 4 | [Ch][Nic] | ||||||||
| Determination of ABS diagrams | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | PPG400 | / | 25 | / | |||
| 2 | [Ch][DHCit] | ||||||||
| 3 | [Ch]Cl | ||||||||
| 4 | [Ch][Lac] | ||||||||
| 5 | [Ch][Gal] | ||||||||
| 6 | [Ch][Nic] | ||||||||
| 7 | [Ch][Van] | ||||||||
| Partition studies | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | PPG400 | Standard ~2500 mg per L | 25 | ~20 | ~50 | ||
| 2 | [Ch][DHCit] | ||||||||
| 3 | [Ch]Cl | ||||||||
| 4 | [Ch][Lac] | ||||||||
| 5 | [Ch][Gal] | ||||||||
| 6 | [Ch][Nic] | ||||||||
| 7 | [Ch][Van] | ||||||||
| Optimization studies | TL | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | PPG400 | Standard ~2500 mg per L | 25 | ~20 | ~50 | |
| 2 | ~16 | ~40 | |||||||
| 3 | ~12 | ~30 | |||||||
| ABS composition (phase ratio) | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | PPG400 | Standard ~2500 mg per L | 25 | ~20 | ~50 | ||
| 2 | ~25 | ~40 | |||||||
| 3 | ~40 | ~6 | |||||||
| Recovery from grape stems | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | PPG400 | 5 mg stem extract per mL | 25 | ~25 | ~40 | ||
| Solubility | 1 | [Ch][DHP] | / | GA standard | 25 | ~50 | / | ||
| 2 | / | PPG400 | RSV standard | 25 | / | ~80 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dimitrijević, A.; Marić, S.; Jocić, A.; Tekić, D.; Mušović, J.; Amaral, J.S. Green Extraction Strategy Using Bio-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Polyphenol Valorization from Grape By-Product. Foods 2024, 13, 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060954
Dimitrijević A, Marić S, Jocić A, Tekić D, Mušović J, Amaral JS. Green Extraction Strategy Using Bio-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Polyphenol Valorization from Grape By-Product. Foods. 2024; 13(6):954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060954
Chicago/Turabian StyleDimitrijević, Aleksandra, Slađana Marić, Ana Jocić, Danijela Tekić, Jasmina Mušović, and Joana S. Amaral. 2024. "Green Extraction Strategy Using Bio-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Polyphenol Valorization from Grape By-Product" Foods 13, no. 6: 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060954
APA StyleDimitrijević, A., Marić, S., Jocić, A., Tekić, D., Mušović, J., & Amaral, J. S. (2024). Green Extraction Strategy Using Bio-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems for Polyphenol Valorization from Grape By-Product. Foods, 13(6), 954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060954