Quantifications of Oleocolloid Matrices Made of Whey Protein and Oleogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
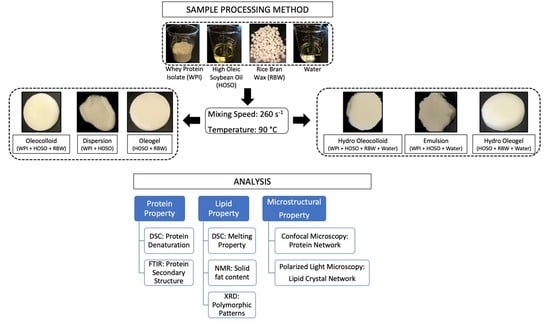
2.2. Oleocolloid (OC) and Hydro-Oleocolloid (HOC) Processing
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5. Solid Fat Content (SFC) via Pulsed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.6. X-ray Diffractometry (XRD)
2.7. Confocal Microscopy
2.8. Polarized Light Microscopy (PLM)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Vries, A.; Hendriks, J.; van der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. Protein oleogels from protein hydrogels via a stepwise solvent exchange route. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13850–13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, C.D.; Tavernier, I.; Okuro, P.K.; Dewettinck, K. Internal and external factors affecting the crystallization, gelation and applicability of wax-based oleogels in food industry. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Auzanneau, F.I.; Rogers, M.A. Advances in edible oleogel technologies—A decade in review. Food Res. Int. 2017, 97, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dassanayake, L.S.K.; Kodali, D.R.; Ueno, S. Formation of oleogels based on edible lipid materials. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Schattenman, D.; de Vos, W.H.; Lesaffer, A.; Dewettinck, K. Preparation and rheological characterization of shellac oleogels and oleogel-based emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Lan, Y.; Cui, L.; Monono, E.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Formation, characterization, and potential food application of rice bran wax oleogels: Expeller-pressed corn germ oil versus refined corn oil. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.; Martins, A.J.; Lopez-Pedrouso, M.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Purrinos, L.; Pastrana, L.M.; Vincente, A.A.; Zapata, C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Evaluation of linseed oil oleogels to partially replace pork backfat in fermented sausages. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 100, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulim-Botega, D.C.; Marangoni, A.G.; Smith, A.K.; Goff, H.D. The potential application of rice bran wax oleogel to replace solid fat and enhance unsaturated fat content in ice cream. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1334–C1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Gredowska, A.; Turhan, O.; Lesaffer, A.; de Vos, W.H.; van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K. Edible applications of shellac oleogels: Spreads, chocolate paste and cakes. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zetzl, A.K.; Marangoni, A.G.; Barbut, S. Mechanical properties of ethylcellulose oleogels and their potential for saturated fat reduction in frankfurters. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemer, H.L.; Limbaugh, M.; Cramer, E.D.; Harper, W.J.; Maleky, F. Vegetable organogels incorporation in cream cheese products. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Vries, A.; Wesseling, A.; van der Linden, E.; Scholten, E. Protein oleogels fromheat-set whey protein aggregates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavernier, I.; Patel, A.R.; van der Meeren, P.; Dewettinck, K. Emulsion-templated liquid oil structuring with soy protein and soy protein: κ-Carrageenan complexes. Food Hydrocoll 2017, 65, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Cui, X.; Cai, W.; Shao, X. Understanding the function of water during the gelation of globular proteins by temperature-dependent near infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 20132–20140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, C.N.; Trevino, S.; Prabhakaran, E.; Scholtz, J.M. Protein structure, stability, and solubility in water and other solvents. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2004, 359, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gosal, W.S.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Globular protein gelation. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, L.D.; Hecht, L.; Wilson, G. The lubricant of life: A proposal that solvent water promotes extremely fast conformational fluctuations in mobile heteropolypeptide structure. Biochemistry 1977, 36, 13143–13147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaee, A.; Mohammadian, M.; Jafari, S.M. Whey and soy protein-based hydrogels and nano-hydrogels as bioactive delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 70, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, S.; Xiao, L.; Ould Eleya, M.M. Whey protein concentrate hydrogels as bioactive carriers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 99, 2470–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Chen, J. Heat-set whey protein emulsion gels: Role of active and inactive filler particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2007, 20, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, L.S.K.; Kodali, D.R.; Ueno, S.; Sato, K. Physical properties of rice bran wax in bulk and oranogels. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijarnprecha, K.; Aryusuk, K.; Santiwattana, P.; Sonwai, S.; Rousseau, D. Structure and rheology of oleogels made from rice bran wax and rice bran oil. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzidi, L.; Boodhoo, M.; Humphrey, K.L.; Narine, S.S. Use of first and second derivatives to accurately determine key parameters of DSC thermographs in lipid crystallization studies. Thermochim. Acta. 2005, 439, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, C.D.; van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K.; Patel, A.R. Evaluating the oil-gelling properties of natural waxes in rice bran oil: Rheological, thermal, and microstructural study. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.I.; Alli, I.; Ismali, A.A.; Gibbs, B.F.; Konishi, Y. Factors affecting molecular characteristics of whey protein gelation. Int. Dairy, J. 1995, 5, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timasheff, S.N. Water as ligand: Preferential binding and exclusion of denaturants in protein unfolding. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 9857–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenicke, R. Stability and stabilization of globular proteins in solution. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 79, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.; McClements, D.J. Impact of preferential interactions on thermal stability and gelation of bovine serum albumin in aqueous sucrose solutions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2600–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanoglu, E. Effect of hydrocolloids on the thermal denaturation of proteins. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakenfull, D.; Scott, A. Hydrophobic interactions in the gelation of high methoxyl pectins. J. Food Sci. 1984, 49, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Burg, B.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Vriend, G.; van der Vinne, B.; Venema, G. Protein stabilization by hydrophobic interactions at the interface. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 220, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- di Cicco, F.; Oosterlinck, F.; Tromp, H.; Sein, A. Comparative study of whey protein isolate gel and polydimethylsiloxane as tribological surfaces to differentiate friction properties of commercial yogurts. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, K.A. Dominant forces in protein folding. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7133–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoi, K.; Rizvi, S.S.H. Rheological characterization of texturized whey protein concentrate-based powders produced by reactive supercritical fluid extrusion. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, M.J.H.; Jayaraman, P.; Fryer, P.J. The effect of temperature and shear rate upon the aggregation of whey protein and its implications for milk fouling. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, A.S.; Puhl, C.; Kadla, J.F.; Khan, S.A. Enzymatic cross-linking of β-lactoglobulin: Conformational properties using FTIR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, T.; Sun, D.; Gao, H.; Gao, Z.; Mu, Z. Effect of ultrasound on the structure and functional properties of transglutaminase-crosslinked whey protein isolate exposed to prior heat treatment. Int. Dairy. J. 2019, 88, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, H.L.; Köhler, U.; Mantsch, H.H. Structural and conformational changes of beta-lactoglobulin B: An infrared spectroscopic study of the effect of pH and temperature. BBA 1988, 957, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Vahedifar, A.; Madadlou, A.; Salami, M. Influence of seeding and stirring on the structural properties sand formation yield of whey protein microgels. Int. Dairy. J. 2018, 79, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, H.; Yousefinejad, S. Interaction study of human serum albumin and ZnS nanoparticles using fluorescence spectrometry. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1037, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Lefèvre, T.; Subirade, M. Structural and interaction properties of β-lactoglobulin as studied by FTIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 1999, 34, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, T.; Subirade, M. Molecular difference in the formation and structure of fine-stranded and particulate β-lactoglobulin gels. Biopolymers 2000, 54, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.I.; Ismail, A.A.; Alli, I. Effects of physiochemical factors on the secondary structure of β-lactoglobulin. J. Dairy Res. 1996, 63, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loughlin, I.B.; Kelly, P.M.; Murray, B.A.; Fitzgerald, R.J.; Brodkorb, A. Concentrated whey protein ingredients: A Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy investigation of thermally induced denaturation. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2015, 68, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngarize, S.; Adams, A.; Howell, N.K. Studies on egg albumen and whey protein interactions by FT-Raman spectroscopy and rheology. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, R.; Gaiani, C.; Jeandel, C.; Ghanbaja, J.; Scher, J. Combined effect of heat treatment and ionic strength on the functionality of whey proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 6260–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L.; Kontopidis, G. The core lipocalin, bovine β-lactoglobulin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins. Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2000, 1482, 136–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, T. Interactions between proteins and polar lipids. In Food Emulsions, 4th ed.; Friberg, S.E., Larsson, K., Sjöblom, J., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 107–173. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, K.; Gupta, M. Potato chip quality and frying oil stability of high oleic acid soybean oil. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, S395–S400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Fu, F.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Preparation of an environmentally friendly emulsion-type lubricant based on crude rice bran wax. Petroleum 2019, 5, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Jung, M.Y.; Min, D.B. Effects of thermally oxidized triglycerides on the oxidative stability of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1988, 65, 1652–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, S.; Tan, C.Y.; Jana, S. Physical characterization of wax/oil crystalline networks. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, C989–C997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hock, C.; Straburg, S.; Haberland, H.; Lessendorf, B.V.; Aguado, A.; Schmidt, M. Melting-point depression by insoluble impurities: A finite size effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 023401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, W.F.; Sapay, N.; Tieleman, D.P. Atomistic simulations of pore formation and closure in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2014, 106, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverstein, K.A.T.; Haymet, A.D.J.; Dill, K.A. The strength of hydrogen bonds in liquid water and around nonpolar solutes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 8037–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Spoel, D.; van Maaren, P.J.; Larsson, P.; Timneanu, N. Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding in hydrophilic and hydrophobic media. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, R.; Naderi, M.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Williams, D.R.; Thielmann, F.; Bouza, P.; Keith, A.R.; Thiele, G.; Burnett, D.J. Effect of milling on particle shape and surface energy heterogeneity of needle-shaped crystals. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavernier, I.; Doan, C.D.; van de Walle, D.; Danthine, S.; Rimaux, T.; Dewettinck, K. Sequential crystallization of high and low melting waxes to improve oil structuring in wax-based oleogels. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 12113–12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purwanti, N.; Smiddy, M.; van der Goot, A.J.; de Vries, R.; Alting, A.; Boom, R. Modulation of rheological properties by heat-induced aggregation of whey protein solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Wen, L.; Wang, L.; Dang, Y.; Zhou, P.; Liang, L. Effect of temperature, calcium and protein concentration on aggregation of whey protein isolate: Formation of gel-like micro-particles. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 51, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Haque, Z.U.; Wilson, W.W. Association tendency of β-lactoglobulin AB purified by gel permeation chromatography as determined by dynamic light scattering under quiescent conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 1996, 10, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.I.; Alli, I.; Ramaswamy, H.; Raghavan, V.G.S. Interactive effects of factors affecting gelation of whey proteins. J. Food Sci. 1997, 62, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolsook, S.; Kupongsak, S. Influence of bleached rice bran wax on the physiochemical properties of organogels and water-in-oil emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2017, 214, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolder, S.G.; Hendrickx, H.; Sagies, L.M.C.; van der Linden, E. Fibril assemblies in aqueous whey protein mixtures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4229–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Ingredient % (w/w) | Sample | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | OG | OC | CE | HOG | HOC | |||||||||
| WPI | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| * HOSO | 97.5 | 95 | 92.5 | 99 | 96.52 | 94.05 | 91.57 | 74.5 | 72.64 | 70.73 | 79.2 | 73.75 | 71.97 | 70.09 |
| * RBW | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.975 | 0.95 | 0.925 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.745 | 0.726 | 0.707 |
| Distilled Water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 22.36 | 21.76 | 20.0 | 23.0 | 22.3 | 21.7 |
| WPI | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 90 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| * HOSO | 97.5 | 95 | 92.5 | 10 | 87.75 | 85.5 | 83.25 | 74.5 | 72.64 | 70.73 | 72 | 67.1 | 65.3 | 63.73 |
| * RBW | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9.75 | 9.5 | 9.25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 7.45 | 7.26 | 7.07 |
| Distilled Water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 22.36 | 21.76 | 20.0 | 23.0 | 22.3 | 21.7 |
| WPI (%) | Processing | Relative % of Whey Protein Secondary Structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid Side Chain | Random Coil | β-Sheet | β-Turns | α-Helix | ||
| 2.5 | No | 0.95 ab ± 0.1 | 14.4 a ± 0.8 | 58.2 b ± 1.2 | 7.84 a ± 1.0 | 18.6 c ± 0.6 |
| Yes | 0.85 a ± 0.1 | 18.2 a ± 0.5 | 56.9 b ± 0.3 | 11.3 ab ± 0.4 | 13.0 a ± 0.2 | |
| 5 | No | 0.59 a ± 0.0 | 17.2 a ± 1.9 | 55.0 ab ± 0.7 | 13.8 b ± 2.1 | 13.3 a ± 1.0 |
| Yes | 0.71 a ± 0.2 | 17.2 a ± 2.4 | 55.0 ab ± 0.3 | 13.7 b ± 2.4 | 13.4 a ± 0.2 | |
| 7.5 | No | 1.38 b ± 0.2 | 18.4 a ± 0.4 | 51.0 a ± 3.2 | 10.2 ab ± 1.1 | 16.2 b ± 1.2 |
| Yes | 0.66 a ± 0.0 | 16.1 a ± 0.5 | 54.9 ab ± 0.5 | 8.76 a ± 0.6 | 19.5 c ± 0.6 | |
| WPI (%) | Processing | Relative % of Whey Protein Secondary Structure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amino Acid Side Chain | Random Coil | β-Sheet | β-Turns | α-Helix | ||
| 2.5 | No | 2.82 ab ± 0.3 | 10.4 a ± 1.5 | 51.5 a ± 2.5 | 15.4 c ± 0.4 | 19.9 d ± 0.9 |
| Yes | 1.90 a ± 0.3 | 17.0 b ± 0.7 | 57.5 b ± 0.7 | 11.5 bc ± 0.5 | 12.0 b ± 0.3 | |
| 5 | No | 0.89 a ± 0.2 | 15.1 ab ± 2.3 | 49.7 a ± 2.5 | 15.0 c ± 2.5 | 17.5 cd ± 1.4 |
| Yes | 2.13 a ± 0.1 | 15.2 ab ± 1.8 | 65.8 c ± 0.2 | 6.71 a ± 1.4 | 9.40 a ± 0.8 | |
| 7.5 | No | 4.59 b ± 2.0 | 16.5 ab ± 0.0 | 48.8 a ± 1.5 | 11.2 bc ± 2.0 | 17.5 c ± 0.3 |
| Yes | 1.85 a ± 0.3 | 18.6 b ± 3.1 | 57.6 b ± 1.2 | 10.1 ab ± 2.0 | 11.8 b ± 0.7 | |
| 1% RBW Samples | ||||||||
| OG | OC | HOG | HOC | |||||
| WPI (%) | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| OM (°C) | 55.3 b ± 0.4 | 47.1 a ± 0.3 | 47.5 a ± 0.5 | 48.0 a ± 1.0 | 47.4 a ± 0.6 | 53.2 b ± 0.7 | 53.5 b ± 1.4 | 53.9 b ± 1.0 |
| MP (°C) | 61.9 a ± 0.7 | 62.1 a ± 0.8 | 62.5 a ± 0.9 | 62.2 a ± 0.4 | 62.2 a ± 0.9 | 62.0 a ± 0.2 | 63.0 a ± 2.1 | 62.8 a ± 1.6 |
| ΔH (J/g) | 0.61 d ± 0.0 | 0.65 d ± 0.0 | 0.51 cd ± 0.1 | 0.38 ac ± 0.1 | 0.60 bd ± 0.0 | 0.41 bc ± 0.1 | 0.27 ab ± 0.0 | 0.21 a ± 0.1 |
| SFC (%) | 0.76 e ± 0.0 | 0.73 de ± 0.1 | 0.67 cd ± 0.1 | 0.63 c ± 0.0 | 0.60 c ± 0.1 | 0.59 bc ± 0.1 | 0.52 ab ± 0.1 | 0.47 a ± 0.1 |
| * SFC (%) | 0.76 b ± 0.0 | 0.75 b ± 0.1 | 0.70 ab ± 0.1 | 0.69 ab ± 0.0 | 0.75 b ± 0.1 | 0.75 b ± 0.1 | 0.72 ab ± 0.1 | 0.64 a ± 0.0 |
| 10% RBW Samples | ||||||||
| OG | OC | HOG | HOC | |||||
| WPI (%) | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| OM (°C) | 52.5 B ± 1.4 | 47.1 A ± 1.7 | 47.7 A± 1.2 | 47.0 A ± 2.1 | 46.8 A ± 0.8 | 51.0 AB ± 2.4 | 50.6 AB ± 1.5 | 50.5 AB ± 0.6 |
| MP (°C) | 71.8 AB ± 0.6 | 73.1 B ± 0.1 | 72.2 AB ± 0.3 | 72.3 AB ± 1.0 | 72.2 A,B ± 0.6 | 71.6 AB ± 0.2 | 71.6 AB ± 0.3 | 70.5 A ± 1.1 |
| ΔH (J/g) | 19.8 C ± 0.4 | 20.1 C ± 0.4 | 20.4 C ± 1.3 | 17.1 B ± 0.7 | 20.1 BC ± 1.6 | 18.6 BC ± 0.8 | 17.1 B ± 1.1 | 12.7 A ± 0.3 |
| SFC (%) | 8.75 D ± 0.3 | 8.35 CD ± 0.3 | 8.63 D ± 0.5 | 7.82 C ± 0.4 | 6.96 B ± 0.1 | 6.44 B ± 0.5 | 6.37 B ± 0.4 | 5.13 A ± 0.6 |
| * SFC (%) | 8.75 B ± 0.3 | 8.56 B ± 0.3 | 9.08 B ± 0.5 | 8.45 B ± 0.5 | 8.70 B ± 0.1 | 8.64 B ± 0.6 | 8.78 B ± 0.5 | 7.25 A ± 0.8 |
| 1% RBW Samples | ||||||||
| OG | OC | HOG | HOC | |||||
| WPI (%) | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| Protein Particle Area (μm2) | NA * | 9.14 ab ± 0.6 | 11.9 bc ± 2.8 | 14.6 c ± 2.5 | NA * | 6.73 a ± 0.7 | 5.88 a ± 1.2 | 6.33 a ± 1.6 |
| Protein % Filled Area | NA* | 5.11 a ± 0.5 | 11.0 bc ± 2.5 | 13.2 c ± 3.5 | NA * | 6.62 ab ± 0.4 | 8.74 abc ± 2.4 | 8.82 abc ± 1.6 |
| Lipid Crystals Particle Area (μm2) | 10.6 b ± 1.4 | 15.2 c ± 1.8 | 16.4 c ± 1.4 | 16.0 c ± 2.1 | 9.55 b ± 2.0 | 5.52 a ± 0.5 | 4.28 a ± 1.2 | 3.37 a ± 0.9 |
| Lipid Crystals % Filled Area | 8.80 cd ± 0.9 | 11.2 de ± 2.9 | 12.4 ef ± 3.5 | 15.1 f ± 2.6 | 5.88 bc ± 1.4 | 3.37 ab ± 0.6 | 2.63 a ± 0.5 | 1.73 a ± 0.5 |
| 10% RBW Samples | ||||||||
| OG | OC | HOG | HOC | |||||
| WPI (%) | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | 7.5 |
| Protein Particle Area (μm2) | NA * | 7.68 AB ± 2.2 | 11.0 B ± 2.2 | 19.1 C ± 1.6 | NA * | 5.51 A ± 0.4 | 5.49 A ± 0.9 | 4.80 A ± 0.9 |
| Protein Network % Filled Area | NA * | 9.93 A ± 2.7 | 11.1 A ± 3.2 | 13.3 A ± 3.0 | NA * | 7.30 A ± 0.9 | 8.30 A ± 2.6 | 10.8 A ± 1.8 |
| Lipid Crystals Particle Area (μm2) | 40.8 C ± 6.8 | 42.1 C ± 3.6 | 46.6 C ± 4.4 | 59.1 D ± 2.7 | 29.8 B ± 4.8 | 11.7 A ± 2.6 | 11.4 A ± 2.1 | 8.23 A ± 1.8 |
| Lipid Crystals % Filled Area | 38.0 B ± 9.4 | 47.5 C ± 1.7 | 49.6 C ± 3.6 | 50.2 C ± 6.1 | 37.0 B ± 5.0 | 23.1 A ± 2.1 | 22.7 A ± 3.4 | 20.6 A ± 4.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Maleky, F. Quantifications of Oleocolloid Matrices Made of Whey Protein and Oleogels. Foods 2020, 9, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111697
Park C, Jimenez-Flores R, Maleky F. Quantifications of Oleocolloid Matrices Made of Whey Protein and Oleogels. Foods. 2020; 9(11):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111697
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Clifford, Rafael Jimenez-Flores, and Farnaz Maleky. 2020. "Quantifications of Oleocolloid Matrices Made of Whey Protein and Oleogels" Foods 9, no. 11: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111697
APA StylePark, C., Jimenez-Flores, R., & Maleky, F. (2020). Quantifications of Oleocolloid Matrices Made of Whey Protein and Oleogels. Foods, 9(11), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111697