Environmentally Friendly Hydrothermal Processing of Melon by-Products for the Recovery of Bioactive Pectic-Oligosaccharides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Standards
2.2. Raw Material
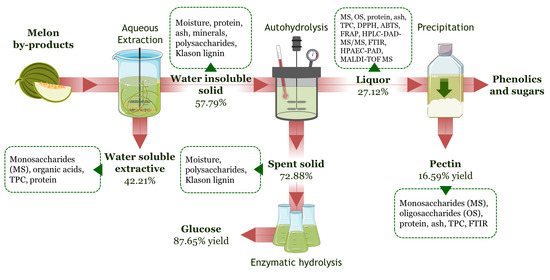
2.3. Aqueous Extraction of Melon by-Products
2.4. Autohydrolysis
2.5. Pectin Precipitation
2.6. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Autohydrolyzed Solids
2.7. Analytical Methods
2.7.1. Analysis of the WISs and Spent Solids from Autohydrolysis Treatment
2.7.2. Chemical Characterization of Liquors
2.7.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
2.7.4. Antioxidant Activity
2.7.5. Identification and Quantification of Major Phenolic Compounds Using HPLC–DAD–MS/MS
2.7.6. Structural Characterization of the Extracted Oligogalacturonides (OGalA)
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
High Performance Anion Exchange Chromatography with Pulsed Amperometric Detection (HPAEC–PAD)
Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectroscopy (MALDI-TOF MS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Characterization of the Raw Material
3.2. Effect of Hydrothermal Processing on Autohydrolysis Liquors
3.2.1. Liquor Composition
3.2.2. Antioxidant Potential
3.3. Pectin Recovery from Autohydrolysis Liquor
3.4. Structural Characterization
3.5. Valorization of the Autohydrolysis Spent Solids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of Food and Agriculture 2019. In Moving Forward on Food Loss and Waste Reduction; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Barilla Center for Food & Nutrition. Food Waste: Causes, Impacts and Proposals; Barilla Center for Food & Nutrition: Parma, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stenmarck, Å.; Jensen, C.; Quested, T.; Moates, G. Estimates of European Food Waste Levels; IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fava, F.; Totaro, G.; Diels, L.; Reis, M.; Duarte, J.; Poggi-varaldo, M.; Ferreira, B.S.; Carioca, O.B. Biowaste biorefinery in Europe: Opportunities and research & development needs. New Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Singh, R.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Macfarlane, D.; Patti, A.F.; Arora, A. Bioactives from fruit processing wastes: Green approaches to valuable chemicals. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2018/850 Amending Directive 1999/31/EC on the Landfill of Waste; OJ L 150; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Directive (EU) 2018/851 Amending Directive 2008/98/EC on Waste; OJ L 150; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2018; pp. 109–140. [Google Scholar]
- Mallek-Ayadi, S.; Bahloul, N.; Kechaou, N. Characterization, phenolic compounds and functional properties of Cucumis melo L. peels. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1691–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Faostat Database. Available online: www.fao.org/faostat (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Aguayo, E.; Escalona, V.H.; Artés, F.A. Metabolic Behavior and Quality Changes of Whole and Fresh Processed Melon. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundo, J.F.; Miller, F.A.; Garcia, E.; Santos, J.R.; Silva, C.L.M.; Brandão, T.R.S. Physicochemical characteristics, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in juice, pulp, peel and seeds of Cantaloupe melon. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, R.; Campos, D.A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M. Valorization of melon fruit (Cucumis melo L.) by-products: Phytochemical and Biofunctional properties with Emphasis on Recent Trends and Advances. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, X.; Gullón, B.; Alonso, J.L.; Yáñez, R. Recovery of high value-added compounds from pineapple, melon, watermelon and pumpkin processing by-products: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolim, P.M.; Fidelis, G.P.; Padilha, C.E.A.; Santos, E.S.; Rocha, H.A.O.; Macedo, G.R. Phenolic profile and antioxidant activity from peels and seeds of melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus) and their antiproliferative effect in cancer cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolim, P.M.; de Oliveira Júnior, S.D.; Mendes de Oliveira, A.C.S.; dos Santos, E.S.; de Macedo, G.R. Nutritional value, cellulase activity and prebiotic effect of melon residues (Cucumis melo L. reticulatus group) as a fermentative substrate. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, N.M.V.; Mondoni, J.; Harada-Padermo, S.S.; Vela-Paredes, R.S.; Berni, P.R.A.; Selani, M.M.; Canniatti Brazaca, S.G. Characterization of apple, pineapple, and melon by-products and their application in cookie formulations as an alternative to enhance the antioxidant capacity. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Antidiabetic Activity and Chemical Composition of Sanbai Melon Seed Oil. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.A.; Albuquerque, T.G.; Alves, R.C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Costa, H.S. Melon (Cucumis melo L.) by-products: Potential food ingredients for novel functional foods? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Khodaiyan, F.; Rezaei, K.; Kiani, H.; Hosseini, S.S. Extraction optimization and physicochemical properties of pectin from melon peel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukumaran, C.; Banupriya, L.; Harinee, S.; Sivaranjani, S.; Sharmila, G.; Rajasekar, V.; Kumar, N.M. Pectin from muskmelon (Cucumis melo var. reticulatus) peels: Extraction optimization and physicochemical properties. 3 Biotech. 2017, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naqash, F.; Masoodi, F.A.; Rather, S.A.; Wani, S.M.; Gani, A. Emerging concepts in the nutraceutical and functional properties of pectin—A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetunji, L.R.; Adekunle, A.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Advances in the pectin production process using novel extraction techniques: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, B.; Gómez, B.; Martínez-Sabajanes, M.; Yáñez, R.; Parajó, J.C.; Alonso, J.L. Pectic oligosaccharides: Manufacture and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, W.; Zou, M.; Lv, R.; Wang, D.; Hou, F.; Feng, H.; Ma, X.; Zhong, J.; Ding, T.; et al. Applications of power ultrasound in oriented modification and degradation of pectin: A review. J. Food Eng. 2018, 234, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Tomar, M.; Saurabh, V.; Mahajan, T.; Punia, S.; Contreras, M.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Rudra, S.G.; Kaur, C.; Kennedy, J.F. Emerging trends in pectin extraction and its anti-microbial functionalization using natural bioactives for application in food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbar, N.; Dejonghe, W.; Gatti, M.; Sforza, S.; Elst, K. Pectic oligosaccharides from agricultural by-products: Production, characterization and health benefits. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, B.; Gullón, B.; Yáñez, R.; Parajó, J.C.; Alonso, J.L. Pectic Oligosacharides from Lemon Peel Wastes: Production, Purification, and Chemical Characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10043–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, M.; Yáñez, R.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J.C. Chemical Production of Pectic Oligosaccharides from Orange Peel Wastes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8470–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Gullón, B.; Schols, H.A.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J.C. Assessment of the Production of Oligomeric Compounds from Sugar Beet Pulp. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4681–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, S.; Patti, A.F.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Arora, A. An integrated green biorefinery approach towards simultaneous recovery of pectin and polyphenols coupled with bioethanol production from waste pomegranate peels. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Singh, R.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; MacFarlane, D.; Patti, A.F.; Arora, A. A hydrocolloid based biorefinery approach to the valorisation of mango peel waste. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, I.; Gordobil, O.; Labidi, J.; Gullón, P. Assessment of suitability of vine shoots for hemicellulosic oligosaccharides production through aqueous processing. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrote, G.; Domínguez, H.; Parajó, J.C. Mild autohydrolysis: An environmentally friendly technology for xylooligosaccharide production from wood. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1999, 74, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila, I.; Gullón, B.; Alonso, J.L.; Labidi, J.; Gullón, P. Vine shoots as new source for the manufacture of prebiotic oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Penín, L.; Vila, C.; Santos, V.; Parajó, J.C. Multi-Stage Hydrothermal Processing of Eucalyptus Globulus Wood: An Experimental Assessment. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2019, 39, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajek, W.; Olejnik, A.; Sip, A. Probiotics, prebiotics and antioxidants as functional foods. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2005, 52, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willats, W.G.T.; Knox, J.P.; Mikkelsen, J.D. Pectin: New insights into an old polymer are starting to gel. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paulo Farias, D.; de Araújo, F.F.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Prebiotics: Trends in food, health and technological applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Sharma, S.; Yahia, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible Utilization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, D.R.; Rotta, E.M.; Sargi, S.C.; Schmidt, E.M.; Bonafe, E.G.; Eberlin, M.N.; Sawaya, A.C.H.F.; Visentainer, J.V. Antioxidant activity, phenolics and UPLC-ESI(-)-MS of extracts from different tropical fruits parts and processed peels. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, J.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Y. Antioxidant activities of peel, pulp and seed fractions of common fruits as determined by FRAP assay. Nutr. Res. 2003, 23, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.I.; Chan, K.W.; Mariod, A.A.; Ismail, M. Phenolic content and antioxidant activity of cantaloupe (cucumis melo) methanolic extracts. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.A.; Fundo, J.F.; Garcia, E.; Santos, J.R.; Silva, C.L.M.; Brandão, T.R.S. Physicochemical and Bioactive Caracterisation of Edible and Waste Parts of “Piel de Sapo” Melon. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Míguez, B.; Gómez, B.; Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Alonso, J.L. Pectic Oligosaccharides and Other Emerging Prebiotics. In Probiotics and Prebiotics in Human Nutrition and Health; InTech: London, UK, 2016; pp. 267–322. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, J.M.; Capek-Menard, E.; Gauvin, H.; Chornet, E. Quality pulp from mixed softwoods as an added value coproduct of a biorefinery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2503–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.; Gullón, B.; Yáñez, R.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J.C. Direct Enzymatic Production of Oligosaccharide Mixtures from Sugar Beet Pulp: Experimental Evaluation and Mathematical Modeling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5510–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gullón, B.; Eibes, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Dávila, I.; Labidi, J.; Gullón, P. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of extracts obtained from the refining of autohydrolysis liquors of vine shoots. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 107, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, B.; Gullón, B.; Remoroza, C.; Schols, H.A.; Parajó, J.C.; Alonso, J.L. Purification, characterization, and prebiotic properties of pectic oligosaccharides from orange peel wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9769–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, D.R.; Rotta, E.M.; Sargi, S.C.; Bonafe, E.G.; Suzuki, R.M.; Souza, N.E.; Matsushita, M.; Visentainer, J.V. Proximate composition, mineral contents and fatty acid composition of the different parts and dried peels of tropical fruits cultivated in Brazil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, X.; Gullón, B.; Alonso, J.L.; Parajó, J.C.; Yáñez, R. Valorization of peanut shells: Manufacture of bioactive oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 183, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinchongkon, K.; Khuwijitjaru, P.; Wiboonsirikul, J.; Adachi, S. Extraction of Oligosaccharides from Passion Fruit Peel by Subcritical Water Treatment. J. Food Process Eng. 2015, 40, e12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, S.Q.; Teoh, W.H.; Tan, C.K.; Yusoff, R.; Ngoh, G.C. Subcritical water extraction of low methoxyl pectin from pomelo (Citrus grandis (L.) Osbeck) peels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lü, X. Characterization of pectic polysaccharides extracted from apple pomace by hot-compressed water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Almagro, N.; Valadez-Carmona, L.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E.; Villamiel, M. Structural characterisation of pectin obtained from cacao pod husk. Comparison of conventional and subcritical water extraction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 217, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.J.; Fan, Z.G.; Wu, Y.Y.; Jiang, Z.G.; Shi, R.C. Eco-friendly extraction and physicochemical properties of pectin from jackfruit peel waste with subcritical water. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 5283–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F. Fruit peels as sources of non-extractable polyphenols or macromolecular antioxidants: Analysis and nutritional implications. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F. Macromolecular antioxidants or non-extractable polyphenols in fruit and vegetables: Intake in four European countries. Food Res. Int. 2015, 74, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Ramirez, M.J.; Orrego, C.E.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Optimization of autohydrolysis conditions to extract antioxidant phenolic compounds from spent coffee grounds. J. Food Eng. 2017, 199, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Armada, L.; Rivas, S.; González, B.; Moure, A. Extraction of phenolic compounds from hazelnut shells by green processes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 255, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, P.; Eibes, G.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Pérez-Rodríguez, N.; Lú-Chau, T.A.; Gullón, B. Green sustainable process to revalorize purple corn cobs within a biorefinery frame: Co-production of bioactive extracts. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leschinsky, M.; Zuckerstätter, G.; Weber, H.K.; Patt, R.; Sixta, H. Effect of autohydrolysis of Eucalyptus globulus wood on lignin structure. Part 1: Comparison of different lignin fractions formed during water prehydrolysis. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Extraction of polysaccharides by autohydrolysis of spent coffee grounds and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gullón, B.; Eibes, G.; Dávila, I.; Moreira, M.T.; Labidi, J.; Gullón, P. Hydrothermal treatment of chestnut shells (Castanea sativa) to produce oligosaccharides and antioxidant compounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 192, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, F.M.; Cautela, D.; Laratta, B. Characterization of Polyphenolic Compounds in Cantaloupe Melon By-Products. Foods 2019, 8, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- M’sakni, N.H.; Majdoub, H.; Roudesli, S.; Picton, L.; Le Cerf, D.; Rihouey, C.; Morvan, C. Composition, structure and solution properties of polysaccharides extracted from leaves of Mesembryanthenum crystallinum. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, K.; Jolie, R.P.; Fraeye, I.; Van Loey, A.M.; Hendrickx, M.E. Comparative study of the cell wall composition of broccoli, carrot, and tomato: Structural characterization of the extractable pectins and hemicelluloses. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, G.; Wu, D.; Wei, C.; Tao, W.; Ye, X.; Linhardt, R.J.; Orfila, C.; Chen, S. Reconsidering conventional and innovative methods for pectin extraction from fruit and vegetable waste: Targeting rhamnogalacturonan I. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpodo, F.M.; Agbenorhevi, J.K.; Alba, K.; Bingham, R.J.; Oduro, I.N.; Morris, G.A.; Kontogiorgos, V. Pectin isolation and characterization from six okra genotypes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassino, A.N.; Barba, F.J.; Brnčić, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Lucini, L.; Brnčić, S.R. Analytical tools used for the identification and quantification of pectin extracted from plant food matrices, wastes and by-products: A review. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Khodaiyan, F.; Labbafi, M.; Saeid Hosseini, S.; Hojjati, M. Pistachio green hull pectin: Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction and evaluation of its physicochemical, structural and functional properties. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Khodaiyan, F.; Yarmand, M.S. Optimization of microwave assisted extraction of pectin from sour orange peel and its physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manrique, G.D.; Lajolo, F.M. FT-IR spectroscopy as a tool for measuring degree of methyl esterification in pectins isolated from ripening papaya fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasambandam, R.; Proctor, A. Determination of pectin degree of esterification by diffuse reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, B.; Yáñez, R.; Parajó, J.C.; Alonso, J.L. Production of pectin-derived oligosaccharides from lemon peels by extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane filtration. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penín, L.; Santos, V.; del Río, J.C.; Parajó, J.C. Assesment on the chemical fractionation of Eucalyptus nitens wood: Characterization of the products derived from the structural components. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, A.; Fiorentini, C.; Vadivel, V.; Moncalvo, A.; Spigno, G. Implementation of auto-hydrolysis process for the recovery of antioxidants and cellulose from wheat straw. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Component | Content |
|---|---|
| Extracts (g/100 g extracts) | |
| Glucose | 36.40 ± 3.18 |
| Sucrose | 5.35 ± 0.24 |
| Fructose | 45.79 ± 0.26 |
| Uronic Acids | 2.79 ± 0.04 |
| Citric Acid | 5.59 ± 1.00 |
| TPC | 0.89 ± 0.02 |
| Protein | 10.81 ± 1.05 |
| WIS (g/100 g WIS) | |
| Glucan | 24.54 ± 0.10 |
| Xylan | 4.89 ± 0.21 |
| Galactan | 3.31 ± 0.21 |
| Mannan | 1.54 ± 0.04 |
| Arabinosyl S. | 1.56 ± 0.11 |
| Acetyl Groups | 2.05 ± 0.35 |
| Galacturonan | 11.99 ± 0.69 |
| Klason lignin | 19.96 ± 1.72 |
| Protein | 11.36 ± 1.86 |
| Ash | 3.36 ± 0.03 |
| mg/100 g WIS | |
| Iron | 8.74 ± 3.97 |
| Potassium | 863.01 ± 109.81 |
| Manganese | 1.83 ± 0.36 |
| Magnesium | 218.73 ± 50.57 |
| Autohydrolysis Liquor | Recovered Pectin | Recovery Yield | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition (g/100 g dw) | |||
| NVC (g/100 g WIS) | 23.22 | 16.59 | 71.43 |
| GOS | 2.50 | 0.14 | 4.07 |
| XOS | 1.40 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| GalOS | 8.15 | 8.05 | 70.50 |
| ManOS | 1.97 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| AraOS | 4.62 | 4.37 | 67.47 |
| RhaOS | 1.56 | 0.51 | 23.37 |
| Ac-OS | 2.05 | 1.57 | 54.68 |
| OGalA | 43.38 | 55.41 | 91.23 |
| Protein | 12.13 | 6.10 | 35.94 |
| Ash | 9.75 | 6.88 | 50.40 |
| TPC | 0.81 | 0.33 | 29.21 |
| Other Parameters | |||
| Moisture (%) | 98.65 | 7.02 | |
| OS/MS ratio (w/w) | 7.56 | 104.15 | |
| DA (molar %) | 15.26 | 9.15 | |
| HG * (molar %) | 62.34 | 77.75 | |
| RG-I * (molar %) | 27.71 | 22.03 | |
| HG/RG-I | 2.25 | 3.53 | |
| Sugar Ratios ** (w/w) | |||
| 1 | 2.76 | 4.29 | |
| 2 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| 3 | 8.17 | 24.27 | |
| m/z | Structure |
|---|---|
| 648.52 | Pent2GalAAc4Na |
| 847.58 | HexPentRhaGalA2MeNa |
| 980.57 | Pent3GalA3MeNa |
| 1174.34 | HexGalA4Me4Ac5Na |
| 1463.65 | Hex2GalA6Me3Na |
| 1603.34 | GalA8Me5Ac2Na |
| 1790.94 | Pent2GalA7Me3Ac5Na |
| 1889.26 | Pent3GalA8Me3Na |
| 2409.23 | Hex1Pent3GalA9Me4Ac4Na |
| 2641.94 | Hex4PentGalA10AcK |
| 3498.19 | Hex4Pent2Rha3GalA11Me3Ac3Na |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rico, X.; Gullón, B.; Yáñez, R. Environmentally Friendly Hydrothermal Processing of Melon by-Products for the Recovery of Bioactive Pectic-Oligosaccharides. Foods 2020, 9, 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111702
Rico X, Gullón B, Yáñez R. Environmentally Friendly Hydrothermal Processing of Melon by-Products for the Recovery of Bioactive Pectic-Oligosaccharides. Foods. 2020; 9(11):1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111702
Chicago/Turabian StyleRico, Xiana, Beatriz Gullón, and Remedios Yáñez. 2020. "Environmentally Friendly Hydrothermal Processing of Melon by-Products for the Recovery of Bioactive Pectic-Oligosaccharides" Foods 9, no. 11: 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111702
APA StyleRico, X., Gullón, B., & Yáñez, R. (2020). Environmentally Friendly Hydrothermal Processing of Melon by-Products for the Recovery of Bioactive Pectic-Oligosaccharides. Foods, 9(11), 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9111702