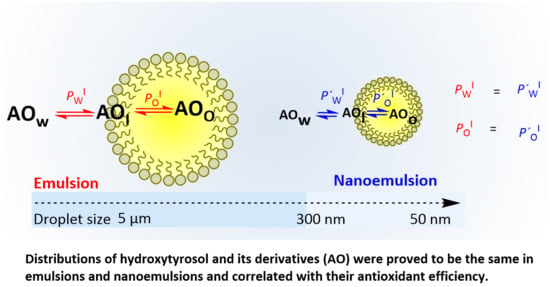
Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions and Its Influence on Their Lipid Oxidation: Droplet Size Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Emulsions and Nanoemulsions
2.3. Average Droplet Size, Polydispersity, and ζ-Potential Measurements of the Prepared Emulsions and Nanoemulsions
2.4. Cyclic Voltammetry
2.5. Efficiency of HT and Its Derivatives in Fish Oil Emulsions and Nanoemulsions
2.6. Determining Antioxidant Distribution and Local Concentrations in Intact Emulsified Systems
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Droplet Size and Polydispersity of the Prepared Emulsified Systems
3.2. Determination of the Partition Constants of HT and Its Derivatives in Intact Fish Oil Emulsions and Nanoemulsions
3.3. Distribution of HT and Its Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsified Systems
3.4. Aqueous, Interfacial, and Oil Concentrations of HT and Its Derivatives in Fish Oil Emulsified Systems
3.5. Effects of the Emulsifier Volume Fraction, and Oil to Water Ratio on the Effective Interfacial Concentrations of HT and Its Derivatives in Emulsions and Nanoemulsions
3.6. Antioxidant Efficiency of HT and Its Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions: Key Insights
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobsen, C.; Nielsen, N.S.; Horn, A.F.; Sørensen, A.D.M. Food Enrichment with Omega-3 Fatty Acids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 0857098861. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.A. Omega-3 fatty acids and hypertension in humans. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secci, G.; Parisi, G. From farm to fork: Lipid oxidation in fish products. A review. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Zhong, Y. Lipid oxidation and improving the oxidative stability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 4067–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, M.E.; Lautenschlaeger, R.; Schmidt, H.; Zeeb, B.; Gibis, M.; Brüggemann, D.A.; Weiss, J. Influence of droplet size on the antioxidant efficacy of oil-in-water emulsions loaded with rosemary in raw fermented sausages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1415–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanner, J. Dietary advanced lipid oxidation endproducts are risk factors to human health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serini, S.; Fasano, E.; Piccioni, E.; Cittadini, A.R.M.; Calviello, G. Dietary n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Paradox of Their Health Benefits and Potential Harmful Effects. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, J.; Yanishlieva, N.; Gordon, M. Antioxidants in Food: Practical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 1855736160. [Google Scholar]
- Barclay, L.R.C.; Vinqvist, M.R. The Chemistry of Phenols; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F. Handbook of Antioxidants for Food Preservation; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; ISBN 1782420975. [Google Scholar]
- Wanasundara, P.K.J.P.; Shahidi, F.; Shahidi, F. Bailey’s Industrial Oil and Fat Products; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.; Costa, M.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Modulating the interfacial concentration of gallates to improve the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiría-Gándara, J.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Enhancement of the antioxidant efficiency of gallic acid derivatives in intact fish oil-in-water emulsions through optimization of their interfacial concentrations. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4429–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C.; Romsted, L.S. A direct correlation between the antioxidant efficiencies of caffeic acid and its alkyl esters and their concentrations in the interfacial region of olive oil emulsions. the pseudophase model interpretation of the “cut-off” effect. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Bravo-Díaz, C.; Vicente, A.A.; Monteiro, L.S.; Paiva-Martins, F. Influence of AO chain length, droplet size and oil to water ratio on the distribution and on the activity of gallates in fish oil-in-water emulsified systems: Emulsion and nanoemulsion comparison. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bravo-Díaz, C.; Romsted, L.S.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F. Using a pseudophase model to determine AO distributions in emulsions: Why dynamic equilibrium matters. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1600277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Díaz, C.; Romsted, L.S.; Liu, C.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Gao, X.; Gu, Q.; Krishnan, G.; Sánchez-Paz, V.; Zhang, Y.; et al. To Model Chemical Reactivity in Heterogeneous Emulsions, Think Homogeneous Microemulsions. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8961–8979. [Google Scholar]
- Berton-Carabin, C.C.; Ropers, M.-H.; Genot, C. Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Involvement of the Interfacial Layer. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 945–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terjung, N.; Löffler, M.; Gibis, M.; Hinrichs, J.; Weiss, J. Influence of droplet size on the efficacy of oil-in-water emulsions loaded with phenolic antimicrobials. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Kobayashi, I.; Nakajima, M. Assessment of Oxidative Stability in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Effect of Emulsification Process, Droplet Size and Storage Temperature. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Durand, E.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Hurdles in predicting antioxidant efficacy in oil-in-water emulsions. Trends food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakaya, K.; Ushio, H.; Matsukawa, S.; Shimizu, M.; Ohshima, T. Effects of droplet size on the oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Lipids 2005, 40, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, G.; Kimura, N.; Hosokawa, M.; Miyashita, K. Effect of Droplet Size on the Oxidative Stability of Soybean Oil TAG and Fish Oil TAG in Oil-in-Water Emulsion. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of vitamin E-enriched nanoemulsions: Factors affecting particle size using spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 391, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Freiría-Gándara, J.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Effects of droplet size on the interfacial concentrations of antioxidants in fish and olive oil-in-water emulsions and nanoemulsions and on their oxidative stability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 562, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, M.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Costa, M.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C.; Monteiro, L.S. Control of antioxidant efficiency of chlorogenates in emulsions: Modulation of antioxidant interfacial concentrations. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 3917–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Costa, M.; Paiva-Martins, F.; Bravo-Díaz, C.; Romsted, L.S. Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol and Its Lipophilic Esters in Intact Olive Oil-in-Water Emulsions: Effects of Antioxidant Hydrophobicity, Surfactant Concentration, and the Oil-to-Water Ratio on the Oxidative Stability of the Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5274–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H. Influence of fatty acids of different unsaturation in the oxidation of purified vegetable oils during microwave irradiation. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1993, 62, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.R.; Weber, M.E.; Idziak, E.S.; Neufeld, R.J.; Cooper, D.G. Determination of interfacial areas in emulsions using turbidimetric and droplet size data: Correction of the formula for emulsifying activity index. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada-Barreiro, S.; Bravo-Diaz, C.; Paiva Martins, F.; Romsted, L.S. A Maximum in Antioxidant Distributions and Efficiencies with Increasing Hydrophobicity of Gallic Acid and its Alkyl Esters. The Pseudophase Model Interpretation of the “Cut-Off” Effect. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2013, 61, 6533–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwinienko, G.; Ingold, K.U. Solvent Effects on the Rates and Mechanisms of Reaction of Phenols with Free Radicals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losada-Barreiro, S.; Sanchez-Paz, V.; Bravo-Diaz, C. Effects of Emulsifier Hydrophile-Lipophile Balance and Emulsifier Concentration on the Distributions of Gallic acid, Propyl Gallate, and alpha-Tocopherol in Corn Oil Emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 389, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| HT | HT2 | HT6 | HT8 | HT12 | HT16 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binary System | (%AOW) | 99.45 ± 0.5 | 83.3 ± 1.1 | ≈0 | ≈0 | ≈0 | ≈0 |
| PWO | 0.008 ± 0.001 | 1.80 ± 0.01 | --- | --- | --- | --- | |
| Emulsion 1:9 O/W | PWI | 34 ± 1 | 207± 39 | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| POI | --- | 115 ± 22 | 89 ± 8 | 119 ± 45 | 97 ± 14 | 75 ± 12 | |
| 102kI(M−1s−1) | 10.6 ± 0.2 | 16.7 ± 5.7 | 19.0 ± 0.3 | 18.7 ± 8.8 | 16.3 ± 0.4 | 16.0 ± 0.2 | |
| Nanoemulsion 1:9 O/W | PWI | 30 ± 4 | 186 ± 14 | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
| POI | ---- | 103 ± 8 | 79 ± 22 | 104 ± 13 | 89 ± 19 | 80 ± 13 | |
| 102kI(M−1s−1) | 19.0 ± 1.3 | 20.7 ± 2.9 | 25.6 ± 0.6 | 23.6 ± 0.2 | 20.2 ± 0.4 | 19.6 ± 0.3 | |
| EC50 I | 5 min | 0.323 ± 0.005 | 0.354 ± 0.009 | 0.300 ± 0.003 | 0.295 ± 0.005 | 0.345 ± 0.005 | 0.331 ± 0.011 |
| 15 min | 0.287 ± 0.004 | 0.309 ± 0.007 | 0.272 ± 0.003 | 0.265 ± 0.005 | 0.319 ± 0.004 | 0.305 ± 0.006 | |
| 60 min | 0.258 ± 0.004 | 0.281 ± 0.004 | 0.247 ± 0.003 | 0.239 ± 0.003 | 0.294 ± 0.006 | 0.298 ± 0.007 | |
| Epa (V) | 0% Tween 80 | 0.418 | 0.421 | 0.404 | 0.412 | 0.402 | 0.403 |
| 2% Tween 80 | ---- | ---- | 0.388 | 0.419 | 0.382 | 0.394 | |
| Emulsion droplet size (ΦI = 0.5, nm) | 1:9 O/W (LEn) II | 8402 ± 162 a | 8564 ± 197 a | 6634 ± 128 b | 5046 ± 114 c | 5689 ± 134 d | 7824 ± 179 e |
| 1:9 O/W (HEn) III | 1280 ± 60 | 1227 ± 57 | 1168 ± 61 | 1145 ± 45 | 1189± 37 | 1235 ± 78 | |
| 4:6 O/W | 4610 ± 203 | 4551 ± 176 | 4465 ± 155 | 4330 ± 117 | 4501 ± 187 | 4534 ± 144 |
| Nanoemulsions | Emulsions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΦO | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 102 ΦI | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| ζ-potential (mV) | −18.1 | −14.2 | −13.5 | −22.6 | nd * | nd * |
| 106 d (m) | 0.304 | 0.231 | 0.166 | 4.71 | 3.12 | 2.73 |
| 1012 Sdroplet (m2) | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 69.7 | 30.6 | 23.4 |
| 1020 Vdroplet (m3) | 1.47 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 5468 | 1589 | 1065 |
| 10−12 Nd | 68 | 155 | 418 | 0.73 | 2.52 | 3.76 |
| Stotal (m2) | 19.7 | 26.0 | 36.1 | 5.1 | 7.7 | 8.8 |
| 102 mT80 available / m2 of S (g) | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.55 | 9.81 | 1.30 | 2.28 |
| 102 mT80, droplet (g) | 0.52 | 0.68 | 0.95 | 0.13 | 0.20 | 0.23 |
| 102 mT80, excess (g) | −0.02 | 0.32 | 1.05 | 0.37 | 0.80 | 1.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, M.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Bravo-Díaz, C.; Monteiro, L.S.; Paiva-Martins, F. Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions and Its Influence on Their Lipid Oxidation: Droplet Size Effects. Foods 2020, 9, 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121897
Costa M, Losada-Barreiro S, Bravo-Díaz C, Monteiro LS, Paiva-Martins F. Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions and Its Influence on Their Lipid Oxidation: Droplet Size Effects. Foods. 2020; 9(12):1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121897
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Marlene, Sonia Losada-Barreiro, Carlos Bravo-Díaz, Luís S. Monteiro, and Fátima Paiva-Martins. 2020. "Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions and Its Influence on Their Lipid Oxidation: Droplet Size Effects" Foods 9, no. 12: 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121897
APA StyleCosta, M., Losada-Barreiro, S., Bravo-Díaz, C., Monteiro, L. S., & Paiva-Martins, F. (2020). Interfacial Concentrations of Hydroxytyrosol Derivatives in Fish Oil-in-Water Emulsions and Nanoemulsions and Its Influence on Their Lipid Oxidation: Droplet Size Effects. Foods, 9(12), 1897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9121897