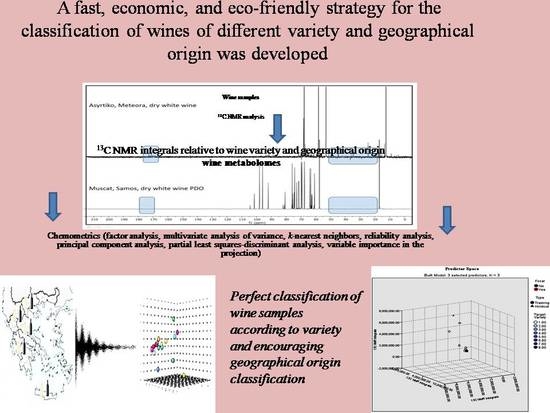
13C NMR-Based Chemical Fingerprint for the Varietal and Geographical Discrimination of Wines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wine Samples and Handling
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. 13C NMR Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Commercial Characteristics of the Wine Samples—Consumer Issues
3.2. 13C NMR Fingerprints of Wine Samples—MANOVA Analysis
3.3. Classification of Wine Samples According to Variety Using the 13C NMR Integrals and Chemometrics
3.3.1. Factor Analysis
3.3.2. k-NN Analysis
3.3.3. Reliability Analysis
4. Classification of Wine Samples According to Geographical Origin Using the 13C NMR Integrals and Chemometrics
Partial Least Squares-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OIV-International Organization of Vine and Wine. 2016. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/ (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Mazzei, P.; Francesca, N.; Moschetti, G.; Piccolo, A. NMR spectroscopy evaluation of direct relationship between soils and molecular composition of red wines from Aglianico grapes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 673, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, P.; Spaccini, R.; Francesca, N.; Moschetti, G.; Piccolo, A. Metabolomic by 1H NMR spectroscopy differentiates “Fiano di Avellino” white wines obtained with different yeast strains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10816–10822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Son, H.S.; Kim, K.M.; Frans, V.D.B.; Hwang, G.S.; Park, W.M.; Lee, C.H. 1H NMR nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic characterization of wines by grape varieties and production areas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8007–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, D.P.; Kallithraka, S.; Mamalos, A. Differentiation of young red wines based on cultivar and geographical origin with application of chemometrics of principal polyphenolic constituents. Talanta 2006, 70, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, L.; Sighinolfi, S.; Marchetti, A.; Tassi, L. Use of lead isotopic ratios as geographical tracer for Lambrusco PDO wines. Molecules 2020, 25, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slaghenaufi, D.; Boscaini, A.; Prandi, A.; Dal Cin, A.; Zandonà, V.; Luzzini, G.; Ugliano, M. Influence of different modalities of grape withering on volatile compounds of young and aged Corvina wines. Molecules 2020, 25, 2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Sykalia, D.; Mannu, A.; Badeka, A.V. Physico-chemical parameters complemented with aroma compounds fired up the varietal discrimination of wine using statistics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, C.D.; Blieke, A.; Ristow, R.; Dietrich, H. Application of FT-MIR spectrometry in wine analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 513, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrile, L.; Zeppa, G.; Giovannozzi, A.M.; Rossi, A.M. Controlling protected designation of origin of wine by Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amargianitaki, M.; Spyros, A. NMR-based metabolomics in wine quality control and authentication. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, B.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, W. Analysis of metabolites in chardonnay dry white wine with various inactive yeasts by 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with pattern recognition analysis. AMB Express 2019, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, H.S.; Hwang, G.S.; Kim, K.M.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, W.M.; Van den Berg, F.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomic studies on geographical grapes and their wines using 1H NMR analysis coupled with multivariate statistics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.-S.; Hwang, G.-S.; Ahn, H.-J.; Park, W.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Hong, Y.-S. Characterization of wines from grape varieties through multivariate statistical analysis of 1H NMR spectroscopic data. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.-S.; Hwang, G.-S.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, E.-Y.; Van den Berg, F.; Park, W.-M.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. 1H NMR-based metabolomic approach for understanding the fermentation behaviors of wine yeast strains. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wines of Greece. 2020. Available online: https://wog.optimedia.gr/ (accessed on 15 February 2020).
- Bagno, A.; Rastrelli, F.; Saielli, G. Prediction of the 1H and 13C NMR Spectra of r-D-Glucose in Water by DFT Methods and MD Simulations. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 7373–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Business Machines (IBM). IBM knowledge center. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/ (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Tavakol, M.; Dennick, R. Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int. J. Med Educ. 2011, 2, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards More Transparent and Integrative Metabolomics Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wehrens, R.; Mevik, B.H. The pls Package: Principal Component and Partial Least Squares Regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 18, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, M. Contributions from Jed Wing and Steve Weston and Andre Williams. Caret: Classification and Regression Training, R Package version 3.45; 2008. Available online: https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/resources/data/report2.pdf (accessed on 20 July 2020).
- Metaboanalyst. Available online: https://www.metaboanalyst.ca/ (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst R 3.0: Toward an Optimized Workflow for Global Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackstadt, A.J.; Hess, A.M. Filtering for increased power for microarray data analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viggiani, L.; Morelli, M.A.C. Characterization of wines by nuclear magnetic resonance: A work study on wines from the basilicata region in Italy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8273–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasiadi, M.; Zira, A.; Magiatis, P.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Mikros, E. 1H NMR-based metabonomics for the classification of Greek wines according to variety, region, and vintage. Comparison with HPLC data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11067–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotakis, C.; Kokkotou, K.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Zervou, M. NMR metabolite fingerprinting in grape derived products: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannu, A.; Ferro, M.; Dugoni, G.C.; Panzeri, W.; Petretto, G.L.; Urgeghe, P.; Mele, A. Improving the recycling technology of waste cooking oils: Chemical fingerprint as tool for non-biodiesel application. Waste Manag. 2019, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, S.; Huebner, E. A fast method for the determination of the ethanol content in wine using widely available routine nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. J. Wine Res. 2014, 25, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Iturmendi, N.; Grelard, A.; Moine, V.; Dufourc, E. Quantitative analysis of Bordeaux red wine precipitates by solid-state NMR: Role of tartrates and polyphenols. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelmann, R.; Fang, F.; Humpfer, E.; Schütz, B.; Bansbach, M.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M. Targeted and non-targeted wine analysis by 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Differentiation of important parameters: Grape variety, geographical origin, year of vintage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5610–5619. [Google Scholar]
- Geana, E.I.; Popescu, R.; Costinel, D.; Dinca, O.R.; Ionete, R.E.; Stefanescu, I.; Artem, V.; Bala, C. Classification of red wines using suitable markers coupled with multivariate statistic analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, S.; Ezernieks, V.; Bastian, S.E.P.; Downey, M.O. Sensory attributes of wine influenced by variety and berry shading discriminated by NMR metabolomics. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brereton, R.G.; Lloyd, G.R. Partial least squares discriminant analysis: Taking the magic away. J. Chemom. 2014, 28, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, Z.; Jacobs, D.; Grigorov, M.; Kochhar, S. Metabolic profiling using principal component analysis, discriminant partial least squares, and genetic algorithms. Talanta 2006, 68, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhuis, J.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Smith, S.; Vis, D.J.; Smilde, A.K.; van Velzen, E.J.J.; van Duijnhoven, J.P.M.; van Dorsten, F.A. Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics 2008, 4, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrés, M.; Platikanov, S.; Tsakovski, S.; Tauler, R. Comparison of the variable importance in projection (VIP) and of the selectivity ratio (SR) methods for variable selection and interpretation. J. Chem. 2015, 29, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Choi, H.H.; Moon, C.S.; Mun, C.W. Comparison of k-nearest neighbor, quadratic discriminant and linear discriminant analysis in classification of electromyogram signals based on the wrist-motion directions. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Wine Samples | Year | Type | Geographical Origin | Variety | Alcohol Volume (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PDO | Zitsa, Ioannina | Debina | 12.0 |
| 2 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PGI | Crete | Malvasia di Candia Aromatica–Chardonnay | 12.5 |
| 3 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PGI | Crete | Syrah–Mandilari | 13.0 |
| 4 | 2017 | Dry Rosé wine—PGI | Crete | Syrah–Mandilari | 13.0 |
| 5 | 2017 | Dry red wine—PGI | Crete | Syrah | 12.5 |
| 6 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PGI | Crete | Vidiano | 13.0 |
| 7 | 2018 | Dry red wine—PGI | Epanomi, Macedonia | Xinomavro | 13.5 |
| 8 | 2018 | Dry white wine—PGI | Epanomi, Macedonia | Malagouzia | 13.5 |
| 9 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PDO | Samos Island | Muscat | 15.0 |
| 10 | 2017 | Dry white wine | Samos Island | Muscat | 12.5 |
| 11 | 2018 | Semi dry rosé wine | Samos Island | Samos red grapes | 12.5 |
| 12 | 2011 | Nectar, white wine naturally sweet—PDO | Samos Island | Muscat | 14.0 |
| 13 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PGI | Letrinoi, Ileia | Refosco | 14.0 |
| 14 | 2015 | Dry red wine—PGI | Letrinoi, Ileia | Daphne Nera–Mavrodafni | 13.0 |
| 15 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PGI | Ileia | Augoustiatis | 13.0 |
| 16 | 2017 | Dry white wine | Ileia | Albariño | 13.5 |
| 17 | 2017 | Demi Sec white wine | Zitsa, Ioannina | Debina | 12.0 |
| 18 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PGI | Meteora | Limniona | 13.0 |
| 19 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PGI | Meteora | Assyrtiko | 14.0 |
| 20 | 2018 | Dry white wine—PGI | Meteora | Malagouzia | 13.0 |
| 21 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PGI | Markopoulo, Athens | Savatiano | 12.5 |
| 22 | 2018 | Dry white wine—PGI | Macedonia | Malagouzia | 12.5 |
| 23 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PGI | Drama | Assyrtiko | 13.5 |
| 24 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PGI | Zitsa, Ioannina | Vlahiko | 12.0 |
| 25 | 2017 | Dry rosé wine—PGI | Korinthos | Agiorgitiko | 13.0 |
| 26 | 2017 | Semi sweet red wine—PGI | Korinthos | Agiorgitiko | 12.0 |
| 27 | 2015 | Dry red wine | Korinthos | Syrah/Merlot/Cabernet | 14.0 |
| 28 | 2017 | Dry red wine—PGI | Kavala | Merlot–Cabernet Sauvignon–Agiorgitiko | 14.0 |
| 29 | 2018 | Dry white wine—PGI | Kavala | Assyrtiko–Sauvignon Blanc | 13.0 |
| 30 | 2017 | Dry white wine—PDO | Mantinia, Messinia | Moschofilero | 12.0 |
| 31 | 2015 | Dry red wine—PGI | Naoussa, Macedonia | Syrah–Xinomavro | 12.0 |
| 32 | 2015 | Dry red wine—PGI | Naoussa, Macedonia | Syrah | 13.0 |
| 33 | 2015 | Dry red wine—Table wine | Naoussa, Macedonia | Xinomavro–Mavroudi–Sefka | 11.0 |
| 34 | 2016 | Dry red wine—PDO | Naoussa, Macedonia | Xinomavro | 12.5 |
| 35 | 2015 | Dry red wine—PGI | Macedonia | Merlot–Xinomavro | 13.0 |
| 36 | 2016 | Dry white varietal wine | Trifylia, Messinia | Chardonnay | 13.5 |
| Group | Samples |
|---|---|
| Crete | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 |
| Ilia | 13, 14, 15, 16 |
| Korinthos | 25, 26, 27 |
| Macedonia | 7, 8, 22, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 |
| Meteora | 18, 19, 20 |
| Samos Island | 9, 10, 11, 12 |
| Others | 1, 17, 21, 23, 24, 28, 29, 30, 36 |
| Wine Samples | Wilks’ Lambda | F | df1 | df2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malvasia di Candia Aromatica–Chardonnay (Other wine varieties)(Crete) | 0.999 | 2.224 | 7 | 17576 | 0.029 |
| Syrah–Mandilari (Syrah +Syrah-based wines) | 0.999 | 3.755 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Syrah–Mandilari (Syrah +Syrah-based wines)(Crete) | 0.998 | 4.562 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Syrah–Mandilari (Syrah +Syrah-based wines)(Crete) | 1.000 | 0.865 | 7 | 17576 | 0.533 |
| Vidiano (Other wine varieties)(Crete) | 0.999 | 2.717 | 7 | 17576 | 0.008 |
| Xinomavro (Xinomavro+Xinomavro-based wines)(Epanomi) | 0.998 | 3.930 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Malagouzia (Epanomi) | 0.997 | 6.429 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Muscat (Samos Island) | 1.000 | 1.208 | 7 | 17576 | 0.294 |
| Muscat (Samos Island) | 0.997 | 7.611 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Samos red grapes wine (Other wine varieties) | 0.998 | 4.177 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Muscat (Samos Island) | 0.999 | 2.883 | 7 | 17576 | 0.005 |
| Refosko (Other wine varieties)(Letrinoi) | 0.999 | 1.453 | 7 | 17576 | 0.179 |
| Daphne Nera–Mavrodafni (Other wine varieties)(Letrinoi) | 0.999 | 3.485 | 7 | 17576 | 0.001 |
| Augoustiatis (Other wine varieties)(Ileia) | 0.999 | 3.257 | 7 | 17576 | 0.002 |
| Albarinó (Other wine varieties)(Ileia) | 0.999 | 1.311 | 7 | 17576 | 0.240 |
| Debina (Zitsa, Ioannina) | 0.998 | 4.105 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Limniona (Other wine varieties)(Meteora) | 0.999 | 1.282 | 7 | 17576 | 0.255 |
| Assyrtiko (Assyrtiko+Assyrtiko-based wines)(Meteora) | 0.999 | 3.335 | 7 | 17576 | 0.001 |
| Malagouzia (Meteora) | 1.000 | 0.362 | 7 | 17576 | 0.925 |
| Savatiano (Other wine varieties)(Markopoulo) | 0.999 | 3.227 | 7 | 17576 | 0.002 |
| Malagouzia (Macedonia) | 0.998 | 3.875 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Assyrtiko (Assyrtiko+Assyrtiko-based wines)(Drama) | 0.999 | 2.996 | 7 | 17576 | 0.004 |
| Vlahiko (Zitsa, Ioannina) | 0.999 | 1.657 | 7 | 17576 | 0.115 |
| Agiorgitiko (Korinthos) | 0.999 | 2.218 | 7 | 17576 | 0.030 |
| Agiorgitiko (Korinthos) | 0.999 | 2.865 | 7 | 17576 | 0.005 |
| Syrah/Merlot/Cabernet Sauvignon (Syrah+Syrah-based wines)(Korinthos) | 0.999 | 3.073 | 7 | 17576 | 0.003 |
| Merlot–Cabernet Sauvignon–Agiorgitiko (Other wine varieties)(Kavala) | 0.999 | 3.394 | 7 | 17576 | 0.001 |
| Assyrtiko/Sauvignon Blanc (Assyrtiko+Assyrtiko-based wines)(Kavala) | 0.999 | 2.663 | 7 | 17576 | 0.009 |
| Moschofilero (Other wine varieties) (Mantinia) | 0.998 | 3.927 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Syrah–Xinomavro (Syrah+Syrah-based wines)(Naoussa) | 0.999 | 3.536 | 7 | 17576 | 0.001 |
| Syrah (Syrah+Syrah-based wines)(Naoussa) | 1.000 | 0.324 | 7 | 17576 | 0.944 |
| Xinomavro–Mavroudi–Sefka (Xinomavro+Xinomavro-based wines)(Naoussa) | 0.999 | 1.688 | 7 | 17576 | 0.107 |
| Xinomavro(Naoussa) | 0.997 | 7.937 | 7 | 17576 | 0.000 |
| Merlot–Xinmavro (Xinomavro+Xinomavro-based wines)(Macedonia) | 0.999 | 2.305 | 7 | 17576 | 0.024 |
| Chardonnay (Other wine varieties)(Trifylia) | 0.999 | 3.686 | 7 | 17576 | 0.001 |
| Partition | Observed | Predicted | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Syrah + Syrah-Based Wines | Muscat | Xinomavro + Xinomavro-Based Wines | Assyrtiko + Assyrtiko-Based Wines | Malagouzia | Other wine Varieties | Agiorgitiko | Debina | Percent Correct | ||
| Training | Syrah+Syrah-based wines | 1560 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99.8% |
| Muscat | 0 | 1533 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99.9% | |
| Xinomavro + Xinmavro-based wines | 0 | 0 | 1515 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99.9% | |
| Assyrtiko + Assyrtiko-based wines | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1539 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99.9% | |
| Malagouzia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1524 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 99.7% | |
| Other wine varieties | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1543 | 5 | 0 | 99.6% | |
| Agiorgitiko | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1577 | 0 | 99.9% | |
| Debina | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1523 | 99.9% | |
| Overall Percent | 12.6% | 12.4% | 12.3% | 12.5% | 12.4% | 12.5% | 12.9% | 12.3% | 99.8% | |
| Holdout | Syrah+Syrah-based wines | 634 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 99.8% |
| Muscat | 0 | 664 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0% | |
| Xinomavro + Xinmavro-based wines | 0 | 0 | 680 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.9% | |
| Assyrtiko + Assyrtiko-based wines | 0 | 0 | 0 | 656 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 99.8% | |
| Malagouzia | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 670 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100.0% | |
| Other wine varieties | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 648 | 1 | 0 | 99.8% | |
| Agiorgitiko | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 619 | 0 | 100.0% | |
| Debina | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 673 | 100.0% | |
| Missing | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Overall Percent | 12.1% | 12.7% | 13.0% | 12.5% | 12.8% | 12.3% | 11.8% | 12.8% | 99.9% | |
| Measure | Component 1 | Component 2 | Component 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 0.15833 | 0.15 | 0.225 |
| R2 | 0.62002 | 0.89925 | 0.97146 |
| Q2 | −0.37807 | −0.1962 | −0.16277 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mannu, A.; Karabagias, I.K.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Baldino, S.; Karabagias, V.K.; Badeka, A.V. 13C NMR-Based Chemical Fingerprint for the Varietal and Geographical Discrimination of Wines. Foods 2020, 9, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081040
Mannu A, Karabagias IK, Di Pietro ME, Baldino S, Karabagias VK, Badeka AV. 13C NMR-Based Chemical Fingerprint for the Varietal and Geographical Discrimination of Wines. Foods. 2020; 9(8):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081040
Chicago/Turabian StyleMannu, Alberto, Ioannis K. Karabagias, Maria Enrica Di Pietro, Salvatore Baldino, Vassilios K. Karabagias, and Anastasia V. Badeka. 2020. "13C NMR-Based Chemical Fingerprint for the Varietal and Geographical Discrimination of Wines" Foods 9, no. 8: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081040
APA StyleMannu, A., Karabagias, I. K., Di Pietro, M. E., Baldino, S., Karabagias, V. K., & Badeka, A. V. (2020). 13C NMR-Based Chemical Fingerprint for the Varietal and Geographical Discrimination of Wines. Foods, 9(8), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081040