Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proteomic Workflows: Discovery and Targeted Proteomics
3. Proteomics Applications for the Detection and Quantification of Fish Allergens
4. Proteomics Applications for the Detection and Quantification of Shellfish Allergens
5. Proteomics Applications in the Diagnosis of Seafood Allergy
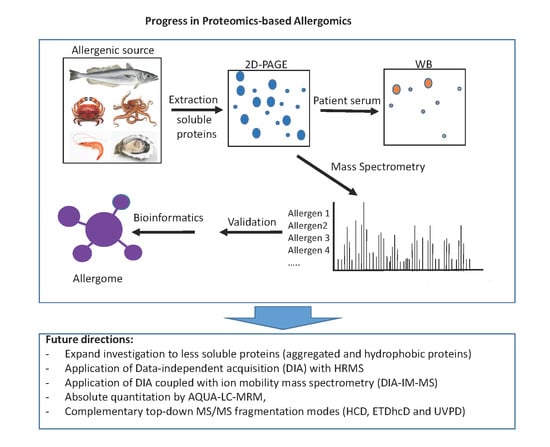
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burks, W.; Tang, M.; Sicherer, S.; Muraro, A.; Eigenmann, P.A.; Ebisawa, M.; Fiocchi, A.; Chiang, W.; Beyer, K.; Wood, R.; et al. ICON: Food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 906–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: A review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matricardi, P.M.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Hoffmann, H.J.; Valenta, R.; Hilger, C.; Hofmaier, S.; Aalberse, R.C.; Agache, I.; Asero, R.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; et al. EAACI Molecular Allergology User’s Guide. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 23, 1–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the evaluation of allergenic foods and food ingredients for labelling purposes. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3894. [Google Scholar]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood allergy: A comprehensive review of fish and shellfish allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeebhay, M.F.; Moscato, G.; Bang, B.E.; Folletti, I.; Lipińska-Ojrzanowska, A.; Lopata, A.L.; Pala, G.; Quirce, S.; Raulf, M.; Sastre, J.; et al. Food processing and occupational respiratory allergy—An EAACI position paper. Allergy 2019, 74, 1852–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Mann, M. Proteomics to study genes and genomes. Nature 2000, 405, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabilloud, T.; Lelong, C. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: A tutorial. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1829–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. De novo mass spectrometry sequencing and characterization of species-specific peptides from nucleoside diphosphate kinase B for the classification of commercial fish species belonging to the family Merlucciidae. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, K.; Albrecht, S.; Schaller, A. Targeted analysis of protein phosphorylation by 2D electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1306, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Pazos, M.; da Rocha, A.P.; Roepstorff, P.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A. Fish proteins as targets of ferrous-catalyzed oxidation: Identification of protein carbonyls by fluorescent labeling on two-dimensional gels and MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7962–7977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, F.; Huang, X.; Majumder, K.; Zhu, Z.; Cai, Z.; Ma, M. Mass spectrometry and two-dimensional electrophoresis to characterize the glycosylation of hen egg white ovomacroglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8209–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinotti, S.; Ranzato, E. 2-DE Gel Analysis: The spot detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1384, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.C.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. Protein analysis by shotgun/bottom-up proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2343–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolters, D.A.; Washburn, M.P.; Yates, J.R., 3rd. An automated multidimensional protein identification technology for shotgun proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5683–5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.C.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.K.; McCormack, A.L.; Yates, J.R., III. An approach to correlate tandem mass spectral data of peptides with amino acid sequences in a protein database. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1994, 5, 976–989. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, R.; Beavis, R.C. TANDEM: Matching proteins with tandem mass spectra. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kall, L.; Canterbury, J.D.; Weston, J.; Noble, W.S.; MacCoss, M.J. Semi-supervised learning for peptide identification from shotgun proteomics datasets. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5383–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M. Peptide sequencing by mass spectrometry for homology searches and cloning of genes. J. Protein Chem. 1997, 16, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Zhang, K.; Hendrie, C.; Liang, C.; Li, M.; Doherty-Kirby, A.; Lajoie, G. PEAKS: Powerful software for peptide de novo sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scigelova, M.; Maroto, F.; Dufresne, C.; Vázquez, J. High Throughput de Novo Sequencing. Available online: http://www.thermo.com/ (accessed on 12 June 2007).
- Bern, M.; Kil, Y.J.; Becker, C. Byonic: Advanced peptide and protein identification software. Curr. Protoc. Bioinf. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateos, J.; Landeira-Abia, A.; Fafián-Labora, J.A.; Fernández-Pernas, P.; Lesende-Rodríguez, I.; Fernández-Puente, P.; Fernández-Moreno, M.; Delmiro, A.; Martín, M.A.; Blanco, F.J.; et al. iTRAQ-based analysis of progerin expression reveals mitochondrial dysfunction, reactive oxygen species accumulation and altered proteostasis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robotti, E.; Marengo, E. 2D-DIGE and fluorescence image analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1664, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Stryiński, R.; Mateos, J.; Pascual, S.; González, A.F.; Gallardo, J.M.; Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Medina, I.; Carrera, M. Proteome profiling of L3 and L4 Anisakis simplex development stages by TMT-based quantitative proteomics. J. Proteom. 2019, 201, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ferrer, D.; Ramos-Fernández, A.; Martínez-Bartolomé, S.; García-Ruiz, P.; Vázquez, J. Quantitative proteomics using 16O/18O labeling and linear ion trap mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2006, 6 (Suppl. 1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.E.; Blagoev, B.; Kratchmarova, I.; Kristensen, D.B.; Steen, H.; Pandey, A.; Mann, M. Stable isotope labelling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, L.N.; Rinner, O.; Schmidt, A.; Letarte, S.; Bodenmiller, B.; Brusniak, M.Y.; Vitek, O.; Aebersold, R.; Müller, M. SuperHirn—A novel tool for high resolution LC-MS-based peptide/protein profiling. Proteomics 2007, 7, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Lopez-Ferrer, D. Fast global phosphoproteome profiling of Jurkat T cells by HIFU-TiO2-SCX-LC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8853–8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry-based fragmentation analysis of glycopeptides. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, I.; Seve, M.; Cunin, V.; Minassian, F.; Poisson, J.F.; Michelland, S.; Bourgoin-Voillard, S. Current trends in protein acetylation analysis. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2019, 16, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornelli, L.; Toby, T.K.; Schachner, L.F.; Doubleday, P.F.; Srzentić, K.; DeHart, C.J.; Kelleher, N.L. Top-down proteomics: Where we are, where we are going? J. Proteom. 2018, 175, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Extensive de novo sequencing of new parvalbumin isoforms using a novel combination of bottom-up proteomics, accurate molecular mass measurement by FTICR-MS, and selected MS/MS ion monitoring. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4393–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Weisbrod, C.; Lopez-Ferrer, D.; Huguet, R.; Gallardo, J.M.; Schwartz, J.; Huhmer, A. Top-Down, High throughput of Thermo-Stable Allergens Using Complementary MS/MS Fragmentation Strategies; Thermo Fisher Scientific: San Jose, CA, USA, 2015; PN64488-EN 0615S. [Google Scholar]
- Borràs, E.; Sabidó, E. What is targeted proteomics? A concise revision of targeted acquisition and targeted data analysis in mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2017, 17, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebersold, R.; Bensimon, A.; Collins, B.C.; Ludwig, C.; Sabido, E. Applications and developments in targeted proteomics: From SRM to DIA/SWATH. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lange, V.; Picotti, P.; Domon, B.; Aebersold, R. Selected reaction monitoring for quantitative proteomics: A tutorial. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, I.; Casas, E.M.; Villar, M.; Ortega-Pérez, I.; López-Ferrer, D.; Martínez-Ruiz, A.; Carrera, M.; Marina, A.; Martínez, P.; Serrano, H.; et al. High-sensitivity analysis of specific peptides in complex samples by selected MS/MS ion monitoring and linear ion trap mass spectrometry: Application to biological studies. J. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 42, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; López-Ferrer, D.; Piñeiro, C.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Fast monitoring of species-specific peptide biomarkers using high-intensity-focused-ultrasound-assisted tryptic digestion and selected MS/MS ion monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5688–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrera, M.; Gallardo, J.M.; Pascual, S.; González, A.F.; Medina, I. Protein biomarker discovery and fast monitoring for the identification and detection of Anisakids by parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2016, 142, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Tate, S.; Röst, H.; Selevsek, N.; Reiter, L.; Bonner, R.; Aebersold, R. Targeted data extraction of the MS/MS spectra generated by data-independent acquisition: A new concept for consistent and accurate proteome analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, O111.016717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beynon, R.J.; Doherty, M.K.; Pratt, J.M.; Gaskell, S.J. Multiplexed absolute quantification in proteomics using artificial QCAT proteins of concatenated signature peptides. Nat. Methods 2005, 2, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereman, M.S.; MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. The development of selected reaction monitoring methods for targeted proteomics via empirical refinement. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Röst, H.; Malmström, L.; Aebersold, R. A computational tool to detect and avoid redundancy in selected reaction monitoring. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO)/International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS) Allergen Nomenclature Home Page. Available online: http://www.allergen.org (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Elsayed, S.; Bennich, H. The primary structure of allergen M from cod. Scand. J. Immunol. 1975, 4, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukrust, L.; Apold, J.; Elsayed, S.; Aas, K. Crossed immunoelectrophoretic and crossed radioimmunoelectrophoretic studies employing a model allergen from codfish. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1978, 57, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrøm, C.D.; van Dô, T.; Hordvik, I.; Endresen, C.; Elsayed, S. Cloning of two distinct cDNAs encoding parvalbumin, the major allergen of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Scand. J. Immunol. 1996, 44, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Universal Protein Resource (Uniprot). Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Allergome. The Platform for Allergen Knowledge. Available online: http://www.allergome.org/ (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Aiello, D.; Materazzi, S.; Risoluti, R.; Thangavel, H.; Di Donna, L.; Mazzotti, F.; Casadonte, F.; Siciliano, C.; Sindona, G.; Napoli, A. A major allergen in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Complete sequences of parvalbumin by MALDI tandem mass spectrometry. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.; Sánchez, R.; Castellanos, M.; Fernández-Escamilla, A.M.; Vázquez-Cortés, S.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Gasset, M. Fish β-parvalbumin acquires allergenic properties by amyloid assembly. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2015, 145, w14128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez, R.; Martínez, J.; Castro, A.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. The amyloid fold of Gad m 1 epitopes governs IgE binding. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tavarez, R.; Carrera, M.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. Reconstruction of fish allergenicity from the content and structural traits of the component β-parvalbumin isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrera, M.; González-Fernández, A.; Magadán, S.; Mateos, J.; Pedrós, L.; Medina, I.; Gallardo, J.M. Molecular characterization of B-cell epitopes for the major fish allergen, parvalbumin, by shotgun proteomics, protein-based bioinformatics and IgE-reactive approaches. J. Proteom. 2019, 200, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Rapid direct detection of the major fish allergen, parvalbumin, by selected MS/MS ion monitoring mass spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, M.; Ahmed, I.; Pavase, T.R. Development of a method for the quantification of fish major allergen parvalbumin in food matrix via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with multiple reaction monitoring. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, A.; Hilger, C.; Lehners-Weber, C.; Codreanu-Morel, F.; Morisset, M.; Metz-Favre, C.; Pauli, G.; de Blay, F.; Revets, D.; Muller, C.P.; et al. Identification of enolases and aldolases as important fish allergens in cod, salmon and tuna: Component resolved diagnosis using parvalbumin and the new allergens. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yang, E.; Liu, C.; Xue, W. Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) allergens characterized by ELISA, SDS-PAGE, 2D gels, Western blotting and MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmilah, M.; Shahnaz, M.; Meinir, J.; Masita, A.; Noormalin, A.; Jamaluddin, M. Identification of parvalbumin and two new thermolabile major allergens of Thunnus tonggol using a proteomics approach. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 162, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Holck, A.L.; Yang, E.; Liu, C.; Xue, W. Tropomyosin from tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) as an allergen. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, J.; Veleiro, B.; Daschner, A.; Cuellar, C. Are fish tropomyosins allergens? Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 116, 74–76.e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Saraiva, J.A.; Aubourg, S.P. Effects of high-pressure treatment on the muscle proteome of hake by bottom-up proteomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4559–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamada, Y.; Nagashima, Y.; Shiomi, K. Identification of collagen as a new fish allergen. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Gordo, M.; Sanchez-Garcia, S.; Cases, B.; Pastor, C.; Vivanco, F.; Cuesta-Herranz, J. Identification of vitellogenin as an allergen in Beluga caviar allergy. Allergy 2008, 6325, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.Y.; Murrell, K.D.; Lymbery, A.J. Fish-borne parasitic zoonoses: Status and issues. Int. J. Parasitol. 2005, 35, 1233–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority). Scientific opinion on risk assessment of parasites in fishery products. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibinu, I.E.; Smooker, P.M.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis Nematodes in Fish and Shellfish—From infection to allergies. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 9, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuizen, N.E.; Lopata, A.L. Anisakis: A food-borne parasite that triggers allergic host defences. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fæste, C.K.; Moen, A.; Schniedewind, B.; Anonsen, J.H.; Klawitter, J.; Christians, U. Development of liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry methods for the quantitation of Anisakis simplex proteins in fish. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1432, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, S.C.; Ciordia, S.; Roberston, L.; Zapico, I.; Jiménez-Ruiz, Y.; Gonzalez-Muñoz, M.; Moneo, I.; Carballeda-Sangiao, N.; Rodriguez-Mahillo, A.; Albar, J.P.; et al. Proteomic profiling and characterization of differential allergens in the nematodes Anisakis simplex sensu stricto and A. pegreffii. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, I.; Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Stryiński, R.; Mateos, J.; Carrera, M. Comparative Proteomics Analysis of Anisakis simplex s.s.-Evaluation of the Response of Invasive Larvae to Ivermectin. Genes 2020, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopata, A.L.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Kamath, S.D. Allergens and molecular diagnostics of shellfish allergy: Part 22 of the Series Molecular Allergology. Allergo J. 2016, 25, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AllFam-The Database of Allergen Families. Available online: http://www.meduniwien.ac.at/allfam (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Laly, S.J.; Sankar, T.V.; Panda, S.K. Identification of allergic proteins of Flower tail shrimp (Metapenaeus dobsonii). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 5415–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadzir, Z.H.M.; Misnan, R.; Murad, S. Identification of tropomyosin as major allergen of white squid (loligo edulis) by two-dimensional immunoblotting and mass spectrometry. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2012, 43, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Wu, C.C.; Tyan, Y.C.; Yu, W.T.; Huang, E.S.; Yu, H.S. Identification of pyruvate kinase as a novel allergen in whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) by specific-IgE present in patients with shrimp allergy. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Lee, C.H.; Tyan, Y.C.; Huang, E.S.; Yu, W.T.; Yu, H.S. Identification of pyruvate kinase 2 as a possible crab allergen and analysis of allergenic proteins in crabs consumed in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortea, I.; Cañas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Mass spectrometry characterization of species-specific peptides from arginine kinase for the identification of commercially relevant shrimp species. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5356–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanaruksombat, S.; Srisomsap, C.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Punyarit, P.; Phiriyangkul, P. Identification of a novel allergen from muscle and various organs in banana shrimp (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2014, 113, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmilah, M.; Shahnaz, M.; Zailatul, H.M.Y.; Noormalin, A.; Normilah, I. Identification of tropomyosin and arginine kinase as major allergens of Portunus pelagicus (blue swimming crab). Trop. Biomed. 2012, 29, 467–478. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, D.X.; Liu, Q.M.; Chen, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Assessment of the sensitizing capacity and allergenicity of enzymatic cross-linked arginine kinase, the crab allergen. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Mao, H.Y.; Cao, M.J.; Cai, Q.F.; Su, W.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, G.M. Purification, physicochemical and immunological characterization of arginine kinase, an allergen of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, S.D.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Voskamp, A.; Komoda, T.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Lopata, A.L. Effect of heat processing on antibody reactivity to allergen variants and fragments of black tiger prawn: A comprehensive allergenomic approach. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.; Kamath, S.D.; Johnston, E.; Zenger, K.R.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Lopata, A.L. Rapid and comprehensive discovery of unreported shellfish allergens using large-scale transcriptomic and proteomic resources. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stella, R.; Sette, G.; Moressa, A.; Gallina, A.; Aloisi, A.M.; Angeletti, R.; Biancotto, G. LC-HRMS/MS for the simultaneous determination of four allergens in fish and swine food products. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Gu, S.; Fang, Z.; Niu, B.; Deng, X.; Guo, D.; Zhu, J.; Han, F. Detection of seven kinds of aquatic product allergens in meat products and seasoning by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 37, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, R.; Monneuse, J.M.; Gemro, E.; Metton, I.; Humpf, H.U.; Brockmeyer, J. New High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled Mass Spectrometry Method for the Detection of Lobster and Shrimp Allergens in Food Samples via Multiple Reaction Monitoring and Multiple Reaction Monitoring Cubed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6219–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.M.A.; Lopata, A.L.; Randell, E.W.; Helleur, R.J. Absolute quantification method and validation of airborne snow crab allergen tropomyosin using tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 37, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.M.A.; Kamath, S.D.; Gagné, S.; Lopata, A.L.; Helleur, R. Comprehensive proteomics approach in characterizing and quantifying allergenic proteins from northern shrimp: Toward better occupational asthma prevention. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Cao, T.T.; Koeberl, M.; Kamath, S.D.; Williamson, N.A.; O’Callaghan, S.; Nie, S.; Mehr, S.S.; et al. Variability of allergens in commercial fish extracts for skin prick testing. Allergy 2019, 74, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, M.; Kuehn, A.; Mills, E.N.C.; Costello, C.A.; Ollert, M.; Smabrekke, L.; Primicerio, R.; Wickman, M.; Klingenberg, C. Cross-reactivity in fish allergy: A double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1170–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asero, R.; Scala, E.; Villalta, D.; Pravettoni, V.; Arena, A.; Billeri, L.; Colombo, G.; Cortellini, G.; Cucinelli, F.; De Cristofaro, M.L.; et al. Shrimp Allergy: Analysis of commercially available extracts for in vivo diagnosis. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappe, U.; Schwager, C. Relevance of lipophilic allergens in food allergy diagnosis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017, 17, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonlokke, J.H.; Bang, B.; Aasmoe, L.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Syron, L.N.; Andersson, E.; Dahlman-Höglund, A.; Lopata, A.L.; Jeebhay, M. Exposures and Health Effects of Bioaerosols in Seafood Processing Workers—A Position Statement. J. Agromed. 2019, 24, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Protein | Seafood Source | Function | Molecular Weight (kDa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | Crustacean | Mollusk | |||
| Aldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase | X | - | - | Oxidation of aldehydes | 41 |
| Aldolase A | X | X | - | Glycolysis | ≈40 |
| Arginine kinase | - | X | X | Metabolism | 38–45 |
| Collagen | X | - | - | Structural | >100 |
| Creatine kinase | X | - | - | Metabolism | ≈40 |
| β-Enolase | X | X | - | Glycolysis | ≈50 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate isomerase | X | - | - | Glycolysis | 60 |
| Glycealdehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | X | - | - | Glycolysis | ≈37 |
| Hemocyanin | - | X | - | O2 transport | 77 |
| L-lactate dehydrogenase | X | - | - | Metabolism | 34 |
| Myosin light chain 1 | - | X | - | Structural | 17–23 |
| Myosin light chain 2 | - | X | - | Structural | 17–23 |
| Ovary development-related protein | - | X | - | Unknown | 28 |
| Paramyosin | - | - | X | Structural | 100 |
| α-Parvalbumin | X | - | - | Ca2+-binding | 10–13 |
| β-Parvalbumin | XX | - | - | Ca2+-binding | 10–13 |
| Pyruvate kinase PKM-like | X | - | - | Metabolism | 65 |
| Sarcoplasmic Ca2+-binding protein | - | X | - | Ca2+ buffering | 20–24 |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | X | X | X | Glycolysis | 28 |
| Tropomyosin | X | XX | X | Structural | 33–39 |
| Troponin C | - | X | - | Structural | ≈20 |
| Troponin I | - | X | - | Structural | ≈30 |
| Vitellogenin | X | X | - | Yolk protein | 180 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrera, M.; Pazos, M.; Gasset, M. Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens. Foods 2020, 9, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081134
Carrera M, Pazos M, Gasset M. Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens. Foods. 2020; 9(8):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081134
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrera, Mónica, Manuel Pazos, and María Gasset. 2020. "Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens" Foods 9, no. 8: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081134
APA StyleCarrera, M., Pazos, M., & Gasset, M. (2020). Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens. Foods, 9(8), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9081134