Self-Regulation of Attention in Children in a Virtual Classroom Environment: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. General Procedure
2.2. Participants and Dataset
2.3. Materials
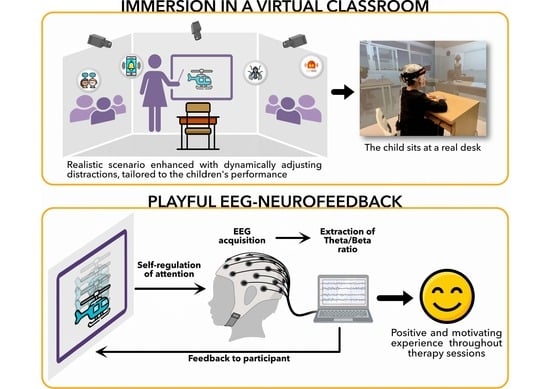
2.3.1. Virtual Classroom
- General Aspects
- Detailed equipment
- VR stimulation
- Script animation
2.3.2. EEG Setup for EEG-NFB Sessions
2.3.3. Simultaneous fMRI-EEG Setup
2.4. Behavioral Tasks
2.4.1. Neurofeedback Training Task
- Calibration Phase
- Helicopter display
- Calculation task as baseline
2.4.2. Sustained Attention Task
2.4.3. Neurofeedback Transfer Task
2.4.4. Behavioral Data Analysis
- Satisfaction survey
- Sustained attention task
2.5. EEG and fMRI Data Preprocessing
2.5.1. EEG Data in MRI
2.5.2. EEG Data in VR
2.5.3. fMRI Data
- Anatomical data
- Functional data
2.6. EEG and fMRI Data Analysis
2.6.1. Resting-State fMRI Networks
2.6.2. EEG Microstates
2.6.3. TBR in EEG-NFB Sessions
2.6.4. Neurofeedback Transfer Task
- EEG
- fMRI
3. Results
3.1. Acceptation, Satisfaction, and Sustaining Motivation
3.2. Feasibility in Children: Quality Assessment of Simultaneous EEG-fMRI Data
3.3. Potential of EEG-NFB Combined with VR: Preliminary Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadeghi, H.; Shabani, Y.; Pakniyat, A.; Karimian, K.; Harorani, M.; Naderi Rajeh, Y. Road Crashes in Adults with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Risky Driving Behavior. Iran. J. Psychiatry 2020, 15, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Sanders, S.; Doust, J.; Beller, E.; Glasziou, P. Prevalence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, e994–e1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochrie, K.D.; Whited, M.C.; Cellucci, T.; Freeman, T.; Corson, A.T. ADHD, depression, and substance abuse risk among beginning college students. J. Am. Coll. Health 2020, 68, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocchi, L.; Bramati, I.E.; Zalesky, A.; Furukawa, E.; Fontenelle, L.F.; Moll, J.; Tripp, G.; Mattos, P. Altered Functional Brain Connectivity in a Non-Clinical Sample of Young Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 17753–17761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldehinkel, M.; Beckmann, C.F.; Franke, B.; Hartman, C.A.; Hoekstra, P.J.; Oosterlaan, J.; Heslenfeld, D.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Mennes, M. Functional connectivity in cortico-subcortical brain networks underlying reward processing in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Khosrowabadi, R.; Albrecht, B.; Pouretemad, H.; Rothenberger, A. ADHD subtypes: Do they hold beyond core symptoms? A multilevel testing of an additive model. Appl. Neuropsychol. Child 2022, 11, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Couture, J. A Review of the Pathophysiology, Etiology, and Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Ann. Pharmacother. 2014, 48, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, J.; Baler, R.D.; Volkow, N.D. Understanding the effects of stimulant medications on cognition in individuals with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A decade of progress. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storebø, O.J.; Pedersen, N.; Ramstad, E.; Kielsholm, M.L.; Nielsen, S.S.; Krogh, H.B.; Moreira-Maia, C.R.; Magnusson, F.L.; Holmskov, M.; Gerner, T.; et al. Methylphenidate for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Children and Adolescents—Assessment of Adverse Events in Non-Randomised Studies. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5, CD012069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.S.; Arnold, L.E.; Swanson, J.M.; Vitiello, B.; Abikoff, H.B.; Greenhill, L.L.; Hechtman, L.; Hinshaw, S.P.; Pelham, W.E.; Wells, K.C.; et al. 3-Year Follow-up of the NIMH MTA Study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 46, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamimura-Nishimura, K.I.; Brinkman, W.B.; Froehlich, T.E. Strategies for improving ADHD medication adherence. Curr. Psychiatr. 2019, 18, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Montero-Marin, J.; Hinze, V.; Crane, C.; Dalrymple, N.; Kempnich, M.E.J.; Lord, L.; Slaghekke, Y.; Tudor, K.; Byford, S.; Dalgleish, T.; et al. Do Adolescents Like School-Based Mindfulness Training? Predictors of Mindfulness Practice and Responsiveness in the MYRIAD Trial. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2023, 62, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, M.; De Ridder, S.; Strehl, U.; Breteler, M.; Coenen, A. Efficacy of Neurofeedback Treatment in ADHD: The Effects on Inattention, Impulsivity and Hyperactivity: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2009, 40, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doren, J.; Heinrich, H.; Bezold, M.; Reuter, N.; Kratz, O.; Horndasch, S.; Berking, M.; Ros, T.; Gevensleben, H.; Moll, G.H.; et al. Theta/beta neurofeedback in children with ADHD: Feasibility of a short-term setting and plasticity effects. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2017, 112, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arns, M.; Kenemans, J.L. Neurofeedback in ADHD and insomnia: Vigilance stabilization through sleep spindles and circadian networks. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeste, S.S.; Frohlich, J.; Loo, S.K. Electrophysiological biomarkers of diagnosis and outcome in neurodevelopmental disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, G.; Makeig, S.; Tsuang, M.T. In search of biomarkers in psychiatry: EEG-based measures of brain function. Am. J. Genet. Part B 2014, 165, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloss, D.; Varma, J.K.; Pringsheim, T.; Nuwer, M.R. Practice advisory: The utility of EEG theta/beta power ratio in ADHD diagnosis: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2016, 87, 2375–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arns, M.; Heinrich, H.; Strehl, U. Evaluation of neurofeedback in ADHD: The long and winding road. Biol. Psychol. 2014, 95, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bink, M.; van Nieuwenhuizen, C.; Popma, A.; Bongers, I.L.; van Boxtel, G.J.M. Behavioral effects of neurofeedback in adolescents with ADHD: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemieux, L.; Allen, P.J.; Franconi, F.; Symms, M.R.; Fish, D.K. Recording of EEG during fMRI experiments: Patient safety. Magn. Reson. Med. 1997, 38, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Grouiller, F.; Ipek, Ö.; Stoermer, R.; Michel, C.M.; Figueiredo, P.; Van Der Zwaag, W.; Gruetter, R. Simultaneous EEG–fMRI at ultra-high field: Artifact prevention and safety assessment. NeuroImage 2015, 105, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.C.; Gardner, E.S.; Chelonis, J.J.; Schulz, E.G.; Flake, R.A.; Diaz, P.F. Estimates of the Validity and Utility of the Conners’ Continuous Performance Test in the Assessment of Inattentive and/or Hyperactive-Impulsive Behaviors in Children. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2007, 35, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grouiller, F.; Jorge, J.; Pittau, F.; van der Zwaag, W.; Iannotti, G.R.; Michel, C.M.; Vulliémoz, S.; Vargas, M.I.; Lazeyras, F. Presurgical brain mapping in epilepsy using simultaneous EEG and functional MRI at ultra-high field: Feasibility and first results. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2016, 29, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramfort, A. MEG and EEG data analysis with MNE-Python. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablin, P.; Cardoso, J.F.; Gramfort, A. Faster Independent Component Analysis by Preconditioning with Hessian Approximations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 4040–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, O.; Markiewicz, C.J.; Blair, R.W.; Moodie, C.A.; Isik, A.I.; Erramuzpe, A.; Kent, J.D.; Goncalves, M.; DuPre, E.; Snyder, M.; et al. fMRIPrep: A robust preprocessing pipeline for functional MRI. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgolewski, K.; Burns, C.D.; Madison, C.; Clark, D.; Halchenko, Y.O.; Waskom, M.L.; Ghosh, S.S. Nipype: A flexible, lightweight and extensible neuroimaging data processing framework in Python. Front. Neuroinform. 2011, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avants, B.; Epstein, C.; Grossman, M.; Gee, J. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med. Image Anal. 2008, 12, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Yuanjie Zheng Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2001, 20, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M.; Bannister, P.; Brady, M.; Smith, S. Improved Optimization for the Robust and Accurate Linear Registration and Motion Correction of Brain Images. NeuroImage 2002, 17, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.W. AFNI: Software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1996, 29, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op De Beeck, H.P. Against hyperacuity in brain reading: Spatial smoothing does not hurt multivariate fMRI analyses? NeuroImage 2010, 49, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.D.; Barnes, K.A.; Snyder, A.Z.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 2142–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, K.R.A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L. The influence of head motion on intrinsic functional connectivity MRI. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmithorst, V.J.; Holland, S.K. Comparison of three methods for generating group statistical inferences from independent component analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging data. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 19, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj-Bouziane, F.; Monfardini, E.; Guedj, C.; Gardechaux, G.; Hynaux, C.; Farnè, A.; Meunier, M. The helmet head restraint system: A viable solution for resting state fMRI in awake monkeys. Neuroimage 2014, 86, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedj, C.; Monfardini, E.; Reynaud, A.J.; Farnè, A.; Meunier, M.; Hadj-Bouziane, F. Boosting Norepinephrine Transmission Triggers Flexible Reconfiguration of Brain Networks at Rest. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, C.F.; Smith, S.M. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2004, 23, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férat, V.; Scheltienne, M.; Brunet, D.; Ros, T.; Michel, C. Pycrostates: A Python library to study EEG microstates. J. Open Source Softw. 2022, 7, 4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Brandeis, D. Inappropriate assumptions about EEG state changes and their impact on the quantification of EEG state dynamics. NeuroImage 2016, 125, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. NeuroImage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férat, V.; Seeber, M.; Michel, C.M.; Ros, T. Beyond broadband: Towards a spectral decomposition of electroencephalography microstates. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 3047–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, P. The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: A method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Fox, P.T.; Miller, K.L.; Glahn, D.C.; Fox, P.M.; Mackay, C.E.; Filippini, N.; Watkins, K.E.; Toro, R.; Laird, A.R.; et al. Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G.L. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannotti, G.R.; Pittau, F.; Michel, C.M.; Vulliemoz, S.; Grouiller, F. Pulse Artifact Detection in Simultaneous EEG–fMRI Recording Based on EEG Map Topography. Brain Topogr. 2015, 28, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevensleben, H.; Holl, B.; Albrecht, B.; Schlamp, D.; Kratz, O.; Studer, P.; Rothenberger, A.; Moll, G.H.; Heinrich, H. Neurofeedback training in children with ADHD: 6-month follow-up of a randomised controlled trial. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2010, 19, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderwal, T.; Kelly, C.; Eilbott, J.; Mayes, L.C.; Castellanos, F.X. Inscapes: A movie paradigm to improve compliance in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage 2015, 122, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greicius, M.D.; Krasnow, B.; Reiss, A.L.; Menon, V. Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Corbetta, M.; Van Essen, D.C.; Raichle, M.E. The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 9673–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A.R.; Barry, R.J.; McCarthy, R.; Selikowitz, M. EEG-defined subtypes of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 2098–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Weibman, D.; Halperin, J.M.; Li, X. A Review of Heterogeneity in Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriette, C.; Ziane, C.; Ben Hamed, S. Neurofeedback for cognitive enhancement and intervention and brain plasticity. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 177, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panksepp, J. Can PLAY diminish ADHD and facilitate the construction of the social brain? J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 16, 57–66. [Google Scholar]






| Name | Description | Asset Link |
|---|---|---|
| School classroom | Classroom used as the 3D environment of the VR simulation | https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/characters/humanoids/2-toon-people-116917, accessed on 25 October 2023 |
| Toon characters | 20 ‘toon kids’ (10 boys and 10 girls) sat at their desks in pairs, all around the (participant) child. The latter was placed in the center of the virtual classroom sitting at a real school desk (which was the center of the CAVE system) | https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/characters/humanoids/humans/toon-kids-55945, accessed on 25 October 2023 |
| Toon people | 2 ‘toon people’ were used to represent the virtual mistress and school’s headmaster | https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/characters/humanoids/2-toon-people-116917, accessed on 25 October 2023 |
| Everyday motion pack—free | Package of animations (idle, sit, walk, talk) used to animate virtual character bodies | https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/3d/animations/everyday-motion-pack-free-115067, accessed on 25 October 2023 |
| SALSA lip sync | Plugin used to animate virtual character faces, to generate various random head and gaze directions, eye blinks, and “look at target” behaviors. It also allowed virtual characters’ lips to move in sync with virtual character’ speech (audio-to-speech) | https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/animation/salsa-lipsync-suite-148442, accessed on 25 October 2023 |
| Character | Type of Stimulation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mistress | Audiovisual |
|
| Headmaster | Audiovisual |
|
| Kids | Visual |
|
| Audiovisual |
| |
| Other | Audiovisual |
|
| Audio |
| |
| Audiovisual |
|
| Questions | Yes | No | Sometimes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Did you like the VR classroom sessions? | 83% | 0% | 17% |
| Were you happy to come and do the experiment? | 100% | 0% | 0% |
| Do you feel that you have improved your ability to fly the helicopter? | 66% | 0% | 33% |
| Did you have a strategy for flying the helicopter? * | 100% | 0% | 0% |
| Do you use these strategies to focus in class? | 17% | 83% | 0% |
| Do you feel like you are able to focus better? | 83% | 0% | 17% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guedj, C.; Tyrand, R.; Badier, E.; Planchamp, L.; Stringer, M.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Férat, V.; Ha-Vinh Leuchter, R.; Grouiller, F. Self-Regulation of Attention in Children in a Virtual Classroom Environment: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121352
Guedj C, Tyrand R, Badier E, Planchamp L, Stringer M, Zimmermann MO, Férat V, Ha-Vinh Leuchter R, Grouiller F. Self-Regulation of Attention in Children in a Virtual Classroom Environment: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(12):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121352
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuedj, Carole, Rémi Tyrand, Emmanuel Badier, Lou Planchamp, Madison Stringer, Myriam Ophelia Zimmermann, Victor Férat, Russia Ha-Vinh Leuchter, and Frédéric Grouiller. 2023. "Self-Regulation of Attention in Children in a Virtual Classroom Environment: A Feasibility Study" Bioengineering 10, no. 12: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121352
APA StyleGuedj, C., Tyrand, R., Badier, E., Planchamp, L., Stringer, M., Zimmermann, M. O., Férat, V., Ha-Vinh Leuchter, R., & Grouiller, F. (2023). Self-Regulation of Attention in Children in a Virtual Classroom Environment: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering, 10(12), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121352