Simultaneous Estimation of the Vertical Stiffness in the Knee and Hip for Healthy Human Subjects during Walking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
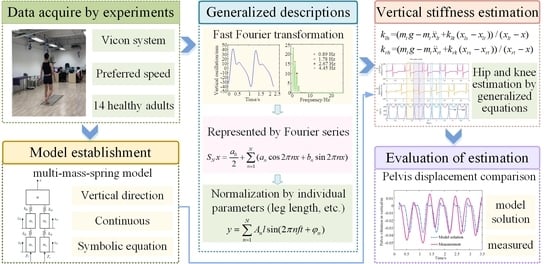
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experiments
2.3. Multi-Mass-Spring Model of the Lower Limbs
2.4. Generalized Description of Kinematics and VGRF
2.5. Estimation of Vertical Stiffness in Joints
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Empirical Parameters of Unified Representation
3.2. The Vertical Stiffness of the Knee
3.3. The Vertical Stiffness of the Hip
3.4. Validation of the Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, S.; Ruina, A.; Tedrake, R.; Wisse, M. Efficient Bipedal Robots Based on Passive-Dynamic Walkers. Science 2005, 307, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, F.; Shen, S. Reproducing vertical human walking loads on rigid level surfaces with a damped bipedal inverted pendulum. Structures 2021, 33, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboola-Dobson, A.; Wei, G.; Ren, L. Biologically inspired design and development of a variable stiffness powered ankle-foot prosthesis. J. Mech. Robot 2019, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Villamañan, M.D.C.; Gonzalez-Vargas, J.; Torricelli, D.; Moreno, J.C.; Pons, J.L. Compliant lower limb exoskeletons: A comprehensive review on mechanical design principles. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil 2019, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saypulaev, M.R.; Zuev, Y.; Saypulaev, G.R. Development of the lower extremity exoskeleton dynamics model using in the task of the patient verticalization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2096, 12042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Han, B.; Wang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Ma, J.; Wei, P. Knee joint biomechanics in physiological conditions and how pathologies can affect it: A systematic review. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2020, 2020, 7451683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, L.; Yi, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, T. Reconstructing walking dynamics from two shank-mounted inertial measurement units. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3040–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; Song, Q. Long time prediction of human lower limb movement based on IPSO-BPNN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1865, 42099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higueras-Ruiz, D.R.; Nishikawa, K.; Feigenbaum, H.; Shafer, M. What is an artificial muscle? A comparison of soft actuators to biological muscles. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 17, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, B.; Li, J.; Bao, Y.; Xu, G. A spring-loaded inverted pendulum model for analysis of human-structure interaction on vibrating surfaces. J. Sound Vib. 2022, 522, 116727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latash, M.L.; Zatsiorsky, V.M. Joint stiffness: Myth or reality. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1993, 12, 653–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struzik, A.; Karamanidis, K.; Lorimer, A.; Keogh, J.W.; Gajewski, J. Application of leg, vertical, and joint stiffness in running performance: A literature overview. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2021, 2021, 9914278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Raychoudhury, S.; Hu, D.; Ren, L.; Liu, J.; Xiu, H.; Liang, W.; Li, B.; Wei, G.; Qian, Z. The impact of locomotor speed on the human metatarsophalangeal joint kinematics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 644582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.R.; Araújo, V.L.; Khuu, A.; Lee, S.; Lewis, C.L.; Souza, T.R.; Holt, K.G.; Fonseca, S.T. Effects of sex and walking speed on the dynamic stiffness of lower limb joints. J. Biomech. 2021, 129, 110803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kooij, H.; Fricke, S.S.; Veld, R.C.; Prieto, A.V.; Keemink, A.Q.; Schouten, A.C.; van Asseldonk, E.H. A device and method to identify hip, knee and ankle joint impedance during walking. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, F.; Takeda, Y.; Kormushev, P.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Ellison, P. Stiffness modulation in a humanoid robotic leg and knee. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 2563–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Guo, W.; Caldwell, D.; Chen, F. Exoskeleton online learning and estimation of human walking intention based on dynamical movement primitives. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Dev. Syst. 2021, 13, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaei, K.; Sawicki, G.; Dollar, A.M. Estimation of quasi-stiffness of the human knee in the stance phase of walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, C.D.C.; Cardoso, T.B.; Gontijo, B.A.; de Magalhães, F.A.; de Souza, T.R.; da Fonseca, S.T.; Ocarino, J.D.M.; Resende, R.A. Hip passive stiffness is associated with midfoot passive stiffness. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2021, 25, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaei, K.; Sawicki, G.; Dollar, A.M. Estimation of Quasi-Stiffness and propulsive work of the human ankle in the stance phase of walking. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rouse, E.J.; Gregg, R.; Hargrove, L.; Sensinger, J.W. The difference between stiffness and quasi-stiffness in the context of biomechanical modeling. IEEE T. Bio.-Med. Eng. 2013, 60, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.B.; DeLuca, P.A. Gait characterization via dynamic joint stiffness. Gait Posture 1996, 4, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Hinman, R.; Creaby, M.; Kemp, G.; Crossley, K.M. Knee joint stiffness during walking in knee osteoarthritis. Arthrit. Care Res. 2010, 62, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpell, B.G.; Ball, N.; Scarvell, J.; Smith, P. A review of models of vertical, leg, and knee stiffness in adults for running, jumping or hopping tasks. J. Sports Sci. 2012, 30, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, P.; Paradisis, G.; Vagenas, G. Leg and vertical stiffness (a)symmetry between dominant and non-dominant legs in young male runners. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 40, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struzik, A.; Winiarski, S.; Zawadzki, J. Inter-Limb Asymmetry of Leg Stiffness in National Second-League Basketball Players during Countermovement Jumps. Symmetry 2022, 14, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Hahn, M.E. Relationship between Joint Stiffness, Limb Stiffness and Whole–Body Center of Mass Mechanical Work across Running Speeds. Biomechanics 2022, 2, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Huang, H.-P.; Lu, H.-Y.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wang, T.-M.; Lu, T.-W. Effects of Tendon Release Surgery on Inter-Limb Leg Stiffness Control in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy during Gait. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamari, J.; Ammarullah, M.; Santoso, G.; Sugiharto, S.; Supriyono, T.; Permana, M.; Winarni, T.; van der Heide, E. Adopted walking condition for computational simulation approach on bearing of hip joint prosthesis: Review over the past 30 years. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, P.; Virekunnas, H.; Sharma, D.; Piche, R.; Cronin, N. Continuous Analysis of Running Mechanics by Means of an Integrated INS/GPS Device. Sensors 2019, 19, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, X.H.; Allen, R.; Sun, J.Q. A stiffness-varying model of human gait. Med. Eng. Phys. 1997, 19, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, Q.; Liu, T. An actuated dissipative spring-mass walking model: Predicting human-like ground reaction forces and the effects of model parameters. J. Biomech. 2019, 90, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielemeyer, J.; Müller, R.; Staufenberg, N.; Renjewski, D.; Abel, R. Ground reaction forces intersect above the center of mass in single support, but not in double support of human walking. J. Biomech. 2021, 120, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Lei, Y.; Liao, W.; Cao, H.; Cao, J. Severity level diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease by ensemble K-nearest neighbor under imbalanced data. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 189, 116113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; Wang, R.; Lei, Y.; Liao, W.; Cao, H. Accurate identification of Parkinson’s disease by distinctive features and ensemble decision trees. Biomed. Signal Process. 2021, 69, 102860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leva, P. Adjustments to Zatsiorsky-Seluyanov’s segment inertia parameters. J. Biomech. 1996, 29, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamari, J.; Ammarullah, M.; Saad, A.; Syahrom, A.; Uddin, M.; van der Heide, E.; Basri, H. The Effect of Bottom Profile Dimples on the Femoral Head on Wear in Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Peiroten, A.; Garcia-Pinillos, F.; Jaen-Carrillo, D.; Carton-Llorente, A.; Abat, F.; Roche-Seruendo, L. Relationship between Connective Tissue Morphology and Lower-Limb Stiffness in Endurance Runners. A Prospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipfert, S.W.; Günther, M.; Renjewski, D.; Grimmer, S.; Seyfarth, A. A model-experiment comparison of system dynamics for human walking and running. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 292, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, J.A.; Gorman, S.; Fitzgerald, G.; Farrokhi, S. Alterations in walking knee joint stiffness in individuals with knee osteoarthritis and self-reported knee instability. Gait Posture 2016, 43, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panero, E.; Anastasio, D.; Massazza, G.; Gastaldi, L. Fourier Analysis of Center of Mass Trajectory in Hemiparetic Gait. In The International Conference of IFToMM ITALY; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Kerrigan, D.; Thirunarayan, M.; Duff-Raffaele, M. The vertical displacement of the center of mass during walking: A comparison of four measurement methods. J. Biomech. Eng. 1998, 120, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Parameters | Pelvis | Thigh | Knee | Shank | Ankle | VGRF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.022 | 0.073 | 0.58 |
| A2 | 0.018 | 0.014 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.040 | 0.08 |
| A3 | 0 | 0.009 | 0.011 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.22 |
| A4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.03 |
| A5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.07 |
| A6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.03 |
| φ1 | −0.93 | −0.59 | −0.59 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 2.47 |
| φ2 | −0.49 | −1.04 | −1.04 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 3.18 |
| φ3 | 0 | −2.14 | −2.14 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.98 |
| φ4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.13 |
| φ5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −0.42 |
| φ6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.15 |
| No | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Errors (%) | 29.14 | 18.87 | 11.94 | 23.22 | 27.95 | 24.00 | 16.45 | 23.49 | 15.47 | 27.95 | 16.48 | 17.76 | 18.34 | 15.62 |
| Models | Components | Aim Stiffness | Gait Phase | Input Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-link conceptual model [31] |  | Joint stiffness of hip and ankle | Stance | Joint angle and moment |
| Spring-mass walking model [32] |  | Leg stiffness | Stance | Leg length and position |
| Statistic model [18,20] |  | Quasi-stiffness of knee and hip separately | Stance | Body weight, height, and walking speed |
| Mass-spring model [39] |  | Leg stiffness | Stance | Angle and leg length change |
| Multi-mass spring model Proposed in this paper |  | Vertical stiffness of knee and hip simultaneous | Entire gait cycle | Body weight, leg length, and walking cadence |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; Liao, W.-H. Simultaneous Estimation of the Vertical Stiffness in the Knee and Hip for Healthy Human Subjects during Walking. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020187
Zhao H, Cao J, Liao W-H. Simultaneous Estimation of the Vertical Stiffness in the Knee and Hip for Healthy Human Subjects during Walking. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huan, Junyi Cao, and Wei-Hsin Liao. 2023. "Simultaneous Estimation of the Vertical Stiffness in the Knee and Hip for Healthy Human Subjects during Walking" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020187
APA StyleZhao, H., Cao, J., & Liao, W. -H. (2023). Simultaneous Estimation of the Vertical Stiffness in the Knee and Hip for Healthy Human Subjects during Walking. Bioengineering, 10(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020187