Hemodynamic Investigation of the Effectiveness of a Two Overlapping Flow Diverter Configuration for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment
Abstract
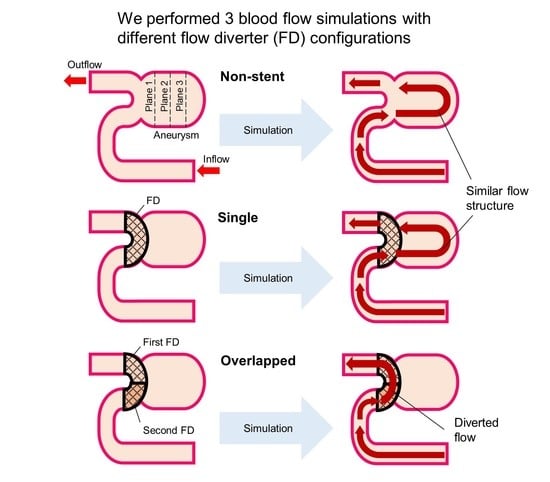
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Inspection Geometry
2.2. Virtual FD Deployment Methods and Stent Patterns
2.3. CFD Simulation Procedure
2.4. Hemodynamic Parameters and Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Blood Flow Characteristics in the Aneurysm
3.2. Validation of CFD Simulation Results: Comparison to Clinical Images
3.3. Quantitative Hemodynamic Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Agreement between Simulated Results and Angiographic Images
4.2. Hemodynamic Differences between Single and Overlapped Stent Patterns
4.2.1. Velocity and MFR
4.2.2. WSS
4.2.3. PLc
4.3. Locally Dense FD Mesh and Its Beneficial Effects on the Hemodynamic Environment
4.4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiebers, D.O.; Whisnant, J.P.; Huston, J., 3rd; Meissner, I.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Piepgras, D.G.; Forbes, G.S.; Thielen, K.; Nichols, D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K. Pathology of intracerebral hemorrhage. Zentralbl Neurochir. 1977, 38, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jakubowski, J.; Kendall, B. Coincidental aneurysms with tumours of pituitary origin. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiantry 1978, 41, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, P.; Li, Y. Flow-diverter devices in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puffer, R.C.; Piano, M.; Lanzino, G.; Valvassori, L.; Kallmes, D.F.; Quilici, L.; Cloft, H.J.; Boccardi, E. Treatment of cavernous sinus aneurysms with flow diversion: Results in 44 patients. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 948–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubicz, B.; Van der Elst, O.; Collignon, L.; Mine, B.; Alghamdi, F. Silk flow-diverter stent for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A series of 58 patients with emphasis on long-term results. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takao, H.; Murayama, Y.; Otsuka, S.; Qian, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Masuda, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Abe, T. Hemodynamic differences between unruptured and ruptured intracranial aneurysms during observation. Stroke 2012, 43, 1436–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouared, R.; Larrabide, I.; Brina, O.; Bouillot, P.; Erceg, G.; Yilmaz, H.; Lovblad, K.; Pereira, V.M. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of flow reduction induced by flow-diverting stents in intracranial aneurysms: A patient-unspecific hemodynamics change perspective. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, N.; Damiano, R.J.; Davies, J.M.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Association between hemodynamic modifications and clinical outcome of intracranial aneurysms treated using flow diverters. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2017, 10135, 101352F. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Verrelli, D.I.; Chong, W.; Ohta, M.; Qian, Y. Haemodynamic effects of stent diameter and compaction ratio on flow-diversion treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A numerical study of a successful and an unsuccessful case. J. Biomech. 2017, 58, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Paliwal, N.; Meng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Hemodynamic Effect of Flow Diverter and Coils in Treatment of Large and Giant Intracranial Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2016, 89, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillot, P.; Brina, O.; Ouared, R.; Yilmaz, H.; Farhat, M.; Erceg, G.; Lovblad, K.-O.; Vargas, M.I.; Kulcsar, Z.; Pereira, V.M. Geometrical deployment for braided stent. Med. Image Anal. 2016, 30, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, D.; Dargush, G.F.; Natarajan, S.K.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Computer modeling of deployment and mechanical expansion of neurovascular flow diverter in patient-specific intracranial aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2012, 31, 2256–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, M.; Raz, E.; Becske, T.; Nelson, P.K. Variable porosity of the pipeline embolization device in straight and curved vessels: A guide for optimal deployment strategy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larrabide, I.; Aguilar, M.L.; Morales, H.G.; Geers, A.J.; Kulcsár, Z.; Rüfenacht, D.; Frangi, A.F. Intra-aneurysmal pressure and flow changes induced by flow diverters: Relation to aneurysm size and shape. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amili, O.; Schiavazzi, D.; Moen, S.; Jagadeesan, B.; Van de Moortele, P.-F.; Coletti, F. Hemodynamics in a giant intracranial aneurysm characterized by in vitro 4D flow MRI. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0188323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, M.D.; Alperin, N.; Lee, S.H.; Holdsworth, D.W.; Steinman, D.A. Characterization of volumetric flow rate waveforms in the normal internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsburger, L.; Reymond, P.; Rufenacht, D.A.; Stergiopulos, N. Intracranial stents being modeled as a porous medium: Flow simulation in stented cerebral aneurysms. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Ahmed, Y.M.; Hassan, A.A. The adverse effects of flow-diverter stent-like devices on the flow pattern of saccular intracranial aneurysm models: Computational fluid dynamics study. Acta Neuochir. (Wien) 2011, 153, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindeev, S.; Arnold, P.G.; Frolov, S.; Prothmann, S.; Liepsch, D.; Balasso, A.; Berg, P.; Kaczmarz, S.; Krischke, J.S. Phase-contrast MRI versus numerical simulation to quantify hemodynamical changes in cerebral aneurysms after flow diverter treatment. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Takao, H.; Fujimura, S.; Dahmani, C.; Ishibashi, T.; Mamori, H.; Fukushima, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Murayama, Y. Selection of helical braided flow diverter stents based on hemodynamic performance and mechanical properties. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebral, J.R.; Pergolizzi, R.S., Jr.; Putman, C.M. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Intracranial Aneurysms:: Qualitative Comparison with Cerebral Angiography. Acad. Radiol. 2007, 14, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mut, F.; Chung, B.J.; Chudyk, J.; Kadirvel, R.; Kallmes, D.F.; Cebral, J.R. Image-based modeling of blood flow in cerebral aneurysms treated with intrasaccular flow diverting devices. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 2019, 35, e3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcsár, Z.; Augsburger, L.; Reymond, P.; Pereira, V.M.; Hirsch, S.; Mallik, A.S.; Millar, J.; Wetzel, S.G.; Wanke, I.; Rüfenacht, D.A. Flow diversion treatment: Intra-aneurismal blood flow velocity and WSS reduction are parameters to predict aneurysm thrombosis. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2012, 154, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peach, T.; Spranger, K.; Ventikos, Y. Virtual flow-diverter treatment planning: The effect of device placement on bifurcation aneurysm haemodynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2017, 231, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geers, A.J.; Morales, H.G.; Larrabide, I.; Butakoff, C.; Bijilenga, P.; Frangi, F.A. Wall shear stress at the initiation site of cerebral aneurysms. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, H.; Tutino, V.M.; Xiang, J.; Siddiqui, A. High WSS or low WSS? Complex interactions of hemodynamics with intracranial aneurysm initiation, growth, and rupture: Toward a unifying hypothesis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 35, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beppu, M.; Tsuji, M.; Ishida, F.; Shirakawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Yoshimura, S. Computational Fluid Dynamics Using a Porous Media Setting Predicts Outcome after Flow-Diverter Treatment. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tian, Z.; Liu, J.; Jing, L.; Paliwal, N.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Siddiui, A.H.; Meng, H.; et al. Flow diverter effect of LVIS stent on cerebral aneurysm hemodynamics: A comparison with Enterprise stents and the Pipeline device. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Lai, L.; Parker, G.; Mitchell, K. Computational hemodynamics analysis of intracranial aneurysms treated with flow diverters: Correlation with clinical outcomes. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damiano, R.J.; Tutino, V.M.; Paliwal, N.; Ma, D.; Davis, J.M.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Compacting a Single Flow Diverter versus Overlapping Flow Diverters for Intracranial Aneurysms: A Computational Study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makoyeva, A.; Bing, F.; Darsaut, T.E.; Salazkin, I.; Raymond, J. The varying porosity of braided self-expanding stents and flow diverters: An experimental study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gentric, J.-C.; Salazkin, I.; Gevry, G.; Raymond, J.; Darsaut, T. Compaction of flow diverters improves occlusion of experimental wide-necked aneurysms. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Xiang, J.; Choi, H.; Dumont, T.M.; Natarajan, S.K.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Enhanced aneurysmal flow diversion using a dynamic push-pull technique: An experimental and modeling study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tse, M.M.Y.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Mitchell, P.J. Current status of pipeline embolization device in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms: A review. World Neurosurg. 2013, 80, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, P.A.; Sirs, J.A. The relationship of plasma fibrinogen, erythrocyte flexibility and blood viscosity. Thromb. Haemost. 1977, 38, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.; Usami, S.; Dellenback, R.J.; Gregersen, M.I.; Nanninga, L.B.; Guest, M.M. Blood viscosity: Influence of erythrocyte aggregation. Science 1967, 157, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaruto, A.M.; Janela, J.; Moura, A.; Sequeira, A. Sensitivity of hemodynamics in a patient specific cerebral aneurysm to vascular geometry and blood rheology. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2011, 8, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, H.G.; Larrabide, I.; Geers, A.J.; Aguilar, M.L.; Frangi, A.F. Newtonian and non-Newtonian blood flow in coiled cerebral aneurysms. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; van Ooij, P.; Veeturi, S.S.; Tutino, V.M.; Zwanenburg, J.J.; Meng, H. Inter-patient variations in flow boundary conditions at middle cerebral artery from 7T PC-MRI and influence on Computational Fluid Dynamics of intracranial aneurysms. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 120, 103759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoda, H.; Takehara, Y.; Kosugi, T.; Terada, M.; Naito, T.; Onishi, Y.; Tanoi, C.; Ayama, K.; Sakahara, H. MR-based computational fluid dynamics with patient-specific boundary conditions for the initiation of a sidewall aneurysm of a basilar artery. Magn. Reason. Med. Sci. 2015, 14, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramalho, S.; Moura, A.; Gambaruto, A.M.; Sequeira, A. Sensitivity to outflow boundary conditions and level of geometry description for a cerebral aneurysm. Int. J. Numer. Method Biomed. Eng. 2012, 28, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saalfeld, A.; Voß, S.; Beuing, O.; Preim, B.; Berg, P. Flow-splitting-based computation of outlet boundary conditions for improved cerebrovascular simulation in multiple intracranial aneurysms. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, A.; Singh, P.; Reymond, P.; Stergiopulos, N.; Patel, U.; Hose, R. Influence of inlet boundary conditions on the local haemodynamics of intracranial aneurysms. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 12, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Parameters | Stent Patterns | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Stent | Single | Overlapped | ||
| Average Velocity Magnitude [×10–3 m/s] | Plane 1 | 64.0 | 45.7 | 37.1 |
| Plane 2 | 57.8 | 39.9 | 15.6 | |
| Plane 3 | 59.6 | 44.1 | 4.62 | |
| MFR [-] | 1.21 | 0.954 | 0.657 | |
| Parameters | Reduction Rate [%] | ||
| Single | Overlapped | ||
| Velocity | Plane 1 | 28.5 | 41.9 |
| Plane 2 | 31.0 | 73.1 | |
| Plane 3 | 25.9 | 92.2 | |
| MFR | 21.3 | 45.8 | |
| WSS | 47.3 | 87.5 | |
| PLc | −56.6 | −60.9 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uchiyama, Y.; Fujimura, S.; Takao, H.; Suzuki, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Karagiozov, K.; Fukudome, K.; Murayama, Y.; Yamamoto, M. Hemodynamic Investigation of the Effectiveness of a Two Overlapping Flow Diverter Configuration for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8100143
Uchiyama Y, Fujimura S, Takao H, Suzuki T, Hayakawa M, Ishibashi T, Karagiozov K, Fukudome K, Murayama Y, Yamamoto M. Hemodynamic Investigation of the Effectiveness of a Two Overlapping Flow Diverter Configuration for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering. 2021; 8(10):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8100143
Chicago/Turabian StyleUchiyama, Yuya, Soichiro Fujimura, Hiroyuki Takao, Takashi Suzuki, Motoharu Hayakawa, Toshihiro Ishibashi, Kostadin Karagiozov, Koji Fukudome, Yuichi Murayama, and Makoto Yamamoto. 2021. "Hemodynamic Investigation of the Effectiveness of a Two Overlapping Flow Diverter Configuration for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment" Bioengineering 8, no. 10: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8100143
APA StyleUchiyama, Y., Fujimura, S., Takao, H., Suzuki, T., Hayakawa, M., Ishibashi, T., Karagiozov, K., Fukudome, K., Murayama, Y., & Yamamoto, M. (2021). Hemodynamic Investigation of the Effectiveness of a Two Overlapping Flow Diverter Configuration for Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment. Bioengineering, 8(10), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering8100143