Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor: Solvent Preparation, Selection and Process Optimization
Abstract
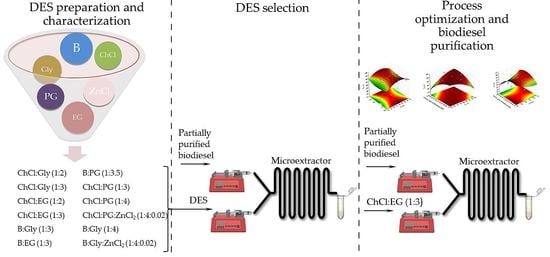
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Chemicals
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Production of Biodiesel in a Batch Reactor
2.2.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents
2.2.3. Measurements/Determination of Physico-Chemical Properties of Prepared Deep Eutectic Solvents
2.2.4. Calculation of Deep Eutectic Solvents Descriptors
2.2.5. Two-Phase Liquid-Liquid Extraction in a Microextractor
2.2.6. Determination of Glycerol and FAME Concentration in the Samples
2.2.7. Data Analysis and Mathematical Modeling
Modeling of Extraction Efficiency Based on DESs Descriptors and Physical Properties
Optimization of Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor
Mathematical Modeling of Glycerol Extraction in a Microextractor
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biodiesel Production in the Batch Reactor
3.2. Deep Eutectic Solvents Preparation and Physico-Chemical Properties
3.3. Glycerol Extraction in a Microextractor with Different Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.4. Influence of Deep Eutectic Solvents Properties on Glycerol Extraction
3.5. Extraction Optimization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franjo, M.; Šalić, A.; Zelić, B. Microstructured devices for biodiesel production by transesterification. Biomass. Convers. Biorefin. 2018, 8, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaosmanoǧlu, F.; Cıǧızoǧlu, K.B.; Tüter, M.; Ertekin, S. Investigation of the refining step of biodiesel production. Energy Fuels 1996, 10, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atadashi, I.M.; Aroua, M.K.; Aziz, A.A. Biodiesel separation and purification: A review. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, H.; Saraeian, A.; Able, C. A comprehensive review on biodiesel purification and upgrading. Biofuel Res. J. 2017, 15, 668–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaber, R.; Shirazi, M.M.A.; Toufaily, J.; Hamieh, A.T.; Noureddin, A.; Ghanavati, H.; Ghaffari, A.; Zenouzi, A.; Karout, A.; Ismail, A.F.; et al. Biodiesel wash-water reuse using microfiltration: Toward zero-discharge strategy for cleaner and economized biodiesel production. Biofuel Res. J. 2015, 2, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.; Ferreira, E.; Soares Dias, A.P.; Gomes, J. Dry washing biodiesel purification using fumed silica sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokač, T.; Gojun, M.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Šalić, A.; Zelić, B. Purification of biodiesel produced by lipase catalyzed transesterification by ultrafiltration: Selection of membranes and analysis of membrane blocking mechanisms. Renew. Energy 2020, 159, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šalić, A.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Gojun, M.; Zelić, B. Biodiesel purification in microextractors: Choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents vs water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Santana-Mayor, Á.; Herrera-Herrera, A.V.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Deep eutectic solvents. Green Sustan. Process Chem. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2020, 2020, 123–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, L.; Kollau, L.; Gomes, M.C. Solubility of Gases in Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Deep Eutectic Solvents for Medicine, Gas Solubilization and Extraction of Natural Substances; Fourmentin, S., Costa Gomes, M., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 131–155. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbaz, K.; Mjalli, F.S.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Using deep eutectic solvents for the removal of glycerol from palm oil-based biodiesel. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 2671–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niawanti, H.; Zullaikah, S. Effect of extraction time on unreacted oil removal in biodiesel purification using deep eutectic solvent. Reaktor 2018, 18, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petračić, A.; Gavran, M.; Škunca, A.; Štajduhar, L.; Sander, A. Deep eutectic solvents for purification of waste cooking oil and crude biodiesel. Sci. J. Energy Eng. 2017, 5, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šalić, A.; Tušek, A.; Fabek, D.; Rukavina, I.; Zelić, B. Aqueous two-phase extraction of polyphenols using a microchannel system—Process optimization and intensification. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Šalić, A.; Zelić, B. Synergy of microtechnology and biotechnology: Microreactors as an effective tool for biotransformation processes. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.Q.; Abbasi, N.M.; Anderson, J.L. Deep eutectic solvents in separations: Methods of preparation, polarity, and applications in extractions and capillary electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1633, 461613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 2003, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents formed between choline chloride and carboxylic acids: Versatile alternatives to ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, S.; Poletti, F.; Zanardi, C.; Pigani, L.; Zanfrognini, B.; Corsi, E.; Dossi, N.; Salomäki, M.; Kivelä, H.; Lukkari, H.J.; et al. Chemical and electrochemical properties of a hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastiras, O.E.; Andreasidou, E.; Samanidou, V. Microextraction techniques with deep eutectic solvents. Molecules 2020, 25, 6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budžaki, S.; Šalić, A.; Zelić, B.; Tišma, M. Enzyme-catalyzed biodiesel production from edible and waste cooking oils. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2015, 29, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagajski Kučan, K.; Rogošić, M. Purification of motor fuels by means of extraction using deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and glycerol. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 94, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogošić, M.; Kučan, K.Z. Deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride and ethylene glycol as media for extractive denitrification/desulfurization/dearomatization of motor fuels. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 72, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučan, K.Z.; Perković, M.; Cmrk, K.; Načinović, D.; Rogošić, M. Betaine + (glycerol or ethylene glycol or propylene glycol) deep eutectic solvents for extractive purification of gasoline. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 12582–12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogošić, M.; Zagajski Kučan, K. Deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and propylene glycol as a potential medium for extraction denitrification of hydrocarbon fuels. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 161, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abranches, D.O.; Zhang, Y.; Maginn, E.J.; Colón, Y.J. Sigma profiles in deep learning: Towards a universal molecular descriptor. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 5630–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benguerba, Y.; Alnashef, I.; Erto, A.; Balsamo, M.; Ernst, B. A quantitative prediction of the viscosity of amine based DESs using Sσ-profile molecular descriptors. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1184, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojun, M.; Šalić, A.; Zelić, B. Integrated microsystems for lipase-catalysed biodiesel production and glycerol removal by extraction or ultrafiltration. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Jurina, T.; Benković, M.; Valinger, D.; Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Application of multivariate regression and artificial neural network modelling for prediction of physical and chemical properties of medicinal plants aqueous extracts. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2020, 16, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panić, M.; Radović, M.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Radošević, K.; Rogošić, M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Jurinjak Tušek, A. Prediction of pH value of aqueous acidic and basic deep eutectic solvent using COSMO-RS σ Profiles’ molecular descriptors. Molecules 2022, 27, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, S.L.; Higdon, J.; Kenis, P.J.A. Microfluidic Strategies to Mix Highly Viscous and/or Non-Newtonian Fluids. In Proceedings of the 2009 AIChE Annual Meeting, Nashville, TN, USA, 8–13 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tišma, M.; Zelić, B.; Vasić-Rački, Đ.; Žnidaršič-Plazl, P.; Plazl, I. Modelling of laccase-catalyzed L-DOPA oxidation in a microreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Paiva, A.; Reis, R.L.; Rita, A.; Duarte, C. Natural deep eutectic solvents from choline chloride and betaine—Physicochemical properties. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellini, F.; Tiecco, M.; Germani, R.; Cardinali, G.; Corte, L.; Roscini, L.; Spreti, N. Novel zwitterionic deep eutectic solvents from trimethylglycine and carboxylic acids: Characterization of their properties and their toxicity. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 55990–56002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craveiro, R.; Aroso, I.; Flammia, V.; Carvalho, T.; Viciosa, M.T.; Dionısio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Paiva, A. Properties and thermal behavior of natural deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi., Y.H. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapeña, D.; Lomba, L.; Artal, M.; Lafuente, C.; Giner, B. Thermophysical characterization of the deep eutectic solvent choline chloride: Ethylene glycol and one of its mixtures with water. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2019, 492, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.Z.; Yin, J.M.; Liu, Q.S.; Li, C.P. Properties of four deep eutectic solvents: Density, electrical conductivity, dynamic viscosity and refractive index. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2015, 31, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ye, F.; Song, N.; Xu, Y. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents formed by choline chloride and phenolic compounds at T = (293.15 to 333.15) K: The influence of electronic effect of substitution group. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 232, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapeña, D.; Bergua, F.; Lomba, L.; Giner, B.; Lafuente, C. A comprehensive study of the thermophysical properties of reline and hydrated reline. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 303, 112679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škulcová, A.; Majová, V.; Dubaj, T.; Jablonský, M. Physical properties and thermal behavior of novel ternary green solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 287, 110991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedghamiz, M.A.; Raeissi, S. Physical properties of deep eutectic solvents formed by the sodium halide salts and ethylene glycol, and their mixtures with water. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 269, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siongco, K.R.; Leron, R.B.; Li, M. Densities, refractive indices, and viscosities of N,N-diethylethanol ammonium chloride-glycerol or ethylene glycol deep eutectic solvents and their aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 65, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, P.B.; González, B.; Salgado, J. José; J. Domínguez, Á. Physical properties of seven deep eutectic solvents based on L -proline or betaine. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, K.; Fatemi, M.H.; Patrice Estellé, P. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs): A short overview of the thermophysical properties and current use as base fluid for heat transfer nanofluids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 321, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of improved deep eutectic solvents using hole theory. Chemphyschem. 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šalić, A.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Sander, A.; Zelić, B. Lipase catalysed biodiesel synthesis with integrated glycerol separation in continuously operated microchips connected in series. New Biotechnol. 2018, 47, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Sara Nidal Abed, S.N.; Al-Attraqchi, O.; Kuche, K.; Tekade, R.T. Computer-Aided Prediction of Pharmacokinetic (ADMET) Properties. In Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research, Dosage Form Design Parameters; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 731–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, E.; Oldland, R.; Liu, Y.A.; Wang, S.; Sandler, S.I.; Chen, C.-C.; Zwolak, M.; Seavey, K.C. Sigma-profile database for using COSMO-Based thermodynamic methods. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 4389–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanquetta, C.R.; Dalla Corte, A.P.; Behling, A.; de Oliveria Piva, L.R.; Netto, S.P.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Sanquetta, M.N.I. Selection criteria for linear regression models to estimate individual tree biomasses in the Atlantic Rain Forest, Brazil. Carbon Balance Manag. 2018, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, Q. Robust bent line regression. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 2017, 185, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, S.E.; Porth, L.S. A Tutorial on the Piecewise Regression Approach Applied to Bedload Transport Data; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2007; pp. 41–51.
- Le Man, H.; Behera, S.K.; Park, H.S. Optimization of operational parameters for ethanol production from Korean food waste leachate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Deep Eutectic Solvent | Abbreviation | Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | Hydrogen Bond Donor | Acceptor:Donor Molar Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Choline chloride:glycerol | ChCl:Gly |  |  | 1:2 1:3 |
| Choline chloride:ethylene glycol | ChCl:EG |  |  | 1:2 1:3 |
| Betaine:glycerol | B:Gly |  |  | 1:3 1:4 |
| Betaine:ethylene glycol | B:EG |  |  | 1:3 |
| Betaine:propylene glycol | B:PG |  |  | 1:3.5 |
| Choline chloride:propylene glycol | ChCl:PG |  |  | 1:3 1:4 |
| Choline chloride:propylene glycol:zinc chloride | ChCl:PG:ZnCl2 |  |  | 1:4:0.02 |
| Betaine:glycerol:zinc chloride | B:Gly:ZnCl2 |  |  | 1:4:0.02 |
| DES | ρ, g/mL | η, Pa s | σ, mS/cm | nD | a, mm2/s | λ, W/(m K) | cp, J/(g K) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl:Gly (1:2) | 1.188 ± 0.002 | 0.369 ± 0.053 | 1.130 ± 0.010 | 1.448 ± 0.000 | 0.097 ± 0.011 | 0.232 ± 0.006 | 2.010 ± 0.193 | [22] |
| ChCl:Gly (1:3) | 1.204 ± 0.001 | 0.316 ± 0.011 | 1.122 ± 0.008 | 1.448 ± 0.000 | 0.097 ± 0.009 | 0.241 ± 0.005 | 2.057 ± 0.140 | [22] |
| ChCl:EG (1:2) | 1.115 ± 0.002 | 0.042 ± 0.000 | 8.610 ± 0.005 | 1.448 ± 0.000 | 0.167 ± 0.002 | 0.227 ± 0.002 | 1.205 ± 0.003 | [23] |
| ChCl:EG (1:3) | 1.113 ± 0.000 | 0.028 ± 0.000 | 9.410 ± 0.010 | 1.448 ± 0.000 | 0.195 ± 0.020 | 0.231 ± 0.008 | 1.055 ± 0.100 | [23] |
| B:Gly (1:3) | 1.223 ± 0.000 | 1.103 ± 0.012 | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 1.478 ± 0.000 | 0.151 ± 0.011 | 0.270 ± 0.004 | 1.455 ± 0.091 | [24] |
| B:EG (1:3) | 1.131± 0.000 | 0.062 ± 0.002 | 0.006 ± 0.001 | 1.456 ± 0.000 | 0.189 ± 0.005 | 0.231 ± 0.002 | 1.071 ± 0.018 | [24] |
| B:PG (1:3.5) | 1.074 ± 0.000 | 0.139± 0.003 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 1.452 ± 0.000 | 0.116 ± 0.003 | 0.206 ± 0.093 | 1.642 ± 0.048 | [24] |
| ChCl:PG (1:3) | 1.078 ± 0.003 | 0.066 ± 0.004 | 3.380 ± 0.009 | 1.458 ± 0.000 | 0.145 ± 0.023 | 0.208 ± 0.013 | 1.347 ± 0.147 | [23] |
| ChCl:PG (1:4) | 1.075 ± 0.134 | 0.049 ± 0.000 | 3.093 ± 0.033 | 1.455 ± 0.000 | 0.217 ± 0.021 | 0.213 ± 0.007 | 0.915 ± 0.063 | |
| ChCl:PG:ZnCl2 (1:4:0.02) | 1.079 ± 0.000 | 0.054 ± 0.002 | 2.290 ± 0.073 | 1.455± 0.000 | 0.219 ± 0.001 | 0.211 ± 0.003 | 0.896 ± 0.034 | |
| B:Gly (1:4) | 1.232 ± 0.006 | 2.431 ± 0.006 | 2.920 ± 0.021 | 1.456 ± 0.000 | 0.138 ± 0.017 | 0.278 ± 0.006 | 1.653 ± 0.173 | |
| B:Gly:ZnCl2 (1:4:0.02) | 1.233 ± 0.000 | 1.406 ± 0.396 | 2.770 ± 0.029 | 1.456 ± 0.000 | 0.094 ± 0.016 | 0.257 ± 0.100 | 2.257 ± 0.355 |
| S1mix | S2mix | S3mix | S4mix | S5mix | S6mix | S7mix | S8mix | S9mix | S10mix | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1mix | 1.000 | 0.260 | 0.038 | −0.439 | 0.287 | 0.357 | 0.341 | 0.095 | −0.299 | 0.085 | −0.489 |
| S2mix | 0.260 | 1.000 | 0.848 | −0.050 | −0.114 | −0.012 | 0.852 | 0.843 | 0.131 | 0.170 | 0.247 |
| S3mix | 0.038 | 0.848 | 1.000 | 0.454 | −0.342 | −0.258 | 0.841 | 0.984 | 0.636 | −0.219 | 0.312 |
| S4mix | −0.439 | −0.050 | 0.454 | 1.000 | −0.647 | −0.689 | 0.011 | 0.373 | 0.903 | −0.418 | 0.348 |
| S5mix | 0.287 | −0.114 | −0.342 | −0.647 | 1.000 | 0.984 | 0.077 | −0.242 | −0.419 | 0.005 | −0.438 |
| S6mix | 0.357 | −0.012 | −0.258 | −0.689 | 0.984 | 1.000 | 0.207 | −0.137 | −0.409 | −0.062 | −0.470 |
| S7mix | 0.341 | 0.852 | 0.841 | 0.011 | 0.077 | 0.207 | 1.000 | 0.913 | 0.356 | −0.323 | −0.001 |
| S8mix | 0.095 | 0.843 | 0.984 | 0.373 | −0.242 | −0.137 | 0.913 | 1.000 | 0.620 | −0.330 | 0.218 |
| S9mix | −0.299 | 0.131 | 0.636 | 0.903 | −0.419 | −0.409 | 0.356 | 0.620 | 1.000 | −0.681 | 0.201 |
| S10mix | 0.085 | 0.170 | −0.219 | −0.418 | 0.005 | −0.062 | −0.323 | −0.330 | −0.681 | 1.000 | 0.248 |
| E | −0.489 | 0.247 | 0.312 | 0.348 | −0.438 | −0.470 | −0.001 | 0.218 | 0.201 | 0.248 | 1.000 |
| MLR | NLR | PLR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Break point | 52.9 ± 5.1 | ||
| b0 | −6.1 ± 4.1 | 3.9 ± 1.7 | −9.0 ± 1.1 40.7 ± 7.9 |
| b1 (S1mix) | −184.1 ± 59.2 | −0.08± 0.03 | −201.2 ± 10.3 −103.1 ± 11.8 |
| b2 (S3mix) | 3.6 ± 1 | 1± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.6 0.3 ± 1 × 10−2 |
| b3 (S4mix) | −1.8 ± 0.6 | −0.5± 0.1 | −1.1 ± 0.1 −0.6 ± 1 × 10−2 |
| b4 (S5mix) | 5.5 ± 2.2 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.4 0.8 ± 2 × 10−2 |
| b5 (S6mix) | −9.2 ± 3.2 | −0.03 ± 0.01 | −3.0 ± 0.2 −0.4 ± 4 × 10−3 |
| R2 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.73 |
| R2adj | 0.46 | 0.52 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 6.39 | 5.36 | 4.47 |
| F−value | F (5,36) = 7.93 | F (5,36) = 7.93 | F (5,36) = 7.93 |
| p−value | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| MLR | NLR | PLR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Break point | 52.9 ± 5.1 | ||
| b0 | 2489 ± 561.4 | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 1310.6 ± 157.1 −4315.7 ± 237.2 |
| b1 (ρ) | −292.3 ± 83.8 | −17.9 ± 4.3 | −2604.4 ± 188.9 −367.9 ± 22.5 |
| b2 (η) | 2 × 10−2±1 × 10−3 | −0.1 ± 3×10−2 | 2 × 10−2 ± 1 × 10−3 −46.9 ± 21.1 |
| b3 (σ) | −0.7 ± 0.5 | −1 × 10−2 ± 3 × 10−3 | 5.2 ± 2.1 1.5 ± 0.6 |
| b4 (nD) | −1573.7 ± 371.3 | 20.7 ± 1.7 | −7991.6 ± 255.6 3084.7 ± 154.1 |
| b5 (a) | −220.5 ± 97.3 | −13.9 ± 4.1 | 694.9 ± 115.7 −317.5 ± 59.7 |
| b6 (λ) | 738.1 ± 18.4 | 16.6 ± 4.22 | 4789.4 ± 321.5 1455.2 ± 118.7 |
| b7 (cp) | −3.2 ± 1.2 | −13.5 ± 3.9 | 217.2 ± 15.8 24.2 ± 3.8 |
| R2 | 0.62 | 0.73 | 0.97 |
| R2adj | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.97 |
| RMSE | 5.89 | 4.47 | 1.45 |
| F−value | F (7,34) = 7.9 | F (7,34) = 7.9 | F (7,34) = 7.9 |
| p−value | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 | p < 0.001 |
| Exp. | T/°C | τ/min | Volume Ratio of Biodiesel:DES | E/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25.00 (−1) | 0.50 (0) | 9:1 (1) | 26.9 ± 3.9 |
| 2 | 55.00 (1) | 0.50 (0) | 9:1 (1) | 52.3 ± 0.2 |
| 3 | 40.00 (0) | 0.50 (0) | 1:1 (0) | 53.1 ± 0.2 |
| 4 | 40.00 (0) | 0.50 (0) | 1:1 (0) | 51.2 ± 0.6 |
| 5 | 55.00 (1) | 0.95 (1) | 1:1 (0) | 50.6 ± 0.4 |
| 6 | 40.00 (0) | 0.05 (−1) | 9:1 (1) | 44.4 ± 0.1 |
| 7 | 40.00 (0) | 0.95 (1) | 1:9 (−1) | 46.2 ± 0.5 |
| 8 | 40.00 (0) | 0.50 (0) | 1:1 (0) | 53.2 ± 0.2 |
| 9 | 25.00 (−1) | 0.05 (−1) | 1:1 (0) | 53.5 ± 0.1 |
| 10 | 55.00 (1) | 0.05 (−1) | 1:1 (0) | 51.7 ± 0.4 |
| 11 | 25.00 (−1) | 0.50 (0) | 1:9 (−1) | 55.3 ± 0.5 |
| 12 | 40.00 (0) | 0.50 (0) | 1:1 (0) | 53.6 ± 0.1 |
| 13 | 40.00 (0) | 0.05 (−1) | 1:9 (−1) | 57.2 ± 0.5 |
| 14 | 40.00 (0) | 0.50 (0) | 1:1 (0) | 54.6 ± 0.7 |
| 15 | 55.00 (1) | 0.50 (0) | 1:9 (−1) | 40.1 ± 1.6 |
| 16 | 25.00 (−1) | 0.95 (1) | 1:1 (0) | 52.9 ± 0.6 |
| 17 | 40.00 (0) | 0.95 (1) | 9:1 (1) | 55.7 ± 0.3 |
| Coefficient | Regression Coefficient ± St. Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| β0 | 61.9 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| β1 (T) | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.005 |
| β2 (τ) | −2 × 10−2 ± 3 × 10−3 | <0.001 |
| β3 (v/v) | −30.9 ± 5.2 | <0.001 |
| β4 (T2) | 15.9 ± 3.0 | <0.001 |
| β5 (τ) | −0.6 ± 6 × 10−2 | <0.001 |
| β6 (v/v) | −3 × 10−3 ± 1 × 10−3 | <0.001 |
| β7 (T × τ) | −2 × 10−2 ± 1 × 10−2 | 0.823 |
| β8 (T × v/v) | 2 × 10−2 ± 1 × 10−3 | <0.001 |
| β9 (τ × v/v) | 0.3 ± 4 × 10−2 | <0.001 |
| RSM model | R2 | 0.93 |
| R2adj | 0.91 | |
| RMSE | 1.96 | |
| F-value | 10.12 | |
| p-value | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anđelović, S.; Božinović, M.; Ćurić, Ž.; Šalić, A.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Kučan, K.Z.; Rogošić, M.; Radović, M.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Zelić, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor: Solvent Preparation, Selection and Process Optimization. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110665
Anđelović S, Božinović M, Ćurić Ž, Šalić A, Jurinjak Tušek A, Kučan KZ, Rogošić M, Radović M, Cvjetko Bubalo M, Zelić B. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor: Solvent Preparation, Selection and Process Optimization. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(11):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110665
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnđelović, Sara, Marko Božinović, Željka Ćurić, Anita Šalić, Ana Jurinjak Tušek, Kristina Zagajski Kučan, Marko Rogošić, Mia Radović, Marina Cvjetko Bubalo, and Bruno Zelić. 2022. "Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor: Solvent Preparation, Selection and Process Optimization" Bioengineering 9, no. 11: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110665
APA StyleAnđelović, S., Božinović, M., Ćurić, Ž., Šalić, A., Jurinjak Tušek, A., Kučan, K. Z., Rogošić, M., Radović, M., Cvjetko Bubalo, M., & Zelić, B. (2022). Deep Eutectic Solvents for Biodiesel Purification in a Microextractor: Solvent Preparation, Selection and Process Optimization. Bioengineering, 9(11), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9110665