An Overview on Sustainability in the Wine Production Chain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Types of Sustainable Wines: Regulatory Issues, Certifications, and Labelling Systems
2.1. Organic Viticulture and Wine Production
2.2. Biodynamic Viticulture and Wine Production
2.3. Other Sustainability Standards and Labelling Systems
3. Statistics and Market Analysis
3.1. Organic Vineyards and Wines
3.2. Biodynamic Vineyards and Wines
3.3. Fairtrade Vineyards and Wines
4. Sustainability in Viticulture
4.1. Effects of Conventional and Sustainable Management on Soil
4.2. Environmental Impacts: A Comparison among Conventional and Sustainable Viticulture
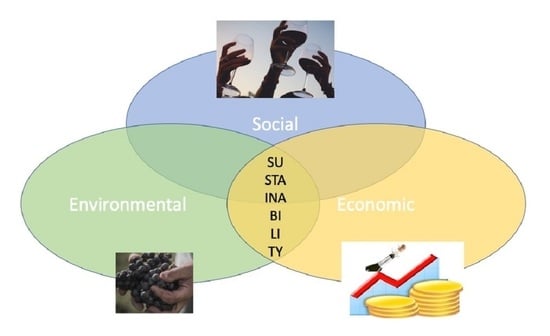
4.3. Indicators of Environmental, Economic, and Social Sustainability
5. Sustainability in Wineries
5.1. The Main Impacts of Wineries
5.2. Winery Approach to Sustainability
6. Sustainability in the Wine Supply Chain
6.1. Contribution of the Wine Supply Chain to the Environmental Impact
6.2. Sustainability Promotion Tools
7. Environmental Impacts of the Wine Life Cycle from Viticulture to Distribution
8. Sustainability in the Waste Management
8.1. Amount and Characteristics of Wastes
8.2. Treatments of Wastes
9. Characteristics of Conventional and Sustainable Wines: Similar or Different?
10. Sustainable Wines: Consumer Perception, Preferences, and Willingness to Pay (WTP)
10.1. Consumer Approach to Sustainability
10.2. Consumer Attitude–Behaviour Gap and Willingness to Pay for Sustainable Wines
10.3. Consumer Perception of the Quality of Sustainable Wines
11. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development, General Assembly Resolution 42/187, 11 December 1987. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/153026 (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- United Nations. World Summit Outcome, Resolution A/60/1. 2005. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/migration/generalassembly/docs/globalcompact/A_RES_60_1.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Ohmart, C. Innovative outreach increases adoption of sustainable winegrowing practices in Lodi region. Calif. Agric. 2008, 62, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peano, C.; Merlino, V.M.; Sottile, F.; Borra, D.; Massaglia, S. Sustainability for food consumers: Which perception? Sustainability 2019, 11, 5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szolnoki, G.; Bosman, J.; Samara, O.; Iselborn, M.; Ferrigato, A.; Tari, K.; Gálvez Egea, N. A cross-cultural comparison of sustainability in the wine industry. In Proceedings of the 6th AWBR International Conference, Bordeaux, France, 9–10 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- OIV. Resolution CST 1/2008—OIV Guidelines for Sustainable Vitiviniculture: Production, Processing and Packaging of Products. 2008. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/2089/cst-1-2008-en.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- FIVS. Global Wine Producers Environmental Sustainability Principles. 2016. Available online: https://www.fivs.org/wp-content/uploads/FIVS-Global-Wine-Producers-Environmental-Sustainability-Principles.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Gilinski, A., Jr.; Newton, S.K.; Fuentes Vega, R. Sustainability in the global wine industry: Concepts and cases. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casini, L.; Cavicchi, A.; Corsi, A.; Santini, C. Hopelessly devoted to sustainability: Marketing challenges to face in the wine business. In Proceedings of the 119th EAAE Seminar ‘Sustainability in the Food Sector: Rethinking the Relationship between the Agro-Food System and the Natural, Social, Economic and Institutional Environments’, Capri, Italy, 30 June–2 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bonn, I.; Fisher, J. Sustainability: The missing ingredient in strategy. J. Bus. Strategy 2011, 32, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, A.; Vastola, A. Sustainable winegrowing: Current perspectives. Int. J. Wine Res. 2015, 7, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martucci, O.; Arcese, G.; Montauti, C.; Acampora, A. Social aspects in the wine sector: Comparison between Social Life Cycle Assessment and VIVA Sustainable Wine Project Indicators. Resources 2019, 8, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- OIV. General Principles of Sustainable Vitiviniculture-Environmental-Social-Economic and Cultural Aspects OIVCST518-2016. 2016. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/en/technical-standards-and-documents/resolutions-of-the-oiv/resolution-cst (accessed on 16 April 2019).
- Scopus. Abstract & Citation Database. 2021. Available online: https://www.elsevier.com/solutions/scopus (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- WoS. Abstract & Citation Database. 2021. Available online: https://apps.webofknowledge.com/WOS_GeneralSearch_input.do?product=WOS&search_mode=GeneralSearch&SID=E1CuPGLUVGqBNwL4Z6x&preferencesSaved= (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Corbo, C.; Lamastra, L.; Capri, E. From environmental to sustainability programs: A review of sustainability initiatives in the Italian wine sector. Sustainability 2014, 6, 2133–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lodi Winegrape Commission. Lodi Rules Sustainable Winegrowing Program. Available online: https://www.lodirules.org/About (accessed on 7 March 2020).
- European Union. Regulation (EC) 834/2007. Council Regulation of 28 June 2007 on organic production and labelling of organic products and repealing Regulation (EEC) No 2092/91. Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, L 189, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) 889/2008. Commission Regulation of 5 September 2008 laying down detailed rules for the implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007 on organic production and labelling of organic products with regard to organic production, labelling and control. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 260, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) 1235/2008. Commission Regulation of 8 December 2008 laying down detailed rules for implementation of Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007 as regards the arrangements for imports of organic products from third countries. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 334, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) 848/2018. European Parliament and Council Regulation of 30 May 2018 on organic production and labelling of organic products and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L 150, 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. Regulatory References. 2021. Available online: https://www.ams.usda.gov/rules-regulations/organic (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Government of Canada. Canadian Organic Standards. 2019. Available online: https://www.inspection.gc.ca/organic-products/standards/eng/1300368619837/1300368673172 (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Araujo, M.V.; da Silva, M.A.C.; de Menezes, D.C.; Bruch, K.L. The perspective of organic wine in Brazil—Trends, demands and production. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences—40th World Congress of Vine and Wine, Sofia, Bulgaria, 29 May–2 June 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GB/T 19630-2019. China National Organic Standard. 2021. Available online: https://certifications.controlunion.com/en/certification-programs/certification-programs/china-national-organic-standard (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- JAS: Organic JAS. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/e/policies/standard/specific/organic_JAS.html (accessed on 19 January 2020).
- GAIN Report Number RS 1823 Russia to Adopt New Law on Organics. 2019. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/report/downloadreportbyfilename?filename=Russia%20to%20Adopt%20New%20Law%20on%20Organics%20_Moscow%20ATO_Russian%20Federation_3-1-2019.pdf (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Food Safety and Standards Organic Foods Regulations. 2017. Available online: https://fssai.gov.in/upload/uploadfiles/files/Gazette_Notification_Organic_Food_04_01_2017.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Australian Certified Organic. Standard 2019 V.1. Available online: https://www.aco.net.au/Downloads/ACOS_2019_V1.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Castellini, A.; Mauracher, C.; Troiano, S. An overview of the biodynamic wine sector. Int. J. Wine Res. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demeter. Available online: https://www.demeter.net (accessed on 11 March 2020).
- European Union. Regulation EU No 1308/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 December 2013. Establishing a common organisation of the markets in agricultural products and repealing Council Regulations (EEC) No 922/72, (EEC) No 234/79, (EC) No 1037/2001 and (EC) No 1234/2007. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, L3470, 671–854. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson, B.; Karlsson, P. Biodynamic, Organic and Natural Winemaking. Sustainable Viticulture and Viniculture; Floris Book: Edinburgh, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vin Natur. 2019. Available online: https://www.vinnatur.org/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- OIV. Resolution OIV-CST 503AB. Greenhouse Gases Accounting in the Vine and Wine Sector—Recognised Gases and Inventory of emissions and Sequestrations. 2015. Available online: http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/4521/publication-bilan-ges-en.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- VIVA. Sustainability and Culture. Technical Specifications. 2011. Available online: http://www.viticolturasostenibile.org/EN/TechSpec.aspx (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Diva. Overview of the Organic Wine Market. 2017. Available online: https://divawine.com/overview-organic-market/ (accessed on 4 April 2020).
- Leboulenger, S. Quels Sont les dix Premiers Marchés Mondiaux du vin bio? 2018. Available online: https://www.lsa-conso.fr/quels-sont-les-dix-premiers-marches-mondiaux-du-vin-bio,304451 (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Sinab. Bio in Cifre 2018, Anticipazioni. Ismea, Mipaaf, Ciheam. Roma. 2018. Available online: http://www.sinab.it/sites/default/files/share/Bio%20in%20cifre%202018%20_%20Anticipazioni_1.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2020).
- Lanfranchi, M.; Schimmenti, E.; Campolo, M.G.; Giannetto, C. The willingness to pay of Sicilian consumers for a wine obtained with sustainable production method: An estimate through an ordered probit sample-selection model. Wine Econ. Policy 2019, 8, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine. Organic Wine Market Grows Fast but Is Set to Remain Niche. 2018. Available online: https://archive.shine.cn/feature/ideal/Organic-wine-market-grows-fast-but-is-set-to-remain-niche/shdaily.shtml (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Fairtrade International. Annual Report 2013–2014. 2014. Available online: http://www.fairtrade.net/fileadmin/user_upload/content/2009/resources/2013-14_AnnualReport_FairtradeIntl_web.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Probst, B.; Schüler, C.; Joergensen, R.G. Vineyard soils under organic and conventional management—microbial biomass and activity indices and their relation to soil chemical properties. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likar, M.; Stres, B.; Rusjan, D.; Potisek, M.; Regvar, M. Ecological and conventional viticulture gives rise to distinct fungal and bacterial microbial communities in vineyard soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, F.; Moser, G.; Müller, H.; Berg, G. Functional and structural microbial diversity in organic and conventional viticulture: Organic farming benefits natural biocontrol agents. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2188–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villanueva-Rey, P.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Comparative life cycle assessment in the wine sector: Biodynamic vs. conventional viticulture activities in NW Spain. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 65, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litskas, V.; Mandoulaki, A.; Vogiatzakis, I.N.; Tzortzakis, N.; Stavrinides, M. Sustainable viticulture: First determination of the environmental footprint of grapes. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsato, E.; Zucchinelli, M.; D’Ammaro, D.; Giubilato, E.; Zabeo, A.; Criscione, P.; Pizzol, L.; Cohen, Y.; Tarolli, P.; Lamastra, L.; et al. Use of multiple indicators to compare sustainability performance of organic vs conventional vineyard management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Brown, I.; Metcalfe, A.; Jerram, C.; Collins, C. Sustainability assessment in wine-grape growing in the new world: Economic, environmental, and social indicators for agricultural businesses. Sustainability 2015, 7, 8178–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moggi, S.; Pagani, A.; Pierce, P. The rise of sustainability in Italian wineries: Key dimensions and practices. Impresa Progett. Electron. J. Manag. 2020, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, I. World Leading Environmental Sustainable Wineries. 2019. Available online: https://wea.org.au/world-leading-environmental-sustainable-wineries/ (accessed on 27 January 2021).
- Gubiani, R.; Pergher, G.; Mainardis, M. The winery in a perspective of sustainability: The parameters to be measured and their reliability. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Portici, Italy, 24–26 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IPPC. Warming of the Climate System is Unequivocal. Report on Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mozell, M.R.; Thach, L. The impact of climate change on the global wine industry: Challenges & solutions. Wine Econ. Policy 2014, 3, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Carroquino, J.; Garcia-Casarejos, N.G.; Gargallo, P. Classification of Spanish wineries according to their adoption of measures against climate change. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118874–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobin Poirier, E.; Plummer, R.; Pickering, J. Climate change adaptation in the Canadian wine industry: Strategies and drivers. Can. Geogr. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomarici, E.; Vecchio, R.; Mariani, A. Wineries’ perception of sustainability costs and benefits: An exploratory study in California. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16164–16174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Annunziata, E.; Pucci, T.; Frey, M.; Zanni, L. The role of organizational capabilities in attaining corporate sustainability practices and economic performance: Evidence from Italian wine industry. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunert, K.G.; Hieke, S.; Wills, J. Sustainability labels on food products: Consumer motivation, understanding and use. Food Policy 2014, 44, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isaak, R. The making of the ecopreneur. Green. Manag. Int. 2002, 38, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugani, B.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Benedetto, G.; Benetto, E. A comprehensive review of carbon footprint analysis as an extended environmental indicator in the wine sector. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 54, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postein, H.J.; Ghinoi, S.; Steiner, B. How to increase sustainability in the Finnish wine supply chain? Insights from a country of origin based greenhouse gas emissions analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, L.; Raggi, A.; De Camillis, C.; Matteucci, P.; Sára, B.; Pagliuca, G. Life cycle approach in an organic wine-making firm: An Italian case-study. In Proceedings of the Fifth Australian Conference on Life Cycle Assessment, Melbourne, Australia, 22–24 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Merli, R.; Preziosi, M.; Acampora, A. Sustainability experiences in the wine sector: Toward the development of an international indicators system. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3791–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valero, A.E.; Howarter, J.A.; Sutherland, J.W. Sustainable Wine Scoring System (SWSS): A life cycle assessment (LCA) multivariable approach. In Proceedings of the BIO Web of Conferences—41st World Congress of Vine and Wine, Punta del Este, Uruguay, 19–23 November 2018; Volume 12, p. 03016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, B.; Dias, A.C.; Machado, M. Life cycle assessment of the supply chain of a Portuguese wine: From viticulture to distribution. Int. J. LCA 2013, 18, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Point, E.; Tyedmers, P.; Naugler, C. Life cycle environmental impacts of wine production and consumption in Nova Scotia, Canada. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 27, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Rosentrater, K.A. Estimating economic and environmental impacts of red-wine-making processes in the USA. Fermentation 2019, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandinelli, R.; Acuti, D.; Fani, V.; Bindi, B.; Aiello, G. 2020 Environmental Practices in the Wine Industry: An Overview of the Italian Market. Available online: https://researchportal.port.ac.uk/portal/files/18631280/BFJ_Environmental_practices_in_the_wine_industry_an_overview_of_the_Italian_market_1_.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zacharof, M.P. Grape winery waste as feedstock for bioconversions: Applying the biorefinery concept. Waste Biomass Valorization 2017, 8, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conradie, A.; Sigge, G.O.; Cloete, T.E. Influence of winemaking practices on the characteristics of winery wastewater and water usage of wineries. S. Afr. J. Enol. 2014, 35, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Naziri, E.; Nenadis, N.; Mantzouridou, F.T.; Tsimidou, M.Z. Valorization of the major agrifood industrial by-products and waste from Central Macedonia (Greece) for the recovery of compounds for food applications. Food Res. Int. 2014, 65, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Moral, R.; Paredes, C.; Pérez-Espinosa, A.; Moreno-Caselles, J.; Pérez-Murcia, M. Agrochemical characterisation of the solid by-products and residues from the winery and distillery industry. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive n. 98. Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on waste and repealing certain Directives. Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, L 312, 3–30. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32008L0098 (accessed on 8 June 2020).
- Acampora, A.; Preziosi, M.; Merli, R.; Lucchetti, M.C. Environmental management systems in the wine industry: Identification of best practices toward a circular economy. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Sustainable Development Research Society Conference, Bogotà, Columbia, 14–16 June 2017; pp. 283–297. [Google Scholar]
- Borrello, M.; Lombardi, A.; Pascucci, S.; Cembalo, L. The seven challenges for transitioning into a bio-based circular economy in the agri-food sector. Recent Pat. Food Nutr. Agric. 2016, 8, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; de los Rios, C.; Rowe, Z.; Charnley, F.A. Conceptual framework for circular design. Sustainability 2016, 8, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maicas, S.; Mateo, J. Sustainability of wine production. Sustainability 2020, 12, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Yokoyama, W.H.; Kim, H. Synbiotic effect of whole grape seed flour and newly isolated kefir lactic acid bacteria on intestinal microbiota of diet-induced obese mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13131–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncevic, Z.; Grahovac, J.; Dodic, S.; Vucurovic, D.; Dodic, J. Utilisation of winery wastewater for xanthan production in stirred tank bioreactor: Bioprocess modelling and optimisation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 117, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.F.; Weller, K.M.; Blue, R.B.; Reganold, J.P. Difference testing of Merlot produced from biodynamically and organically grown wine grapes. J. Wine Res. 2009, 20, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, L.; Zea, I.; Villafuerte, I.; Medina, M. Comparison of odor-active compounds in Sherry wines processed from ecologically and conventionally grown Pedro Ximenez Grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, J.; Pardo, F.; Zafrilla, P. Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of organic and conventional grapes and wines. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2010, 23, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassoni, A.; Tango, N.; Ferri, M. Comparison of biogenic amine and polyphenol profiles of grape berries and wines obtained following conventional, organic and biodynamic agricultural and oenological practices. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kecskeméti, E.; Berkelmann-Löhnertz, B.; Reineke, A. Are epiphytic microbial communities in the carposphere of ripening grape clusters (Vitis vinifera L.) different between conventional, organic, and biodynamic grapes? PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0160852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Picone, G.; Trimigno, A.; Tessarin, P.; Donnini, S.; Rombolà, A.D.; Capozzi, F. 1H NMR foodomics reveals that the biodynamic and the organic cultivation managements produce different grape berries (Vitis vinifera L. cv. Sangiovese). Food Chem. 2016, 213, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghi, L.; Versari, A.; Marcolini, E.; Parpinello, G.G. Metabonomic investigation by 1H-NMR to discriminate between red wines from organic and biodynamic grapes. Food Nutr. Sci. 2019, 5, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parpinello, G.P.; Ricci, A.; Rombolà, A.D.; Nigro, G.; Versari, A. Comparison of Sangiovese wines obtained from stabilized organic and biodynamic vineyard management systems. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; La Torre, G.L.; Potortì, A.G.; Saitta, M.; Alfa, M.; Dugo, G. Organic wine safety: UPLC-FLD determination of Ochratoxin A in Southern Italy wines from organic farming and winemaking. Food Control 2016, 59, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali Čepo, D.; Pelajić, M.; Vinković Vrček, I.; Krivohlavek, A.; Žuntar, I.; Karoglan, M. Differences in the levels of pesticides, metals, sulphites and ochratoxin A between organically and conventionally produced wines. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdiarmid, J.I.; Kyle, J.; Horgan, G.W.; Loe, J.; Fyfe, C.; Johnstone, A.; McNeill, G. Sustainable diets for the future: Can we contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by eating a healthy diet? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zander, K.; Hamm, U. Consumer preferences for additional ethical attributes of organic food. Food Qual. Pref. 2010, 21, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, G.; Smith, D.E.; Mitry, D. Sustainable viticulture and winery practices in California: What is it, and do customers care? Int. J. Wine Res. 2009, 2, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, S.L.; Cohen, D.; Cullen, R.; Wratten, S.D.; Fountain, J. Consumer attitudes regarding environmentally sustainable wine: An exploratory study of the New Zealand marketplace. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sellers-Rubio, R.; Nicolau-Gonzalbez, J.L. Estimating the willingness to pay for a sustainable wine using a heckit model. Wine Econ. Policy 2016, 5, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangelico, R.M.; Vocalelli, D. Green Marketing: An analysis of definitions, strategy steps, and tools through a systematic review of the literature. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Mora, C.; Menozzi, D. Factors driving sustainable choice: The case of wine. Brit. Food J. 2016, 118, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijboom, F.L.; Brom, F.W. Ethics and sustainability: Guest or guide? On sustainability as a moral ideal. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2012, 25, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghvanidze, S.; Velikova, N.; Dodd, T.H.; Oldewage-Theron, W. Consumers’ environmental and ethical consciousness and the use of the related food products information: The role of perceived consumer effectiveness. Appetite 2016, 107, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Migliore, G.; Verneau, F.; Schifani, G.; Cembalo, L. Are “good guys” more likely to participate in local agriculture? Food Qual. Pref. 2015, 45, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.B.; Chai, L.T. Attitude towards the environment and green products: Consumers’ perspective. Manag. Sci. Eng. 2010, 4, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Schüufele, I.; Hamm, U. Organic wine purchase behaviour in Germany: Exploring the attitude-behaviour-gap with data from a household panel. Food Qual. Pref. 2018, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Gao, Z.; Zeng, Y. Willingness to pay for the “green food” in China. Food Policy 2014, 45, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogari, G.; Mora, C.; Menozzi, D. Sustainable wine labeling: A framework for definition and consumers’ perception. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Attitudes of European Citizens towards the Environment, Report. Special Eurobarometer 416. 2014. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/commfrontoffice/publicopinion/archives/ebs/ebs_416_en.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Remaud, H.; Mueller, S.; Chvyl, P.; Lockshin, L. Do Australian wine consumers value organic wine? In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of the Academy of Wine Business Research, Siena, Italy, 17–19 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tait, P.; Saunders, C.; Dalziel, P.; Rutherford, P.; Driver, T.; Guenther, M. Estimating wine consumer preferences for sustainability attributes: A discrete choice experiment of Californian Sauvignon blanc purchasers. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine Monitor 2018. Available online: http://winemonitor.it (accessed on 10 October 2018).
- Galati, A.; Schifani, G.; Crescimanno, M.; Migliore, G. “Natural wine” consumers and interest in label information: An analysis of willingness to pay in a new Italian wine market segment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, R. Determinants of willingness-to-pay for sustainable wine: Evidence from experimental auctions. Wine Econ. Policy 2013, 2, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginon, E.; Ares, G.; dos Santos Laboissière, L.H.; Brouard, J.; Issanchou, S.; Deliza, R. Logos indicating environmental sustainability in wine production: An exploratory study on how do Burgundy wine consumers perceive them. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klohr, B.; Fleuchaus, R.; Theuvsen, L. Who is buying sustainable wine? A lifestyle segmentation of German wine consumers. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference of Academy of Wine Business Research, Geisenheim, Germany, 28–30 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abraben, L.A.; Grogan, K.A.; Gao, Z. Organic price premium or penalty? A comparative market analysis of organic wines from Tuscany. Food Policy 2017, 69, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, R. Would you pay a price premium for a sustainable wine? The voice of the Spanish consumer. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capitello, R.; Sirieix, L. Consumers’ perceptions of sustainable wine: An exploratory study in France and Italy. Economies 2019, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sogari, G.; Pucci, T.; Aquilani, B.; Zanni, L. Millennial generation and environmental sustainability: The role of social media in the consumer purchasing behavior for wine. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallenti, G.; Troiano, S.; Marangon, F.; Bogoni, P.; Campisi, B.; Cosmina, M. Environmentally sustainable versus aesthetic values motivating millennials’ preferences for wine purchasing: Evidence from an experimental analysis in Italy. Agric. Food Econ. 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, K.H.; Reed, M. Do ecolabels cheapen wines? J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, A.; Pomarici, E.; Vecchio, R.; Mariani, A. Do consumers want more nutritional and health information on wine labels? Insight from the EU and USA. Nutrients 2016, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annunziata, A.; Pomarici, E.; Vecchio, R.; Mariani, A. Nutritional information and health warnings on wine labels: Exploring consumer interest and preferences. Appetite 2016, 106, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.; Locksin, L.; Saltman, Y.; Blanford, J. Message on a bottle: The relative influence of wine back label information on wine choice. Food Qual. Pref. 2010, 21, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation EU No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L304, 18–63. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, M.; Ballco, P.; López-Galán, B.; De Magistris, T.; Verneau, F. Exploring consumers’ perception and willingness to pay for “Non-Added Sulphite” wines through experimental auctions: A case study in Italy and Spain. Wine Econ. Pol. 2017, 6, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, M.; Di Vita, G.; Monaco, L. Exploring environmental consciousness and consumer preferences for organic wines without sulfites. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 120, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanigro, M.; Appleby, C.; Menke, S.D. The wine headache: Consumer perceptions of sulfites and willingness to pay for non-sulfited wines. Food Qual. Pref. 2014, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, W.V.; Valentin, D.; Reedman, P.; Grose, C.; Green, J.A. Expectation or sensorial reality? An empirical investigation of the biodynamic calendar for wine drsinkers. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Key Dimensions | Measures and Actions |
|---|---|
| Environmental | Recovery of rainwater |
| Reduced production of wastewater and recycle wastewater | |
| Recovery and recycle of wastes | |
| Waste-to-energy | |
| Recovery of energy and heat | |
| Use of renewable resources | |
| Acquisition of green cars and delivery trucks | |
| Use of low-impact innovative materials for packaging | |
| Economic | Reduced consumption of water |
| Reduced consumption of energy | |
| Sequestration and reuse of CO2 produced with fermentation | |
| Recognisability on the market | |
| Social | Protection of health and safety |
| Ethical reputation | |
| Exploitation of local resources, workers, and growers | |
| Corporate welfare |
| Stage of the Chain | Sustainable Practices | Effects on | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air | Water | Plant/ Soil | Landscape/ Society | ||
| Grape production | Promote the use of organic substances | √ | √ | ||
| Promote the use of a high level of automation | √ | √ | |||
| Implement actions to protect soil | √ | ||||
| Promote the more efficient micro-irrigation | √ | ||||
| Promote the use of precision agriculture | √ | ||||
| Preserve and promote biodiversity | √ | √ | |||
| Promote the production of compost starting from pruning residues | √ | ||||
| Reduce the use of fertilizing and agrochemicals | √ | √ | √ | ||
| Wine production | Reduce the use of chemical substances | √ | |||
| Promote the use of bio-materials to realise the cellar structures | √ | √ | |||
| Promote the recovery of waste to produce energy | √ | √ | |||
| Promote the use of the so-called clean energy | √ | ||||
| Construction of hypogeal or partially buried structures | √ | ||||
| Promote the recovery and use of rainwater | √ | ||||
| Bottling and Distribution | Use of recycled or alternative materials to produce bottles | √ | |||
| Replace paper communication with digital communication | √ | √ | |||
| Use of recycled materials to produce labels | √ | ||||
| Use of recycled materials to produce packaging | √ | ||||
| Favouring 0 km production by bringing production sites closer to sales markets | √ | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baiano, A. An Overview on Sustainability in the Wine Production Chain. Beverages 2021, 7, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7010015
Baiano A. An Overview on Sustainability in the Wine Production Chain. Beverages. 2021; 7(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaiano, Antonietta. 2021. "An Overview on Sustainability in the Wine Production Chain" Beverages 7, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7010015
APA StyleBaiano, A. (2021). An Overview on Sustainability in the Wine Production Chain. Beverages, 7(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages7010015