The Ionic Liquid Property Explorer: An Extensive Library of Task-Specific Solvents
Abstract
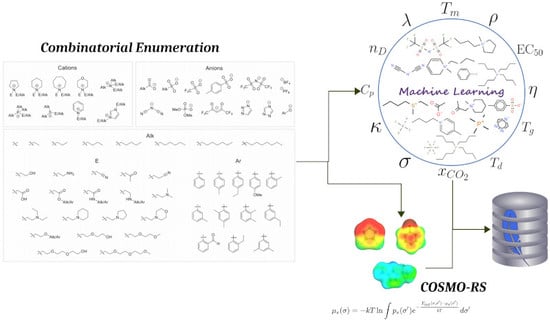
:1. Introduction
2. Data Description
2.1. Workflow
2.2. Ionic Liquid Library
2.3. Graphical Summary of the Data Set
3. Methods
3.1. Machine Learning
3.2. COSMO-RS Evaluation
4. Database Exploration and Use
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL | Ionic Liquids |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| RF | Random Forest |
| GBM | Generalized Boosted Models |
| COSMO-RS | Conductor like Screening Model for Real Solvents |
| hfac | Hexafluoroacetylacetonate |
| DCA | Dicyanamide |
| NTf2 | Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| PF6 | Hexafluorophosphate |
| HOMO | Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital |
| LUMO | Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital |
References
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, J. Ionic Liquids as Lubricant Additives: A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3209–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrucho, I.; Branco, L.; Rebelo, L. Ionic Liquids in Pharmaceutical Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2014, 5, 527–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Tachikawa, N.; Forsyth, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Howlett, P.C.; Elliott, G.D.; Davis, J.H.; Watanabe, M.; Simon, P.; Angell, C.A. Energy applications of ionic liquids. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Lei, Z. Ionic Liquids in Selective Oxidation: Catalysts and Solvents. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6929–6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plechkova, N.V.; Seddon, K.R. Applications of ionic liquids in the chemical industry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedermeyer, H.; Hallett, J.P.; Villar-Garcia, I.J.; Hunt, P.A.; Welton, T. Mixtures of ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilawe, N.V.; Fu, J.; Ramanathan, S.; Wong, B.M.; Wu, J. Chemical and Radiation Stability of Ionic Liquids: A Computational Screening Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 27757–27767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karu, K.; Ruzanov, A.; Ers, H.; Ivaništšev, V.; Lage-Estebanez, I.; de la Vega, J.G. Predictions of Physicochemical Properties of Ionic Liquids with DFT. Computation 2016, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izgorodina, E.I. Towards large-scale fully ab initio calculations of ionic liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4189–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.A.; Huang, X. Machine Learning-based Virtual Screening and Its Applications to Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 3347–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, P.B.; Mesta, M.; Shil, S.; Lastra, J.M.G.; Jacobsen, K.W.; Thygesen, K.S.; Schmidt, M.N. Machine learning-based screening of complex molecules for polymer solar cells. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 241735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, D.; Saito, T.; Ujita, W.; Oyama, H. How can machine-learning methods assist in virtual screening for hyperuricemia? A healthcare machine-learning approach. J. Biomed. Inform. 2016, 64, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Muzny, C.D.; Kazakov, A.; Diky, V.; Magee, J.W.; Widegren, J.A.; Chirico, R.D.; Marsh, K.N.; Frenkel, M. ILThermo: A Free-Access Web Database for Thermodynamic Properties of Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2007, 52, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduszyński, K.; Domańska, U. Viscosity of Ionic Liquids: An Extensive Database and a New Group Contribution Model Based on a Feed-Forward Artificial Neural Network. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, V.; Alsberg, B.K. Quantitative structure-property relationship modelling of thermal decomposition temperatures of ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybinska-Fryca, A.; Sosnowska, A.; Puzyn, T. Prediction of dielectric constant of ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, V.; Evjen, S.; Knuutila, H.K.; Fiksdahl, A.; Alsberg, B.K. Predicting Ionic Liquid Melting Points using Machine Learning. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, V.; Raj, J.J.; Evjen, S.; Lethesh, K.C.; Fiksdahl, A. In silico prediction and experimental verification of ionic liquid refractive indices. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A.; Eckert, F. COSMO-RS: A novel and efficient method for the a priori prediction of thermophysical data of liquids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2000, 172, 43–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paduszyński, K. An overview of the performance of the COSMO-RS approach in predicting the activity coefficients of molecular solutes in ionic liquids and derived properties at infinite dilution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 11835–11850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Gani, R.; Kontogeorgis, G.M. Application of COSMO-RS and UNIFAC for ionic liquids based gas separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 192, 816–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlen, J.; Masuch, K.; Leonhard, K. Modelling cellulose solubilities in ionic liquids using COSMO-RS. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izgorodina, E.I.; Seeger, Z.L.; Scarborough, D.L.A.; Tan, S.Y.S. Quantum Chemical Methods for the Prediction of Energetic, Physical, and Spectroscopic Properties of Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6696–6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharaj, R.; Banerjee, T. COSMO-RS-Based Screening of Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents in Denitrification Studies. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8705–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeliński, T.; Cysewski, P. Screening of ionic liquids for efficient extraction of methylxanthines using COSMO-RS methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, S.R.; Harun, R.; Biak, D.A.; Hussain, S.; Ghani, W.W.A.K.; Khezri, R.; Wilfred, C.; Elgharbawy, A. Screening of Suitable Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents for Extraction of Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) from Microalgae Biomass Using COSMO-RS Model. Molecules 2019, 24, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Dai, C.; Yu, G.; Lei, Z. Parameterization of COSMO-RS model for ionic liquids. Green Energy Environ. 2018, 3, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüller, A.; Hähnke, V.; Schneider, G. SmiLib v2.0: A Java-Based Tool for Rapid Combinatorial Library Enumeration. Mol. Inf. 2007, 26, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toplak, M.; Močnik, R.; Polajnar, M.; Bosnić, Z.; Carlsson, L.; Hasselgren, C.; Demšar, J.; Boyer, S.; Zupan, B.; Stålring, J. Assessment of Machine Learning Reliability Methods for Quantifying the Applicability Domain of QSAR Regression Models. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korotcenkov, G. Ionic Liquids in Gas Sensors. In Integrated Analytical Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.; Mutalib, M.A.; Ismail, M.F.; Suleman, H.; Lethesh, K.C.; Pilus, R.B.M. Thermodynamic modelling of liquid-liquid extraction of naphthenic acid from dodecane using imidazolium based phenolate ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Application of ionic liquids for dissolving cellulose and fabricating cellulose-based materials: State of the art and future trends. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, K.; Oshino, Y.; Tachikawa, N.; Toshima, K.; Katayama, Y. Electrodeposition of palladium from palladium(II) acetylacetonate in an amide-type ionic liquid. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 52, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, P.; Nagy, N.V.; Alegria, E.C.; Pombeiro, A.J.; Correia, I. The solvation and electrochemical behavior of copper acetylacetonate complexes in ionic liquids. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1060, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, S.; Garciá, J.; Larriba, M.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Rodríguez, F. Sulfonate-Based Ionic Liquids in the Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Aromatic Hydrocarbons. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 3188–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.; Raiguel, S.; Binnemans, K. Sulfonic acid functionalized ionic liquids for dissolution of metal oxides and solvent extraction of metal ions. Chem. Comm. 2015, 51, 9006–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunashima, K.; Kodama, S.; Sugiya, M.; Kunugi, Y. Physical and electrochemical properties of room-temperature dicyanamide ionic liquids based on quaternary phosphonium cations. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 56, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deive, F.J.; Rivas, M.A.; Rodríguez, A. Study of thermodynamic and transport properties of phosphonium-based ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2013, 62, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Branco, L.C.; Crespo, J.G.; Nunes, M.C.; Raymundo, A.; Afonso, C.A.M. Comparison of Physicochemical Properties of New Ionic Liquids Based on Imidazolium, Quaternary Ammonium, and Guanidinium Cations. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 8478–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maton, C.; Vos, N.D.; Stevens, C.V. Ionic liquid thermal stabilities: Decomposition mechanisms and analysis tools. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R.; Lu, L.; Deng, Y. Novel Cyclic Sulfonium-Based Ionic Liquids: Synthesis, Characterization, and Physicochemical Properties. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, L.G.; Espel, J.R.; Onink, F.; Meindersma, G.W.; de Haan, A.B. Density, Viscosity, and Surface Tension of Synthesis Grade Imidazolium, Pyridinium, and Pyrrolidinium Based Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2009, 54, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deetlefs, M.; Shara, M.; Seddon, K.R. Refractive Indices of Ionic Liquids. In ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, M.; Forte, P.; Gomes, M.C.; Lopes, J.C.; Rebelo, L. Densities and refractive indices of imidazolium- and phosphonium-based ionic liquids: Effect of temperature, alkyl chain length, and anion. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, N.M.; Mutalib, M.A.; Man, Z.; Bustam, M.A.; Murugesan, T. Thermophysical properties of 1-alkylpyridinum bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide ionic liquids. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2010, 42, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, H. (Ed.) Electrochemical Aspects of Ionic Liquids; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdin, M.; de Loos, T.W.; Vlugt, T.J. State-of-the-Art of CO2 Capture with Ionic Liquids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 8149–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.P.T.; Cho, C.W.; Yun, Y.S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, D.O.; Pereira, C.S. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids. In Ionic Liquids in Lipid Processing and Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecilla, J.S.; Palomar, J.; Lemus, J.; Rodríguez, F. A quantum-chemical-based guide to analyze/quantify the cytotoxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.J.P. MOPAC2016. Stewart Computational Chemistry: Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 2016. Available online: http://openmopac.net (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Venkatraman, V.; Alsberg, B.K. Predicting CO 2 capture of ionic liquids using machine learning. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, V.; Alsberg, B.K. KRAKENX: Software for the generation of alignment-independent 3D descriptors. J. Mol. Model. 2016, 22, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, V. KrakenX. 2019. Available online: https://gitlab.com/vishsoft/krakenx (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Ionic Liquids Physicochemical Properties; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, J.A.P.; Carvalho, P.J.; Oliveira, N.M.C. Predictive methods for the estimation of thermophysical properties of ionic liquids. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanser, T.; Barber, C.; Marchaland, J.F.; Werner, S. Applicability domain: Towards a more formal definition$. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2016, 27, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Better Bootstrap Confidence Intervals. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamt, A. The COSMO and COSMO-RS solvation models. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2011, 1, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckert, F.; Klamt, A. COSMOtherm Version C3.0, Release 16.01; COSMOlogic GmbH & Co. KG: Leverkusen, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Team, S.D. SQLite Version 3.27.2. 2019. Available online: https://www.sqlite.org/releaselog/3_27_2.html (accessed on 21 June 2019).
- Lowe, D.M.; Corbett, P.T.; Murray-Rust, P.; Glen, R.C. Chemical Name to Structure: OPSIN, an Open Source Solution. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Cation | #Molecules | # Ionic Liquids |
|---|---|---|
| ammonium | 179466 | 6819708 |
| azepanium | 5460 | 207480 |
| imidazolium | 5460 | 207480 |
| morpholinium | 5460 | 207480 |
| phosphonium | 7914 | 300732 |
| piperidinium | 5460 | 207480 |
| pyridinium | 1040 | 39520 |
| pyrrolidinium | 5460 | 207480 |
| sulphonium | 3576 | 135888 |
| Property | ML | Calibration | Validation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (C) | 1369 | 141 | RF | 1486 | 44 (15) | 0.67 | 726 | 45 (33) | 0.66 |
| (C) | 327 | 109 | Cubist | 442 | 21 (2) | 0.62 | 202 | 19 (12) | 0.62 |
| (C) | 538 | 192 | RF | 833 | 39 (12) | 0.77 | 455 | 35 (25) | 0.8 |
| (mPa·s) | 847 | 227 | GBM | 4658 | 0.17 (0.06) | 0.94 | 3994 | 0.35 (0.23) | 0.76 |
| (kg/m) | 333 | 120 | RF | 9225 | 12.23 (2.65) | 0.99 | 7731 | 49.10 (28.34) | 0.93 |
| (J/K/mol) | 115 | 48 | GBM | 6320 | 0.042 (0.012) | 0.99 | 2763 | 0.28 (0.19) | 0.91 |
| (N/m) | 131 | 68 | GBM | 1863 | 0.001 (0.0002) | 0.97 | 1117 | 0.004 (0.0027) | 0.79 |
| 237 | 85 | GBM | 1646 | 0.006 (0.002) | 0.97 | 1456 | 0.017 (0.011) | 0.83 | |
| 78 | 74 | GBM | 6084 | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.98 | 4839 | 0.09 (0.06) | 0.86 | |
| M | 114 | 25 | Cubist | 157 | 0.52 (0.05) | 0.79 | 70 | 0.40 (0.30) | 0.86 |
| (S/m) | 158 | 80 | GBM | 1433 | 0.05 (0.01) | 0.98 | 1251 | 0.15 (0.10) | 0.79 |
| (W/m/K) | 28 | 28 | GBM | 326 | 0.005 (0.002) | 0.95 | 147 | 0.009 (0.006) | 0.89 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venkatraman, V.; Evjen, S.; Chellappan Lethesh, K. The Ionic Liquid Property Explorer: An Extensive Library of Task-Specific Solvents. Data 2019, 4, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020088
Venkatraman V, Evjen S, Chellappan Lethesh K. The Ionic Liquid Property Explorer: An Extensive Library of Task-Specific Solvents. Data. 2019; 4(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenkatraman, Vishwesh, Sigvart Evjen, and Kallidanthiyil Chellappan Lethesh. 2019. "The Ionic Liquid Property Explorer: An Extensive Library of Task-Specific Solvents" Data 4, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020088
APA StyleVenkatraman, V., Evjen, S., & Chellappan Lethesh, K. (2019). The Ionic Liquid Property Explorer: An Extensive Library of Task-Specific Solvents. Data, 4(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/data4020088