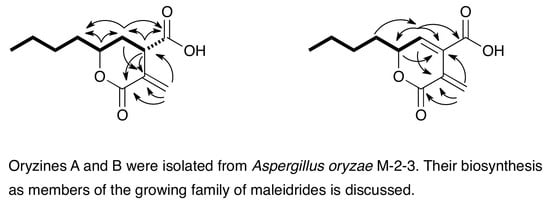
Oryzines A & B, Maleidride Congeners from Aspergillus oryzae and Their Putative Biosynthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Fermentation and Extraction
2.3. Isolation of Oryzine A 3 and Oryzine B 4
2.4. Spectroscopic and Spectrometric Data
2.4.1. Oryzine A 3
2.4.2. Oryzine B 4
2.5. Oryzine Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Structure Elucidation
3.2. Identification of A Putative Oryzine Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
3.3. Characteristics of the Putative Oryzine BGC
3.4. Proposed Biosynthesis of the Oryzines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, H.S.; Jun, S.C.; Han, K.H.; Hong, S.B.; Yu, J.H. Diversity, Application and synthetic biology of industrially important aspergillus fungi. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 100, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pariza, M.W.; Johnson, E.A. Evaluating the safety of microbial enzyme preparations used in food processing: Update for a new century. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 33, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, W.; Cox, R.J.; He, J.; Chen, F. Recent advances in reconstructing microbial secondary metabolites biosynthesis in Aspergillus spp. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 739–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schor, R.; Schotte, C.; Wibberg, D.; Kalinowski, J.; Cox, R.J. Three previously unrecognised classes of biosynthetic enzymes revealed during the production of xenovulene A. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.M.; Alberti, F.; Kilaru, S.; Collins, C.M.; De Mattos-Shipley, K.; Hartley, A.J.; Hayes, P.; Griffin, A.; Lazarus, C.M.; Cox, R.J.; et al. Identification and manipulation of the pleuromutilin gene cluster from Clitopilus passeckerianus for increased rapid antibiotic production. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.; Szwalbe, A.J.; Mulholland, N.P.; Vincent, J.L.; Bailey, A.M.; Willis, C.L.; Simpson, T.J.; Cox, R.J. Heterologous production of fungal maleidrides reveals the cryptic cyclization involved in their biosynthesis. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6784–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, R.; Minami, A.; Tsukagoshi, T.; Sato, N.; Sahara, T.; Ohgiya, S.; Gomi, K.; Oikawa, H. Total biosynthesis of diterpene aphidicolin, a specific inhibitor of dna polymerase α: Heterologous expression of four biosynthetic genes in Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, M.; Yamada, O.; Gomi, K. Genomics of Aspergillus oryzae: Learning from the history of koji mold and exploration of its future. DNA Res. 2008, 15, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rank, C.; Klejnstrup, M.L.; Petersen, L.M.; Kildgaard, S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Held Gotfredsen, C.; Ostenfeld Larsen, T. Comparative chemistry of Aspergillus oryzae (RIB40) and A. flavus (NRRL 3357). Metabolites 2012, 2, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaaban, M.; El-Metwally, M.M.; Nasr, H. A new diketopiperazine alkaloid from Aspergillus oryzae. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, R.; Chen, C.-J.; Hu, S.-S.; Ge, H.-M.; Zhu, W.-Y.; Tan, R.-X.; Jiao, R.-H. Drimane Sesquiterpenoids from the Aspergillus oryzae QXPC-4. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bao, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, K.; Han, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R.; Ren, J.; Yin, W.; Wang, W.; et al. Asperorydines A-M: Prenylated Tryptophan-Derived Alkaloids with Neurotrophic Effects from Aspergillus oryzae. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Z.; Liou, G.Y.; Yuan, G.F. Comparison of Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus oryzae by amplified fragment length polymorphism. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 2004, 45, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, M.; Asai, K.; Sano, M.; Tanaka, T.; Kumagai, T.; Terai, G.; Kusumoto, K.I.; Arima, T.; Akita, O.; Kashiwagi, Y.; et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of Aspergillus oryzae. Nature 2005, 438, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshime, Y.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Kitamoto, K.; Ebizuka, Y.; Nonaka, T.; Fujii, I. Aspergillus oryzae type III polyketide synthase CsyA is involved in the biosynthesis of 3,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 4785–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marui, J.; Ohashi-Kunihiro, S.; Ando, T.; Nishimura, M.; Koike, H.; Machida, M. Penicillin biosynthesis in Aspergillus oryzae and its overproduction by genetic engineering. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marui, J.; Yamane, N.; Ohashi-Kunihiro, S.; Ando, T.; Terabayashi, Y.; Sano, M.; Ohashi, S.; Ohshima, E.; Tachibana, K.; Higa, Y.; et al. Kojic acid biosynthesis in Aspergillus oryzae is regulated by a Zn(II)2Cys6transcriptional activator and induced by kojic acid at the transcriptional level. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomi, K.; Iimura, Y.; Hara, S. Integrative Transformation of Aspergillus oryzae with a Plasmid Containing the Aspergillus nidulans argB Gene. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1987, 51, 2549–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakeer, W. Overexpression of Secondary Metabolism Genes from Magnaporthe grisea and Beauveria bassiana. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stanke, M.; Steinkamp, R.; Waack, S.; Morgenstern, B. Augustus: A web server for gene finding in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W309–W312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter-Hovhannisyan, V.; Lomsadze, A.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Borodovsky, M. Gene prediction in novel fungal genomes using an ab initio algorithm with unsupervised training. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. Detecting Sequence Homology at the Gene Cluster Level with MultiGeneBlast. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carver, T.J.; Rutherford, K.M.; Berriman, M.; Rajandream, M.A.; Barrell, B.G.; Parkhill, J. ACT: The Artemis comparison tool. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3422–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, K.M.; Bakeer, W.; Yakasai, A.A.; Song, Z.; Pedrick, J.; Wasil, Z.; Bailey, A.M.; Lazarus, C.M.; Simpson, T.J.; Cox, R.J. Rational Domain Swaps Decipher Programming in Fungal Highly Reducing Polyketide Synthases and Resurrect an Extinct Metabolite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 16635–16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneghan, M.N.; Yakasai, A.A.; Williams, K.; Kadir, K.A.; Wasil, Z.; Bakeer, W.; Fisch, K.M.; Bailey, A.M.; Simpson, T.J.; Cox, R.J.; et al. The programming role of trans-acting enoyl reductases during the biosynthesis of highly reduced fungal polyketides. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwalbe, A.; Williams, K.; O’Flynn, D.; Bailey, A.; Mulholland, N.; Vincent, J.; Willis, C.; Cox, R.; Simpson, T. Novel nonadride, heptadride and maleic acid metabolites from the byssochlamic acid producer Byssochlamys fulva IMI 40021–an insight into the biosynthesis of maleidrides. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17088–17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, K.; Szwalbe, A.; Dickson, C.; Desson, T.; Mulholland, N.; Vincent, J.; Clough, J.; Bailey, A.; Butts, C.; Willis, C.; et al. Genetic and chemical characterisation of the cornexistin pathway provides further insight into maleidride biosynthesis. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7965–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesters, N.C.J.E.; O’Hagan, D. Biosynthesis of the fungal metabolite, piliformic acid (2-hexylidene-3-methylsuccinic acid). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin. Trans. 1 1997, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn, K.; Ludewig, K.; Aust, H.-J.; Dräger, S.; Schulz, B. Biologically active metabolites from fungi. 3. Sporothriolide, discosiolide, and 4-epi-ethisolide New furofurandiones from Sporothrix sp., Discosia sp., and Pezicula livida. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1994, 47, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surup, F.; Kuhnert, E.; Lehmann, E.; Heitkämper, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Fournier, J.; Stadler, M. Sporothriolide derivatives as chemotaxonomic markers for Hypoxylon monticulosum. Mycology 2014, 5, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchman, T.S.; Schmidt, E.W.; Trail, F.; Rarick, M.D.; Linz, J.E.; Townsend, C.A. Hexanoate synthase, a specialized type I fatty acid synthase in aflatoxin B1biosynthesis. Bioorg. Chem. 2001, 29, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanti, N.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cary, J.W.; Joubran, J.; Linz, J.E. Structure and function of fas-1A, a gene encoding a putative fatty acid synthetase directly involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiang, Y.; Ahuja, M.; Oakley, C.; Entwistle, R.; Asokan, A.; Zutz, C.; Wang, C.; Oakley, B. Development of Genetic Dereplication Strains in Aspergillus nidulans Results in the Discovery of Aspercryptin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 55, 1662–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Chen, R.; Liu, Q.; He, Y.; He, K.; Ding, X.; Kang, L.; Guo, X.; Xie, N.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Orange, red, yellow: Biosynthesis of azaphilone pigments in Monascus fungi. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 4917–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Krivoruchko, A.; Grininger, M.; Zhao, Z.; Nielsen, J. Expanding the product portfolio of fungal type I fatty acid synthases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 360–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene | GenBank Acc. No. | Proposed Function | Closest UniProtKB Hit (Query Coverage/Identity) |
|---|---|---|---|
| oryC | XP_023094066 | Transporter | Sugar transporter STL1, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, P39932 (94%/33%) |
| oryD | - | Dehydrogenase | Histidinol dehydrogenase 1, Bacillus clausii, Q5WIU9 (99%/56%) |
| oryfasA | XP_001827206 | Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha | Fatty acid synthase subunit alpha, Aspergillus nidulans, Q5B7V0 (99%/46%) |
| oryE | XP_001827205 | Citrate synthase | Citrate synthase, Dictyostelium discoideum, Q86AV6 (97%/38%) |
| oryF | XP_001827204 | Transporter | Efflux pump VrtL, Penicillium aethiopicum, D7PHY8 (95%/39%) |
| oryG | XP_001827203 | Alpha-ketoglut- -arate dependent dioxygenase | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent sulfonate dioxygenase, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Q12358 (88%/32%) |
| oryH | XP_023094065 | Lactonase | Gluconolactonase, Zymomonas mobilis, Q01578 (52%/28%) |
| oryJ | XP_023094064 | - | Lysine--tRNA ligase, Bacillus cereus, B7JK84 (24%/30%) |
| oryK | XP_001827200 | - | Ankyrin repeat and KH domain-containing protein mask, Drosophila melanogaster, Q9VCA8 (36%/27%) |
| oryL | XP_023094061 | Lactonase | Gluconolactonase, Zymomonas mobilis, Q01578 (66%/25%) |
| oryM | XP_001827196 | Aconitate decarboxylase | Cis-aconitate decarboxylase, Aspergillus terreus, Q0C8L3 (98%/55%) |
| oryN | XP_001827195 | Transporter | Citrinin biosynthesis cluster MFS transporter Mrr1, Monascus ruber, A0A161CLJ6 (93%/48%) |
| oryO | XP_023094060 | Transcription factor | Uncharacterized transcriptional regulatory protein C530.05, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, O59741 (24%/40%) |
| oryP | - | Acyl-CoA ligase | Acyl-CoA synthetase family member 3, Homo sapiens, Q4G176 (92%/23%) |
| oryQ | - | P450 monooxygenase (truncated) | Probable sterigmatocystin biosynthesis P450 monooxygenase StcF, Aspergillus nidulans, Q12609 (82%/49%) |
| oryfasB | XP_001827193 | Fatty acid synthase subunit beta | Fatty acid synthase subunit beta, Yarrowia lipolytica, P34229 (99%/40%) |
| oryR | XP_001827192 | 2-Methylcitrate dehydratase | 2-methylcitrate dehydratase, Escherichia coli, P77243 (96%/49%) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wasil, Z.; Kuhnert, E.; Simpson, T.J.; Cox, R.J. Oryzines A & B, Maleidride Congeners from Aspergillus oryzae and Their Putative Biosynthesis. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030096
Wasil Z, Kuhnert E, Simpson TJ, Cox RJ. Oryzines A & B, Maleidride Congeners from Aspergillus oryzae and Their Putative Biosynthesis. Journal of Fungi. 2018; 4(3):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030096
Chicago/Turabian StyleWasil, Zahida, Eric Kuhnert, Thomas J. Simpson, and Russell J. Cox. 2018. "Oryzines A & B, Maleidride Congeners from Aspergillus oryzae and Their Putative Biosynthesis" Journal of Fungi 4, no. 3: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030096
APA StyleWasil, Z., Kuhnert, E., Simpson, T. J., & Cox, R. J. (2018). Oryzines A & B, Maleidride Congeners from Aspergillus oryzae and Their Putative Biosynthesis. Journal of Fungi, 4(3), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4030096