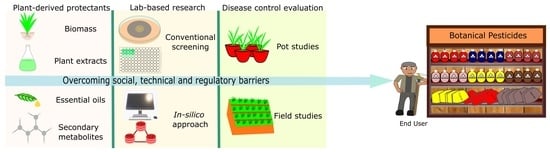
Plant-Derived Protectants in Combating Soil-Borne Fungal Infections in Tomato and Chilli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Management of Soil-Borne Diseases in Tomato and Chilli
2.1. Using Crude Plant Extracts, Essential Oils, and Purified Secondary Metabolites (Lab-to-Land Approach)
2.2. Using Total Phytobiomass (Land to Land Approach)
3. Antifungal Screening Assays of PDPs
3.1. Conventional Approach
3.2. In Silico Approach
4. Hurdles in Bringing Pest-Protection Research to Market
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haq, I.U.; Sarwar, M.K.; Faraz, A.; Latif, M.Z. Synthetic chemicals: Major component of plant disease management. In Plant Disease Management Strategies for Sustainable Agriculture through Traditional and Modern Approaches; Haq, I.U., Ijaz, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 53–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhary, K.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, S.; Pathak, R.; Jangir, M. Ocimum sp.: Source of biorational pesticides. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 686–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraiza, M.P.; González-Coloma, A.; Andres, M.F.; Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Domínguez-Núñez, J.A.; Da Costa, A.C., Jr.; Navarro-Rocha, J.; Calderón-Guerrero, C. Antifungal effect of essential oils. In Potential Essent. Oils; Hany El-Shemy, Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kala, S.; Sogan, N.; Naik, S.N.; Patanjali, P.K.; Kumar, J. Biopesticides: Formulations and Delivery Techniques. In Natural Remedies for Pest, Disease and Weed Control; Egbuna, C., Sawicka, B., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Lengai, G.M.W.; Muthomi, J.W.; Mbega, E.R. Phytochemical activity and role of botanical pesticides in pest management for sustainable agricultural crop production. Sci. Afr. 2020, 7, e00239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, E.V.R.; Proença, P.L.F.; Oliveira, J.L.; Bakshi, M.; Abhilash, P.C.; Fraceto, L.F. Use of botanical insecticides for sustainable agriculture: Future perspectives. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loi, M.; Paciolla, C.; Logrieco, A.F.; Mulè, G. Plant bioactive compounds in pre-and postharvest management for aflatoxins reduction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamwal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Puri, S. Plant growth regulator mediated consequences of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 9, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveau, R.; Fontaine, J.; Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui, A. Essential oils as potential alternative biocontrol products against plant pathogens and weeds: A Review. Foods 2020, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, H.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Haron, F.F.; Gafur, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Datta, R. Pythium damping-off and root rot of capsicum annuum l.: Impacts, diagnosis, and management. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancard, D. Tomato Diseases: Identification, Biology and Control: A Colour Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kadoglidou, K.; Chatzopoulou, P.; Maloupa, E.; Kalaitzidis, A.; Ghoghoberidze, S.; Katsantonis, D. Mentha and oregano soil amendment induces enhancement of tomato tolerance against soilborne diseases, yield and quality. Agronomy 2020, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozkaya, H.O.; Ergun, T. The effects of Allium tuncelianum extract on some important pathogens and total phenolic compounds in tomato and pepper. Pak. J. Bot 2017, 49, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, A. Disease management of tomato through PGPB: Current trends and future perspective. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, D.F.; Lopes, E.A.; Moraes, A.R.F.; Soares, M.S.; Visôtto, L.E.; Oliveira, C.R.; Valente, V.M.M. Formulation of botanicals for the control of plant-pathogens: A review. Crop Prot. 2018, 110, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongai, D.; Pulcini, P.; Pesce, B.; Milano, F. Antifungal activity of pomegranate peel extract against Fusarium wilt of tomato. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 147, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rodriguez, D.J.; Gaytán-Sánchez, N.A.; Rodríguez-García, R.; Hernández-Castillo, F.D.; Díaz-Jiménez, L.; Villarreal-Quintanilla, J.A.; Flores-López, M.L.; Carrillo-Lomelí, D.A.; Peña-Ramos, F.M. Antifungal activity of Juglans spp. and Carya spp. ethanol extracts against Fusarium oxysporum on tomato under greenhouse conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 138, 111442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji-Hedfi, L.; Larayedh, A.; Hammas, N.C.; Regaieg, H.; Horrigue-Raouani, N. Biological activities and chemical composition of Pistacia lentiscus in controlling Fusarium wilt and root-knot nematode disease complex on tomato. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlokwe, M.T.P.; Kena, M.A.; Mamphiswana, N.D. Evaluating crude extracts of Monsonia burkeana and Moringa oleifera against Fusarium wilt of tomato. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B Soil Plant Sci. 2018, 68, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu’nisa, A.; Hiola, S.F.; Ali, A. The effectiveness of the formulation of Cocoa Pod Husk (Theobroma cacao L.) based botanical fungicides on Fusarium wilt disease on tomato plants. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1244, 012036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, P.G.; Ramírez, D.G.; Mejía, E.Z.; Ocampo, S.A.; Díaz, C.N.; Rojas Martínez, R.I. Extracts of Stevia rebaudiana against Fusarium oxysporum associated with tomato cultivation. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 2020, 259, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Jabeur, M.; Ghabri, E.; Myriam, M.; Hamada, W. Thyme essential oil as a defense inducer of tomato against gray mold and Fusarium wilt. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Rajendran, S.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, S.; Kundu, B. Antifungal activities of selected essential oils against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici 1322, with emphasis on Syzygium aromaticum essential oil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, N.K.; Srivastava, A.; Kataria, A.; Dubey, S.; Sharma, S.; Kundu, B. Clove and lemongrass oil based non-ionic nanoemulsion for suppressing the growth of plant pathogenic Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 123, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaili, A.; Mazoir, N.; Rifai, L.A.; Koussa, T.; Makroum, K.; Kabil, E.M.; Benharref, A.; Faize, M. Triterpene derivatives from Euphorbia enhance resistance against Verticillium wilt of tomato. Phytochemistry 2017, 135, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smaili, A.; Rifai, L.A.; Mazoir, N.; Koussa, T.; Faize, L.; Alburquerque, N.; Burgos, L.; Makroum, K.; Malika, B.; Benharref, A.; et al. Semisynthetic Triterpenes derived from Euphorbia officinarum as plant growth promoters and inducers of disease resistance. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 38, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekam, P.N.; Martini, S.; Nguefack, J.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Stefani, E. Phenolic compounds profile of water and ethanol extracts of Euphorbia hirta L. leaves showing antioxidant and antifungal properties. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 127, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, A.; Caradonia, F.; Matere, A.; Battaglia, V. Using plant essential oils to control Fusarium wilt in tomato plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, I.M. Control of damping-off disease in some plants using environmentally safe biocides. Pakistan J. Bot. 2017, 49, 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Kalleli, F.; Abid, G.; Ben Salem, I.; Boughalleb-M’Hamdi, N.; M’Hamdi, M. Essential oil from fennel seeds (Foeniculum vulgare) reduces Fusarium wilt of tomato (Solanum lycopersicon). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2020, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefzi, A.; Abdallah, R.A.B.; Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H.; Ammar, N.; Medimagh-Saïdana, S.; Haouala, R.; Daami-Remadi, M. Management of Fusarium crown and root rot of tomato by Solanum linnaeanum L. extracts. Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam) 2018, 238, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefzi, A.; Jabnoun-Khiareddine, H.; Aydi Ben Abdallah, R.; Ammar, N.; Medimagh-Saïdana, S.; Haouala, R.; Daami-Remadi, M. Suppressing Fusarium crown and root rot infections and enhancing the growth of tomato plants by Lycium arabicum Schweinf. Ex Boiss. extracts. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akladious, S.A.; Isaac, G.S.; Abu-Tahon, M.A. Induction and resistance against Fusarium wilt disease of tomato by using sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) extract. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 95, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekam, P.N.; Martini, S.; Nguefack, J.; Tagliazucchi, D.; Mangoumou, G.N.; Stefani, E. Activity of extracts from three tropical plants towards fungi pathogenic to tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2019, 58, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Prakesh, H.G.; Palat, R.; Bahar, J. Induced synthesis of defense molecules in tomato (Solamum lycopercicum L.) against Fusarium wilt through plant extracts. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2019, 48, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhou, X.G.; Wu, F.Z. Effects of root exudates from potato onion on Verticillium dahliae. Allelopath. J. 2018, 43, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; Wang, F. Transcriptome analysis reveals the effects of Chinese Chive (Allium tuberosum R.) extract on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici spore germination. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, Y.D.; Gade, R.M.; Shitole, A.V. Evaluation of antifungal activities of extracts of Aegle marmelos, Syzygium cumini and Pongamia pinnata against Pythium debaryanum. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 79, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rodríguez, D.J.; Trejo-González, F.A.; Rodríguez-García, R.; Díaz-Jimenez, M.L.V.; Sáenz-Galindo, A.; Hernández-Castillo, F.D.; Villarreal-Quintanilla, J.A.; Peña-Ramos, F.M. Antifungal activity in vitro of Rhus muelleri against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 75, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohan, S.; Perveen, R. Phytochemical analysis and antifungal efficacy of rhizome extracts of various plants against Fusarium wilt and root rot of tomato. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthomi, J.W.; Lengai, G.M.W.; Wagacha, M.J.; Narla, R.D. In vitro activity of plant extracts against some important plant pathogenic fungi of tomato. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2017, 11, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, S.; Javaid, A.; Shoaib, A.; Javed, S.; Qaisar, U. Antifungal activity of aerial parts of Cenchrus pennisetiformis against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Planta Daninha 2018, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nugroho, C.; Mirnia, E.; Cumagun, C.J.R. Antifungal activities of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) Aqueous Extract Against against Sclerotium rolfsii, causal agent of damping-off on tomato seedling. Agrivita J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 41, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, J. Antifungal activity and biochemical response of cuminic acid against Phytophthora capsici Leonian. Molecules 2016, 21, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Švecová, E.; Colla, G.; Crinò, P. Antifungal activity of Boerhavia diffusa L. extract against Phytophthora spp. in tomato and pepper. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, J.; Farhang, V.; Javadi, T.; Nazemi, J. Antifungal effect of plant essential oils on controlling Phytophthora species. Plant Pathol. J. 2016, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, M.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, K.Z. Efficacy of selected plant extracts and biocontrol agents against damping-off (Pythium aphanidermatum) of chilli. Res. Environ. Life Sci. 2017, 10, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, N.A.; Atiq, M.; Javed, N.; Ye, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.; Syed, R.N.; Lodhi, A.M.; Khan, B.; Iqbal, O.; Dou, D. Antimicrobial effect of Chinese medicinal plant crude extracts against Rhizoctonia solani and Pythium aphanidermatum. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 3941–3949. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Ouyang, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Yang, D.; Fang, W.; Cao, A.; Guo, M. Effects of oil extracts of Eupatorium adenophorum on Phytophthora capsici and other plant pathogenic fungi in vitro. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 140, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, N.; Mahmoud, N.; Saleh, R. Effect of some biotic and abiotic applications on control of Fusarium wilt of Pepper plants. Egypt. J. Phytopathol. 2016, 44, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.J.; Long, X.H.; Li, E.Z. Evaluation of antifungal phenolics from Helianthus tuberosus L. leaves against Phytophthora capsici leonian by chemometric analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mongiano, G.; Zampieri, E.; Morcia, C.; Titone, P.; Volante, A.; Terzi, V.; Tamborini, L.; Valé, G.; Monaco, S. Application of plant-derived bioactive compounds as seed treatments to manage the rice pathogen Fusarium fujikuroi. Crop Prot. 2021, 148, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghrouchni, H.; El Barnossi, A.; Salamatullah, A.M.; Bourhia, M.; Alzahrani, A.; Alkaltham, M.S.; Alyahya, H.K.; Tahiri, N.E.H.; Imtara, H.; Var, I. Carvacrol: A promising environmentally friendly agent to fight seeds damping-off diseases induced by fungal species. Agronomy 2021, 11, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Jiang, M.; Jin, H.; Tao, K.; Hou, T. Unraveling the polypharmacology of a natural antifungal product, eugenol, against Rhizoctonia solani. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3469–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal-Gurel, F.; Liyanapathiranage, P.; Addesso, K.M. Effect of Brassica crop-based biofumigation on soilborne disease suppression in woody ornamentals. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 42, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pane, C.; Villecco, D.; Zaccardelli, M. Combined use of Brassica carinata seed meal, thyme oil and a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain for controlling three soil-borne fungal plant diseases. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gentry, T.; Hu, P.; Pierson, E.; Gu, M.; Yin, S. Impact of brassicaceous seed meals on the composition of the soil fungal community and the incidence of Fusarium wilt on chili pepper. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 90, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hammouri, A.A.; Al-Kofahi, S.D.; Ibbini, J.H.; Abusmier, S.A.; Sanogo, S. Effect of biofumigation by Calligonum polygonoides, dry olive leaves, and ash of olive leaves on chilli pepper growth and recovery of Rhizoctonia solani. Acta Agric. Slov. 2018, 111, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurjar, M.S.; Ali, S.; Akhtar, M.; Singh, K.S. Efficacy of plant extracts in plant disease management. Agric. Sci. 2012, 3, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Favre-Godal, Q.; Queiroz, E.F.; Wolfender, J.L. Latest developments in assessing antifungal activity using TLC-bioautography: A review. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, T.C.; Studholme, D.J.; Talbot, N.J.; Haynes, K. New and improved techniques for the study of pathogenic fungi. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, G.; Jeon, J. Computer-aided drug discovery in plant pathology. Plant Pathol. J. 2017, 33, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Roy, K.; Leszczynski, J. On Applications of QSARs in Food and Agricultural Sciences: History and Critical Review of Recent Developments. In Advances in QSAR Modeling: Applications in Pharmaceutical, Chemical, Food, Agricultural and Environmental Sciences; Roy, K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 203–302. [Google Scholar]
- Amoroso, V.B.; Mendez, R.A.; Junio, H.A.; Molino, R.J.E.J.; Pescadero, I.R.; Villalobos, A.P. Characterization of a natural fungicide from an indigenous plant Tasmannia piperita (Hook. f.) Miers Extract: Stability, Metabolomics, and In silico Studies. Philipp. J. Sci. 2021, 150, 355–370. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, K.S.; Bhangu, S.K.; Pathak, R.K.; Yadav, I.S.; Chhuneja, P. Identification of natural lead compounds for leaf rust of Wheat: A molecular docking and simulation study. J. Proteins Proteomics 2020, 11, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, J.G.D.M.; Fernandes, L.S.; Dos Santos, R.V.; Tasic, L.; Fill, T.P. Virulence factors in the phytopathogen-host interactions: An overview. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 7555–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, N.; Giachero, M.L.; Declerck, S.; Ducasse, D.A. Macrophomina phaseolina: General characteristics of pathogenicity and methods of control. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 634397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorokina, M.; Steinbeck, C. Review on natural products databases: Where to find data in 2020. J. Cheminform. 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdés-Jiménez, A.; Peña-Varas, C.; Borrego-Muñoz, P.; Arrue, L.; Alegría-Arcos, M.; Nour-Eldin, H.; Dreyer, I.; Nuñez-Vivanco, G.; Ramírez, D. Psc-db: A structured and searchable 3d-database for plant secondary compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.K.R.D.; Silva, J.R.A.; Nascimento, S.B.; Luz, S.F.M.D.; Meireles, E.N.; Alves, C.N.; Ramos, A.R.; Maia, J.G.S. Antifungal activity and computational study of constituents from Piper divaricatum essential oil against Fusarium infection in black pepper. Molecules 2014, 19, 17926–17942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos, V.A.; Perina, F.J.; Alves, E.; Sartorelli, J.; Moura, A.M.; Oliveira, D.F. Anadenanthera colubrina (Vell.) Brenan produces steroidal substances that are active against Alternaria alternata (Fr.) Keissler and that may bind to oxysterol-binding proteins. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadharsini, K.; Saravanakumar, S.; Bharathi, N.; Ramalingam, J. Exploring the competence of phytochemical compounds to combat anthracnose disease of cucumber-an in silico approach. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pani, G.; Dessì, A.; Dallocchio, R.; Scherm, B.; Azara, E.; Delogu, G.; Migheli, Q.M. Natural phenolic inhibitors of trichothecene biosynthesis by the wheat fungal pathogen Fusarium culmorum: A computational insight into the structure-activity relationship. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, A.; Kalske, A. Plant secondary metabolite diversity and species interactions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2018, 49, 115–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical Insecticides in the Twenty-First Century—Fulfilling Their Promise ? Annu. Rev. 2020, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ivase, T.J.-P.; Nyakuma, B.B.; Ogenyi, B.U.; Balogun, A.D.; Hassan, M.N. Current status, challenges and prospects of biopesticide utilization in Nigeria. Acta Univ. Sapientiae Agric. Environ. 2017, 9, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keswani, C.; Dilnashin, H.; Birla, H.; Singh, S.P. Regulatory barriers to Agricultural Research commercialization: A case study of biopesticides in India. Rhizosphere 2019, 11, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, D.; Bailey, A.S.; Tatchell, G.M.; Davidson, G.; Greaves, J.; Grant, W.P. The development, regulation and use of biopesticides for integrated pest management. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 366, 1987–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguzzo, F.; Zabini, F. Sustainable Crop Protection and Farming. In Agri-Food and Forestry Sectors for Sustainable Development; Sustainable Development Goals Series; Meneguzzo, F., Zabini, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lykogianni, M.; Bempelou, E.; Karamaouna, F.; Aliferis, K.A. Do pesticides promote or hinder sustainability in agriculture? The challenge of sustainable use of pesticides in modern agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Joint Meeting of the Chemicals Committee and the Working Party on Chemicals, Pesticides and Biotechnology Guidance Document on Botanical Active Substances Used in Plant Protection Products; Series on Pesticides No. 90 JT03412077; OECD Environment, Health and Safety Publications: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, J.; Dutta, V.; Arora, N.K. Biopesticides in India: Technology and sustainability linkages. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damalas, C.A.; Koutroubas, S.D. Current status and recent developments in biopesticide use. Agriculture 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Pathogen | Source Plant | Plant Part | Solvent | Major Bioactive Compounds | In-Vitro Control | In Vivo Disease Control | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V. dahliae | Euphorbia officinarum | Latex | Not available | Oxidation derivatives of 31-norlanostenol | No inhibition at 10 µg/mL compound concentration | Seed treatment in 5 mL of 10 µg/mL compound concentration of derivatives reduced the disease symptoms | [25] |
| Euphorbia resisnifera | Latex | Not available | Oxidation derivatives of α-euphorbol | Insignificant inhibition at 10 µg/mL compound concentration | Seed treatment in 5 mL of 10 µg/mL compound concentration of derivatives reduced the disease symptoms | ||
| V. dahliae | Euphorbia officinarum | Latex | Not available | Oxidation derivatives of lupeol acetate and 31-norlanostenol | 56–60% reduction in conidia formation at 100 µg/mL compound concentration | Spraying of seedling with 10 µg/mL compound concentration of derivatives reduced the disease symptoms | [26] |
| Essential oil | |||||||
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Thymus vulgaris | Not available | - | Thymol, α-pinene | MIC50 A = 152 µg/mL | Soil treatment with 300 µg/mL oil concentration resulted in 32.2% efficacy in disease severity reduction | [28] |
| Eugenia caryophyllata | Not available | - | Eugenol | MIC50 = 172 µg/mL | Soil treatment with 300 µg/mL oil concentration resulted in 42.4% efficacy in disease severity reduction | ||
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Syzygium aromaticum | Not available | - | Eugenol, E-caryophyllene, α-humulene, caryophyllene oxide, | IC50 B = 18.22 ppm; MIC C = 31.25 ppm; MFC D = 125 ppm | 86.5% reduction in disease incidence when 5 mL of 5% aqueous emulsion of essential oil used for 150 cm3 soil | [23] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Syzygium aromaticum + Cymbopogon citratus (1:1) | Not available | - | Eugenol, E-caryophyllene and Geranial, Neral | For the 5% (w/w) nanoemulsion prepared, MIC = 4000 mg/L; MFC = 5000 mg/L | 67.51% disease control when 5 mL of 4000 mg/L concentration of 5% (w/w) nanoemulsion used for 150 cm3 soil treatment | [24] |
| F. solani | Oreganum vulgare | Not available | - | Not available | For the emulsifiable concentrate prepared, 100% mycelial inhibition at 4000 ppm concentration | Seed treatement with 4000 ppm concentration of emulsifiable concentrate for 8 h resulted in 50% reduction in pre-emergence damping-off | [29] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. radicis lycopersici | Foeniculum vulgare | Seeds | - | Trans-anethole, L-fenchone, Estragole, Limonene | 83% reduction in mycelial growth at 500 µL/mL oil concentration | 40–60% reduction in disease severity when the soil was drenched with 50 mL of 500 µL/mL oil concentration | [30] |
| Plant extract | |||||||
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici; P. deliense; R. solani; S. sclerotiorum; S. rolfsii | Allium tuncelianum | Not available | 96% ethanol | Not available | Not available | Soil treatment with 10 mL of 1.5% extract significantly reduced the disease severity against all pathogens | [13] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Punica granatum | Peel | Water | Punicalagins and ellagic acids | 83% mycelial inhibition at 0.5% (w/v) purified extract concentration | Soil treatment with 0.5% (w/w) extract concentration reduced disease incidence to half | [16] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. radicis lycopersici | Solanum linnaeanum | Leaf | Water | Not available | 61% mycelial inhibition at 4% (v/v) extract concentration | Substrate drench at 25 mL/seedling with 30% (w/v) extract concentration reduced leaf & root damage and vascular discoloration by 92.30% and 97.56%, respectively | [31] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici | Lycium arabicum | Leaf | Distilled water | Not available | 33.5% mycelial inhibition at 4% (v/v) extract concentration | Soil drenched with 25 mL of 30% (v/v) extract concentration reduced disease symptoms by 84.6% | [32] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici race 3 | Ocimum basilicum | Leaves and flowers | Water | Not available | Not available | Seed soaked in 20% aqueous extract for 10 h reduced disease incidence to 18% as compared to 94.7% in control | [33] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Moringa oleifera | Leaves | Methanol | Not available | 21% reduction in mycelial growth at 4 g/mL concentration | Soil treatment with 250 mL of 4 g/mL extract concentration significantly reduced disease symptoms | [19] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Theobroma cacao | Pod husk | Acetone: Water (7:3) | Not available | Not available | 100 mL of 8% (v/v) extract formulation per plant reduced wilt incidence to 23.8% compared to 100% in control | [20] |
| F. oxysporum | Juglans microcarpa | Leaf | Ethanol | Vitamin E acetate, Phytol, Benzeneethanamine, | Not available | Root treatment with 5000 mg/L extract concentration reduced disease incidence to 37.5% | [17] |
| Juglans mollis | Leaf | Ethanol | Hexanedioic acid dioctyl ester, Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester, | Not available | -do- | ||
| F. oxysporum | Stevia rebaudiana | Leaf | Hexane | Austroinulin | 54.9% mycelial inhibition at 833 ppm extract concentration | Substrate treatment with 3 mL of 500 ppm extract caused a reduction in stunting incidences | [21] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Pistacia lentiscus | Leaf | Water | Quercetin, Protocatechuic acid, Chlorogenic acid | 82.40% mycelial inhibition at 5% (v/v) extract concentration | 29.17% disease incidence in treatment as compared to 83.33% in untreated control when treatment was done using 100% extract | [18] |
| R. solani | Euphorbia hirta | Leaf | 70% Ethanol | Phenols, alkaloids, and polysaccharides | 100% mycelial inhibition at 10 mg/mL concentration | Spray treatment with 2.50 mg/mL extract concentration reduced disease incidence by 29.24% | [34] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Allium sativum | Cloves | Water | Not available | Not available | Spray treatment reduced disease incidence by 8.40% compared to 84.46% in control | [35] |
| Azadirachta indica | Leaf | Water | Not available | Not available | Spray treatment reduced disease incidence by 10.70% compared to 84.46% in control | ||
| Zingiber officinale | Rhizome | Water | Not available | Not available | Spray treatment reduced disease incidence by 11.90% compared to 84.46% in control | ||
| V. dahliae | Allium cepa var. aggregatum | Root exudate | Deionized water | Not available | 0.1 g/mL extract concentration mixed with media (1:1) caused significant reduction in mycelial biomass | Not available | [36] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici | Allium tuberosum | Leaf | Water | Not available | EC50 E = 0.40 g/mL | Not available | [37] |
| P. debaryanum | Aegle marmelos | Leaf | Methanol | Not available | 100% inhibition at 1000 µL extract concentration | Soil treatment with 4% extract concentration reduced pre and post-emergence damping-off incidences to 16.22% and 34.67% as compared to 35.90% and 42.67% in control, respectively | [38] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Rhus muelleri | Leaf | Ethanol | Ethyl isoallocholate, 7,8-epoxylanostan-11-ol, 3-acetoxy | MIC50 = 3363 ppm; MIC90 F = 11,793 ppm | Not available | [39] |
| R. solani | Euphorbia hirta | Leaf | 70% ethanol | Hydroxycinnamic acids, Hydroxybenzoic acids, Isocoumarins, Elagitannins | IC50 = 3.66 mg/mL | Not available | [27] |
| -do- | -do- | Water | Gallotannins, Hydroxybenzoic acids, Hydroxycinnamic acids, Flavonols | IC50 = 32.14 mg/mL | Not available | ||
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici; F. solani | Allium sativum | Bulb | Water | Flavanoid, terpenoid, saponin, steroids, tannins, cardiac glycoside, coumarins | 100% mycelial growth inhibition at 8% extract concentration | Not available | [40] |
| P. ultimum | Curcuma longa | Rhizome | 95% Ethanol | Not available | 55.6% mycelial inhibition at 2% (v/v) extract concentration | Not available | [41] |
| F. oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici | Cenchrus pennisetiformis | Shoot | Ethyl acetate sub-fraction of methanol extract | Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl-ester, Phenol, 2,4-bis{1,1-dimethlethyl}- | 100% decline in fungal biomass production at 12.5 mg/mL concentration | Not available | [42] |
| S. rolfsii | Ocimum basilicum | Leaf | Water | Not available | 33.35% reduction in mycelial growth at 100% concentration | Soil drenching with 100 mL of 100% extract concentration reduced damping-off incidences by 30% | [43] |
| Pathogen | Source Plant | Plant Part | Solvent | Major Bioactive Compounds | In-Vitro Control | In-Vivo Disease Control | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure compound | |||||||
| Ph. capsici | Cuminum cyminum | Seed | Not available | Cuminic acid | EC50 (Mycelial growth) = 14.54 ± 5.23 µg/mL; EC50 (Zoospore germination) = 6.97 ± 2.82 µg/mL | Irrigation with 10 mL of 1000 µg/mL compound concentration exhibited 70.89% disease control efficacy | [44] |
| Essential oil | |||||||
| Ph. capsici | Cymbopogon citratus | Leaf | - | z-citral, β-geranial, caryophyllene | EC50 = 31.473 ppm | Soil drenching with 50 mL of 100 ppm oil concentration reduced disease severity by 60.5% | [46] |
| Ph. capsici | Eupatorium adenophorum | Leaf | - | OA (9-oxo-agerophorone), ODA (9-oxo-10, 11-dehydro- agerophorone) | MIC = 500 µg/mL | Not available | [49] |
| F. oxysporum | Syzygium aromaticum | Not available | - | Eugenol | MIC = 0.25% (w/v) | Seedling treatment with 0.5% (w/v) essential oil concentration reduced disease severity index to 56.20% compared to 100% in control in greenhouse | [50] |
| Plant extract | |||||||
| Ph. capsici | Boerhavia diffusa | Root | Methanol | Not available | MIC = 0.5% | 1% plant extract concentration at 6 mL/plant reduced disease symptoms significantly | [45] |
| P. aphanidermatum | Lantana camara | Leaf | Water | Not available | Not available | Seed treatment reduced pre-emergence and post-emergence damping-off incidences to 7.08% and 10.31% as compared to 40% and 62.32% in control | [47] |
| P. aphanidermatum | Glycyrrhiza uralensis | Root | Ethyl acetate subfraction of 80% methanol extract | Not available | 62.6% mycelial inhibition at 10 µg/mL extract concentration | Seed treatment resulted in 82% seed germination and 21.95% seedling mortality as compared to 50% and 96% in control | [48] |
| R. solani | -do- | -do- | -do- | Not available | 77.6% mycelial inhibition at 10 µg/mL extract concentration | Seed treatment resulted in 88% seed germination and 13.63% seedling mortality as compared to 54% and 85.18% in control | |
| Ph. capsici | Helianthus tuberosus | Leaf | n-Butanol fraction of 70% ethanol extract | Methyl quercetin glycoside (MQG) Caffeoylquinic acid isomer | IC50 = 0.839 g/L | Not available | [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arora, H.; Sharma, A.; Poczai, P.; Sharma, S.; Haron, F.F.; Gafur, A.; Sayyed, R.Z. Plant-Derived Protectants in Combating Soil-Borne Fungal Infections in Tomato and Chilli. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020213
Arora H, Sharma A, Poczai P, Sharma S, Haron FF, Gafur A, Sayyed RZ. Plant-Derived Protectants in Combating Soil-Borne Fungal Infections in Tomato and Chilli. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(2):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleArora, Himanshu, Abhishek Sharma, Peter Poczai, Satyawati Sharma, Farah Farhanah Haron, Abdul Gafur, and R. Z. Sayyed. 2022. "Plant-Derived Protectants in Combating Soil-Borne Fungal Infections in Tomato and Chilli" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 2: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020213
APA StyleArora, H., Sharma, A., Poczai, P., Sharma, S., Haron, F. F., Gafur, A., & Sayyed, R. Z. (2022). Plant-Derived Protectants in Combating Soil-Borne Fungal Infections in Tomato and Chilli. Journal of Fungi, 8(2), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020213