Volume Phase Transition in Gels: Its Discovery and Development
Abstract
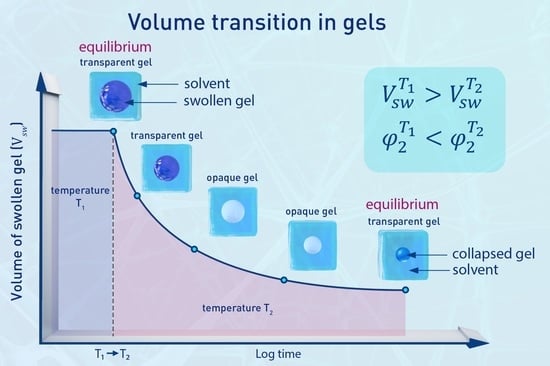
:1. Introduction
2. Mean-Field Description of Volume Phase Transition
3. The Mixing Contribution
4. The Elastic Contribution and Swelling Change of the Chemical Potential
- volume of solvent molecule with respect to the volume of lattice site: increasing causes decreasing of swelling degree;
- effective functionality of an elastically active crosslink which can vary between 3 and chemical functionality for perfect network: increasing causes decreasing of degree of swelling;
- concentration of elastically active network chains; with increasing swelling degree decreases;
- the interaction function and its concentration dependence: increasing usually contributes positively to (decreases the region of thermodynamic stability). The concentration dependence can cause VPT behavior;
- , is the volume fraction of diluent present during network formation: increasing increases degree of swelling; too high may cause reaction induced phase separation during formation of the network.
Swelling Under Constraint
- by changing molar volume of solvent molecule;
- somewhat by changing functionality of cross-links;
- by changing cross-link density (i.e., the concentration of EANCs);
- by changing the interaction function and its concentration dependence through (minor); changes of the chemical composition of the gel polymer (e.g., copolymerization) or small change in the solvent structure;
- by increasing or decreasing dilution during network formation.
5. Tools for Fine Tuning of Volume Phase Transition
6. Equilibrium Theory vs. Experimental Observations
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millar, J.R. Improvements relating to ion-exchange resins and their manufacture 1958. UK Patent 849.122, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, J.R.; Smith, D.G.; Marr, W.E.; Kressman, T.R.E. 33. Solvent-modified polymer networks. Part I. The preparation and characterisation of expanded-network and macroporous styrene–divinylbenzene copolymers and their sulphonates. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.R.; Smith, D.G.; Marr, W.E.; Kressman, T.R.E. 527. Solvent-modified polymer networks. Part III. Cation-exchange equilibria with some univalent inorganic and organic ions. J. Chem. Soc. 1964, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.R.; Smith, D.G.; Marr, W.E.; Kressman, T.R.E. 515. Solvent-modified polymer networks. Part II. Effect of structure on cation-exchange kinetics in sulphonated styrene–divinylbenzene copolymers. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 2779–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.R.; Smith, D.G.; Kressman, T.R.E. 45. Solvent-modified polymer networks. Part IV. Styrene–divinyl-benzene copolymers made in the presence of non-solvating diluents. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidl, J.; Malinský, J.; Dušek, K.; Heitz, W. Makroporöse Styrol-Divinylbenzol-Copolymere und ihre Verwendung in der Chromatographie und zur Darstellung von Ionenaustauschern. In Fortschritte der Hochpolymeren-Forschung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1967; pp. 113–213. [Google Scholar]
- Rosi, N.L. Hydrogen Storage in Microporous Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2003, 300, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953; ISBN 0-8014-0134-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dušek, K. Phase separation during the formation of three-dimensional polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Lett. 1965, 3, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K. Phase separation during the formation of three-dimensional polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part. C Polym. Symp. 1967, 16, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K.; Seidl, J.; Malinský, J. Phase separation in the copolymerization of styrene and divinylbenzene in the presence of diluents: Comparison of experiment with theory. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1967, 32, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K.; Sedláček, B. Structure and properties of hydrophilic polymers and their gels. XI. Microsyneresis in swollen poly(ethylene glycol methacrylate) gels induced by changes of temperature. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1969, 34, 136–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusek, K.; Prins, W. Structure and Elasticity of Non-Crystalline Polymer Networks. Adv. Polym. Sci. 1969, 6, 1–102. [Google Scholar]
- Dušek, K.; Patterson, D. Transition in swollen polymer networks induced by intramolecular condensation. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-2 Polym. Phys. 1968, 6, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T. Collapse of Gels and the Critical Endpoint. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 40, 820–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Fillmore, D.; Sun, S.-T.; Nishio, I.; Swislow, G.; Shah, A. Phase Transitions in Ionic Gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1980, 45, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Tanaka, T. Volume phase transition and related phenomena of polymer gels. In Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions I; Dušek, K., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 109, pp. 1–62. ISBN 978-3-540-56791-2. [Google Scholar]
- Dušek, K. (Ed.) Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions II; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 110, ISBN 3-540-56970-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Smart Hydrogel Modelling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; ISBN 978-3-642-02367-5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Urban, M.W. Recent advances and challenges in designing stimuli-responsive polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtering, W.; Saunders, B.R. Gel architectures and their complexity. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3695–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerlach, G.; Arndt, K.-F. (Eds.) Hydrogel Sensors and Actuators. Engineering and Technology, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; ISBN 978-3-540-75645-3. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, J.R.; Abu-Salih, S.; Khaleque, T.; Hanula, S.; Moussa, W. Modeling Theories of Intelligent Hydrogel Polymers. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2008, 5, 1942–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramarenko, E.Y.; Philippova, O.E.; Khokhlov, A.R. Polyelectrolyte networks as highly sensitive polymers. Polym. Sci. Ser. C 2006, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Li, H.; Chen, J.P.; Lam, K.Y. Modeling Investigation of Hydrogel Volume Transition. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2004, 13, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasa, J.; Ilavský, M.; Dušek, K. Deformational, swelling, and potentiometric behavior of ionized poly(methacrylic acid) gels. I. Theory. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1975, 13, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Pérez, M.; Maroto-Centeno, J.A.; Forcada, J.; Hidalgo-Alvarez, R. Gel swelling theories: The classical formalism and recent approaches. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, H. Polymer Solutions, 1st ed.; Butterworths Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Prange, M.M.; Hooper, H.H.; Prausnitz, J.M. Thermodynamics of aqueous systems containing hydrophilic polymers or gels. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, K.F.; Dudowicz, J. Lattice Cluster Theory for Pedestrians: The Incompressible Limit and the Miscibility of Polyolefin Blends. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 6681–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudowicz, J.; Freed, K.F.; Madden, W.G. Role of molecular structure on the thermodynamic properties of melts, blends, and concentrated polymer solutions: Comparison of Monte Carlo simulations with the cluster theory for the lattice model. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 4803–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.F.; Dudowicz, J.; Freed, K.F. Lattice model of equilibrium polymerization. VI. Measures of fluid “complexity” and search for generalized corresponding states. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 224901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, D. Free Volume and Polymer Solubility. A Qualitative View. Macromolecules 1969, 2, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.C.; Lacombe, R.H. Statistical Thermodynamics of Polymer Solutions. Macromolecules 1978, 11, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orwoll, R.A.; Flory, P.J. Equation-of-state parameters for normal alkanes. Correlation with chain length. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 6814–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, G.N.I.; Haslam, A.J.; Galindo, A.; Jackson, G. Developing optimal Wertheim-like models of water for use in Statistical Associating Fluid Theory (SAFT) and related approaches. Mol. Phys. 2006, 104, 3561–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.N.; Rubinstein, M. Thermoreversible Gelation in Solutions of Associative Polymers. 1. Statics. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F.; Ishida, M. Microphase Formation in Mixtures of Associating Polymers. Macromolecules 1997, 30, 1836–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, F.; Katsumoto, Y.; Nakano, S.; Kita, R. LCST phase separation and thermoreversible gelation in aqueous solutions of stereo-controlled poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)s. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukalin, E.B.; Douglas, J.F.; Freed, K.F. Multistep relaxation in equilibrium polymer solutions: A minimal model of relaxation in “complex” fluids. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 129, 094901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dušek, K.; Choukourov, A.; Dušková-Smrčková, M.; Biederman, H. Constrained Swelling of Polymer Networks: Characterization of Vapor-Deposited Cross-Linked Polymer Thin Films. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 4417–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K.; Dušková-Smrčková, M.; Šomvársky, J. Effect of Constraints on Swelling of Polymer Networks. Macromol. Symp. 2015, 358, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušková-Smrčková, M.; Dušek, K. How to Force Polymer Gels to Show Volume Phase Transitions. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knychała, P.; Timachova, K.; Banaszak, M.; Balsara, N.P. 50th Anniversary Perspective: Phase Behavior of Polymer Solutions and Blends. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3051–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Daoust, H. Osmotic pressures of moderately concentrated polymer solutions. J. Polym. Sci. 1957, 25, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K. Solubility of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) in some aliphatic alcohols. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1969, 34, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erman, B.; Flory, P.J. Critical phenomena and transitions in swollen polymer networks and in linear macromolecules. Macromolecules 1986, 19, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šolc, K.; Dušek, K.; Koningsveld, R.; Berghmans, H. “Zero” and “Off-Zero” Critical Concentrations in Solutions of Polydisperse Polymers with Very High Molar Masses. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1995, 60, 1661–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerkerke, R.; Koningsveld, R.; Berghmans, H.; Dusek, K.; Solc, K. Phase Transitions in Swollen Networks. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroze, F.; Nies, E.; Berghmans, H. Phase transitions in the system poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/water and swelling behaviour of the corresponding networks. J. Mol. Struct. 2000, 554, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer-Soenen, H.; Moerkerke, R.; Berghmans, H.; Koningsveld, R.; Dušek, K.; Šolc, K. Zero and Off-Zero Critical Concentrations in Systems Containing Polydisperse Polymers † with Very High Molar Masses. 2. The System Water−Poly(vinyl methyl ether). Macromolecules 1997, 30, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerkerke, R.; Meeussen, F.; Koningsveld, R.; Berghmans, H.; Mondelaers, W.; Schacht, E.; Dušek, K.; Šolc, K. Phase Transitions in Swollen Networks. 3. Swelling Behavior of Radiation Cross-Linked Poly(vinyl methyl ether) in Water. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2223–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erman, B.; Mark, J.E. Structures and Properties of Rubberlike Networks, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-19-508237-0. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdov, A.D.; Christiansen, J.D. A simplified model for equilibrium and transient swelling of thermo-responsive gels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 75, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; Christiansen, J.D. Mechanical response and equilibrium swelling of temperature-responsive gels. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 94, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.; Swaddiwudhipong, S.; Yang, Z. Inhomogeneous large deformation study of temperature-sensitive hydrogel. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoujing, Z.; Zishun, L. Phase Transition of Temperature-Sensitive Hydrogel Under Mechanical Constraint. J. Appl. Mech. 2018, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. The fast homogeneous diffusion of hydrogel under different stimuli. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 137, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhou, S. Volume Phase Transition of Swollen Gels: Discontinuous or Continuous? Macromolecules 1997, 30, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koningsveld, R.; Stockmayer, W.H.; Kennedy, J.W.; Kleintjens, L.A. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Multicomponent Polymer Systems. XI. Dilute and Concentrated Polymer Solutions in Equilibrium. Macromolecules 1974, 7, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, P.; Gordon, M. Graph-Like State of Matter. 14. Statistical Thermodynamics of Semidilute Polymer Solution. Macromolecules 1980, 13, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmayer, W.H. Bridging Treatment of Polymer Solutions In Good Solvents. In Integration of Fundamental Polymer Science and Technology—4; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dušek, K.; Sedláček, B. Effect of diluents on the microsyneresis in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) gels induced by temperature changes. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1971, 36, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K.; Sedláček, B. Structural changes in swollen polymer gels induced by solvent exchange. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 1973, 38, 3434–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dušek, K. Inhomogeneities Induced by Crosslinking in the Course of Crosslinking Copolymerization. In Polymer Networks; Chompff, A.J., Newman, S., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 245–260. ISBN 978-1-4757-6212-9. [Google Scholar]
- Style, R.W.; Sai, T.; Fanelli, N.; Ijavi, M.; Smith-Mannschott, K.; Xu, Q.; Wilen, L.A.; Dufresne, E.R. Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in an Elastic Network. Phys. Rev. X 2018, 8, 011028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikkai, F.; Shibayama, M. Gel-size dependence of temperature-induced microphase separation in weakly-charged polymer gels. Polymer 2007, 48, 2387–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-W.; Dimitriyev, M.S.; Souslov, A.; Nikolov, S.V.; Marquez, S.M.; Alexeev, A.; Goldbart, P.M.; Fernández-Nieves, A. Extreme thermodynamics with polymer gel tori: Harnessing thermodynamic instabilities to induce large-scale deformations. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 020501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitriyev, M.S.; Chang, Y.-W.; Goldbart, P.M.; Fernández-Nieves, A. Swelling thermodynamics and phase transitions of polymer gels. Nano Futur. 2019, 3, 042001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mussel, M.; Horkay, F. Experimental Evidence for Universal Behavior of Ion-Induced Volume Phase Transition in Sodium Polyacrylate Gels. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 7831–7835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Sun, S.-T.; Hirokawa, Y.; Katayama, S.; Kucera, J.; Hirose, Y.; Amiya, T. Mechanical instability of gels at the phase transition. Nature 1987, 325, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, E.S.; Orkisz, M.; Sun, S.-T.; Li, Y.; Tanaka, T. Origin of Structural Inhomogeneities in Polymer Gels. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 6791–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- László, K.; Guillermo, A.; Fluerasu, A.; Moussaïd, A.; Geissler, E. Microphase Structure of Poly(N -isopropylacrylamide) Hydrogels As Seen by Small- and Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering and Pulsed Field Gradient NMR. Langmuir 2010, 26, 4415–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuki, A. Theory of phase transition in polymer gels. In Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions I.; Dušek, K., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 109, pp. 63–121. ISBN 978-3-540-56791-2. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, D.; Kuwayama, T.; Ohno, N. Effect of geometrical imperfections on swelling-induced buckling patterns in gel films with a square lattice of holes. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilavsky, M. Phase transition in swollen gels. 2. Effect of charge concentration on the collapse and mechanical behavior of polyacrylamide networks. Macromolecules 1982, 15, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilavský, M. Effect of phase transition on swelling and mechanical behavior of synthetic hydrogels. In Responsive Gels: Volume Transitions I; Dušek, K., Ed.; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; Volume 109, pp. 173–206. ISBN 978-3-540-56791-2. [Google Scholar]
- Spěváček, J. NMR investigations of phase transition in aqueous polymer solutions and gels. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dušek, K.; Dušková-Smrčková, M. Volume Phase Transition in Gels: Its Discovery and Development. Gels 2020, 6, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030022
Dušek K, Dušková-Smrčková M. Volume Phase Transition in Gels: Its Discovery and Development. Gels. 2020; 6(3):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030022
Chicago/Turabian StyleDušek, Karel, and Miroslava Dušková-Smrčková. 2020. "Volume Phase Transition in Gels: Its Discovery and Development" Gels 6, no. 3: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030022
APA StyleDušek, K., & Dušková-Smrčková, M. (2020). Volume Phase Transition in Gels: Its Discovery and Development. Gels, 6(3), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels6030022