Synthesis and Characterization of Silver–Strontium (Ag-Sr)-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles
Abstract
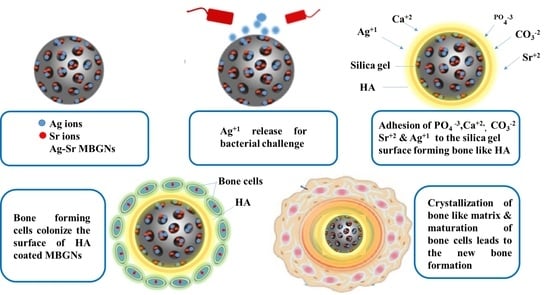
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological Characterization
2.2. Compositional Analysis
2.3. Zeta Potential
2.4. Ion-Release Profile
2.5. Antibacterial Study (Turbidity Test)
2.6. Disc Diffusion Test (Inhibition Halo Method)
2.7. In Vitro Bioactivity Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Ag-Sr-Containing MBGNs (Stöber Process)
4.3. Characterization of Ag-Sr-Doped MBGNs
4.3.1. Morphological Characterization
4.3.2. Compositional Analysis
4.3.3. Zeta Potential
4.3.4. Ion-Release Profile
4.3.5. Antibacterial Studies
4.3.6. Disc Diffusion Test
4.3.7. In Vitro Bioactivity Test
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aqib, R.; Kiani, S.; Bano, S.; Wadood, A.; Ur Rehman, M.A. Ag-Sr Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Loaded Chitosan/Gelatin Coating for Orthopedic Implants. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Peng, S.; Feng, P.; Shuai, C. Bone biomaterials and interactions with stem cells. Bone Res. 2017, 5, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J.A.; Interface, J.R.S.; Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castan, O. Biomaterials in orthopaedics Biomaterials in orthopaedics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trampuz, A.; Osmon, D.R.; Hanssen, A.D.; Steckelberg, J.M.; Patel, R. Molecular and antibiofilm approaches to prosthetic joint infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 414, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, M.A.; Bastan, F.E.; Nawaz, A.; Nawaz, Q.; Wadood, A. Electrophoretic deposition of PEEK/bioactive glass composite coatings on stain less steel for orthopedic applications: An optimization for in vitro bioactivity and adhesion strength. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 1849–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Bano, S.S.; Yasir, M.; Wadood, A.; Ur Rehman, M.A.; Rehman, M.A.U. Ag and Mn-doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles incorporated into the chitosan/gelatin coatings deposited on PEEK/bioactive glass layers for favorable osteogenic differentiation and antibacterial activity. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, B.; Kummer, K.M.; Tarquinio, K.M.; Webster, T.J. Decreased Staphylococcus aureus biofilm growth on anodized nanotubular titanium and the effect of electrical stimulation. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postler, A.; Lützner, C.; Beyer, F.; Tille, E.; Lützner, J. Analysis of Total Knee Arthroplasty revision causes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khatoon, Z.; Mctiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T. Bacterial bio fi lm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon 2018, 4, e01067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ur Rehman, M.A.; Ferraris, S.; Goldmann, W.H.; Perero, S.; Bastan, F.E.; Nawaz, Q.; Confiengo, G.G.; Di Ferraris, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial and Bioactive Coatings Based on Radio Frequency Co-Sputtering of Silver Nanocluster-Silica Coatings on PEEK/Bioactive Glass Layers Obtained by Electrophoretic Deposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32489–32497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, O.; Wahaj, M.; Akhtar, M.A.; Ur Rehman, M.A. Fabrication and Characterization of Ag–Sr-Substituted Hydroxyapatite/Chitosan Coatings Deposited via Electrophoretic Deposition: A Design of Experiment Study. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 22984–22992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.; Ribeiro, M.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P.; Ribeiro, M.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. studying bacterial-material interactions Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions. Biomatter 2012, 2, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hench, L.L. The story of Bioglass®. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppe, A.; Mouriño, V.; Boccaccini, A.R. Therapeutic inorganic ions in bioactive glasses to enhance bone formation and beyond. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 254–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leena, R.S.; Vairamani, M.; Selvamurugan, N. Alginate/Gelatin scaffolds incorporated with Silibinin-loaded Chitosan nanoparticles for bone formation in vitro. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017, 158, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, A.N.; Tilocca, A. Structure and biological activity of glasses and ceramics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Huang, X.; Yu, C.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qiao, S.; Lu, G.; Zhao, D. The in-vitro bioactivity of mesoporous bioactive glasses. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhauser, F.; Wilkesmann, S.; Nawaz, Q.; Hohenbild, F.; Rehder, F.; Saur, M.; Fellenberg, J.; Moghaddam, A.; Ali, M.S.; Peukert, W.; et al. Effect of manganese, zinc, and copper on the biological and osteogenic properties of mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. A 2020, e37136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Ur Rehman, M.A. Chitosan/gelatin-based bioactive and antibacterial coatings deposited via electrophoretic deposition. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccini, F.W.; Rehder, F.; Decker, S.; Kunisch, E.; Moghaddam, A.; Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Ionic dissolution products of Cerium-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles promote cellular osteogenic differentiation and extracellular matrix formation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 16, 035028. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Sui, B.; Ilyas, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Porous bioactive glass micro-and nanospheres with controlled morphology: Developments, properties and emerging biomedical applications. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 300–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhauser, F.; Wilkesmann, S.; Nawaz, Q.; Schmitz, S.I.; Moghaddam, A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Osteogenic properties of manganese-doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. A 2020, 108, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawaz, Q.; Fuentes-Chandía, M.; Tharmalingam, V.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Leal-Egaña, A.; Boccaccini, A.R. Silibinin releasing mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles with potential for breast cancer therapy. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 29111–29119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Q.; Atiq, M.; Rehman, U.; Burkovski, A.; Schmidt, J.; Beltrán, A.M.; Shahid, A.; Alber, N.K.; Peukert, W.; Boccaccini, A.R.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of manganese containing mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, D. Extension of the stöber method to construct mesoporous SiO2 and TiO2 shells for uniform multifunctional core-shell structures. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greasley, S.L.; Page, S.J.; Sirovica, S.; Chen, S.; Martin, R.A.; Riveiro, A.; Hanna, J.V.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Controlling particle size in the Stöber process and incorporation of calcium. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Fan, W.; Chang, J. Functional mesoporous bioactive glass nanospheres: Synthesis, high loading efficiency, controllable delivery of doxorubicin and inhibitory effect on bone cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2710–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciotti, I.; Lombardi, M.; Bianco, A.; Ravaglioli, A.; Montanaro, L. Sol-gel derived 45S5 bioglass: Synthesis, microstructural evolution and thermal behaviour. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 1849–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, A.; Meszaros, R.; Stähli, C.; Romeis, S.; Schmidt, J.; Peukert, W.; Marelli, B.; Nazhat, S.N.; Wondraczek, L.; Lao, J.; et al. In vitro reactivity of Cu doped 45S5 Bioglass® derived scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Dai, X.; Lu, M.; Hüser, N.; Taccardi, N.; Boccaccini, A.R. Synthesis of copper-containing bioactive glass nanoparticles using a modified Stöber method for biomedical applications. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozon, D.; Zheng, K.; Boccardi, E.; Liu, Y.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R. Synthesis of monodispersed Ag-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles via surface modification. Materials 2016, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, K.; Fan, Y.; Torre, E.; Balasubramanian, P.; Taccardi, N.; Cassinelli, C.; Morra, M.; Iviglia, G.; Boccaccini, A.R. Incorporation of Boron in Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Reduces Inflammatory Response and Delays Osteogenic Differentiation. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020, 37, 2000054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, Q.; Fastner, S.; Rehman, M.A.U.; Ferraris, S.; Perero, S.; di Confiengo, G.G.; Yavuz, E.; Ferraris, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Multifunctional stratified composite coatings by electrophoretic deposition and RF co-sputtering for orthopaedic implants. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7920–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, N.D.; Balu, R.; Sampath Kumar, T.S. Strontium-substituted calcium deficient hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 2700–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.Y.; Noh, I.S.; Zhang, S.M. Silicate-doped hydroxyapatite and its promotive effect on bone mineralization. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković, V.; Iyer, M.A.; Wu, V.M. One ion to rule them all: The combined antibacterial, osteoinductive and anticancer properties of selenite-incorporated hydroxyapatite. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1430–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem Bastan, F.; Ur Rehman, M.A.; Ustel, F. Thermo-physical insights into a series of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchi, A.; Tamjid, E.; Pishbin, F.; Boccaccini, A.R. Recent progress in inorganic and composite coatings with bactericidal capability for orthopaedic applications. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rashidy, A.A.; Waly, G.; Gad, A.; Hashem, A.A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Kaya, S.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Sami, I. Preparation and in vitro characterization of silver-doped bioactive glass nanoparticles fabricated using a sol-gel process and modified Stöber method. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2018, 483, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, A.; Balossier, G.; Kannan, S.; Rajeswari, S. Elaboration of sol-gel derived apatite films on surgical grade stainless steel for biomedical applications. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 2288–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.; Ur Rehman, M.A.; Rehman, M.A.U. Improvement in the surface properties of stainless steel via zein/hydroxyapatite composite coatings for biomedical applications. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, J.; Wong, M.E.K. The integrated processes of hard tissue regeneration with special emphasis on fracture healing. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 1996, 82, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R. Molecular mechanisms of bone resorption An update. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1995, 66, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Neff, L.; Louvard, D.; Courtoy, P.J. Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: Evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localization of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 2210–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellucci, D.; Sola, A.; Cacciotti, I.; Bartoli, C.; Gazzarri, M.; Bianco, A.; Chiellini, F.; Cannillo, V. Mg- and/or Sr-doped tricalcium phosphate/bioactive glass composites: Synthesis, microstructure and biological responsiveness. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk, R.S.; Atiq, M.; Rehman, U.; Munawar, M.A.; Schubert, D.W.; Goldmann, W.H.; Dusza, J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Curcumin-Containing Orthopedic Implant Coatings Deposited on Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone/Bioactive Glass/Hexagonal Boron Nitride Layers by Electrophoretic Deposition. Coatings 2019, 9, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabia, Z.; Akhtach, S.; Mabrouk, K.E.; Bricha, M.; Nouneh, K.; Ballamurugan, A. Tantalum doped SiO2-CaO-P2O5based bioactive glasses: Investigation of in vitro bioactivity and antibacterial activities. Biomed. Glas. 2020, 6, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Particles | Zeta Potential ± SD (Standard Deviation) (mV) |
|---|---|
| MBGNs | |
| Ag MBGNs | |
| Sr MBGNs | |
| Ag-Sr MBGNs |
| Time (h) | MBGNs | Ag-Sr MBGNs | Ag MBGNs | Sr MBGNs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 0.020 ± 0.003 | 0.025 ± 0.004 | 0.010 ± 0.005 |
| 2 | 0.010 ± 0.003 | 0.030 ± 0.005 | 0.025 ± 0.008 | 0.020 ± 0.007 |
| 3 | 0.040 ± 0.005 | 0.040 ± 0.005 | 0.030 ± 0.007 | 0.055 ± 0.009 |
| 4 | 0.050 ± 0.007 | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 0.008 ± 0.003 | 0.065 ± 0.012 |
| 6 | 0.070 ± 0.008 | 0.005 ± 0.001 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | 0.090 ± 0.032 |
| 24 | 0.190 ± 0.010 | 0 ± 0 | 0 ± 0 | 0.205 ± 0.12 |
| Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles Type | Composition (mol.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | SrO | AgO | |
| MBGNs | 70 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| 5Sr-MBGNs | 70 | 25 | 5 | 0 |
| 1Ag-MBGNs | 70 | 29 | 0 | 1 |
| 5Sr-1Ag MBGNs | 70 | 24 | 5 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bano, S.; Akhtar, M.; Yasir, M.; Salman Maqbool, M.; Niaz, A.; Wadood, A.; Ur Rehman, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver–Strontium (Ag-Sr)-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Gels 2021, 7, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020034
Bano S, Akhtar M, Yasir M, Salman Maqbool M, Niaz A, Wadood A, Ur Rehman MA. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver–Strontium (Ag-Sr)-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Gels. 2021; 7(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleBano, Shaher, Memoona Akhtar, Muhammad Yasir, Muhammad Salman Maqbool, Akbar Niaz, Abdul Wadood, and Muhammad Atiq Ur Rehman. 2021. "Synthesis and Characterization of Silver–Strontium (Ag-Sr)-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles" Gels 7, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020034
APA StyleBano, S., Akhtar, M., Yasir, M., Salman Maqbool, M., Niaz, A., Wadood, A., & Ur Rehman, M. A. (2021). Synthesis and Characterization of Silver–Strontium (Ag-Sr)-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles. Gels, 7(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7020034