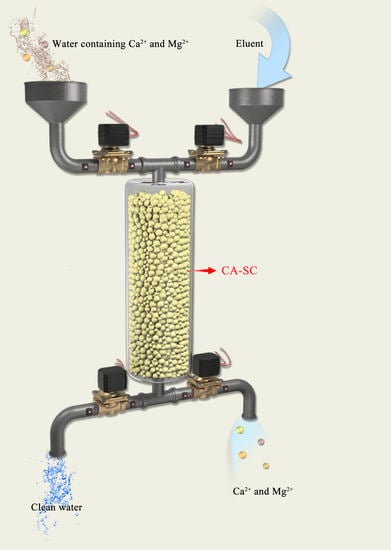
Effective Removal of Calcium and Magnesium Ions from Water by a Novel Alginate–Citrate Composite Aerogel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterizations
2.2. Effect of the Concentrations of Sodium Alginate and Ethylenediamine
2.3. Effect of Solution pH
2.4. Influence of Contact Time
2.5. Influence of Ambient Temperature
2.6. Adsorption Ability of CA–SC
2.7. Maximum Adsorption Capacity
2.8. Adsorption Mechanism
2.9. Regeneration and Recycling Performance
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Instruments
4.2. Preparation of CA–SC
4.3. Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Navalon, S.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H. Ca2+ and Mg2+ present in hard waters enhance trihalomethane formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.F.; Esteves, V.I.; Santos, E.B.H. Solar photodegradation of oxytetracycline in brackish aquaculture water: New insights about effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 372, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiss, F.L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Synthesis of layered double hydroxides containing Mg2+, Zn2+, Ca2+ and Al3+ layer cations by co-precipitation methods—A review. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 383, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.C.; Linga, P.; Park, K.-N.; Choi, S.-J.; Lee, J.D. Seawater desalination by gas hydrate process and removal characteristics of dissolved ions (Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, B3+, Cl−, SO42−). Desalination 2014, 353, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Adlii, A.; Eid, M.H.; Abukhadra, M.R. Effective decontamination of Ca2+ and Mg2+ hardness from groundwater using innovative muscovite based sodalite in batch and fixed-bed column studies; dynamic and equilibrium studies. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 241, 103817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, R.; Xi, Q.; Li, T.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, C.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Adsorption equilibrium, kinetics, and dynamic separation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions from phosphoric acid–nitric acid aqueous solution by strong acid cation resin. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 2930–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Nieto, C.H.; Palacios, N.A.; Verbeeck, K.; Prévoteau, A.; Rabaey, K.; Flexer, V. Membrane electrolysis for the removal of Mg2+ and Ca2+ from lithium rich brines. Water Res. 2019, 154, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Colombi Ciacchi, L.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in Nanoporous Membranes for Water Purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Halah, A.; Machado, D.; González, N.; Contreras, J.; López-Carrasquero, F. Use of super absorbent hydrogels derivative from acrylamide with itaconic acid and itaconates to remove metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 46999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Ishag, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Mei, P.; Meng, Q.; Sun, Y. Recent investigations and progress in environmental remediation by using covalent organic framework-based adsorption method: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Alharbi, W.; BinSharfan, I.I.; Khan, R.A.; Alsalme, A. Aminophosphonic Acid Functionalized Cellulose Nanofibers for Efficient Extraction of Trace Metal Ions. Polymers 2020, 12, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahas, S.; Osman, A.I.; Arafat, A.S.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.A.H.; Salman, H.M. Facile and affordable synthetic route of nano powder zeolite and its application in fast softening of water hardness. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Bai, X.; Kang, Y.; Hao, W.; Li, R. Effective removal of Mg2+ and Ca2+ ions by mesoporous LTA zeolite. Desalination 2014, 341, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Yakout, A.A.; Abdel-Aal, H.; Osman, M.M. Immobilization of Fusarium verticillioides fungus on nano-silica (NSi–Fus): A novel and efficient biosorbent for water treatment and solid phase extraction of Mg(II) and Ca(II). Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazari, S.A.; Ali, E.; Abro, R.; Khan, F.S.A.; Ahmed, I.; Ahmed, M.; Nizamuddin, S.; Siddiqui, T.H.; Hossain, N.; Mubarak, N.M.; et al. Nanomaterials: Applications, waste-handling, environmental toxicities, and future challenges—A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Z. Highly efficient removal of copper ions from water by using a novel alginate-polyethyleneimine hybrid aerogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, G.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Wu, A. Highly efficient removal of toxic Pb2+ from wastewater by an alginate-chitosan hybrid adsorbent. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Layered composite based on halloysite and natural polymers: A carrier for the pH controlled release of drugs. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10887–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, A.M.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Structural and Technological Approach to Reveal the Role of the Lipid Phase in the Formation of Soy Emulsion Gels with Chia Oil. Gels 2021, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalheim, M.Ø.; Omtvedt, L.A.; Bjørge, I.M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Mano, J.F.; Aachmann, F.L.; Strand, B.L. Mechanical Properties of Ca-Saturated Hydrogels with Functionalized Alginate. Gels 2019, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clapacs, Z.; Neal, S.; Schuftan, D.; Tan, X.; Jiang, H.; Guo, J.; Rudra, J.; Huebsch, N. Biocompatible and Enzymatically Degradable Gels for 3D Cellular Encapsulation under Extreme Compressive Strain. Gels 2021, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, V.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Polysaccharides/Halloysite nanotubes for smart bionanocomposite materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, A. Preparation of modified sodium alginate aerogel and its application in removing lead and cadmium ions in wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deze, E.G.; Papageorgiou, S.K.; Favvas, E.P.; Katsaros, F.K. Porous alginate aerogel beads for effective and rapid heavy metal sorption from aqueous solutions: Effect of porosity in Cu2+ and Cd2+ ion sorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikula, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Ligas, B.; Witek-Krowiak, A. Preparation of hydrogel composites using Ca2+ and Cu2+ ions as crosslinking agents. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadir, N.N.A.; Shahadat, M.; Ismail, S. Formulation study for softening of hard water using surfactant modified bentonite adsorbent coating. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 137, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehr, M.N.; Zarrabi, M.; Kazemian, H.; Amrane, A.; Yaghmaian, K.; Ghaffari, H.R. Removal of hardness agents, calcium and magnesium, by natural and alkaline modified pumice stones in single and binary systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahmirzadi, M.A.A.; Hosseini, S.S.; Tan, N.R. Enhancing removal and recovery of magnesium from aqueous solutions by using modified zeolite and bentonite and process optimization. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 3529–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnitz, O.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Gil, L.F. Removal of Ca(II) and Mg(II) from aqueous single metal solutions by mercerized cellulose and mercerized sugarcane bagasse grafted with EDTA dianhydride (EDTAD). Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Güzel, F.; Yakut, H.; Topal, G. Determination of kinetic and equilibrium parameters of the batch adsorption of Mn(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution by black carrot (Daucus carota L.) residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mendieta, A.; Olguín, M.T.; Solache-Ríos, M. Biosorption properties of green tomato husk (Physalis philadelphica Lam) for iron, manganese and iron–manganese from aqueous systems. Desalination 2012, 284, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.M.; Ahmed, S.A.; Fadl, A.A. Removal of calcium ions from aqueous solutions by sugar cane bagasse modified with carboxylic acids using microwave-assisted solvent-free synthesis. Desalination 2011, 278, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, S.R.; Rubio, J. Removal of Mn2+ from aqueous solution by manganese oxide coated zeolite. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhade, A.V.; Kankrej, S.R. An Efficient Cost-Effective Removal of Ca2+, Mg2+, and Cu2+ Ions from Aqueous Medium Using Chlorosodalite Synthesized from Coal Fly Ash. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2017, 62, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Chen, S.; Wei, H.; Fan, J.; Xu, Q.; Min, Y. Micropores of pure nanographite spheres for long cycle life and high-rate lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23062–23070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greczynski, G.; Hultman, L. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Towards reliable binding energy referencing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 107, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Models | Formulas | Parameters | Ca2+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pseudo-first-order | qt = qe (1 − exp(−k1t)) | qe (mg/g) | 28.395 | 17.266 |
| standard error for qe | 0.395 | 0.268 | ||
| k1 (L/min) | 0.021 | 0.020 | ||
| standard error for k1 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| R2 | 0.984 | 0.982 | ||
| pseudo-second-order | qt = qe (1 – 1/(1+qek2t)) | qe (mg/g) | 31.873 | 19.467 |
| standard error for qe | 0.405 | 0.312 | ||
| k2 (L/min) | 8.114 × 10−4 | 0.001 | ||
| standard error for k2 | 5.804 × 10−5 | 1.128× 10−4 | ||
| R2 | 0.994 | 0.991 |
| CA–SC | Initial Concentration (mM) | Removal Efficiency (%) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| In deionized water | 1.5 (Ca2+) | 96.5 | 29.0 |
| 1.5 (Mg2+) | 96.8 | 17.6 | |
| 1.5 (Cu2+) | 96.6 | 46.0 | |
| 1.5 (Zn2+) | 94.2 | 46.2 | |
| 1.5 (Co2+) | 96.8 | 42.8 | |
| 1.5 (Cr3+) | 96.8 | 37.8 | |
| 1.5 (Pb2+) | 95.2 | 147.9 | |
| 1.5 (Ca2+, Mg2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Cr3+, Pb2+) | 87.2 (Ca2+), 86.5 (Mg2+), 94.6 (Cu2+), 73.0 (Zn2+), 68.7 (Co2+), 87.3 (Cr3+), 88.9 (Pb2+) | 26.2 (Ca2+), 15.8 (Mg2+), 45.1 (Cu2+), 35.8 (Zn2+), 30.3 (Co2+), 34.0 (Cr3+), 138.2 (Pb2+) | |
| In tap water | 1.5 (Ca2+) | 92.9 | 27.9 |
| 1.5 (Mg2+) | 90.9 | 16.6 | |
| In lake water | 1.5 (Ca2+) | 91.2 | 27.4 |
| 1.5 (Mg2+) | 90.1 | 16.4 | |
| In river water | 1.5 (Ca2+) | 89.8 | 26.9 |
| 1.5 (Mg2+) | 88.8 | 16.2 |
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Maximum Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous LTA zeolite | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 61.27 (Ca2+), 9.24 (Mg2+) | [13] |
| Modified bentonite | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 14.63 (Ca2+), 14.63 (Mg2+) | [27] |
| Alkaline modified pumice stones | Ca2+ | 57.2–62.3 | [28] |
| Modified zeolite | Mg2+ | 26.2 | [29] |
| Chemically modified cellulose | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 15.6 (Ca2+), 13.5 (Mg2+) | [30] |
| Sugar cane bagasse | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 46.1 (Ca2+), 23.5 (Mg2+) | [30] |
| Rice husk | Mg2+ | 3.87 | [31] |
| Green tomato husk | Mg2+ | 6.76 | [32] |
| Sugar cane bagasse modified with citric acid | Ca2+ | 26.52 | [33] |
| Sugar cane bagasse modified with tartaric | Ca2+ | 14.72 | [33] |
| Activated Chilean zeolite | Mg2+ | 0.774 | [34] |
| Black carrot residues | Mg2+ | 3.871 | [31] |
| Aluminosilicate chlorosodalite | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 49.26 (Ca2+), 32.25 (Mg2+) | [35] |
| CA–SC | Ca2+, Mg2+ | 62.38 (Ca2+), 36.23 (Mg2+) | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, M. Effective Removal of Calcium and Magnesium Ions from Water by a Novel Alginate–Citrate Composite Aerogel. Gels 2021, 7, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030125
Wang Z, Feng Z, Yang L, Wang M. Effective Removal of Calcium and Magnesium Ions from Water by a Novel Alginate–Citrate Composite Aerogel. Gels. 2021; 7(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhuqing, Zhongmin Feng, Leilei Yang, and Min Wang. 2021. "Effective Removal of Calcium and Magnesium Ions from Water by a Novel Alginate–Citrate Composite Aerogel" Gels 7, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030125
APA StyleWang, Z., Feng, Z., Yang, L., & Wang, M. (2021). Effective Removal of Calcium and Magnesium Ions from Water by a Novel Alginate–Citrate Composite Aerogel. Gels, 7(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030125