Shellac Gum/Carrageenan Alginate-Based Core–Shell Systems Containing Peppermint Essential Oil Formulated by Mixture Design Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preliminary Studies
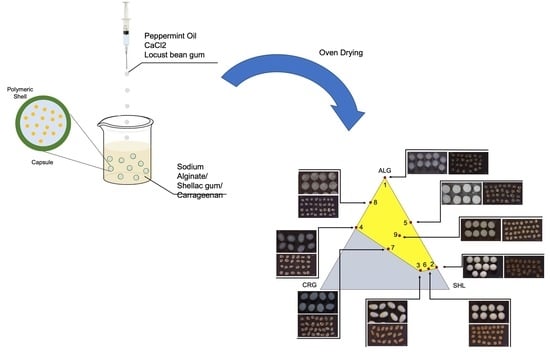
2.2. Mixture Design: Constraints and Feasible Region Definition
2.3. Correlations
2.4. Morphology and Dimensions
2.5. Essential Oil Content
2.6. Swelling
2.7. In Vitro Essential Oil Release Profile
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Methods
4.2.1. Preliminary Studies
4.2.2. Capsules Preparation
4.2.3. Mixture Design
Constraints and Feasible Region Definition
Statistical Analysis
4.2.4. Characterization of Core–Shell Systems
Morphology and Dimensions
Essential Oil Content
Swelling Studies
In Vitro Essential Oil Release Test
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loscertales, G.; Barrero, A.; Guerrero, I.; Cortijo, R.; Marquez, M.; Gañán-Calvo, A.M. Micro/nano encapsulation via electrified coaxial liquid jets. Science 2002, 295, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Dou, C.; Chang, S.; Xie, Z.; Yu, D.G.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J. Core–shell Eudragit S100 nanofibers prepared via triaxial electrospinning to provide a colon-targeted extended drug release. Polymers 2020, 12, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, I.H.; Chun, H.J.; Park, K.; Han, D.K. Fabrication of core-shell microcapsules using PLGA and alginate for dual growth factor delivery system. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.; Renard, D.; Adiwijaya, Z.; Karaoglan, E.; Poncelet, D. Oil encapsulation in core–shell alginate capsules by inverse gelation. I: Dripping methodology. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, R.A.; Laftah, W.A.; Hashim, S. Core–shell polymers: A review. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15543–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abang, S.; Chan, E.S.; Poncelet, D. Effects of process variables on the encapsulation of oil in Ca-alginate capsules using an inverse gelation technique. J. Microencapsul. 2012, 29, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M. Handbook of Encapsulation and Controlled Release; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lopedota, A.A.; Arduino, I.; Lopalco, A.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Cutrignelli, A.; Laquintana, V.; Racaniello, G.F.; Franco, M.; La Forgia, F.; Fontana, S.; et al. From oil to microparticulate by prilling technique: Production of polynucleate alginate beads loading Serenoa Repens oil as intestinal delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.; Poncelet, D.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Renard, D. Oil encapsulation in core–shell alginate capsules by inverse gelation II: Comparison between dripping techniques using W/O or O/W emulsions. J. Microencapsul. 2017, 34, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.H.; Chiang, P.Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Kokawa, M.; Islam, M.Z. Producing liquid-core hydrogel beads by reverse spherification: Effect of secondary gelation on physical properties and release characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglio Bonda, A.; Regis, L.; Giovannelli, L.; Segale, L. Alginate/maltodextrin and alginate/shellac gum core-shell capsules for the encapsulation of peppermint essential oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.H.; Spuches, F.C.; Hero, J.S.; Alanis, A.F.; Martinez, M.A.; Romero, C.M. Impact of prosopis nigra gum exudate in alginate core-shell synthesis by inverse gelation technique. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.Y.; Lam, W.H.; Ho, K.W.; Voo, W.P.; Lee, M.F.X.; Lim, H.P.; Lim, S.L.; Tey, B.T.; Poncelet, D.; Chan, E.S. Advances in fabricating spherical alginate hydrogels with controlled particle designs by ionotropic gelation as encapsulation systems. Particuology 2016, 24, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Pongjanyakul, T.; Priprem, A. Molecular interaction in alginate beads reinforced with sodium starch glycolate or magnesium aluminum silicate, and their physical characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 293, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.; Sankar, S. Trivalent ion cross-linked pH sensitive alginate-methyl cellulose blend hydrogel beads from aqueous template. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 57, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, K.; Penning, M.; Wächterbach, E.; Maskos, M.; Langguth, P. Investigation of various shellac grades: Additional analysis for identity. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Y.; Leopold, C.S. Development of shellac-coated sustained release pellet formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 42, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorram, F.; Ramezanian, A.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Shellac, gelatin and Persian gum as alternative coating for orange fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wen, H.F.; Yu, D.G.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, D.F. Electrosprayed hydrophilic nanocomposites coated with shellac for colon-specific delayed drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2018, 143, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, T.; Matricardi, P.; Marianecci, C.; Alhaique, F. Polysaccharide hydrogels for modified release formulations. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; Silva, D.B., Jr.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, A.C.M.; Cunha-Filho, M.S.S.; Gelfuso, G.M.; Gratieri, T. Evolution of quality on pharmaceutical design: Regulatory requirement? Accredit. Qual. Assur. 2017, 22, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foglio Bonda, A.; Rinaldi, M.; Segale, L.; Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Vecchio, C.; Pattarino, F. Nanonized itraconazole powders for extemporary oral suspensions: Role of formulation components studied by a mixture design. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 83, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kpodo, F.M.; Afoakwa, E.O.; Amoa, B.B.; Saalia, F.K.S.; Budu, A.S. Application of multiple component constraint mixture design for studying the effect of ingredient variations on the chemical composition and physico-chemical properties of soy-peanut-cow milk. Int. Food Res. J. 2013, 20, 811–818. [Google Scholar]
- Buruk Sahin, Y.; Aktar Demirtaş, E.; Burnak, N. Mixture design: A review of recent applications in the food industry. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 22, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, S.N.; Colombo, P.; Colombo, G.; Rekkas, D.M. Design of experiments (DoE) in pharmaceutical development. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, P.; Zacco, R.; Rekkas, D.M.; Politis, S.; Garofalo, E.; Del Gaudio, P.; Aquino, R. Application of experimental design for the development of soft-capsules through a prilling, inverse gelation process. J. Drug Del. Sci. Technol. 2018, 49, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, F.; Ma, J. Ionically cross-linked sodium alginate/ĸ-carrageenan double-network gel beads with low-swelling, enhanced mechanical properties, and excellent adsorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeesh, P.M.; Reshma, J.; Nibisha, P.; Franklin, J.; Jinu, G. Alginate/k-carrageenan and alginate/gelatin composite hydrogel beads for controlled drug release of curcumin. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2019, 10, 508–514. [Google Scholar]
- Messaoud, G.B.; Sánchez-González, L.; Probst, L.; Jeandel, C.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Desobry, S. Physico-chemical properties of alginate/shellac aqueous-core capsules: Influence of membrane architecture on riboflavin release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobet, M.; Mouaddab, M.; Cayot, N.; Bonny, J.M.; Guichard, E.; Le Quéré, J.L.; Moreau, C.; Foucat, L. The effect of salt content on the structure of iota-carrageenan systems: 23Na DQF NMR and rheological studies. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, P.; Segale, L.; Giovannelli, L.; Foglio Bonda, A.; Pattarino, F. Self-emulsifying excipient platform for improving technological properties of alginate-hydroxypropylcellulose pellets. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 499, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadnia, Z.; Zohuriaan-Mehr, M.J.; Kabiri, K.; Jamshidi, A.; Mobedi, H. Ionically cross-linked carrageenan-alginate hydrogel beads. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2008, 19, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Ni, B.; Xie, L. k-carrageenan sodium alginate beads and superabsorbent coated nitrogen fertilizer with slow-release, water-retention, and anticompaction properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remunan-Lopez, C.; Bodmeier, R. Mechanical, water uptake and permeability properties of crosslinking chitosan glutamate and alginate films. J. Control. Release 1997, 44, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Experimental Point | Mixture Composition (w/w%) | Gelling Bath Solid Content (w/v%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate | Carrageenan | Shellac Gum | ||
| P1 | 100.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| P2 | 20.00 | 0.00 | 80.00 | 5.00 |
| P3 | 17.24 | 13.79 | 68.97 | 5.80 |
| P4 | 55.56 | 44.44 | 0.00 | 1.80 |
| P5 | 60.00 | 0.00 | 40.00 | 1.67 |
| P6 | 18.62 | 6.90 | 74.48 | 5.37 |
| P7 | 36.40 | 29.12 | 34.48 | 2.75 |
| P8 | 77.78 | 22.22 | 0.00 | 1.29 |
| P9 | 48.20 | 14.56 | 37.24 | 2.07 |
| Exp. Point | Wet Capsules | Dried Capsules | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF ± SD | Diameter (mm ± SD) | Oil Content/Unit (mg ± SD) | Weight/Unit (mg ± SD) | SF ± SD | Diameter (mm ± SD) | Oil Content/Unit (mg ± SD) | Weight/Unit (mg ± SD) | |
| P1 | 0.777 ± 0.066 | 3.91 ± 0.30 | 0.712 ± 0.04 | 35.78 ± 3.21 | 0.803 ± 0.065 | 1.76 ± 0.23 | 0.765 ± 0.01 | 2.61 ± 0.21 |
| P2 | 0.866 ± 0.025 | 3.84 ± 0.21 | 0.700 ± 0.04 | 31.92 ± 2.39 | 0.822 ± 0.019 | 1.81 ± 0.18 | 0.689 ± 0.04 | 3.81 ± 0.08 |
| P3 | 0.808 ± 0.052 | 4.26 ± 0.68 | 0.686 ± 0.14 | 41.31 ± 2.82 | 0.794 ± 0.033 | 2.17 ± 0.44 | 0.686 ± 0.09 | 4.62 ± 0.32 |
| P4 | 0.742 ± 0.054 | 4.33 ± 0.24 | 0.800 ± 0.02 | 47.56 ± 3.86 | 0.739 ± 0.095 | 1.89 ± 0.45 | 0.861 ± 0.08 | 3.29 ± 0.25 |
| P5 | 0.820 ± 0.020 | 3.99 ± 0.20 | 0.810 ± 0.03 | 39.76 ± 6.52 | 0.793 ± 0.043 | 1.73 ± 0.17 | 0.892 ± 0.08 | 2.64 ± 0.74 |
| P6 | 0.878 ± 0.006 | 4.17 ± 0.24 | 0.738 ± 0.05 | 38.58 ± 1.48 | 0.830 ± 0.025 | 1.91 ± 0.16 | 0.780 ± 0.20 | 4.58 ± 0.15 |
| P7 | 0.791 ± 0.040 | 4.45 ± 0.61 | 0.829 ± 0.04 | 39.01 ± 2.25 | 0.777 ± 0.061 | 2.03 ± 0.35 | 0.858 ± 0.03 | 3.78 ± 0.44 |
| P8 | 0.750 ± 0.050 | 4.00 ± 0.35 | 0.673 ± 0.02 | 38.17 ± 1.42 | 0.777 ± 0.063 | 1.85 ± 0.24 | 0.732 ± 0.05 | 2.54 ± 0.09 |
| P9 | 0.832 ± 0.045 | 4.18 ± 0.29 | 0.751 ± 0.03 | 33.32 ± 0.31 | 0.789 ± 0.062 | 1.86 ± 0.23 | 0.826 ± 0.04 | 3.41 ± 0.07 |
| Variable | Model | p-Value | Adjusted R² | Predicted R² |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF WET | Linear | 0.001 | 0.82 | 0.76 |
| SF DRY | Linear | 0.002 | 0.78 | 0.65 |
| Diameter DRY | Special Cubic | 0.031 | 0.88 | 0.42 |
| Weight unit DRY | Quadratic | 0.008 | 0.90 | 0.68 |
| Swelling | Quadratic | 0.002 | 0.94 | 0.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foglio Bonda, A.; Candiani, A.; Pertile, M.; Giovannelli, L.; Segale, L. Shellac Gum/Carrageenan Alginate-Based Core–Shell Systems Containing Peppermint Essential Oil Formulated by Mixture Design Approach. Gels 2021, 7, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040162
Foglio Bonda A, Candiani A, Pertile M, Giovannelli L, Segale L. Shellac Gum/Carrageenan Alginate-Based Core–Shell Systems Containing Peppermint Essential Oil Formulated by Mixture Design Approach. Gels. 2021; 7(4):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040162
Chicago/Turabian StyleFoglio Bonda, Andrea, Alessandro Candiani, Martina Pertile, Lorella Giovannelli, and Lorena Segale. 2021. "Shellac Gum/Carrageenan Alginate-Based Core–Shell Systems Containing Peppermint Essential Oil Formulated by Mixture Design Approach" Gels 7, no. 4: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040162
APA StyleFoglio Bonda, A., Candiani, A., Pertile, M., Giovannelli, L., & Segale, L. (2021). Shellac Gum/Carrageenan Alginate-Based Core–Shell Systems Containing Peppermint Essential Oil Formulated by Mixture Design Approach. Gels, 7(4), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040162