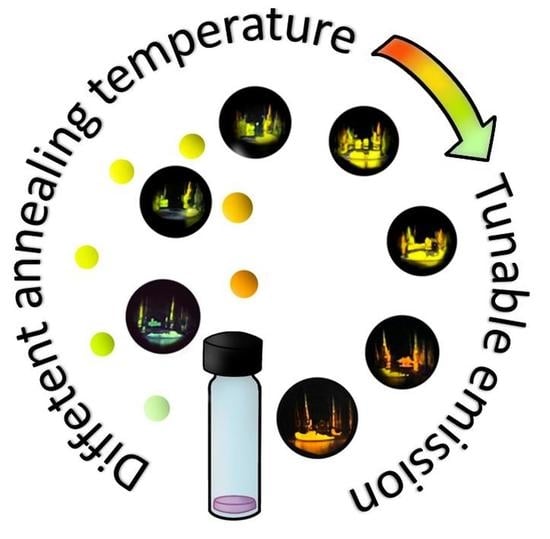
Concentration-Dependent Emission of Annealed Sol-Gel Layers Incorporated with Rhodamine 19 and 6G as the Route to Tunable High-Temperature Luminescent Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
- (1)
- Effects in the immediate environment of the organic dye (shift of the emission maximum with a change in concentration or change in pH, organic dye decomposition during the heating process);
- (2)
- Preservation of the dye in the silica parent matrix.
2.1. Effect in the Immediate Environment of the Organic Dye (Spectroscopic Study)
2.2. Preservation of the Dye in the Silica Matrix (Spectroscopic and Thermal Study)
2.3. Chemical/Physical Etching Tests
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacCraith, B.D. Light-emitting-diode-based oxygen sensing using evanescent wave excitation of a dye-doped sol-gel coating. Opt. Eng. 1994, 33, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCraith, B.D.; McDonagh, C.M.; O’Keeffe, G.; McEvoy, A.K.; Butler, T.; Sheridan, F.R. Sol-gel coatings for optical chemical sensors and biosensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 29, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruszewski, K.; Andrzejewski, D.; Strek, W. Thermal sensor based on luminescence of Ru(bpy)32+ entrapped in sol-gel glasses. J. Lumin. 1997, 72–74, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetter, N.U.; Ramos de Miranda, A.; Pecoraro, É.; Lima Ribeiro, S.J.; Jimenez-Villar, E. Dynamic random lasing in silica aerogel doped with rhodamine 6G. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29678–29685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, J.N.; Menzies, D.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Simon, G.P.; Spiccia, L. TiO2 sol–gel blocking layers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2006, 9, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suherman, S.; Hakim, M.S.; Kuncaka, A. Optical Chemical Sensor Based on 2,2-Furildioxime in Sol-Gel Matrix for Determination of Ni2+ in Water. Processes 2021, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, A.; Badocco, D.; Bogialli, S.; Cappellin, L.; Pastore, P. Behavior of Sulfonephthalein and Azo dyes as effective pH sensors in hybrid materials. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Jana, P.; Ghosh, K. A naphthalimide-linked new pyridylazo phenol derivative for selective sensing of cyanide ions (CN-) in sol-gel medium. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, N.K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, Y. Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 2003, 421, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Rao, V. Luminiscent dye Rhodamine 6G doped monolithic and transparent TEOS silica xerogels and spectral properties. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2003, 4, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, A.V.; Kumar, U. Correlation between photophysical properties and lasing performances of Rhodamine-19 in three types of sol–gel glass hosts. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.V.; Kumar, U. Effect of method of preparation on photophysical properties of Rh-B impregnated sol-gel hosts. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2002, 306, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F.; Levy, D. Rhodamine 19 Fluorescent Dimers Resulting from Dye Aggregation on the Porous Surface of Sol−Gel Silica Glasses. Langmuir 2003, 19, 2782–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte, F.; Mackenzie, J.D.; Levy, D. Rhodamine fluorescent dimers adsorbed on the porous surface of silica gels. Langmuir 2000, 16, 7377–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbonaro, C.M.; Ricci, P.C.; Grandi, S.; Marceddu, M.; Corpino, R.; Salis, M.; Anedda, A. On the formation of aggregates in silica–rhodamine 6G type II hybrids. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, I.Y.Y.; Cole, M.T. One-pot synthesis of intercalating ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Lett. 2013, 90, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; He, J.; Deng, L.; Cao, H. Synthesis and characterization of functionalized rhodamine B-doped silica nanoparticles. Opt. Mater. 2009, 31, 1715–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, J.; Castro, G.R.; Martines, M.A.U. Comparision among different pH values of Rhodamine B Solution Impregnated into Mesoporous Silica. Orbital Electron. J. Chem. Electron. J. Chem. 2013, 5, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Rasalingam, S.; Peng, R.; Koodali, R.T. An investigation into the effect of porosities on the adsorption of rhodamine B using titania–silica mixed oxide xerogels. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.L.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Bhatia, S. Effect of annealing temperature on the characteristics, sonocatalytic activity and reusability of nanotubes TiO2 in the degradation of Rhodamine B. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 100, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synak, A.; Bojarski, P.; Grobelna, B.; Kułak, L.; Lewkowicz, A. Determination of Local Dye Concentration in Hybrid Porous Silica Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11385–11392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikiori, H.; Setiawan, R.A.; Kawamoto, S.; Takagi, S.; Teshima, K.; Fujii, T. Dimerization of xanthene dyes in sol–gel titania films. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshpande, A.V.; Kumar, U. Efficient lasing action from Rhodamine-110 (Rh-110) impregnated sol–gel silica samples prepared by dip method. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangełowa-Jankowska, S.; Jankowski, D.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Grobelna, B.; Bojarski, P. Surface Plasmon-Coupled Emission of Rhodamine 110 Aggregates in a Silica Nanolayer. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3626–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Monte, F.; Ferrer, M.L.; Levy, D. Preferred Formation of Coplanar Inclined Fluorescent J-Dimers in Rhodamine 101 Doped Silica Gels. Langmuir 2001, 17, 4812–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, B.J.; Chronister, E.L. Temperature-dependent optical dephasing in sol-gel glasses: Photon echo measurements of rhodamine 101 and quinizarin doped aluminosilica xerogels. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 9880–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungerford, G.; Suhling, K.; Ferreira, J.A. Comparison of the fluorescence behaviour of rhodamine 6G in bulk and thin film tetraethylorthosilicate derived sol–gel matrices. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 1999, 129, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anedda, A.; Carbonaro, C.M.; Clemente, F.; Corpino, R.; Grandi, S.; Magistris, A.; Mustarelli, P.C. Rhodamine 6G–SiO2 hybrids: A photoluminescence study. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2005, 351, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjo, M.T.; Stefani, V.; Benvenutti, E.V.; Costa, T.M.H.; Ramminger, G. de O.; Gallas, M.R. Synthesis of ORMOSIL silica/rhodamine 6G: Powders and compacts. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, S.A.; Stolik, S.; Palomino, R.; Lozada, R.; Persson, C.; Pepe, I.; da Silva, A.F. Influence of rhodamine 6G doping on the optical properties of TiO2 sol-gel films. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 073516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.Q.; Dang, N.H. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of Rhodamine 800 Aqueous Solution and Dye-Doped Polymer Thin-Film: Concentration and Solvent Effects. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 4813–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Aparicio, F.J.; Espinós, J.P.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Barranco, A. Rhodamine 6G and 800 J-heteroaggregates with enhanced acceptor luminescence (HEAL) adsorbed in transparent SiO2 GLAD thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zane, A.; McCracken, C.; Knight, D.; Young, T.; Lutton, A.; Olesik, J.; Waldman, J.; Dutta, P. Uptake of bright fluorophore core-silica shell nanoparticles by biological systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritula, I.; Bezkrovnaya, O.; Lopin, A.; Kolybaeva, M.; Gurkalenko, Y.; Puzikov, V.; Maslov, V.; Plaksiy, A. Active media based on SiO2 matrices with incorporated molecules of rhodamine dyes. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 63, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdończyk, M.; Potaniec, B.; Skoreński, M.; Cybińska, J. Development of Efficient One-Pot Methods for the Synthesis of Luminescent Dyes and Sol–Gel Hybrid Materials. Materials 2021, 15, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potaniec, B.; Zdończyk, M.; Cybińska, J. Controlled Synthesis of Luminescent Xanthene Dyes and Use of Ionic Liquid in Thermochromic Reaction. Molecules 2022, 27, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myerson, A.S.; Erdemir, D.; Lee, A.Y. Dye Lasers; Schäfer, F.P., Ed.; Topics in Applied Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1973; Volume 1, ISBN 978-3-540-51558-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Blaszczyk-Lezak, I.; Espinós, J.P.; Hamad, S.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Barranco, A. Incorporation and Thermal Evolution of Rhodamine 6G Dye Molecules Adsorbed in Porous Columnar Optical SiO2 Thin Films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 9140–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, T.; Kurumoto, N.; Sagawa, N. Structure and formation mechanism of blue-light-emitting centers in silicon and silica-based nanostructured materials. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 233203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaymardanov, Z.S.; Kurbanov, S.S.; Rakhimov, R.Y. The effect of packing density on luminescence of amorphous SiO2 nanoparticles. Opt. Spectrosc. 2016, 120, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, C.; Leite, A.; Couto, M.G.M.; Moniz, T.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Gameiro, P.; Silva, A.M.G.; Rangel, M. Tuning the limits of pH interference of a rhodamine ion sensor by introducing catechol and 3-hydroxy-4-pyridinone chelating units. Dye. Pigment. 2014, 110, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Wong, K.; Tanner, P.A. A Reversible Rhodamine B Based pH Probe with Large Pseudo-Stokes Shift. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 816–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.; Euler, W.B. Rhodamine 6G Structural Changes in Water/Ethanol Mixed Solvent. J. Fluoresc. 2018, 28, 1431–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zehentbauer, F.M.; Moretto, C.; Stephen, R.; Thevar, T.; Gilchrist, J.R.; Pokrajac, D.; Richard, K.L.; Kiefer, J. Fluorescence spectroscopy of Rhodamine 6G: Concentration and solvent effects. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 121, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penzkofer, A.; Leupacher, W. Fluorescence behaviour of highly concentrated rhodamine 6G solutions. J. Lumin. 1987, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bujdák, J.; Iyi, N. Molecular Aggregation of Rhodamine Dyes in Dispersions of Layered Silicates: Influence of Dye Molecular Structure and Silicate Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboshi, A.; Kurumoto, N.; Yamada, T.; Uchino, T. Influence of Thermal Treatments on the Photoluminescence Characteristics of Nanometer-Sized Amorphous Silica Particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 8483–8488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubin, R.F.; Fletcher, A.N. Fluorescence quantum yields of some rhodamine dyes. J. Lumin. 1982, 27, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J.; Bryce, D.L. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-470-91401-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekar, R. Organic photonics: Prospective nano/micro scale passive organic optical waveguides obtained from π-conjugated ligand molecules. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhuo, M.-P.; Wang, X.-D.; Wei, G.-Q.; Liao, L.-S. Optical waveguides based on one-dimensional organic crystals. PhotoniX 2021, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, D.; Lauermann, M.; Koeber, S.; Appel, P.; Alloatti, L.; Palmer, R.; Dumon, P.; Freude, W.; Leuthold, J.; Koos, C. Lasing in silicon–organic hybrid waveguides. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasiński, P.; Rogoziński, R. Rib waveguides fabricated by means of chemical etching of sol–gel SiO2:TiO2 films. Opt. Commun. 2005, 245, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasio, B.; Malfatti, L.; Innocenzi, P. Photodegradation of rhodamine 6G dimers in silica sol–gel films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 271, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Rhodamine 19 | Emission Maximum (nm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 585 | 580 | 571 | 564 | 556 | Organic dye solution used as reference | |
| Concentration in gel | 10−3 mol/L | 5 × 10−4 mol/L | 10−4 mol/L | 5 × 10−5 mol/L | 10−6 mol/L | [43,44] |
| Rhodamine 6G | Emission maximum (nm) | |||||
| 588 | 577 | 570 | 551 | Organic dye solution used as reference | ||
| Concentration in gel | 5 × 10−3 mol/L | 5 × 10−4 mol/L | 10−4 mol/L | 5 × 10−7 mol/L | [46] | |
| Dopant (Organic Dye) | Δm [%] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30–50 °C | 50–138 °C | 138–200 °C | 200–450 °C | 450–600 °C | ∑ Δm | |
| Rh6G | 0.47 | 2.94 | 2.88 | 3.74 | 2.16 | 12.20 |
| Rh19 | 0.66 | 2.81 | 2.51 | 4.55 | 2.11 | 12.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdończyk, M.; Potaniec, B.; Fiedot-Toboła, M.; Baraniecki, T.; Cybińska, J. Concentration-Dependent Emission of Annealed Sol-Gel Layers Incorporated with Rhodamine 19 and 6G as the Route to Tunable High-Temperature Luminescent Materials. Gels 2022, 8, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070408
Zdończyk M, Potaniec B, Fiedot-Toboła M, Baraniecki T, Cybińska J. Concentration-Dependent Emission of Annealed Sol-Gel Layers Incorporated with Rhodamine 19 and 6G as the Route to Tunable High-Temperature Luminescent Materials. Gels. 2022; 8(7):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070408
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdończyk, Maria, Bartłomiej Potaniec, Marta Fiedot-Toboła, Tomasz Baraniecki, and Joanna Cybińska. 2022. "Concentration-Dependent Emission of Annealed Sol-Gel Layers Incorporated with Rhodamine 19 and 6G as the Route to Tunable High-Temperature Luminescent Materials" Gels 8, no. 7: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070408
APA StyleZdończyk, M., Potaniec, B., Fiedot-Toboła, M., Baraniecki, T., & Cybińska, J. (2022). Concentration-Dependent Emission of Annealed Sol-Gel Layers Incorporated with Rhodamine 19 and 6G as the Route to Tunable High-Temperature Luminescent Materials. Gels, 8(7), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070408