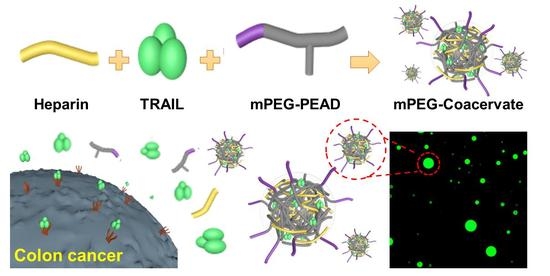
Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy of TRAIL
2.2. Characterization of mPEG-PEAD and mPEG-Coacervate
2.3. Cargo TRAIL Release Phenomenon
2.4. Cargo Protection Ability of mPEG-Coa
2.5. Inhibition of Tumor Recurrence via mPEG-Coa-Mediated TRAIL Delivery
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. In Vitro Anticancer Efficacy of TRAIL
4.3. Synthesis of mPEG-PEAD
4.4. Fabrication of TRAIL-Loaded mPEG-Coacervate
4.5. Rheological Measurements
4.6. Release Kinetics of Cargo TRAIL form mPEG-Coacervate
4.7. Cargo TRAIL Protection Ability against Protease
4.8. Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence Study
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eng, C.; Jacome, A.A.; Agarwal, R.; Hayat, M.H.; Byndloss, M.X.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Bailey, C.; Lieu, C.H. A comprehensive framework for early-onset colorectal cancer research. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e116–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawicki, T.; Ruszkowska, M.; Danielewicz, A.; Niedzwiedzka, E.; Arlukowicz, T.; Przybylowicz, K.E. A Review of Colorectal Cancer in Terms of Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Development, Symptoms and Diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.R.; Kang, Y.; Hollett, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Gu, Z.P.; Wu, J. Polymeric nanoparticles for colon cancer therapy: Overview and perspectives. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7779–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S.; Subramanium, V.D.; Dharanivasan, G.; Murugesan, R.; Verma, R.S. Strategies for targeted drug delivery in treatment of colon cancer: Current trends and future perspectives. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1224–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Albalawi, R.; Pottoo, F.H. Trends in targeted delivery of nanomaterials in colon cancer diagnosis and treatment. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haria, P.D.; Baheti, A.D.; Palsetia, D.; Ankathi, S.K.; Choudhari, A.; Guha, A.; Saklani, A.; Sinha, R. Follow-up of colorectal cancer and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.F.; Zhang, Y.; Si, X.H.; Yao, H.C.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.D.; Zhao, J.Y.; Ma, C.; He, C.L.; Tang, Z.H.; et al. Biopolymer Immune Implants’ Sequential Activation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity for Colorectal Cancer Postoperative Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Karstedt, S.; Montinaro, A.; Walczak, H. Exploring the TRAILs less travelled: TRAIL in cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snajdauf, M.; Havlova, K.; Vachtenheim, J.; Ozaniak, A.; Lischke, R.; Bartunkova, J.; Smrz, D.; Strizova, Z. The TRAIL in the Treatment of Human Cancer: An Update on Clinical Trials. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 628332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.P.; Li, M.X.; Wang, A.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.T. Nanocarriers for TRAIL delivery: Driving TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 13879–13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brin, E.; Wu, K.; Dagostino, E.; Kuo, M.M.C.; He, Y.; Shia, W.J.; Chen, L.C.; Stempniak, M.; Hickey, R.; Almassy, R.; et al. TRAIL stabilization and cancer cell sensitization to its pro-apoptotic activity achieved through genetic fusion with arginine deiminase. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36914–36928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.; Gajendiran, M.; Yoon, M.; Hwang, M.P.; Wang, Y.D.; Kang, B.J.; Kim, K. Enhanced Skull Bone Regeneration by Sustained Release of BMP-2 in Interpenetrating Composite Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 4239–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Chen, W.C.W.; Heo, Y.; Wang, Y.D. Polycations and their biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 60, 18–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Jung, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Kang, B.J.; Kim, K. Dual delivery of stem cells and insulin-like growth factor-1 in coacervate-embedded composite hydrogels for enhanced cartilage regeneration in osteochondral defects. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Hwang, M.P.; Wang, Y.D.; Kim, K. Influence of fiber architecture and growth factor formulation on osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in coacervate-coated electrospun fibrous scaffolds. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 79, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Johnson, N.R.; Gao, J.; Wang, Y. Human progenitor cell recruitment via SDF-1alpha coacervate-laden PGS vascular grafts. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9877–9885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, U.; Lee, M.S.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.; Hwang, M.P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.S.; Kim, K. Coacervate-mediated exogenous growth factor delivery for scarless skin regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 90, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Ahmad, T.; Lee, J.; Awada, H.K.; Wang, Y.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.; Yang, H.S. Dual delivery of growth factors with coacervate-coated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofiber improves neovascularization in a mouse skin flap model. Biomaterials 2017, 124, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Gajendiran, M.; Kim, K. Development of Polymer Coacersome Structure with Enhanced Colloidal Stability for Therapeutic Protein Delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 1900207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.; Gajendiran, M.; Kim, K. Influence of PEG chain length on colloidal stability of mPEGylated polycation based coacersomes for therapeutic protein delivery. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.Z. TRAIL-based gene delivery and therapeutic strategies. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Frew, A.J.; Smyth, M.J. The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 782–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Shah, K. TRAIL of Hope Meeting Resistance in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artykov, A.A.; Yagolovich, A.V.; Dolgikh, D.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Trushina, D.B.; Gasparian, M.E. Death Receptors DR4 and DR5 Undergo Spontaneous and Ligand-Mediated Endocytosis and Recycling Regardless of the Sensitivity of Cancer Cells to TRAIL. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 733688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.L.; Liu, Y.C.; Park, Y.R.; Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, I.H.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, D.G.; Kim, S.W. Parthenolide enhances sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to TRAIL by inducing death receptor 5 and promotes TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, F.F.; Cao, W.P.; Liang, X.J. Nanostructural Systems Developed with Positive Charge Generation to Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1162–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, T.K.; James, A.D.; Zaccagna, F.; Grist, J.T.; Deen, S.; Kennerley, A.; Riemer, F.; Kaggie, J.D.; Gallagher, F.A.; Gilbert, F.J.; et al. Sodium homeostasis in the tumour microenvironment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Rev. Cancer 2019, 1872, 188304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, S.K.; Harris, L.A.; Xie, D.; Deforge, L.; Totpal, K.; Bussiere, J.; Fox, J.A. Preclinical studies to predict the disposition of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in humans: Characterization of in vivo efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.H.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.W.; Huard, J.; Wang, Y.D. Injectable fibroblast growth factor-2 coacervate for persistent angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13444–13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, M.T.P.; Fecek, R.J.; Qin, T.Y.; Storkus, W.J.; Wang, Y.D. Single injection of IL-12 coacervate as an effective therapy against B16-F10 melanoma in mice. J. Control. Release 2020, 318, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.C.; Dharmasivam, M.; Richardson, D.R. The Role of Extracellular Proteases in Tumor Progression and the Development of Innovative Metal Ion Chelators That Inhibit Their Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. USA 2020, 21, 6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, G.; Kim, S.; Kim, K. Development of Folate-Thioglycolate-Gold Nanoconjugates by Using Citric Acid-PEG Branched Polymer for Inhibition of MCF-7 Cancer Cell Proliferation. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 3257–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Jwa, Y.; Hong, J.; Kim, K. Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets. Gels 2022, 8, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070427
Kim S, Jwa Y, Hong J, Kim K. Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets. Gels. 2022; 8(7):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070427
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sungjun, Yerim Jwa, Jiyeon Hong, and Kyobum Kim. 2022. "Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets" Gels 8, no. 7: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070427
APA StyleKim, S., Jwa, Y., Hong, J., & Kim, K. (2022). Inhibition of Colon Cancer Recurrence via Exogenous TRAIL Delivery Using Gel-like Coacervate Microdroplets. Gels, 8(7), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070427