Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Thickened Drinks
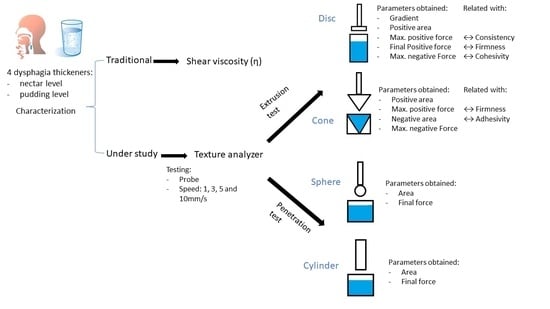
2.3. Texture Analyzer Tests
2.3.1. Extrusion Tests
Extrusion with Disc
Extrusion with Cone and Cone Shape Holder
2.3.2. Penetration Test
Penetration with a Spherical Probe
Penetration with a Cylindrical Probe
2.4. Rheological Measurement of Thickeners
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizing Dysphagia Thickeners Using the Texture Analyzer
3.1.1. Extrusion Tests
3.1.2. Penetration Test
3.2. Effect of Test Speed
3.3. Relationship of Texture Analyzer Parameters with Traditional Viscosity Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolivar-Prados, M.; Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Guida, S.; Nascimento, W.V.; Martin, A.; Vilardell, N.; Fernández, O.O.; Ripken, D.; Lansink, M.; et al. Effect of a gum-based thickener on the safety of swallowing in patients with poststroke oropharyngeal dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 31, e13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, R.; Vilardell, N.; Clavé, P.; Speyer, R. Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: White Paper by the European Society for Swallowing Disorders (ESSD). Dysphagia 2016, 31, 232–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cichero, J.A. Thickening agents used for dysphagia management: Effect on bioavailability of water, medication and feelings of satiety. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Romea, M.; Palomera, E.; Almirall, J.; Cabré, M.; Serra-Prat, M.; Clavé, P. Pathophysiology of oropharyngeal dysphagia in the frail elderly. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, P.; Arreola, V.; Romea, M.; Medina, L.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. Accuracy of the volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of oropharyngeal dysphagia and aspiration. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S.K.; McAdam, C.P.; Brailey, K.; Foundas, A.L. Clinical Assessment of Swallowing and Prediction of Dysphagia Severity. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 1997, 6, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-de la Fuente, E.; Ekberg, O.; Gallegos, C. Rheological aspects of swallowing and dysphagia. In Dysphagia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar-Prados, M.; Tomsen, N.; Arenas, C.; Ibáñez, L.; Clave, P. A bit thick: Hidden risks in thickening products’ labelling for dysphagia treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadde, E.K.; Chen, J. Shear and extensional rheological characterization of thickened fluid for dysphagia man-agement. J. Food Eng. 2019, 245, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, K.; Hayakawa, F.; Kazami, Y.; Ishihara, S.; Nakao, S.; Funami, T.; Nishinari, K. Electromyographic texture characterization of hydrocolloid gels as model foods with varying mastication and swallowing difficulties. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.J.; White, C.; McKenzie, S.; Belafsky, P.C. Effects of bolus rheology on aspiration in patients with dys-phagia. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2014, 114, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moret-Tatay, A.; Garcia, J.R.; Martí-Bonmatí, E.; Hernando, I.; Hernández, M.J. Commercial thickeners used by patients with dysphagia: Rheological and structural behaviour in different food matrices. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.I.; Tyler, P.; Borgognone, M.G.; Eriksen, B.M. Relationships between shear rheology and sensory attributes of hydrocolloid-thickened fluids designed to compensate for impairments in oral manipulation and swallowing. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, L.J.; Li, D.; Özkan, N.; Li, S.J.; Mao, Z.H. Rheological properties of waxy maize starch and xanthan gum mixtures in the presence of sucrose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadde, E.; Nicholson, T.; Dysphagia, J.C. Evaluation of Thickened Fluids Used in Dysphagia Management Using Extensional Rheology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://idp.springer.com/authorize/casa?redirect_uri=https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00455-019-10012-1&casa_token=WSgk13AoO00AAAAA:-msVzeX8-UFpBK6yzcmtVhQHB07fuUvi6tIeqz19L-rZarmM7u4T3170IPuds9aKq66-SmI7woi-5kx7 (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Waqas, M.Q.; Wiklund, J.; Altskär, A.; Ekberg, O.; Stading, M. Shear and extensional rheology of commercial thickeners used for dysphagia management. J. Texture Stud. 2017, 48, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, J.; Oliveira, F.; Salvaro, D.; Maffezzolli, G.; de Mello, J.; Vicente, A.; Cunha, R. Rheology and soft tribology of thickened dispersions aiming the development of oropharyngeal dysphagia-oriented products. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, O.; Yamada, A.; Rigby, N.M.; Hanawa, T.; Kawano, Y.; Sarkar, A. Gellan gum: A new member in the dysphagia thickener family. Biotribology 2019, 17, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cichero, J.A.; Steele, C.; Duivestein, J.; Clavé, P.; Chen, J.; Kayashita, J.; Dantas, R.; Lecko, C.; Speyer, R.; Lam, P.; et al. The Need for International Terminology and Definitions for Texture-Modified Foods and Thickened Liquids Used in Dysphagia Management: Foundations of a Global Initiative. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2013, 1, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cichero, J.A.Y. Adjustment of food textural properties for elderly patients. J. Texture Stud. 2016, 47, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez González, O.; Zabaleta Vélez de Mendizábal, I.; Galarza Iriarte, U.; Vicente Martín, M.S.; de Vega Castaño, M.C.; Salmerón Egea, J. Nutrición Hospitalaria. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Cevoli, C.; Balestra, F.; Ragni, L.; Fabbri, A. Rheological characterisation of selected food hydrocolloids by traditional and simplified techniques. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, A.; Varela, P.; Sanz, T.; Fiszman, S.M. Native tapioca starch as a potential thickener for fruit fillings. Evaluation of mixed models containing low-methoxyl pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 35, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.S.; Tudorica, C.M. Carbohydrate-based fat replacers in the modification of the rheological, textural and sensory quality of yoghurt: Comparative study of the utilisation of barley beta-glucan, guar gum and inulin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.D.; Fernández, C.; Olivares, M.D.; Canet, W. Comparative Characterization of Dietary Fibre-Enriched Frozen/Thawed Mashed Potatoes. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 1022–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badia-Olmos, C.; Laguna, L.; Rizo, A.; Tárrega, A. Dysphagia thickeners in context of use: Changes in thickened drinks viscosity and thixotropy with temperature and time of consumption. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Cao, M.-J.; Liu, G.-M. Texture analyzers for food quality evaluation. Eval. Technol. Food Qual. 2019, 17, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasaruddin, F.; Chin, N.; Yusof, Y. Effect of Processing on Instrumental Textural Properties of Traditional Dodol Using Back Extrusion. Int. J. Food Prop. 2012, 15, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M. Food Texture and Viscosity: Concept and Measurement. Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=es&lr=&id=S2HNnvSOuf8C&oi=fnd&pg=PP2&dq=Food+texture+and+viscosity:+Concept+and+measurement&ots=u-KPurVSsu&sig=XqqtXliUTLb1Vk5F6_2EO0hpnUQ (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Vallons, K.J.R.; Helmens, H.J.; Oudhuis, A.A.C.M. Effect of human saliva on the consistency of thickened drinks for individuals with dysphagia. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2014, 50, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, F.C.; Gómez, I.; Merino, G.; Beriain, M.J. Textural characteristics of safe dishes for dysphagic patients: A multivariate analysis approach. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, M.; Fiszman, S. Instrumental texture profile analysis with particular reference to gelled systems. J. Texture Stud. 1996, 27, 597–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, A. Texture profile analysis How important are the parameters? J. Texture Stud. 2010, 41, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, K.T.; Glasgow, S. On The Texture Profile Analysis Test. In Proceedings of the Chemeca, Sydney, Australia, 26–29 October 2012; pp. 749–760. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, A.N.; Morris, E.R.; Taylor, L.J. Oral Perception of Viscosity in. J. Texture Stud. 1983, 14, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Hort, J.; Wolf, B. Predicting sensory perceptions of thickened solutions based on rheological analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavé, P.; De Kraa, M.; Arreola, V.; Girvent, M.; Farré, R.; Palomera, E.; Serra-Prat, M. The effect of bolus viscosity on swallowing function in neurogenic dysphagia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellyer, J. Quality Testing with Instrumental Texture Analysis in Food Manufactering. Middleboro, MA: LPI. 2004. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/download/32424621/Quality_testing_with_instrumental_texture_analysis_in_food_manufacturing.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2022).
- Riera, S.A.; Rovira, J.; Kothari, M.; Clavé, P. A modification of the Tomass, a clinical test to assess the oral preparatory phase of different food textures. In Proceedings of the 6th International conference on Food Oral Processing, Valencia, Spain, 12–14 July 2021. [Google Scholar]



| Thickener | Ingredients |
|---|---|
| A | Maltodextrin, xanthan gum, and potassium chloride |
| B | Modified maize starch |
| C | Modified maize starch |
| D | Maltodextrin, thickeners (modified starch (maize), tara gum, xanthan gum, guar gum) |
| Thickeners | Grams per 100 mL | |
|---|---|---|
| Nectar | Pudding | |
| A | 1.2 g | 3.6 g |
| B | 4.1 g | 8.2 g |
| C | 4.0 g | 8.0 g |
| D | 5.0 g | 9.0 g |
| Test Type | Probe | Selected Parameter | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion with disc | With disc (back-extrusion disc A/BE35) | Gradient | N/mm |
| Positive area from the curve | N.mm | ||
| First positive peak force | N | ||
| Final positive peak force | N | ||
| Maximum negative force peak | N | ||
| Extrusion with cone | With cone TTC Spreadability Rig | Maximum positive peak force | N |
| Positive area from the curve | N.mm | ||
| Maximum negative peak force | N | ||
| Negative area from the curve | N.mm | ||
| Sphere penetration | Positive area from the curve | N.mm | |
| Maximum positive peak force | N | ||
| Cylinder penetration | Positive area from the curve | N.mm | |
| Maximum positive peak force | N | ||
| Extrusion with Disc | Extrusion with Cone | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickener | Gradient (N/mm) | Positive Area (N.mm) | Max. Positive Force (N) | Final Positive Force (N) | Max. Negative Force (N) | Max. Positive Force (N) | Positive Area (N.mm) | Max. Negative Force (N) | Negative Area (N.mm) | |
| Nectar level | A | 0.028 bc (0.004) | 4.742 b (0.147) | 0.107 b (0.003) | 0.128 d (0.004) | 0.087 b (0.002) | 0.337 b (0.014) | 0.837 b (0.015) | 0.193 b (0.006) | 0.648 b (0.062) |
| B | 0.027 c (0.001) | 5.657 a (0.239) | 0.095 c (0.001) | 0.169 b (0.015) | 0.069 bc (0.011) | 0.424 b (0.038) | 0.814 b (0.056) | 0.163 b (0.114) | 0.418 c (0.096) | |
| C | 0.041 a (0.004) | 4.837 b (0.494) | 0.093 c (0.009) | 0.147 c (0.008) | 0.067 c (0.008) | 0.364 b (0.022) | 0.683 b (0.030) | 0.073 b (0.011) | 0.295 c (0.041) | |
| D | 0.033 b (0.002) | 4.831 b (0.206) | 0.174 a (0.009) | 0.195 a (0.006) | 0.178 a (0.015) | 0.856 a (0.085) | 1.714 a (0.210) | 0.876 a (0.448) | 1.868 a (0.144) | |
| Pudding level | A | 0.025 c (0.002) | 6.010 c (0.121) | ---- | 0.248 c (0.007) | 0.177 d (0.000) | 0.594 d (0.028) | 1.425 d (0.017) | 0.353 d (0.016) | 0.051 d (0.001) |
| B | 0.089 a (0.006) | 20.112 b (0.945) | ----- | 0.788 b (0.028) | 0.970 b (0.013) | 1.891 b (0.057) | 4.822 b (0.208) | 1.603 b (0.021) | 0.139 b (0.006) | |
| C | 0.070 b (0.009) | 19.467 b (0.431) | ----- | 0.759 b (0.016) | 0.929 c (0.024) | 1.563 c (0.042) | 4.032 c (0.108) | 1.308 c (0.024) | 0.116 c (0.005) | |
| D | 0.079 ab (0.002) | 28.216 a (0.617) | ----- | 1.088 a (0.023) | 1.249 a (0.019) | 3.138 a (0.132) | 7.468 a (0.069) | 2.774 a (0.071) | 0.228 a (0.006) | |
| Penetration with Sphere | Penetration with Cylinder | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickener | Area (N.mm) | Final Force (N) | Area (N.mm) | Final Force (N) | |
| Nectar level | A | 0.326 ab | 0.020 a | 2.167 c | 0.126 b |
| (0.052) | (0.003) | (0.043) | (0.005) | ||
| B | 0.160 c | 0.014 b | 2.404 ab | 0.140 a | |
| (0.04) | (0.002) | (0.123) | (0.004) | ||
| C | 0.351 a | 0.024 a | 2.493 a | 0.143 a | |
| (0.051) | (0.002) | (0.031) | (0.005) | ||
| D | 0.264 b | 0.024 a | 2.342 b | 0.141 a | |
| (0.023) | (0.002) | (0.076) | (0.005) | ||
| Pudding level | A | 0.242 c | 0.025 c | 2.276 c | 0.186 c |
| (0.033) | (0.003) | (0.081) | (0.004) | ||
| B | 1.363 a | 0.087 a | 5.147 b | 0.377 b | |
| (0.084) | (0.004) | (0.272) | (0.021) | ||
| C | 1.012 b | 0.070 b | 4.826 b | 0.360 b | |
| (0.079) | (0.001) | (0.176) | (0.013) | ||
| D | 1.265 a | 0.074 b | 5.900 a | 0.451 a | |
| (0.083) | (0.002) | (0.226) | (0.012) | ||
| Thickener | Test Speed (mm s−1) | Extrusion with Disc | Extrusion with Cone | Penetration with Sphere | Penetration with Cylinder | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Force | Final Force | Cohesivity | Max. Positive Force | Max. Negative Force | Final Force | Final Force | ||
| A | 1 | 0.107 c (0.003) | 0.128 c (0.004) | 0.087 ab (0.002) | 0.337 b (0.014) | 0.193 ab (0.005) | 0.020 a (0.003) | 0.126 a (0.005) |
| A | 3 | 0.118 b (0.001) | 0.142 ab (0.005) | 0.092 a (0.009) | 0.407 a (0.009) | 0.202 ab (0.011) | 0.020 a (0.003) | 0.130 a (0.004) |
| A | 5 | 0.119 b (0.001) | 0.134 bc (0.006) | 0.079 b (0.009) | 0.353 b (0.008) | 0.188 b (0.012) | 0.017 ab (0.003) | 0.126 a (0.010) |
| A | 10 | 0.127 a (0.000) | 0.146 a (0.002) | 0.083 ab (0.001) | 0.423 a (0.014) | 0.220 a (0.023) | 0.014 b (0.000) | 0.134 a (0.006) |
| B | 1 | 0.095 b (0.001) | 0.169 ab (0.015) | 0.069 b (0.011) | 0.424 a (0.038) | 0.163 a (0.113) | 0.014 a (0.002) | 0.140 a (0.004) |
| B | 3 | 0.108 a (0.004) | 0.163 b (0.014) | 0.080 ab (0.009) | 0.423 a (0.047) | 0.093 a (0.008) | 0.017 a (0.005) | 0.137 a (0.012) |
| B | 5 | 0.114 a (0.010) | 0.186 a (0.007) | 0.095 a (0.008) | 0.399 a (0.026) | 0.100 a (0.016) | 0.016 a (0.003) | 0.137 a (0.008) |
| B | 10 | 0.106 a (0.005) | 0.180 ab (0.004) | 0.068 b (0.012) | 0.362 a (0.026) | 0.069 a (0.015) | 0.019 a (0.004) | 0.138 a (0.006) |
| C | 1 | 0.093 a (0.009) | 0.147 c (0.008) | 0.067 a (0.008) | 0.364 c (0.022) | 0.073 c (0.011) | 0.024 a (0.002) | 0.143 a (0.005) |
| C | 3 | 0.091 a (0.005) | 0.161 ab (0.006) | 0.042 c (0.011) | 0.482 b (0.004) | 0.109 bc (0.010) | 0.015 b (0.002) | 0.118 c (0.003) |
| C | 5 | 0.093 a (0.005) | 0.151 bc (0.006) | 0.051 bc (0.006) | 0.494 b (0.011) | 0.139 b (0.018) | 0.018 b (0.004) | 0.135 b (0.001) |
| C | 10 | 0.095 a (0.006) | 0.164 a (0.005) | 0.059 a (0.005) | 0.599 a (0.087) | 0.204 a (0.050) | 0.016 b (0.002) | 0.121 c (0.002) |
| D | 1 | 0.174 d (0.009) | 0.195 d (0.006) | 0.178 ab (0.015) | 0.856 c (0.085) | 0.876 a (0.448) | 0.024 a (0.002) | 0.141 b (0.005) |
| D | 3 | 0.228 b (0.009) | 0.240 b (0.009) | 0.170 b (0.013) | 1.002 bc (0.072) | 0.560 a (0.017) | 0.021 ab (0.001) | 0.144 b (0.004) |
| D | 5 | 0.314 a (0.005) | 0.321 a (0.003) | 0.190 a (0.004) | 1.054 b (0.094) | 0.586 a (0.053) | 0.019 b (0.001) | 0.141 b (0.003) |
| D | 10 | 0.213 c (0.005) | 0.217 c (0.003) | 0.128 c (0.003) | 1.278 a (0.006) | 0.587 a (0.026) | 0.022 ab (0.001) | 0.152 a (0.003) |
| Thickener | Test Speed (mm s−1) | Extrusion with Disc | Extrusion with Cone | Penetration with Sphere | Penetration with Cylinder | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Final Force | Cohesivity | Max. Positive Force | Max. Negative Force | Final Force | Final Force | ||
| A | 1 | 0.248 c (0.007) | 0.177 a (0.000) | 0.594 c (0.028) | 0.353 a (0.016) | 0.025 a (0.003) | 0.186 b (0.004) |
| A | 3 | 0.277 bc (0.007) | 0.168 b (0.003) | 0.689 b (0.031) | 0.303 b (0.015) | 0.026 a (0.002) | 0.205 a (0.002) |
| A | 5 | 0.295 b (0.020) | 0.165 a (0.006) | 0.731 ab (0.022) | 0.307 b (0.015) | 0.025 a (0.002) | 0.213 a (0.001) |
| A | 10 | 0.343 a (0.022) | 0.163 a (0.003) | 0.765 a (0.006) | 0.239 c (0.006) | 0.027 a (0.002) | 0.215 a (0.011) |
| B | 1 | 0.788 d (0.028) | 0.970 ab (0.013) | 1.891 b (0.057) | 1.603 a (0.021) | 0.087 c (0.004) | 0.377 c (0.021) |
| B | 3 | 1.005 c (0.023) | 0.996 a (0.026) | 1.995 ab (0.097) | 1.291 b (0.020) | 0.093 bc (0.003) | 0.472 b (0.020) |
| B | 5 | 1.058 b (0.014) | 0.946 ab (0.052) | 2.052 a (0.068) | 1.330 b (0.053) | 0.105 ab (0.003) | 0.505 b (0.030) |
| B | 10 | 1.191 a (0.025) | 0.929 b (0.010) | 1.992 ab (0.099) | 1.009 c (0.047) | 0.116 a (0.002) | 0.546 a (0.012) |
| C | 1 | 0.759 d (0.016) | 0.929 a (0.024) | 1.563 c (0.042) | 1.308 c (0.024) | 0.070 a (0.000) | 0.360 d (0.013) |
| C | 3 | 0.965 c (0.035) | 0.910 a (0.010) | 2.060 b (0.061) | 1.519 ab (0.070) | 0.085 a (0.002) | 0.437 c (0.004) |
| C | 5 | 1.014 b (0.007) | 0.910 a (0.019) | 2.174 b (0.122) | 1.582 a (0.102) | 0.099 a (0.001) | 0.456 b (0.011) |
| C | 10 | 1.138 a (0.019) | 0.901 a (0.028) | 2.463 a (0.041) | 1.409 bc (0.010) | 0.068 a (0.007) | 0.508 a (0.005) |
| D | 1 | 1.088 d (0.023) | 1.249 a (0.019) | 3.138 b (0.132) | 2.774 a (0.071) | 0.074 d (0.002) | 0.451 d (0.012) |
| D | 3 | 1.368 c (0.015) | 1.200 bc (0.007) | 3.287 b (0.036) | 2.358 b (0.037) | 0.094 c (0.003) | 0.601 c (0.022) |
| D | 5 | 1.506 b (0.063) | 1.224 ab (0.024) | 3.867 a (0.174) | 2.804 a (0.136) | 0.103 b (0.003) | 0.636 b (0.022) |
| D | 10 | 1.758 a (0.020) | 1.188 c (0.006) | 3.886 a (0.180) | 2.251 b (0.107) | 0.123 a (0.004) | 0.767 a (0.015) |
| Nectar | Pudding | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickener | ɳ10 | ɳ50 | ɳ300 | ɳ10 | ɳ50 | ɳ300 |
| A | 0.604 a | 0.148 a | 0.041 b | 1.962 c | 0.414 d | 0.094 c |
| B | 0.504 ab | 0.122 b | 0.030 c | 11.890 a | 2.660 b | 0.634 b |
| C | 0.355 b | 0.105 b | 0.027 c | 10.408 b | 2.375 c | 0.582 b |
| D | 0.349 b | 0.129 ab | 0.055 a | 11.933 a | 3.324 a | 0.792 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baixauli, R.; Bolivar-Prados, M.; Ismael-Mohammed, K.; Clavé, P.; Tárrega, A.; Laguna, L. Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful? Gels 2022, 8, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070430
Baixauli R, Bolivar-Prados M, Ismael-Mohammed K, Clavé P, Tárrega A, Laguna L. Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful? Gels. 2022; 8(7):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070430
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaixauli, Raquel, Mireia Bolivar-Prados, Kovan Ismael-Mohammed, Pere Clavé, Amparo Tárrega, and Laura Laguna. 2022. "Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful?" Gels 8, no. 7: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070430
APA StyleBaixauli, R., Bolivar-Prados, M., Ismael-Mohammed, K., Clavé, P., Tárrega, A., & Laguna, L. (2022). Characterization of Dysphagia Thickeners Using Texture Analysis—What Information Can Be Useful? Gels, 8(7), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070430