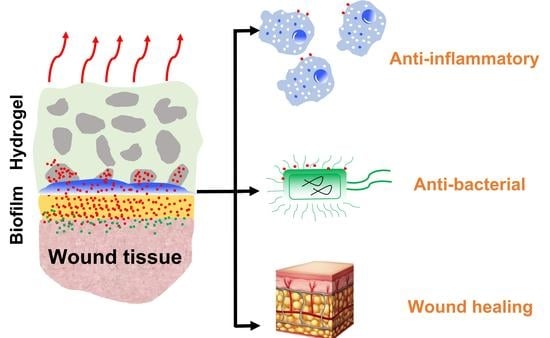
Antibacterial and Angiogenic Poly(ionic liquid) Hydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Properties of Hydrogels
2.2. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Hydrogels
2.3. In Vitro DFO Release and Hemolysis Assay of Hydrogels
2.4. In Vitro Transwell and Angiogenesis Assay of Hydrogels
2.5. In Vitro Anti-Inflammation Activity of Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of EPL-SH
4.3. Synthesis of Imidazole-SH
4.4. Synthesis of MAH-Lys
4.5. Preparation of Antibacterial Hydrogels Containing DFO
4.6. Characterization of Hydrogels
4.7. Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Assay of Hydrogels
4.8. Hemolytic and Cytocompatibility Assay of Hydrogels
4.9. Cells Angiogenesis and Trasnswell Assay of HUVECs
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Shang, Y.Y.; Zou, Y.; Xiao, M.; Huang, H.L.; Zhu, S.J.; Liu, N.B.; Li, J.N.; Wang, W.; Zhu, P. Injectable Hypoxia-Induced Conductive Hydrogel to Promote Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 56681–56691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantari, K.; Mostafavi, E.; Afifi, A.M.; Izadiyan, Z.; Jahangirian, H.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Webster, T.J. Wound dressings functionalized with silver nanoparticles: Promises and pitfalls. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2268–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.F.; Huang, R.K.; Zheng, B.N.; Guo, W.T.; Li, C.K.; He, W.Y.; Wei, Y.G.; Du, Y.; Wang, H.M.; Wu, D.C.; et al. Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpet, D.E. Why does SARS-CoV-2 survive longer on plastic than on paper? Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, T.T.; Pan, X.L. Metal-Organic-Framework-Based Materials for Antimicrobial Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3808–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.T.; Wang, X.S.; Yu, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.S.; Deng, M.W.; Zhao, D.Y.; Ji, S.W.; Jia, N.Q.; Zhang, W.J. gamma-PGA hydrogel loaded with cell-free fat extract promotes the healing of diabetic wounds. J. Mat. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8395–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wu, W.; Lei, Y.; Gaucher, C.; Pei, S.C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Xia, X.F. Edaravone-Loaded Alginate-Based Nanocomposite Hydrogel Accelerated Chronic Wound Healing in Diabetic Mice. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.X.; Chen, X.L.; Shen, X.R.; He, Y.; Chen, W.; Luo, Q.; Ge, W.H.; Yuan, W.H.; Tang, X.; Hou, D.Y.; et al. Preparation of chitosan-collagen-alginate composite dressing and its promoting effects on wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, G.H.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Meng, W.Q.; Zhang, X.; Du, F.F.; Lee, S.X. Ag@MOF-loaded chitosan nanoparticle and polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate/chitosan bilayer dressing for wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, F.; Liu, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, D. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by sodium alginate to obtain silver-loaded composite wound dressing with enhanced mechanical and antimicrobial property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.J.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Wang, J.L.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.Y.; Jin, J. Layer-by-Layer Construction of Cu2+/Alginate Multilayer Modified Ultrafiltration Membrane with Bioinspired Superwetting Property for High-Efficient Crude-Oil-in-Water Emulsion Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.M.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.M.; Li, C.Y.; Zheng, Y.F.; Cui, Z.D.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liang, Y.Q.; et al. Antibacterial Hybrid Hydrogels. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescignano, N.; Hernandez, R.; Lopez, L.D.; Calvillo, I.; Kenny, J.M.; Mijangos, C. Preparation of alginate hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles: A facile approach for antibacterial applications. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Huang, X.B.; Hang, R.Q.; Yao, X.H. Light-assisted rapid sterilization by a hydrogel incorporated with Ag3PO4/MoS2 composites for efficient wound disinfection. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Qu, Y.C.; Yu, Q.; Chen, H. Gold nanoparticle layer: A versatile nanostructured platform for biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 2175–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.P.; Wang, Y.K. Anisotropic Photonics Topological Transition in Hyperbolic Metamaterials Based on Black Phosphorus. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.H.; Tan, L.F.; Ren, X.L.; Wu, Q.; Shao, H.B.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y.X.; Meng, X.W. Interlayer expansion of 2D MoS2 nanosheets for highly improved photothermal therapy of tumors in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13989–13992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, T.H.; Zhou, X.P. Alkylation of Ammonium Salts Catalyzed by Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid Catalysts. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1095–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure-Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(ionic liquids) and Poly(ionic liquid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Zou, X.; Sun, Z.; Guo, J.; Yan, F. Recyclable, Healable, and Tough Ionogels Insensitive to Crack Propagation. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Shi, R.; Ren, Y.; Peng, W.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, W.; Sun, Z.; Guo, J.; et al. A “Two-in-One” Strategy for Flexible Aqueous Batteries Operated at −80 °C. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.B.; Shi, Z.Y.; Mahadevegowda, S.H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, K.X.; Koh, C.H.; Ruan, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Zeden, M.S.; Pee, C.J.E.; et al. Designer broad-spectrum polyimidazolium antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31376–31385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wen, C.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Janaswamy, S.; Zhu, B.; Song, S. Effect of ε-polylysine addition on κ-carrageenan gel properties: Rheology, water mobility, thermal stability and microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-N.; Ye, Q.-Q.; Hou, W.-F.; Zhang, G.-Q. Development of antibacterial ε-polylysine/chitosan hybrid films and the effect on citrus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Islam, M.T.; Masuda, Y.; Honjoh, K.I.; Miyamoto, T. Transcriptional changes involved in inhibition of biofilm formation by ε-polylysine in Salmonella Typhimurium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5427–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B.; Dhaliwal, H.K.; Portillo-Lara, R.; Shirzaei Sani, E.; Abdi, R.; Amiji, M.M.; Annabi, N. Local Immunomodulation Using an Adhesive Hydrogel Loaded with miRNA-Laden Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Healing. Small 2019, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taus, F.; Salvagno, G.; Canè, S.; Fava, C.; Mazzaferri, F.; Carrara, E.; Petrova, V.; Barouni, R.M.; Dima, F.; Dalbeni, A.; et al. Platelets Promote Thromboinflammation in SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchio, P.; Guerra-Ojeda, S.; Vila, J.M.; Aldasoro, M.; Victor, V.M.; Mauricio, M.D. Targeting Early Atherosclerosis: A Focus on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8563845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Guo, L.; Wicks, J.; Ling, C.; Zhao, X.; Yan, Y.F.; Qi, J.; Cui, W.G.; Deng, L.F. Quickly promoting angiogenesis by using a DFO-loaded photo-crosslinked gelatin hydrogel for diabetic skin regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 3770–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Jia, P.; Kang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, P.; Yan, Y.; Zuo, G.; Guo, L.; Jiang, M.; et al. Upregulating Hif-1α by Hydrogel Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Rapidly Recruiting Angiogenesis Relative Cells in Diabetic Wound. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Ma, X.; Pranantyo, D.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Truong, V.X. Robust anti-infective multilayer coatings with rapid self-healing property. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.; Blakey, I.; Whittaker, A.K. Hydrophilic and Amphiphilic Polyethylene Glycol-Based Hydrogels with Tunable Degradability Prepared by “Click” Chemistry. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, C.; Wang, R.; Yao, X.; Guo, P.; Yuan, W.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Xie, X. The fabrication of a highly efficient self-healing hydrogel from natural biopolymers loaded with exosomes for the synergistic promotion of severe wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sheng, C.; Zhou, C. Fast Gelation of Poly(ionic liquid)-Based Injectable Antibacterial Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.B. Thiol–ene “click” reactions and recent applications in polymer and materials synthesis: A first update. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 4820–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Sheng, C.; Gao, L.; Guo, J.; Li, P.; Liu, B. Engineering poly(ionic liquid) semi-IPN hydrogels with fast antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 413, 127429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.N.; Li, F.; Guo, Z.R.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, X.Y.; Zhe, T.T.; Cao, Y.Y.; Wang, L.; Lu, Q.Y.; et al. Silver nanoparticle-embedded hydrogel as a photothermal platform for combating bacterial infections. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, S.; Kang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xia, C.; Yu, Y.; Li, J. Facile biomimetic self-coacervation of tannic acid and polycation: Tough and wide pH range of underwater adhesives. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 127069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, X.; Lu, X.; Zuo, B.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Injectable Silk Nanofiber Hydrogels for Sustained Release of Small-Molecule Drugs and Vascularization. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4077–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Lautenschlaeger, C.; Kempe, K.; Tauhardt, L.; Schubert, U.S.; Fischer, D. Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) as alternative for the stealth polymer poly(ethylene glycol): Comparison of in vitro cytotoxicity and hemocompatibility. Macromol. Biosci. 2012, 12, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lu, Q.Q.; Cui, L.; Zong, M.L.; Guo, Y.X.; Liu, L.L.; Pan, D.D.; Wu, Z. The fatty acid profiles of mixed fermented milk and its anti-inflammation properties in an LPS-induced RAW264.7 cell model. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2465–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Y.; Huang, Z.L.; Huang, J.; Xu, B.; Huang, X.Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Z.Y. Exosomal circRNA-100338 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via enhancing invasiveness and angiogenesis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Cui, H.; Shen, J.; Chang, J.; Li, H.; He, Y. Bioactive Injectable Hydrogels Containing Desferrioxamine and Bioglass for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30103–30114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, R.Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tam, A.; Yan, Y.F.; Shen, H.K.; Zhang, Y.S.; Qi, J.; Feng, Y.; et al. An injectable self-healing coordinative hydrogel with antibacterial and angiogenic properties for diabetic skin wound repair. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, L.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, Y.Y.; Lin, Z.; Yu, Y.S.; Mi, B.B.; Liu, G.H.; Xiao, X.F.; et al. Angiogenesis-based diabetic skin reconstruction through multifunctional hydrogel with sustained releasing of M2 Macrophage-derived exosome. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Li, Q.; Ryu, M.O.; Nam, A.; An, J.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, S.M.; Song, W.J.; Youn, H.Y. Preconditioning of canine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells with deferoxamine potentiates anti-inflammatory effects by directing/reprogramming M2 macrophage polarization. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2020, 219, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, D.D.; Hao, H.J.; Tong, C.A.; Liu, J.J.; Dong, L.; Zheng, J.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Liu, H.L.; Fu, X.B.; Han, W.D. LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, C.; Tan, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, K.; Zhou, C.; Guo, M. Antibacterial and Angiogenic Poly(ionic liquid) Hydrogels. Gels 2022, 8, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080476
Sheng C, Tan X, Huang Q, Li K, Zhou C, Guo M. Antibacterial and Angiogenic Poly(ionic liquid) Hydrogels. Gels. 2022; 8(8):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080476
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Chengju, Xuemei Tan, Qing Huang, Kewen Li, Chao Zhou, and Mingming Guo. 2022. "Antibacterial and Angiogenic Poly(ionic liquid) Hydrogels" Gels 8, no. 8: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080476
APA StyleSheng, C., Tan, X., Huang, Q., Li, K., Zhou, C., & Guo, M. (2022). Antibacterial and Angiogenic Poly(ionic liquid) Hydrogels. Gels, 8(8), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080476